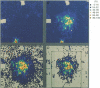
Abstract
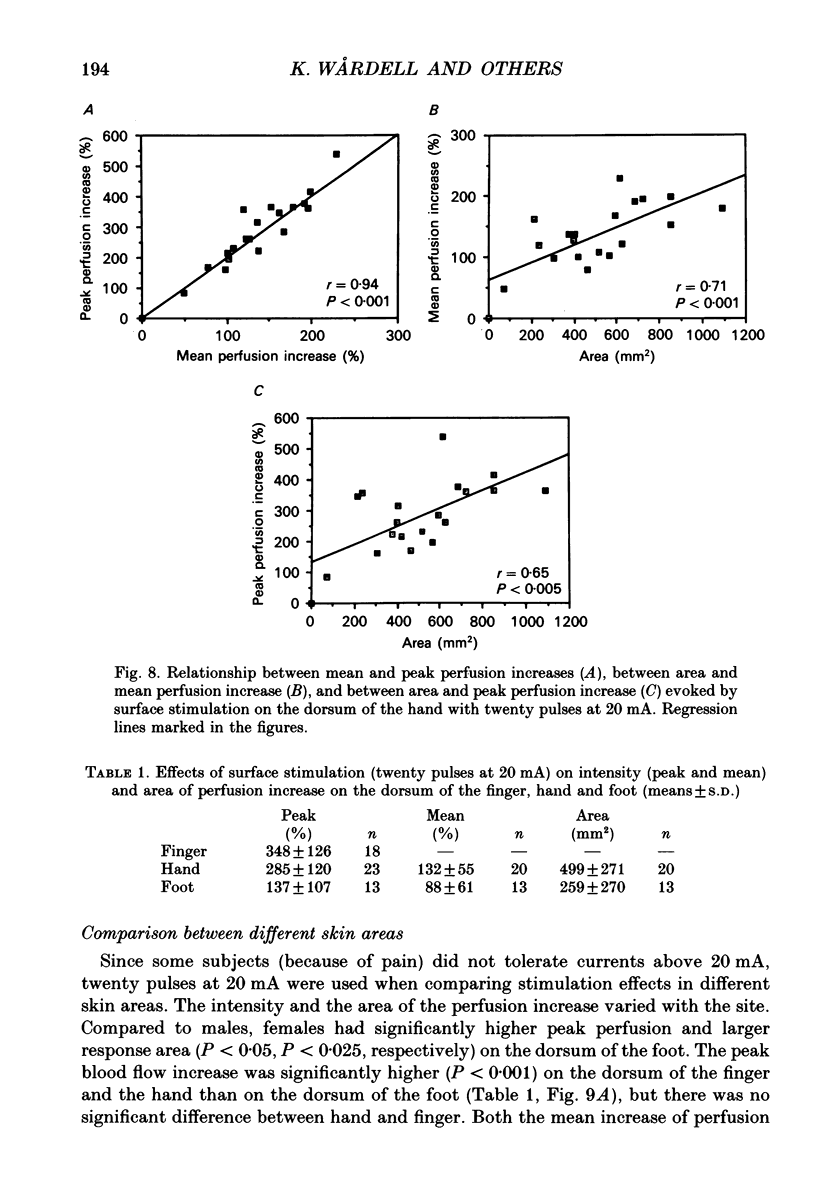
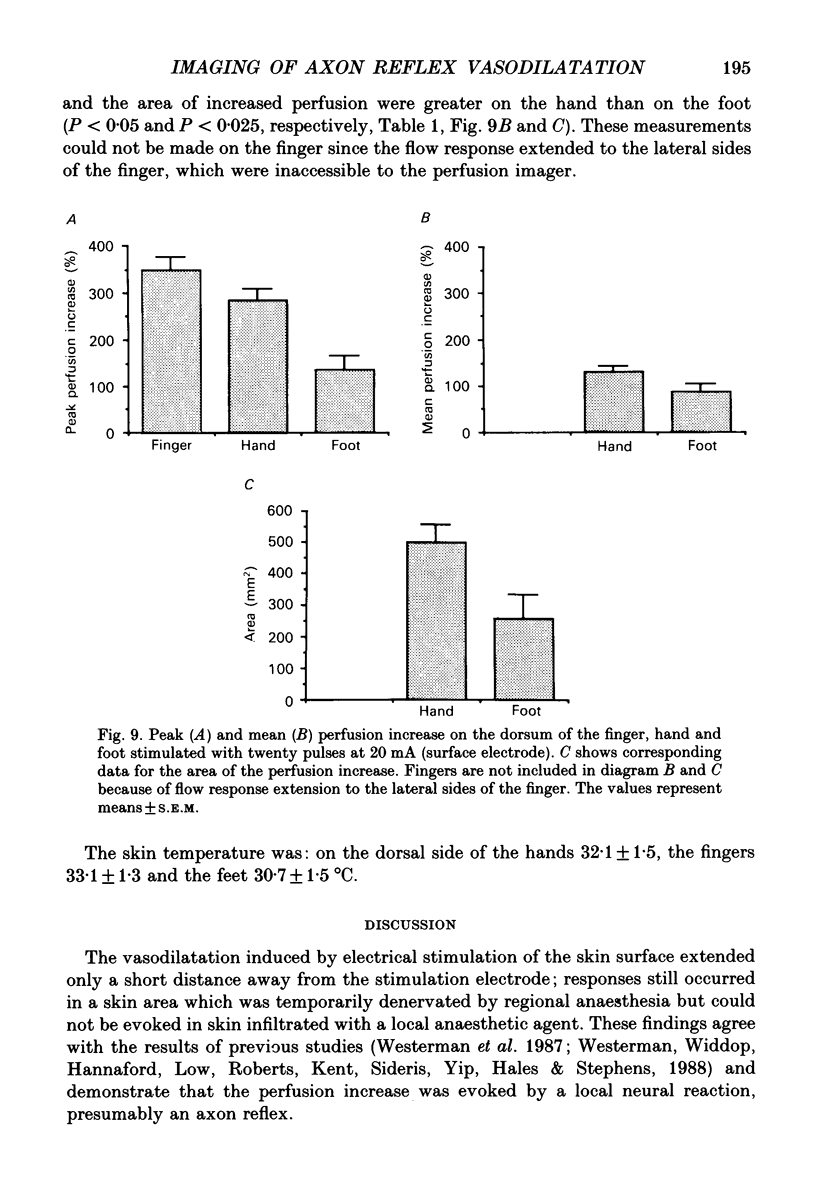
1. Laser Doppler perfusion imaging was used to map the cutaneous vascular axon response induced by trains of electrical skin stimuli (1 ms, 2 Hz) on the dorsum of the hand, finger and foot in twenty-four healthy subjects. Conduction anaesthesia was applied to nerves supplying the stimulated skin areas. Subtraction of images recorded before and after stimulation was used for data analysis of the intensity and area of the response. 2. The stimulation evoked a localized perfusion increase around the stimulating electrode which lasted approximately 30 min and increased in intensity and area with increasing stimulation strength to a maximum at 20 pulses and 20 mA. The intensity and area of the response was greater on the hand than on the foot. 3. Approximating the response area as a circle, the maximal perfusion increase in the hand extended 9 +/- 3 mm (mean +/- S.D.) outside the perimeter of the stimulating electrode. When stimulating within skin which had been subjected to surface anaesthesia, no response occurred, but when stimulating at the border of surface-anaesthetized skin, the perfusion increase extended 2 +/- 1 mm (mean +/- S.D.) into anaesthetized skin. 4. The results show that the perfusion increase must have been due in part to impulse conduction to, and release of transmitters from, axon endings terminating in skin outside the contact area of the probe. It is concluded that the area of perfusion increase corresponds to the size of the receptive fields of afferent polymodal C fibres.
Full text
PDF


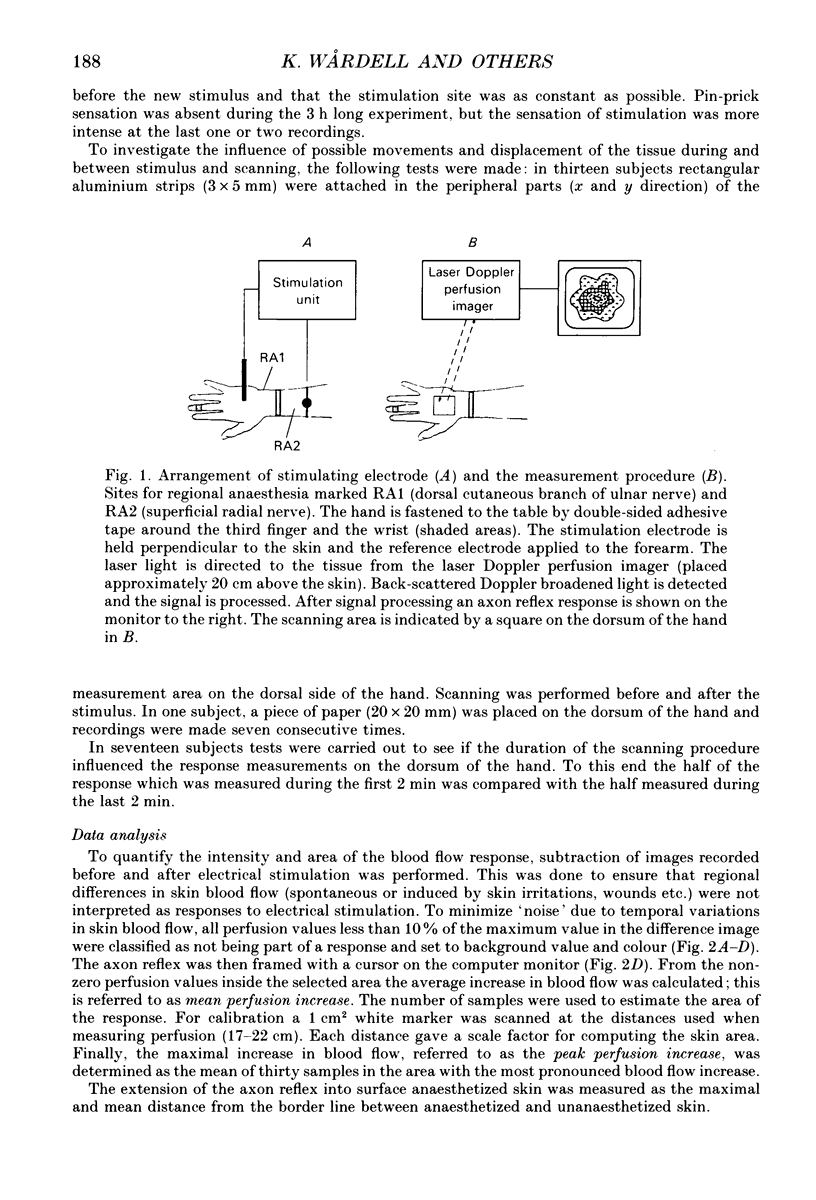



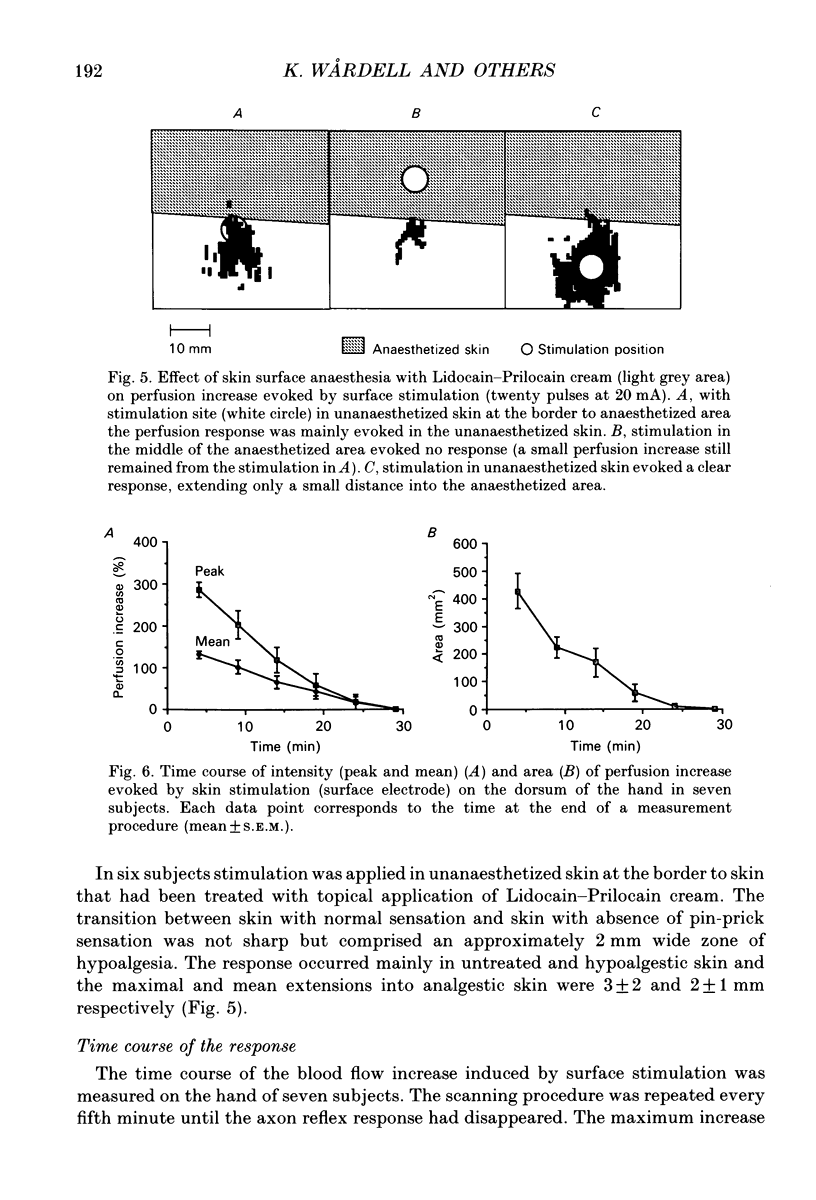
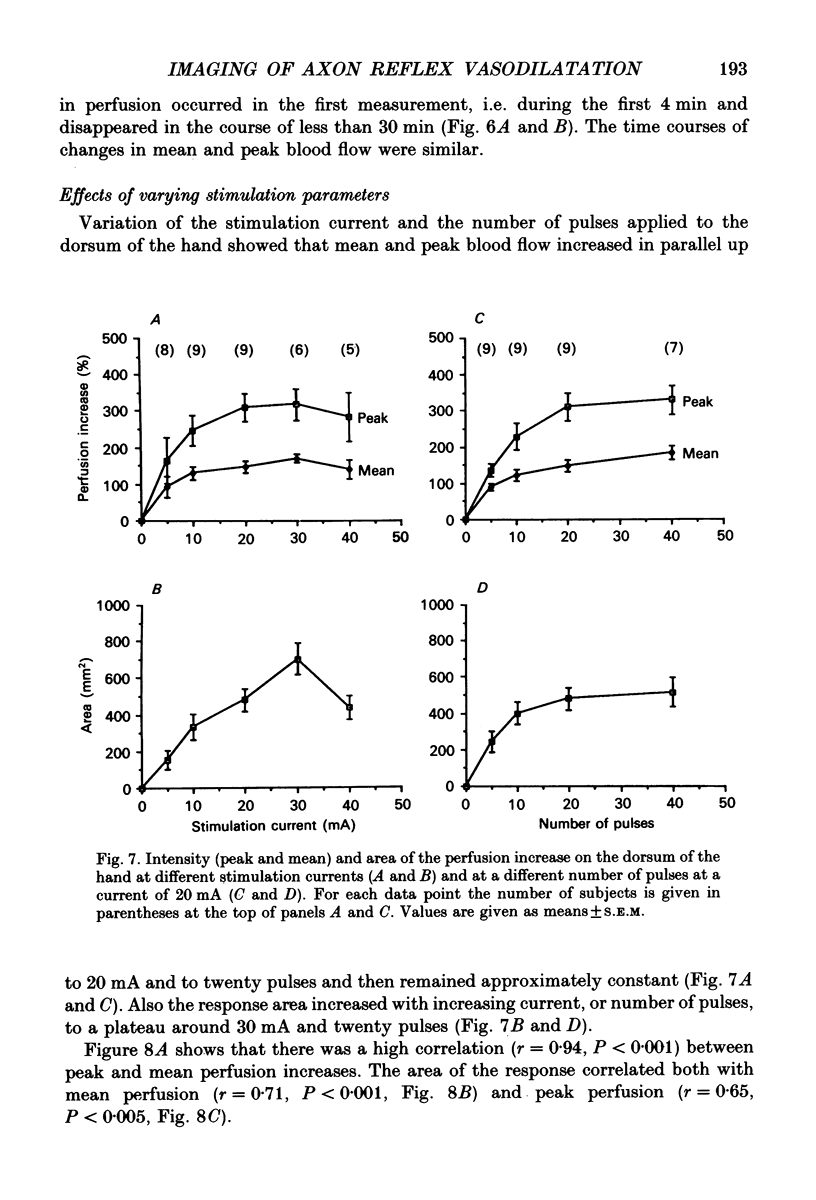




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blumberg H., Wallin B. G. Direct evidence of neurally mediated vasodilatation in hairy skin of the human foot. J Physiol. 1987 Jan;382:105–121. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chahl L. A. Antidromic vasodilatation and neurogenic inflammation. Pharmacol Ther. 1988;37(2):275–300. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(88)90029-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook K. A., Odland G. F. Regional differences in the thickness (cell layers) of the human stratum corneum: an ultrastructural analysis. J Invest Dermatol. 1974 Apr;62(4):415–422. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12701670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornyak M. E., Naver H. K., Rydenhag B., Wallin B. G. Sympathetic activity influences the vascular axon reflex in the skin. Acta Physiol Scand. 1990 May;139(1):77–84. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1990.tb08899.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jancsó N., Jancsó-Gábor A., Szolcsányi J. Direct evidence for neurogenic inflammation and its prevention by denervation and by pretreatment with capsaicin. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1967 Sep;31(1):138–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1967.tb01984.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørum E., Lundberg L. E., Torebjörk H. E. Peripheral projections of nociceptive unmyelinated axons in the human peroneal nerve. J Physiol. 1989 Sep;416:291–301. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenins P. Identification of the unmyelinated sensory nerves which evoke plasma extravasation in response to antidromic stimulation. Neurosci Lett. 1981 Sep 1;25(2):137–141. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(81)90321-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magerl W., Westerman R. A., Möhner B., Handwerker H. O. Properties of transdermal histamine iontophoresis: differential effects of season, gender, and body region. J Invest Dermatol. 1990 Mar;94(3):347–352. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12874474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson G. E., Tenland T., Oberg P. A. Evaluation of a laser Doppler flowmeter for measurement of tissue blood flow. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 1980 Oct;27(10):597–604. doi: 10.1109/TBME.1980.326582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson G. E., Tenland T., Obert P. A. A new instrument for continuous measurement of tissue blood flow by light beating spectroscopy. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 1980 Jan;27(1):12–19. doi: 10.1109/TBME.1980.326686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasyk K. A., Thomas S. V., Hassett C. A., Cherry G. W., Faller R. Regional differences in capillary density of the normal human dermis. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1989 Jun;83(6):939–947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szolcsányi J. Antidromic vasodilatation and neurogenic inflammation. Agents Actions. 1988 Feb;23(1-2):4–11. doi: 10.1007/BF01967170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenland T., Salerud E. G., Nilsson G. E., Oberg P. A. Spatial and temporal variations in human skin blood flow. Int J Microcirc Clin Exp. 1983;2(2):81–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Hees J., Gybels J. C nociceptor activity in human nerve during painful and non painful skin stimulation. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1981 Jul;44(7):600–607. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.44.7.600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westerman R. A., Low A., Pratt A., Hutchinson J. S., Szolcsanyi J., Magerl W., Handwerker H. O., Kozak W. M. Electrically evoked skin vasodilatation: a quantitative test of nociceptor function in man. Clin Exp Neurol. 1987;23:81–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]