Abstract
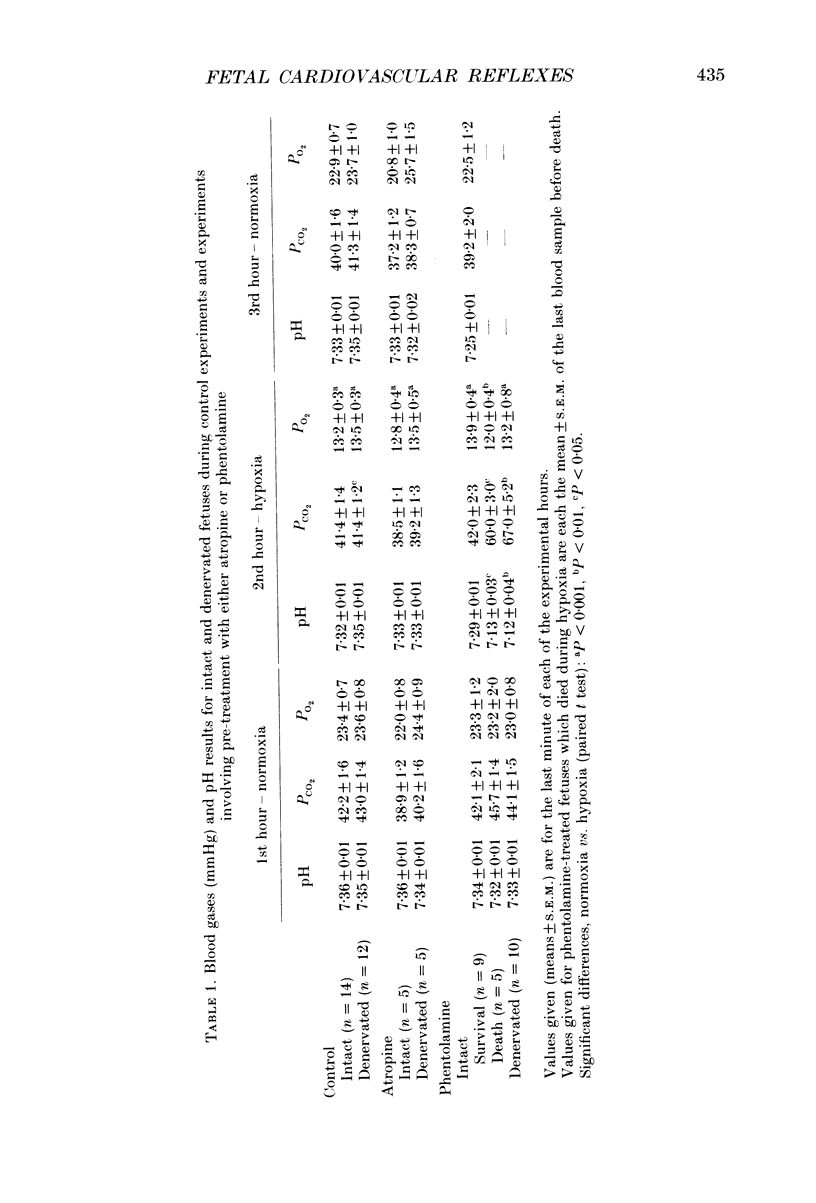
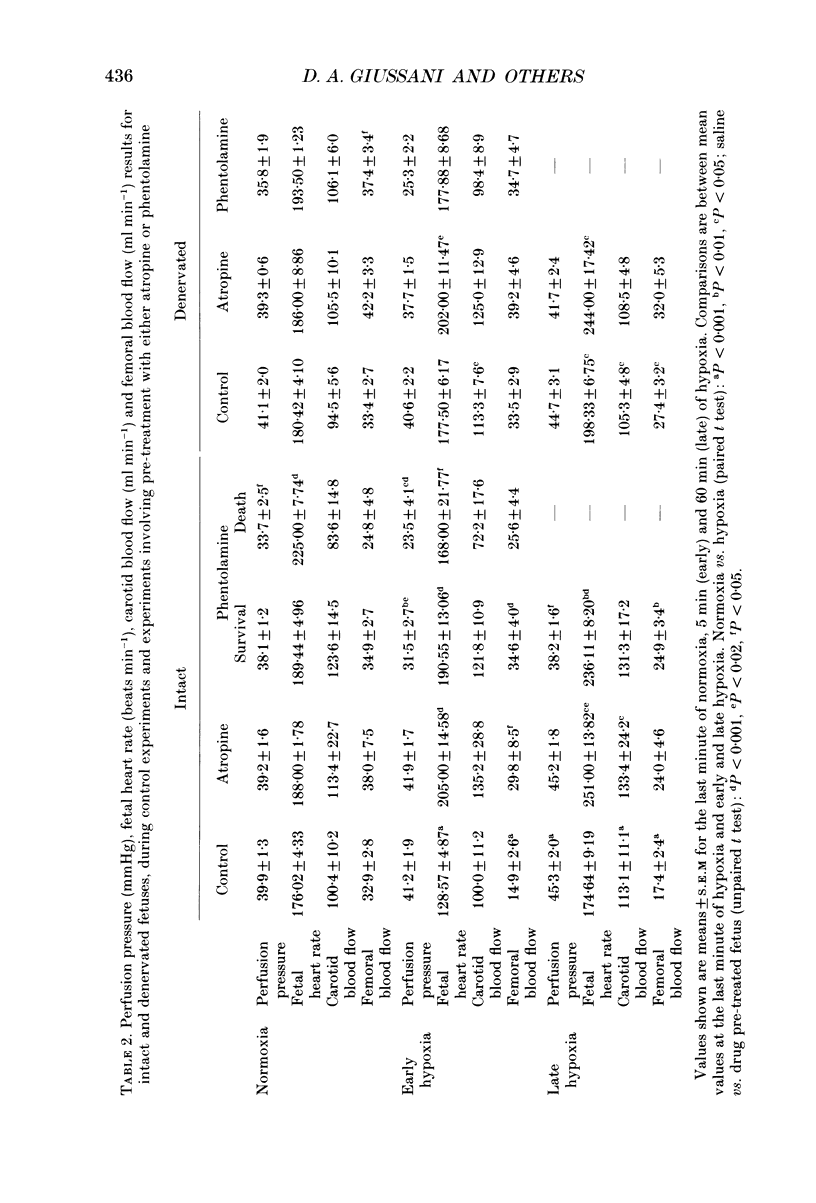
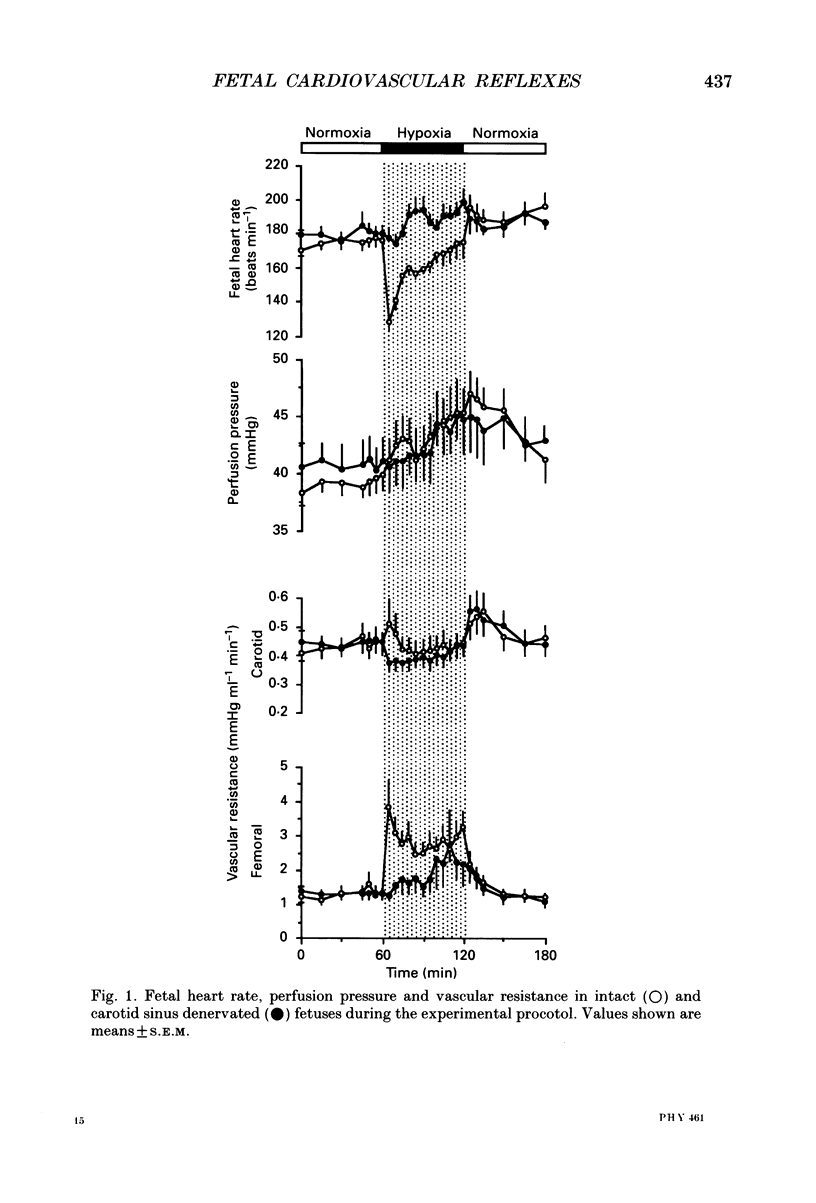
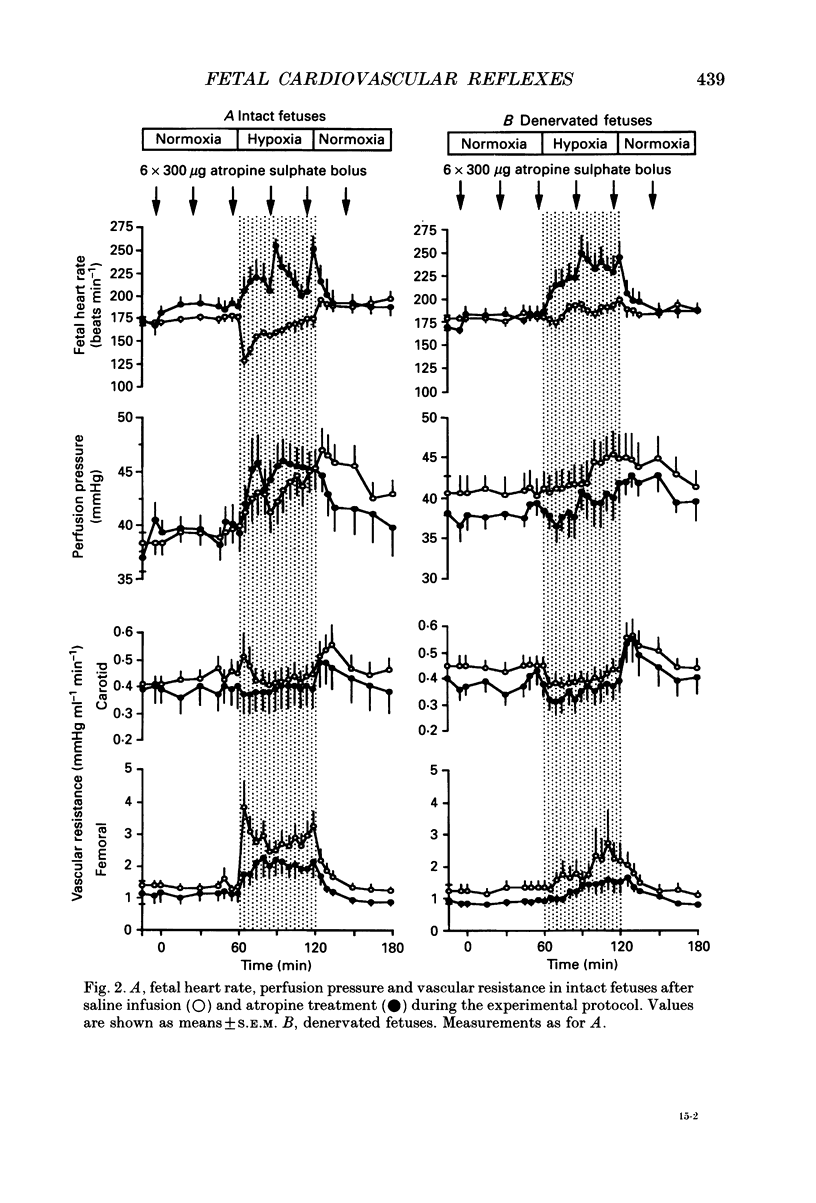
1. We studied the effects of acute isocapnic hypoxia on arterial and central venous pressures, carotid and femoral blood flows and heart rate in intact and carotid denervated fetal sheep between 118 and 125 days gestation, after pre-treatment with either saline, atropine or phentolamine. Electrocortical activity (ECoG) and the incidence of fetal breathing movements (FBM) were also compared between intact and carotid denervated fetuses. 2. There were no significant differences between intact and denervated fetuses in any variable measured during normoxia. Soon after the onset of hypoxia a marked bradycardia occurred in intact, but not in denervated fetuses. Femoral blood flow and femoral vascular resistance (perfusion pressure/femoral blood flow) increased in intact, but not in denervated fetuses. Carotid blood flow increased in both groups of fetuses during hypoxia, but carotid vascular resistance did not change. During hypoxia, the incidence of FBM and low-voltage ECoG was similarly reduced in both groups of fetuses. 3. Atropine produced a rise in fetal heart rate during the control period in intact but not in denervated fetuses. At the onset of hypoxia atropine prevented the initial bradycardia seen in intact fetuses. In denervated fetuses a further increase in heart rate occurred throughout the hypoxia. 4. All denervated fetuses treated with phentolamine died during the hypoxic challenge, but nine out of fourteen intact fetuses treated with phentolamine survived. 5. In intact fetuses which survived hypoxia after treatment with phentolamine, the increase in arterial blood pressure was smaller and the increase in femoral resistance did not occur. In these fetuses a rise in heart rate occurred in hypoxia. Carotid vascular resistance decreased during hypoxia after administration of phentolamine. 6. Our results indicate that the initial cardiovascular responses of the late gestation sheep fetus to hypoxia are reflex, and that the carotid chemoreceptors provide the afferent limb of this reflex. The bradycardia is mediated through a muscarinic pathway, as it is blocked by atropine. The femoral vasoconstriction is mediated through an alpha-adrenergic mechanism, mediated both neurally by a carotid chemoreflex and via catecholamines released directly from the adrenal medulla. Both these components are blocked by phentolamine. 7. The differences in survival between intact and denervated fetuses during hypoxia after phentolamine suggest that the carotid chemoreflex response to hypoxia involves mechanisms in addition to vagal efferents to the heart and alpha-adrenergic actions at peripheral blood vessels.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




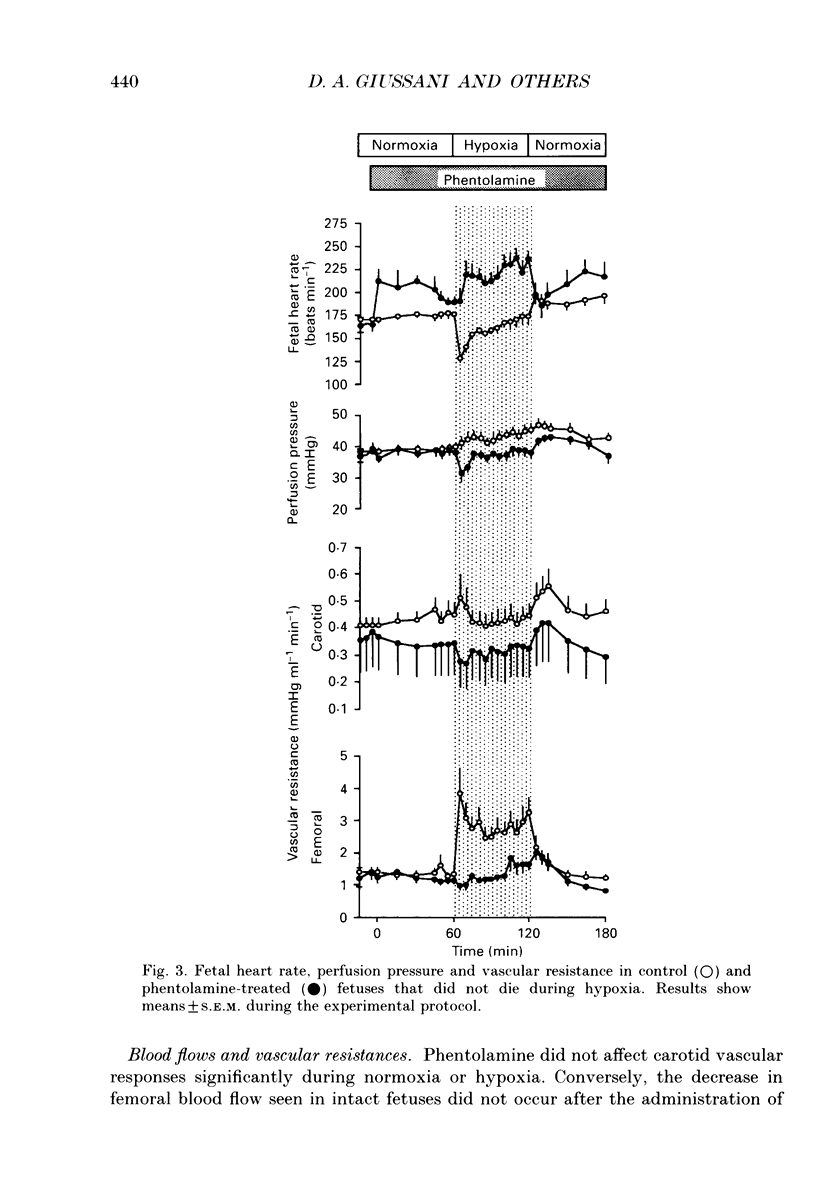
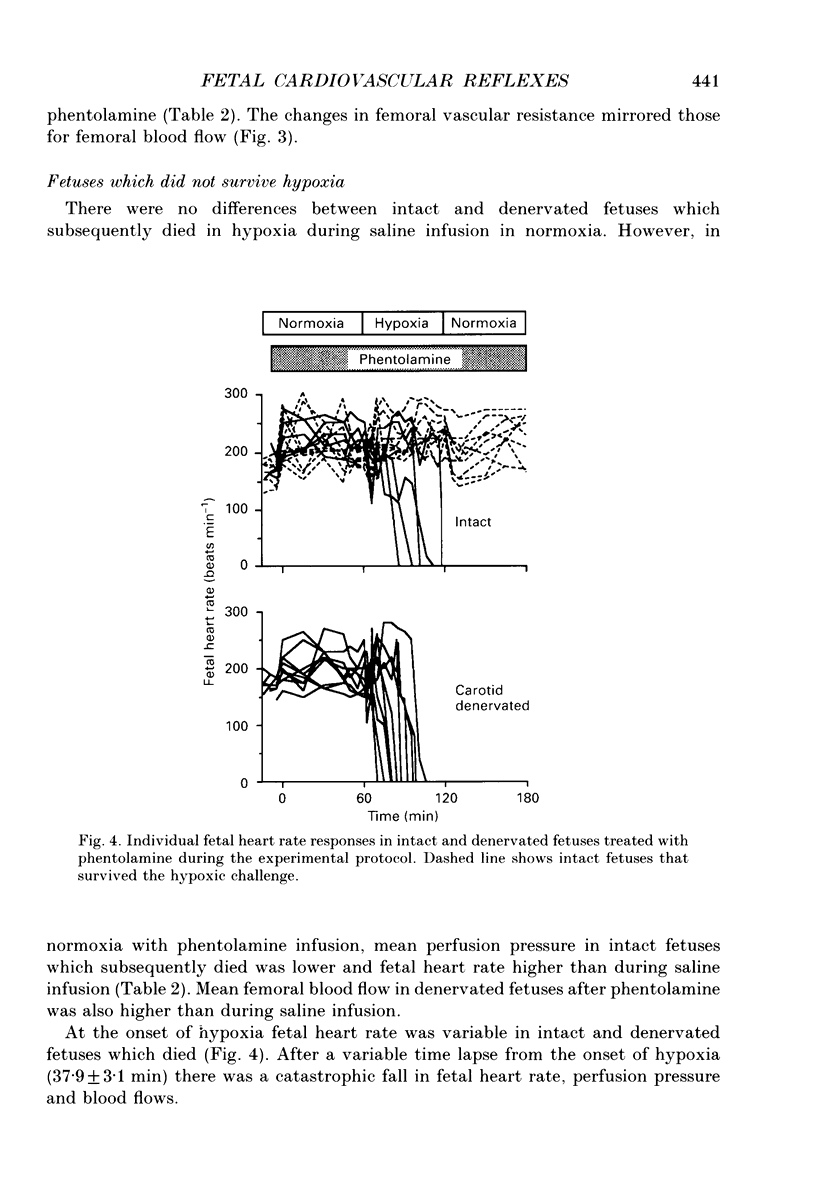




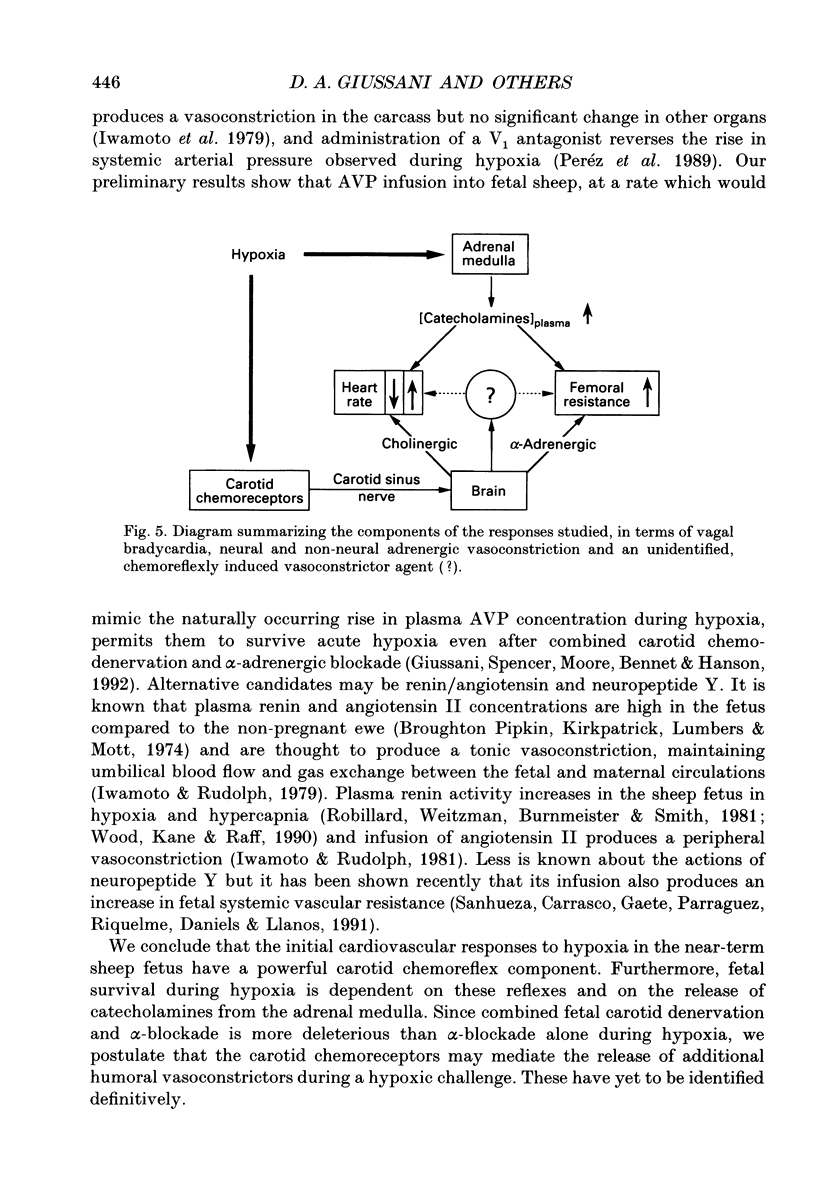



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blanco C. E., Dawes G. S., Hanson M. A., McCooke H. B. Carotid baroreceptors in fetal and newborn sheep. Pediatr Res. 1988 Sep;24(3):342–346. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198809000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanco C. E., Dawes G. S., Hanson M. A., McCooke H. B. The response to hypoxia of arterial chemoreceptors in fetal sheep and new-born lambs. J Physiol. 1984 Jun;351:25–37. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanco C. E., Dawes G. S., Walker D. W. Effect of hypoxia on polysynaptic hind-limb reflexes of unanaesthetized fetal and new-born lambs. J Physiol. 1983 Jun;339:453–466. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block B. S., Schlafer D. H., Wentworth R. A., Kreitzer L. A., Nathanielsz P. W. Intrauterine asphyxia and the breakdown of physiologic circulatory compensation in fetal sheep. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1990 May;162(5):1325–1331. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(90)90046-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boddy K., Dawes G. S., Fisher R., Pinter S., Robinson J. S. Foetal respiratory movements, electrocortical and cardiovascular responses to hypoxaemia and hypercapnia in sheep. J Physiol. 1974 Dec;243(3):599–618. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broughton Pipkin F., Lumbers E. R., Mott J. C. Factors influencing plasma renin and angiotensin II in the conscious pregnant ewe and its foetus. J Physiol. 1974 Dec;243(3):619–636. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn H. E., Sacks E. J., Heymann M. A., Rudolph A. M. Cardiovascular responses to hypoxemia and acidemia in fetal lambs. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1974 Nov 15;120(6):817–824. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(74)90587-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel S. S., Stark R. I., Zubrow A. B., Fox H. E., Husain M. K., James L. S. Factors in the release of vasopressin by the hypoxic fetus. Endocrinology. 1983 Nov;113(5):1623–1628. doi: 10.1210/endo-113-5-1623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawes G. S., Duncan S. L., Lewis B. V., Merlet C. L., Owen-Thomas J. B., Reeves J. T. Hypoxaemia and aortic chemoreceptor function in foetal lambs. J Physiol. 1969 Mar;201(1):105–116. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawes G. S., Gardner W. N., Johnston B. M., Walker D. W. Breathing in fetal lambs: the effect of brain stem section. J Physiol. 1983 Feb;335:535–553. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawes G. S., Lewis B. V., Milligan J. E., Roach M. R., Talner N. S. Vasomotor responses in the hind limbs of foetal and new-born lambs to asphyxia and aortic chemoreceptor stimulation. J Physiol. 1968 Mar;195(1):55–81. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heistad D. D., Marcus M. L., Ehrhardt J. C., Abboud F. M. Effect of stimulation of carotid chemoreceptors on total and regional cerebral blood flow. Circ Res. 1976 Jan;38(1):20–25. doi: 10.1161/01.res.38.1.20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itskovitz J., LaGamma E. F., Bristow J., Rudolph A. M. Cardiovascular responses to hypoxemia in sinoaortic-denervated fetal sheep. Pediatr Res. 1991 Oct;30(4):381–385. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199110000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itskovitz J., Rudolph A. M. Denervation of arterial chemoreceptors and baroreceptors in fetal lambs in utero. Am J Physiol. 1982 May;242(5):H916–H920. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1982.242.5.H916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwamoto H. S., Rudolph A. M. Effects of angiotensin II on the blood flow and its distribution in fetal lambs. Circ Res. 1981 Feb;48(2):183–189. doi: 10.1161/01.res.48.2.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwamoto H. S., Rudolph A. M. Effects of endogenous angiotensin II on the fetal circulation. J Dev Physiol. 1979 Aug;1(4):283–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwamoto H. S., Rudolph A. M., Keil L. C., Heymann M. A. Hemodynamic responses of the sheep fetus to vasopressin infusion. Circ Res. 1979 Mar;44(3):430–436. doi: 10.1161/01.res.44.3.430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwamoto H. S., Rudolph A. M., Mirkin B. L., Keil L. C. Circulatory and humoral responses of sympathectomized fetal sheep to hypoxemia. Am J Physiol. 1983 Nov;245(5 Pt 1):H767–H772. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1983.245.5.H767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen A., Hohmann M., Künzel W. Dynamic changes in organ blood flow and oxygen consumption during acute asphyxia in fetal sheep. J Dev Physiol. 1987 Dec;9(6):543–559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. T., Ritchie J. W. The effects of adrenergic blockade on fetal response to hypoxia. J Dev Physiol. 1983 Aug;5(4):211–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. T., Robinson R. O. Plasma catecholamines in foetal and adult sheep. J Physiol. 1975 Jun;248(1):15–33. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. T., Roebuck M. M., Walker D. W., Johnston B. M. Modulation of the responses of fetal sheep to adrenergic stimulation by adrenal demedullation and chemical sympathectomy. J Dev Physiol. 1989 Jan;11(1):45–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. T., Roebuck M. M., Walker D. W., Johnston B. M. The role of the adrenal medulla and peripheral sympathetic nerves in the physiological responses of the fetal sheep to hypoxia. J Dev Physiol. 1988 Feb;10(1):17–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. T., Roebuck M. M., Walker D. W., Lagercrantz H., Johnston B. M. Cardiovascular, metabolic and endocrine effects of chemical sympathectomy and of adrenal demedullation in fetal sheep. J Dev Physiol. 1987 Aug;9(4):347–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer S. Z. Sixth gaddum memorial lecture, National Institute for Medical Research, Mill Hill, January 1977. Presynaptic receptors and their role in the regulation of transmitter release. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Aug;60(4):481–497. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb07526.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis A. B., Donovan M., Platzker A. C. Cardiovascular responses to autonomic blockade in hypoxemic fetal lambs. Biol Neonate. 1980;37(5-6):233–242. doi: 10.1159/000241281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews J. N., Altman D. G., Campbell M. J., Royston P. Analysis of serial measurements in medical research. BMJ. 1990 Jan 27;300(6719):230–235. doi: 10.1136/bmj.300.6719.230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. J., Hanson M. A. The role of peripheral chemoreceptors in the rapid response of the pulmonary vasculature of the late gestation sheep fetus to changes in PaO2. J Dev Physiol. 1991 Sep;16(3):133–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. J., Parkes M. J., Nijhuis J. G., Hanson M. A. The incidence of breathing movements of fetal sheep in normoxia and hypoxia after peripheral chemodenervation and brain-stem transection. J Dev Physiol. 1989 Mar;11(3):147–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murai D. T., Lee C. C., Wallen L. D., Kitterman J. A. Denervation of peripheral chemoreceptors decreases breathing movements in fetal sheep. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1985 Aug;59(2):575–579. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1985.59.2.575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parer J. T., Krueger T. R., Harris J. L. Fetal oxygen consumption and mechanisms of heart rate response during artificially produced late decelerations of fetal heart rate in sheep. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1980 Feb 15;136(4):478–482. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(80)90674-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeters L. L., Sheldon R. E., Jones M. D., Jr, Makowski E. L., Meschia G. Blood flow to fetal organs as a function of arterial oxygen content. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1979 Nov 1;135(5):637–646. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(16)32989-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piacquadio K. M., Brace R. A., Cheung C. Y. Role of vasopressin in mediation of fetal cardiovascular responses to acute hypoxia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1990 Oct;163(4 Pt 1):1294–1300. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(90)90709-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff H., Kane C. W., Wood C. E. Arginine vasopressin responses to hypoxia and hypercapnia in late-gestation fetal sheep. Am J Physiol. 1991 Jun;260(6 Pt 2):R1077–R1081. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1991.260.6.R1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuss M. L., Parer J. T., Harris J. L., Krueger T. R. Hemodynamic effects of alpha-adrenergic blockade during hypoxia in fetal sheep. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1982 Feb 15;142(4):410–415. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(16)32381-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robillard J. E., Weitzman R. E., Burmeister L., Smith F. G., Jr Developmental aspects of the renal response to hypoxemia in the lamb fetus. Circ Res. 1981 Jan;48(1):128–138. doi: 10.1161/01.res.48.1.128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph A. M. Distribution and regulation of blood flow in the fetal and neonatal lamb. Circ Res. 1985 Dec;57(6):811–821. doi: 10.1161/01.res.57.6.811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph A. M. The fetal circulation and its response to stress. J Dev Physiol. 1984 Feb;6(1):11–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rurak D. W. Plasma vasopressin levels during hypoxaemia and the cardiovascular effects of exogenous vasopressin in foetal and adult sheep. J Physiol. 1978 Apr;277:341–357. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker A. M., Cannata J. P., Dowling M. H., Ritchie B. C., Maloney J. E. Age-dependent pattern of autonomic heart rate control during hypoxia in fetal and newborn lambs. Biol Neonate. 1979;35(3-4):198–208. doi: 10.1159/000241173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. A., Hanson M. A. Role of the carotid chemoreceptors in the respiratory response of newborn lambs to alternate pairs of breaths of air and a hypoxic gas. J Dev Physiol. 1990 Mar;13(3):157–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood C. E., Kane C., Raff H. Peripheral chemoreceptor control of fetal renin responses to hypoxia and hypercapnia. Circ Res. 1990 Sep;67(3):722–732. doi: 10.1161/01.res.67.3.722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaffe H., Parer J. T., Block B. S., Llanos A. J. Cardiorespiratory responses to graded reductions of uterine blood flow in the sheep fetus. J Dev Physiol. 1987 Aug;9(4):325–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


