Abstract
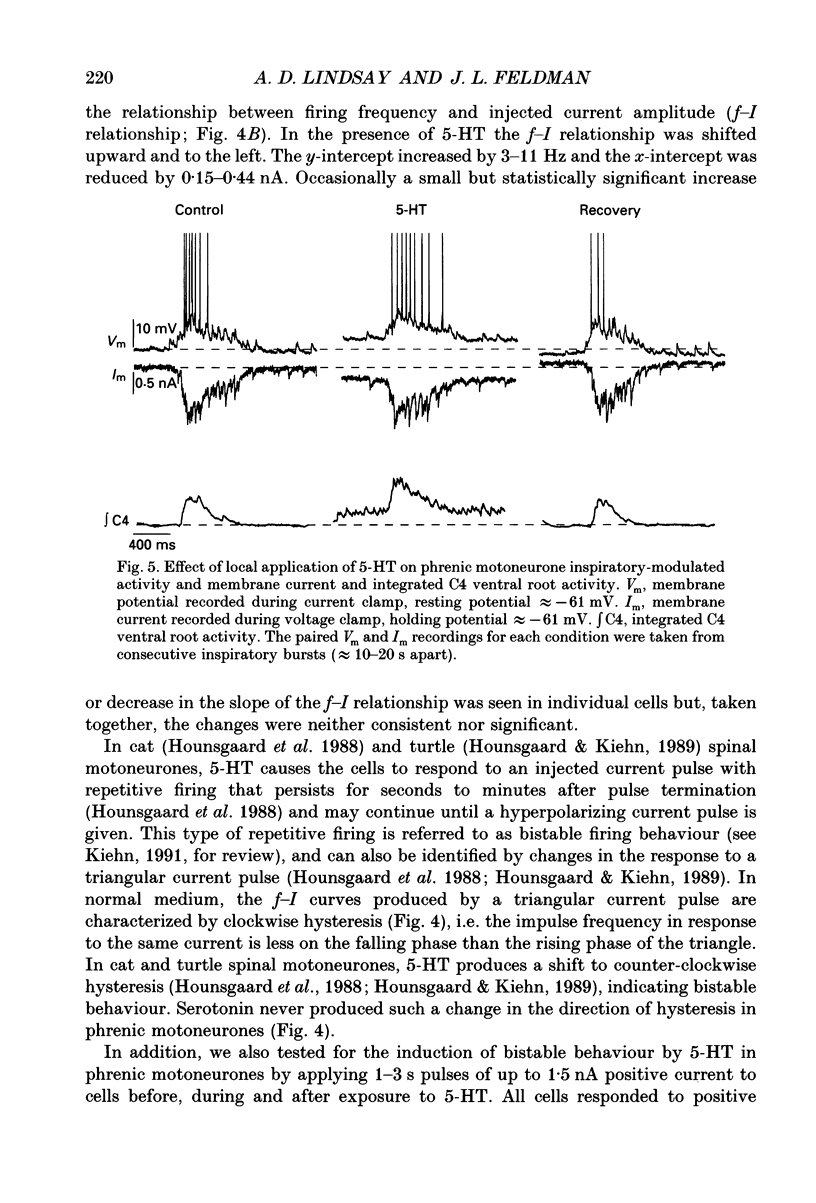
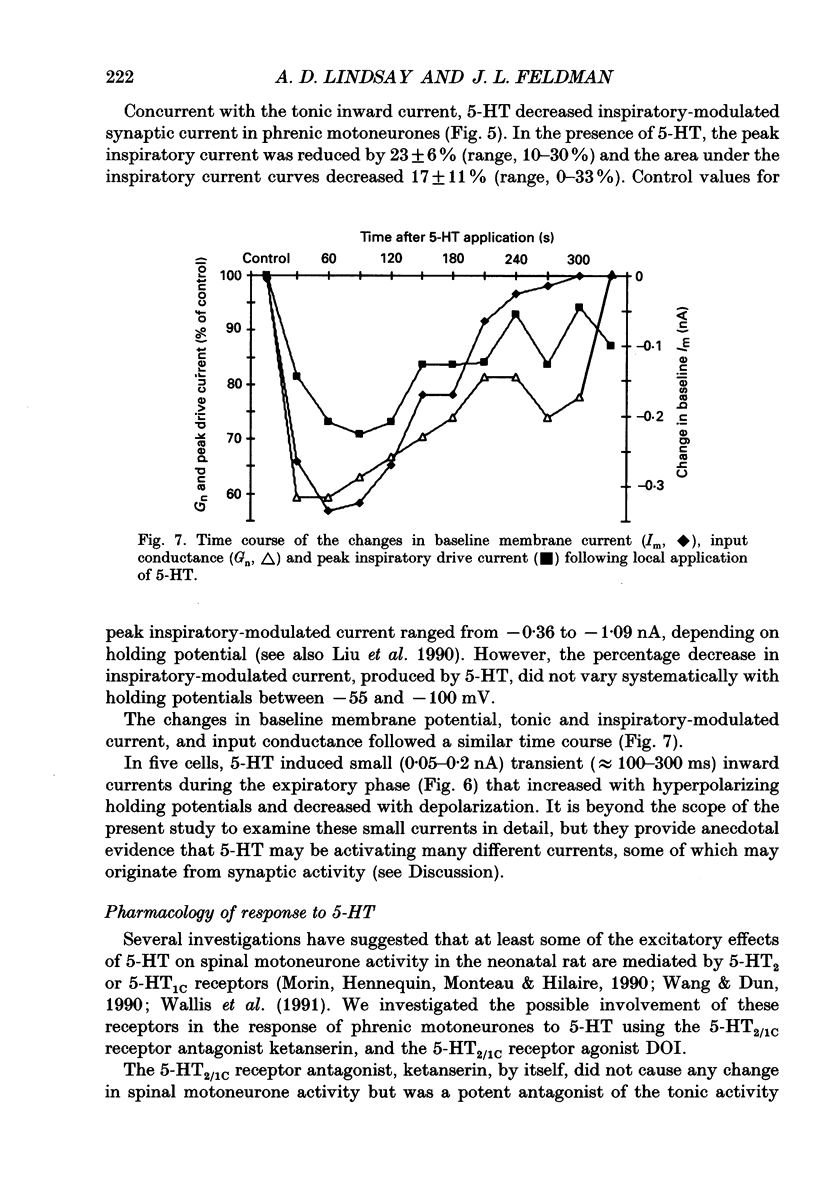
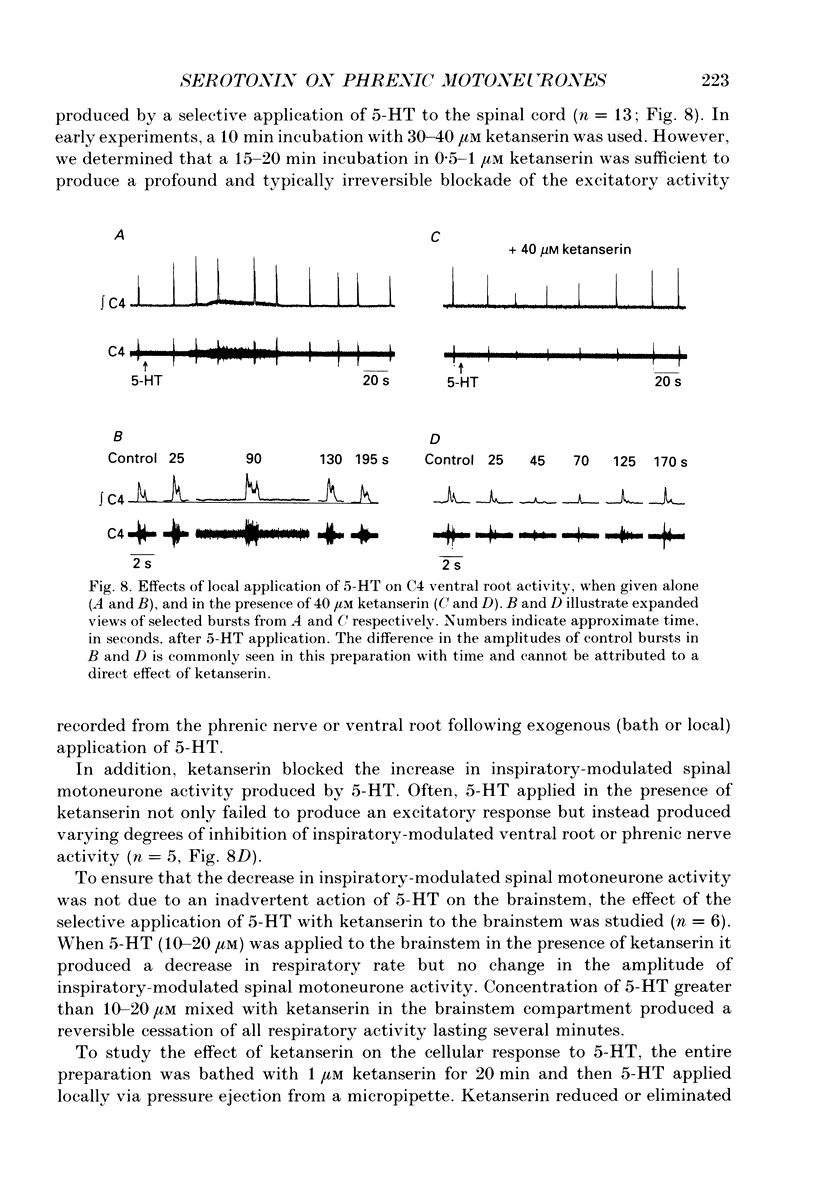
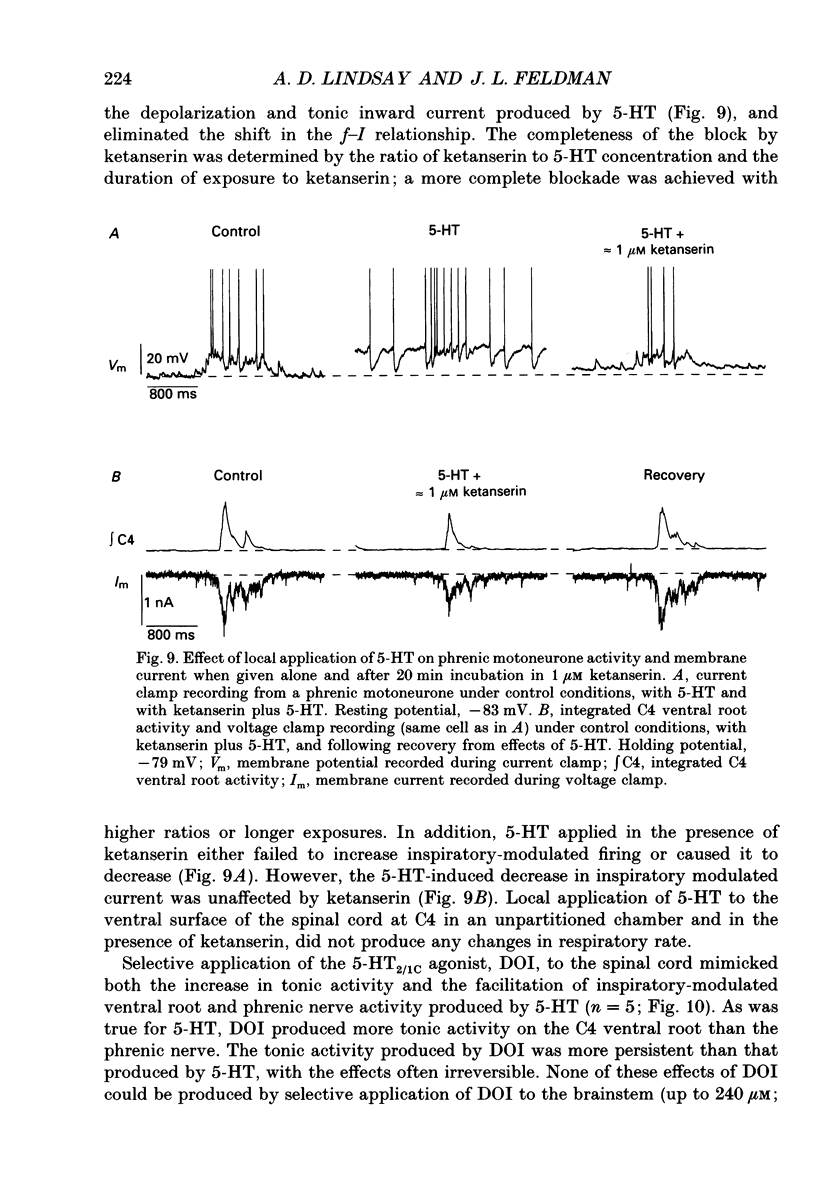
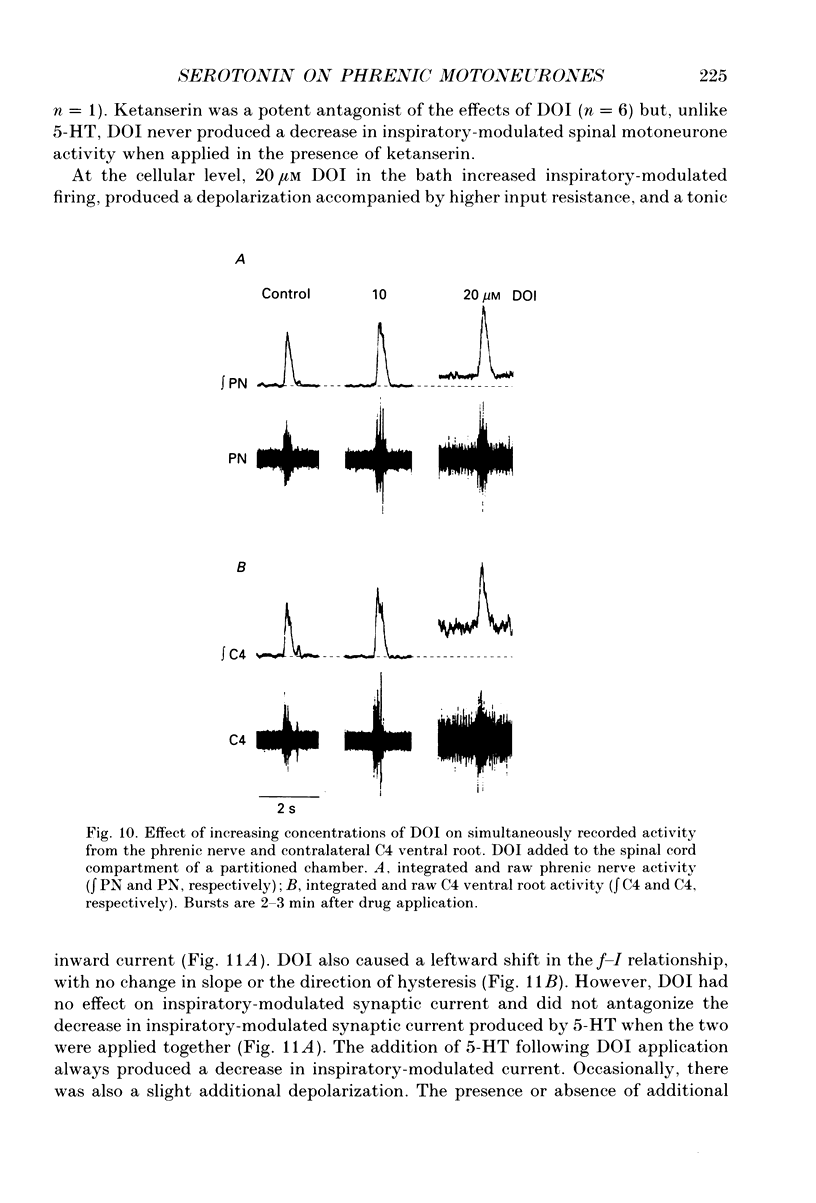
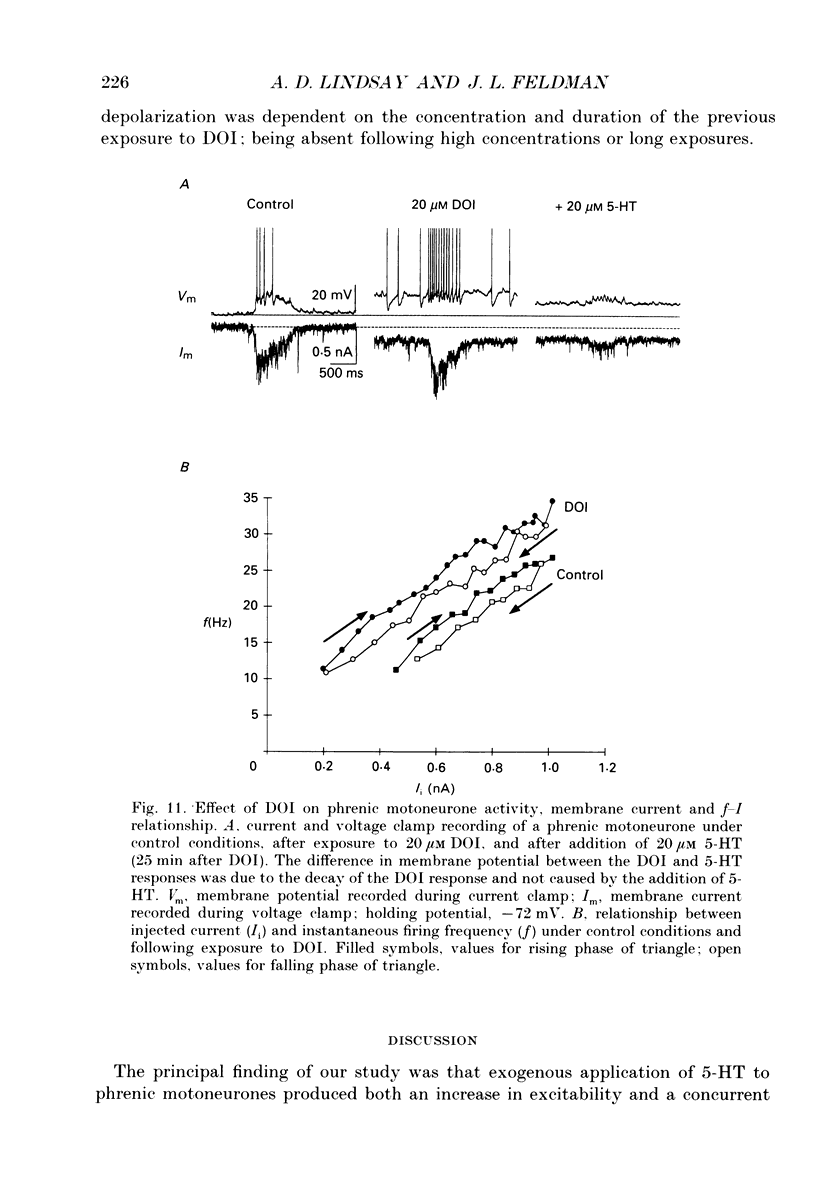
1. The effects of serotonin on phrenic motoneurones were studied in an in vitro preparation of the isolated brainstem and spinal cord from neonatal rats. 2. Serotonin (5-HT; > or = 5-10 microM) increased inspiratory-modulated phrenic nerve activity and produced a small amount of tonic activity during expiration. Inspiratory-modulated activity of the fourth cervical ventral root also increased, but was accompanied by robust tonic activity, which often obscured the rhythmic activity. 3. Serotonin, in both normal and tetrodotoxin-containing medium, depolarized phrenic motoneurones and increased cell input resistance. Serotonin also increased inspriatory-modulated firing as well as the response of phrenic motoneurones to injected current. The y-intercept of the relationship between firing frequency and injected current (f-I) was increased, but the slope was not affected. There was no bistable firing behaviour. 4. Under voltage clamp conditions, 5-HT produced a tonic inward current of 0.07-0.37 nA. This current increased with less negative holding potentials and decreased with more negative holding potentials (-75 to -90 mV) but did not reverse. 5. In addition, 5-HT decreased inspiratory-modulated synaptic current by 23 +/- 6%. The degree of attenuation was not affected by holding potential. The time course of the decrease in inspiratory-modulated synaptic current was similar to the changes seen in tonic inward current and input resistance. 6. Depolarization, tonic inward current, and shift in the f-I relationship produced by 5-HT were antagonized by the 5-HT2/1C receptor antagonist ketanserin and mimicked by the 5-HT2/1C agonist 1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminopropane HCl (DOI). However, the 5-HT induced decrease in inspiratory-modulated synaptic current was not reduced by ketanserin nor mimicked by DOI. 7. We conclude that exogenously applied 5-HT simultaneously increases cell excitability and decreases inspiratory-modulated synaptic current in phrenic motoneurones via different types of receptors. When these responses occurred simultaneously, the increase in excitability predominated and the net effect was an augmentation of inspiratory-modulated phrenic motoneurone activity.
Full text
PDF


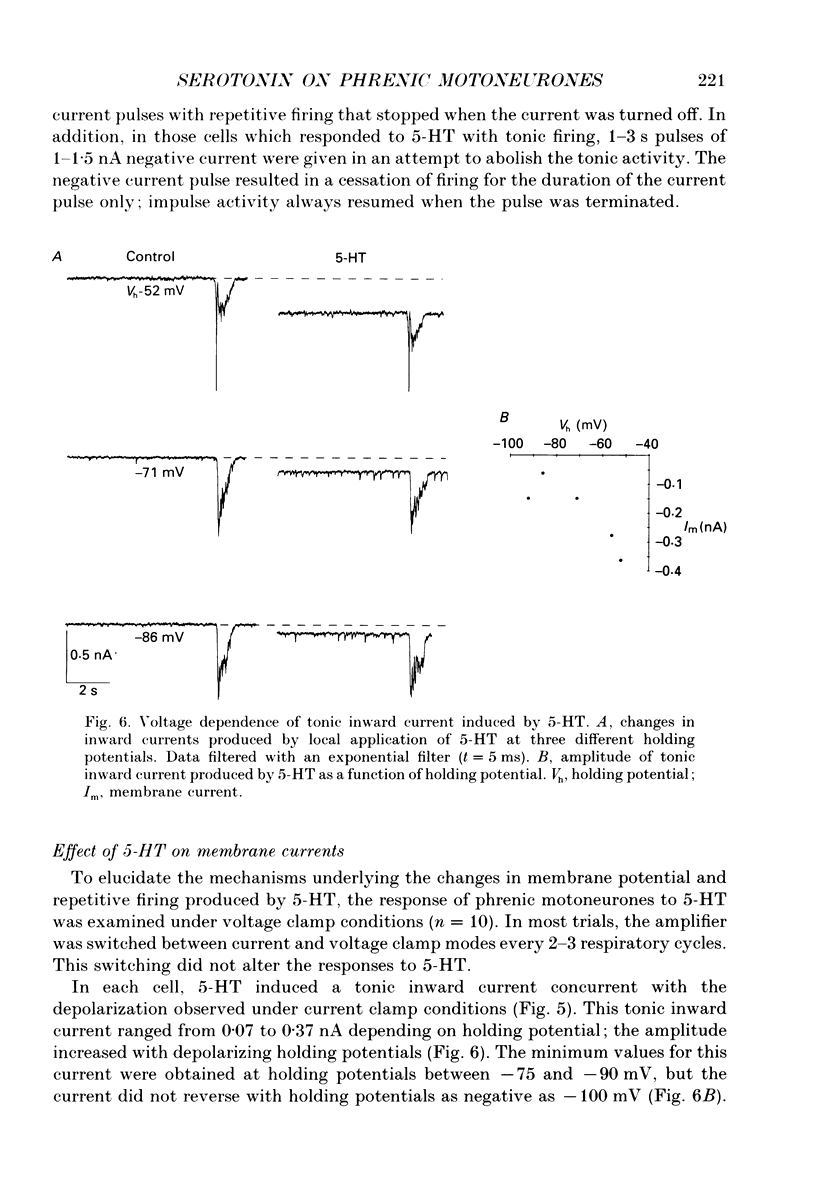







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrade R., Nicoll R. A. Pharmacologically distinct actions of serotonin on single pyramidal neurones of the rat hippocampus recorded in vitro. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;394:99–124. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azmitia E. C., Whitaker-Azmitia P. M. Awakening the sleeping giant: anatomy and plasticity of the brain serotonergic system. J Clin Psychiatry. 1991 Dec;52 (Suppl):4–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baskys A., Niesen C. E., Davies M. F., Carlen P. L. Modulatory actions of serotonin on ionic conductances of hippocampal dentate granule cells. Neuroscience. 1989;29(2):443–451. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90071-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger A. J., Takahashi T. Serotonin enhances a low-voltage-activated calcium current in rat spinal motoneurons. J Neurosci. 1990 Jun;10(6):1922–1928. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-06-01922.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bobker D. H., Williams J. T. Ion conductances affected by 5-HT receptor subtypes in mammalian neurons. Trends Neurosci. 1990 May;13(5):169–173. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90042-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bobker D. H., Williams J. T. Serotonin agonists inhibit synaptic potentials in the rat locus ceruleus in vitro via 5-hydroxytryptamine1A and 5-hydroxytryptamine1B receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Jul;250(1):37–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colino A., Halliwell J. V. Differential modulation of three separate K-conductances in hippocampal CA1 neurons by serotonin. Nature. 1987 Jul 2;328(6125):73–77. doi: 10.1038/328073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hicks T. P., Krupa M., Crépel F. Selective effects of serotonin upon excitatory amino acid-induced depolarizations of Purkinje cells in cerebellar slices from young rats. Brain Res. 1989 Jul 17;492(1-2):371–376. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90922-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtman J. R., Jr, Dick T. E., Berger A. J. Involvement of serotonin in the excitation of phrenic motoneurons evoked by stimulation of the raphe obscurus. J Neurosci. 1986 Apr;6(4):1185–1193. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-04-01185.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtman J. R., Jr, Dick T. E., Berger A. J. Serotonin-mediated excitation of recurrent laryngeal and phrenic motoneurons evoked by stimulation of the raphe obscurus. Brain Res. 1987 Aug 4;417(1):12–20. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90174-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hounsgaard J., Hultborn H., Jespersen B., Kiehn O. Bistability of alpha-motoneurones in the decerebrate cat and in the acute spinal cat after intravenous 5-hydroxytryptophan. J Physiol. 1988 Nov;405:345–367. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hounsgaard J., Kiehn O. Serotonin-induced bistability of turtle motoneurones caused by a nifedipine-sensitive calcium plateau potential. J Physiol. 1989 Jul;414:265–282. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D. A., White S. R. Receptor subtypes mediating facilitation by serotonin of excitability of spinal motoneurons. Neuropharmacology. 1990 Sep;29(9):787–797. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(90)90151-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs B. L. Serotonin and behavior: emphasis on motor control. J Clin Psychiatry. 1991 Dec;52 (Suppl):17–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joëls M., Shinnick-Gallagher P., Gallagher J. P. Effect of serotonin and serotonin analogues on passive membrane properties of lateral septal neurons in vitro. Brain Res. 1987 Aug 4;417(1):99–107. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90183-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. S., Larkman P., Penington N. J., Rainnie D. G., McAllister-Williams H., Hodgkiss J. Serotonin receptor heterogeneity and the role of potassium channels in neuronal excitability. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1991;287:177–191. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-5907-4_15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalley P. M. Responses of phrenic motoneurones of the cat to stimulation of medullary raphe nuclei. J Physiol. 1986 Nov;380:349–371. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalley P. M. Serotoninergic and non-serotoninergic responses of phrenic motoneurones to raphe stimulation in the cat. J Physiol. 1986 Nov;380:373–385. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larkman P. M., Penington N. J., Kelly J. S. Electrophysiology of adult rat facial motoneurones: the effects of serotonin (5-HT) in a novel in vitro brainstem slice. J Neurosci Methods. 1989 May;28(1-2):133–146. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(89)90018-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leger L., Descarries L. Serotonin nerve terminals in the locus coeruleus of adult rat: a radioautographic study. Brain Res. 1978 Apr 21;145(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90791-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay A. D., Greer J. J., Feldman J. L. Phrenic motoneuron morphology in the neonatal rat. J Comp Neurol. 1991 Jun 8;308(2):169–179. doi: 10.1002/cne.903080204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu G., Feldman J. L., Smith J. C. Excitatory amino acid-mediated transmission of inspiratory drive to phrenic motoneurons. J Neurophysiol. 1990 Aug;64(2):423–436. doi: 10.1152/jn.1990.64.2.423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzon N. M., Foehring R. C. Relationship between repetitive firing and afterhyperpolarizations in human neocortical neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1992 Feb;67(2):350–363. doi: 10.1152/jn.1992.67.2.350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maura G., Barzizza A., Folghera S., Raiteri M. Release of endogenous aspartate from rat cerebellum slices and synaptosomes: inhibition mediated by a 5-HT2 receptor and by a 5-HT1 receptor of a possibly novel subtype. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;343(3):229–236. doi: 10.1007/BF00251120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin D., Hennequin S., Monteau R., Hilaire G. Serotonergic influences on central respiratory activity: an in vitro study in the newborn rat. Brain Res. 1990 Dec 10;535(2):281–287. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91611-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin D., Monteau R., Hilaire G. Compared effects of serotonin on cervical and hypoglossal inspiratory activities: an in vitro study in the newborn rat. J Physiol. 1992;451:605–629. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin D., Monteau R., Hilaire G. Serotonin and cervical respiratory motoneurones: intracellular study in the newborn rat brainstem-spinal cord preparation. Exp Brain Res. 1991;84(1):229–232. doi: 10.1007/BF00231779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagano N., Ono H., Fukuda H. Functional significance of subtypes of 5-HT receptors in the rat spinal reflex pathway. Gen Pharmacol. 1988;19(6):789–793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Uchimura N. 5-Hydroxytryptamine acts at 5-HT2 receptors to decrease potassium conductance in rat nucleus accumbens neurones. J Physiol. 1989 Oct;417:1–12. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panicker M. M., Parker I., Miledi R. Receptors of the serotonin 1C subtype expressed from cloned DNA mediate the closing of K+ membrane channels encoded by brain mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2560–2562. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salzman S. K., Hirofuji E., Llados-Eckman C., MacEwen G. D., Beckman A. L. Monoaminergic responses to spinal trauma. Participation of serotonin in posttraumatic progression of neural damage. J Neurosurg. 1987 Mar;66(3):431–439. doi: 10.3171/jns.1987.66.3.0431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid K., Böhmer G., Merkelbach S. Serotonergic control of phrenic motoneuronal activity at the level of the spinal cord of the rabbit. Neurosci Lett. 1990 Aug 14;116(1-2):204–209. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90411-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. C., Feldman J. L. In vitro brainstem-spinal cord preparations for study of motor systems for mammalian respiration and locomotion. J Neurosci Methods. 1987 Oct;21(2-4):321–333. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(87)90126-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Berger A. J. Direct excitation of rat spinal motoneurones by serotonin. J Physiol. 1990 Apr;423:63–76. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T. Inward rectification in neonatal rat spinal motoneurones. J Physiol. 1990 Apr;423:47–62. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vu E. T., Krasne F. B. Evidence for a computational distinction between proximal and distal neuronal inhibition. Science. 1992 Mar 27;255(5052):1710–1712. doi: 10.1126/science.1553559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis D. I., Connell L. A., Kvaltinova Z. Further studies on the action of 5-hydroxytryptamine on lumbar motoneurones in the rat isolated spinal cord. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1991 Apr;343(4):344–352. doi: 10.1007/BF00179038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallén P., Buchanan J. T., Grillner S., Hill R. H., Christenson J., Hökfelt T. Effects of 5-hydroxytryptamine on the afterhyperpolarization, spike frequency regulation, and oscillatory membrane properties in lamprey spinal cord neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1989 Apr;61(4):759–768. doi: 10.1152/jn.1989.61.4.759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang M. Y., Dun N. J. 5-Hydroxytryptamine responses in neonate rat motoneurones in vitro. J Physiol. 1990 Nov;430:87–103. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu S. Y., Wang M. Y., Dun N. J. Serotonin via presynaptic 5-HT1 receptors attenuates synaptic transmission to immature rat motoneurons in vitro. Brain Res. 1991 Jul 19;554(1-2):111–121. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90178-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhan W. Z., Ellenberger H. H., Feldman J. L. Monoaminergic and GABAergic terminations in phrenic nucleus of rat identified by immunohistochemical labeling. Neuroscience. 1989;31(1):105–113. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90033-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang L. Effects of 5-hydroxytryptamine on cat spinal motoneurons. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1991 Feb;69(2):154–163. doi: 10.1139/y91-022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


