Abstract
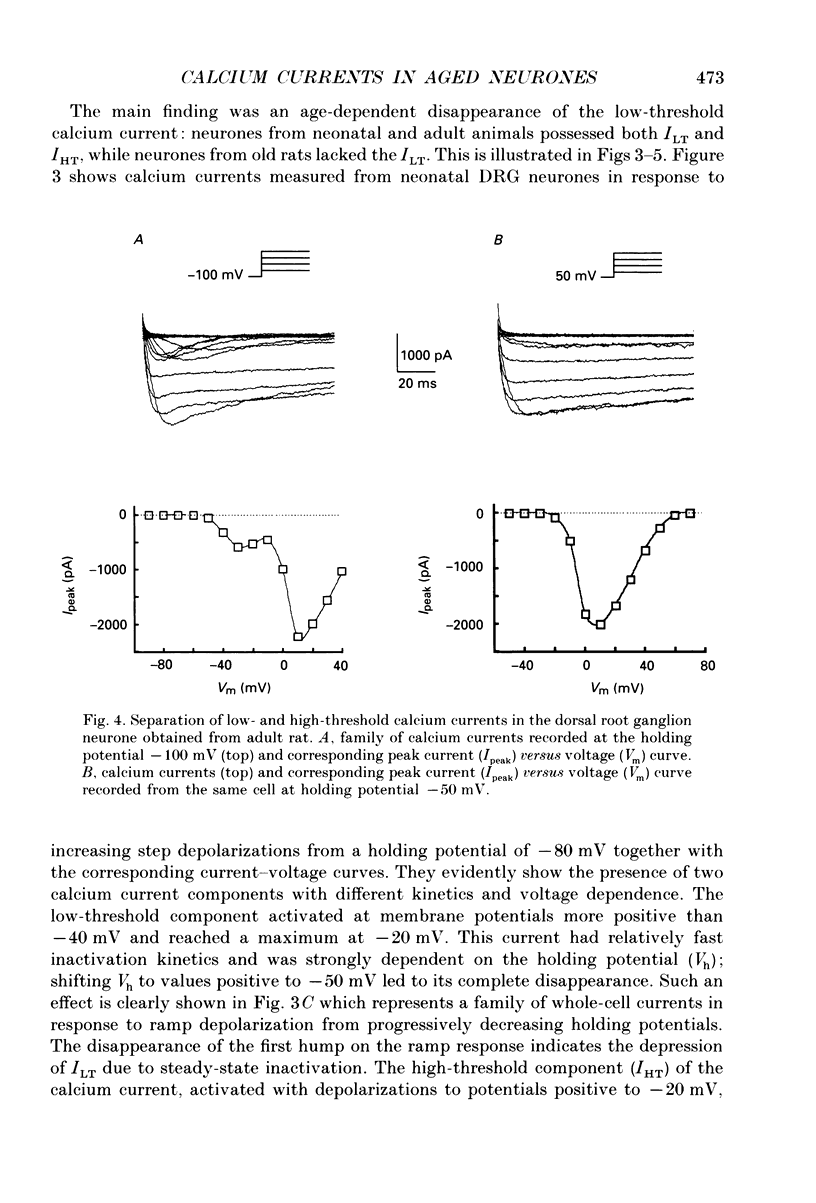
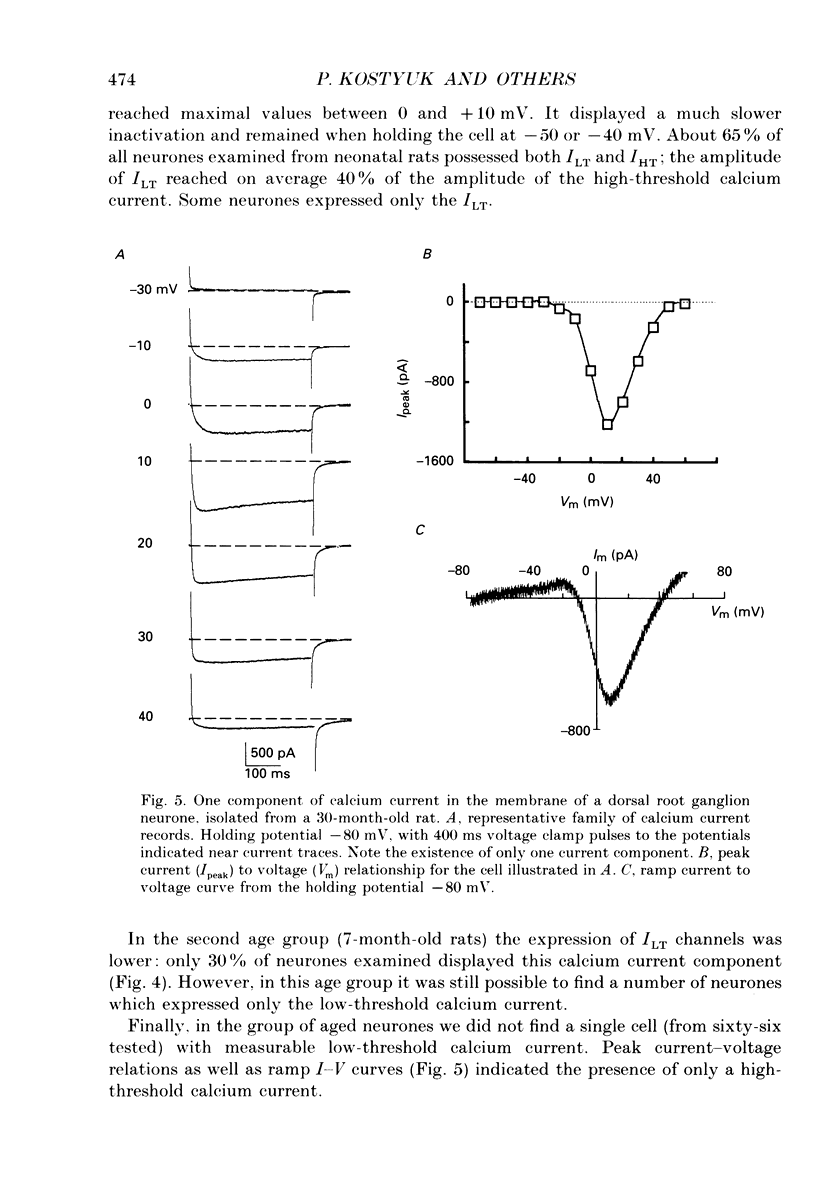
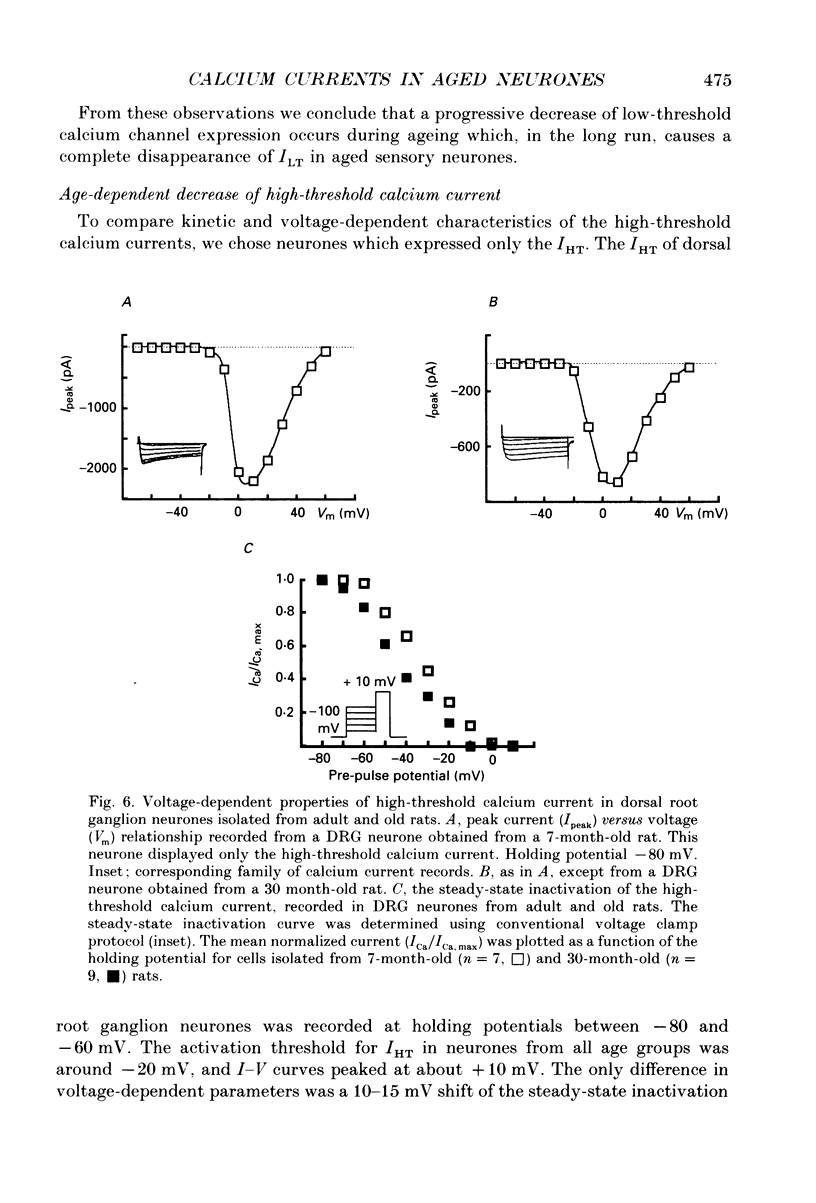
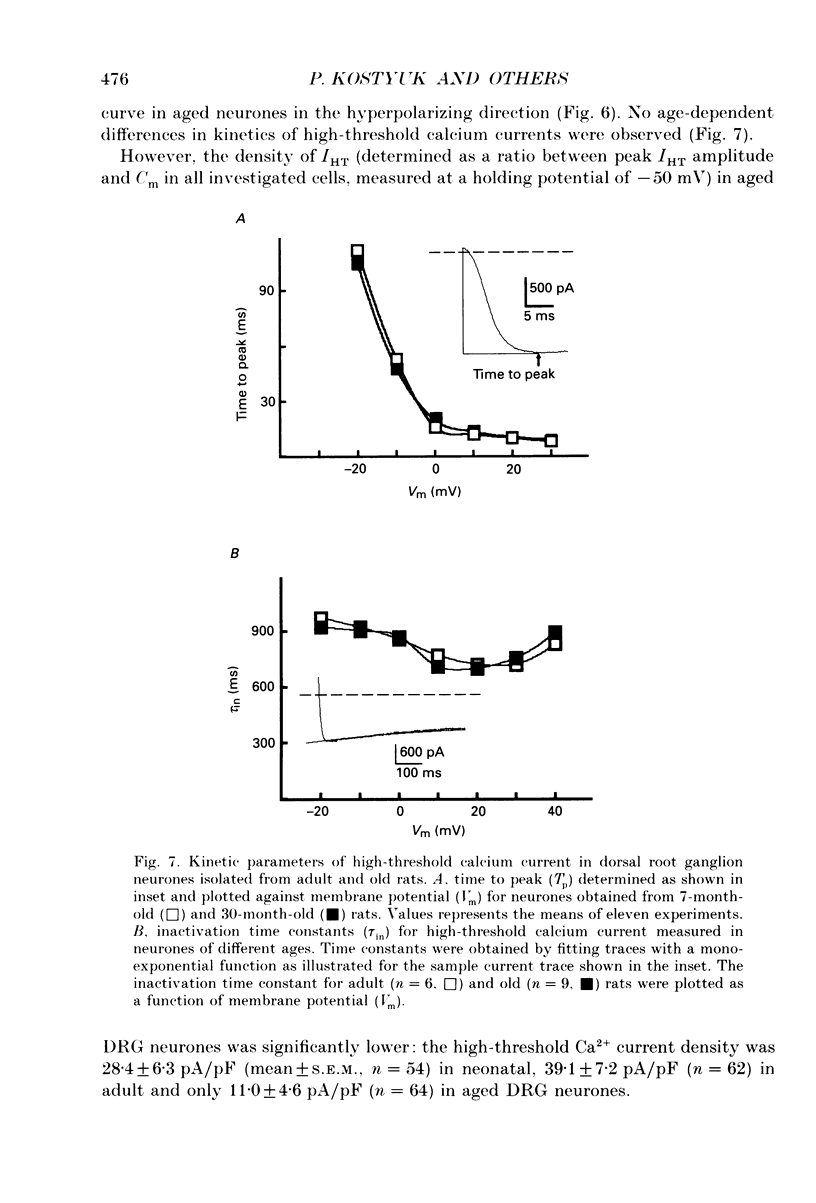
1. The whole-cell voltage clamp technique was used to record calcium currents in the somatic membrane of rat cultured dorsal root ganglion neurones. 2. Neurones were enzymatically isolated from animals of three age groups (neonatal, 2-7 days; adult, 7 months; and old, 30 months) and maintained in primary culture 3-14 days. 3. The neurones isolated from neonatal and old rats showed two distinct types of Ca2+ currents, a low-threshold transient current and a high-threshold sustained current, whereas neurones from old rats showed only a high-threshold calcium current. 4. The density of the high-threshold calcium current was 28.4 +/- 6.3 pA/pF (mean +/- S.E.M., n = 54) in neonatal, 39.1 +/- 7.2 pA/pF (n = 62) in adult and 11.0 +/- 4.6 pA/pF (n = 64) in old dorsal root ganglion neurones. 5. We found no difference in elementary high-threshold Ca2+ current characteristics in neurones from different age groups. The single-channel conductance was (with 60 mM Ca2+ in the recording pipette) 16.0 +/- 2.7 pS (mean +/- S.E.M., n = 9) in neonatal, 16.2 +/- 1.7 pS (n = 11) in adult and 16.4 +/- 1.2 pS (n = 12) in old neurones. 6. Current-voltage relations and kinetics of high-threshold calcium currents showed no detectable age-dependent difference. 7. The run-down of high-threshold calcium currents in dorsal root ganglion neurones from old rats was practically insensitive to intracellular administration of cyclic AMP and ATP. The same intervention caused a significant deceleration of Ca2+ current run-down in the majority of neonatal and in some adult cells. 8. We suggest that the disappearance of the low-threshold calcium current and reduction of high-threshold calcium current with ageing is due to a depression of calcium channel expression during late ontogenesis. The decrease of sensitivity of high-threshold calcium channels to phosphorylation by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase in aged neurones could also be a reason for altered turnover between silent and functional pools of calcium channels, which may underlie the age-dependent decline in the density of high-threshold calcium channels.
Full text
PDF


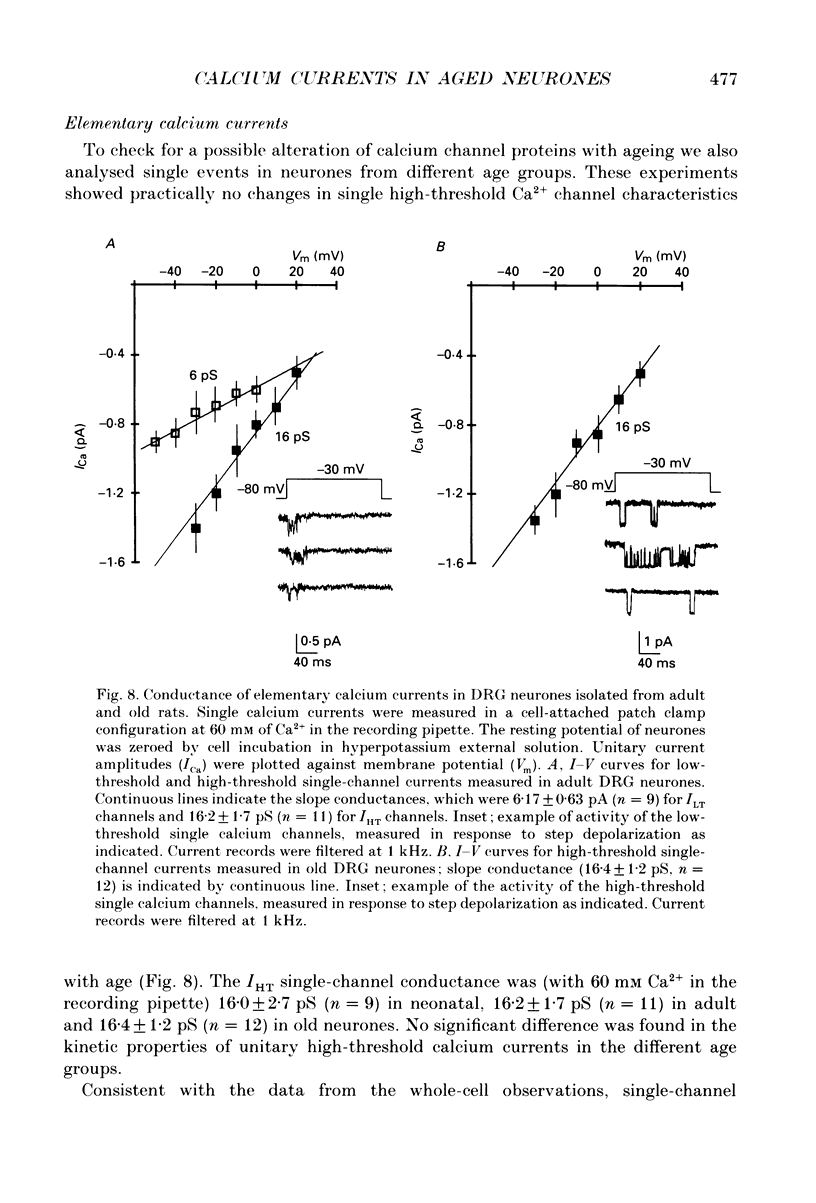
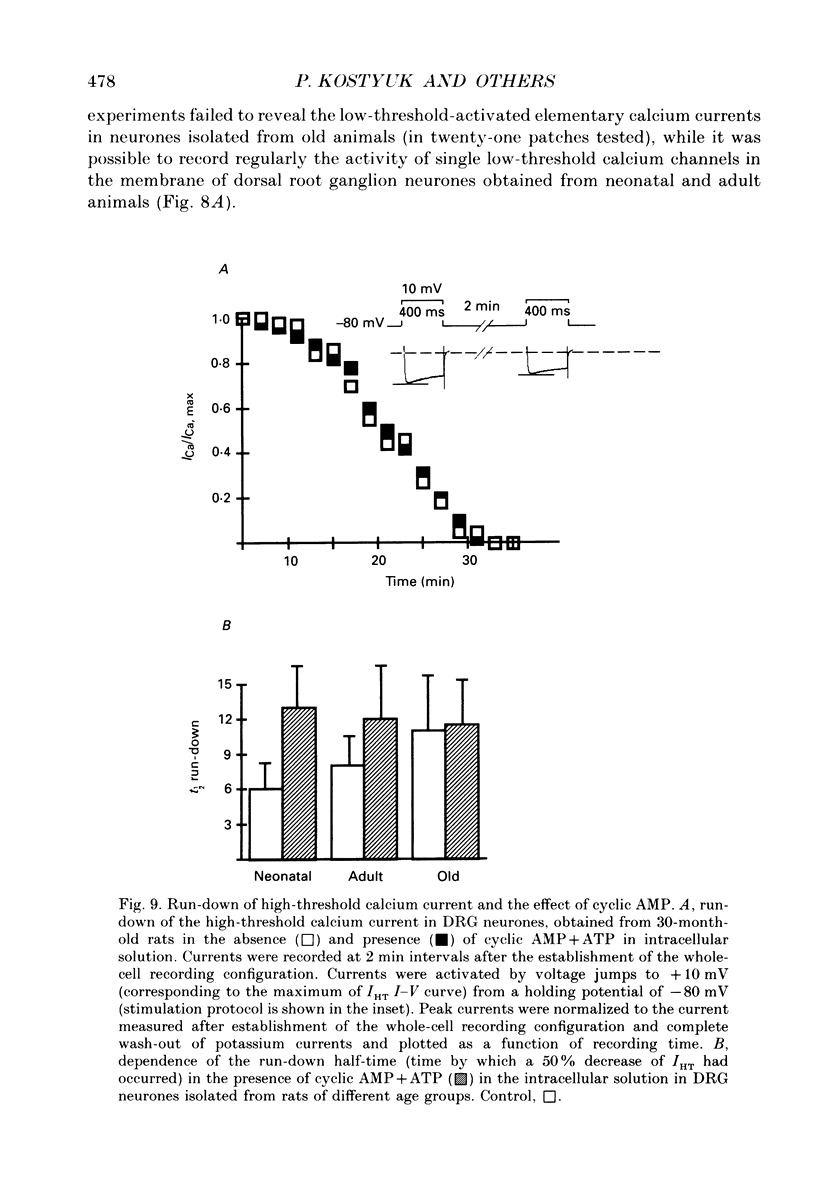

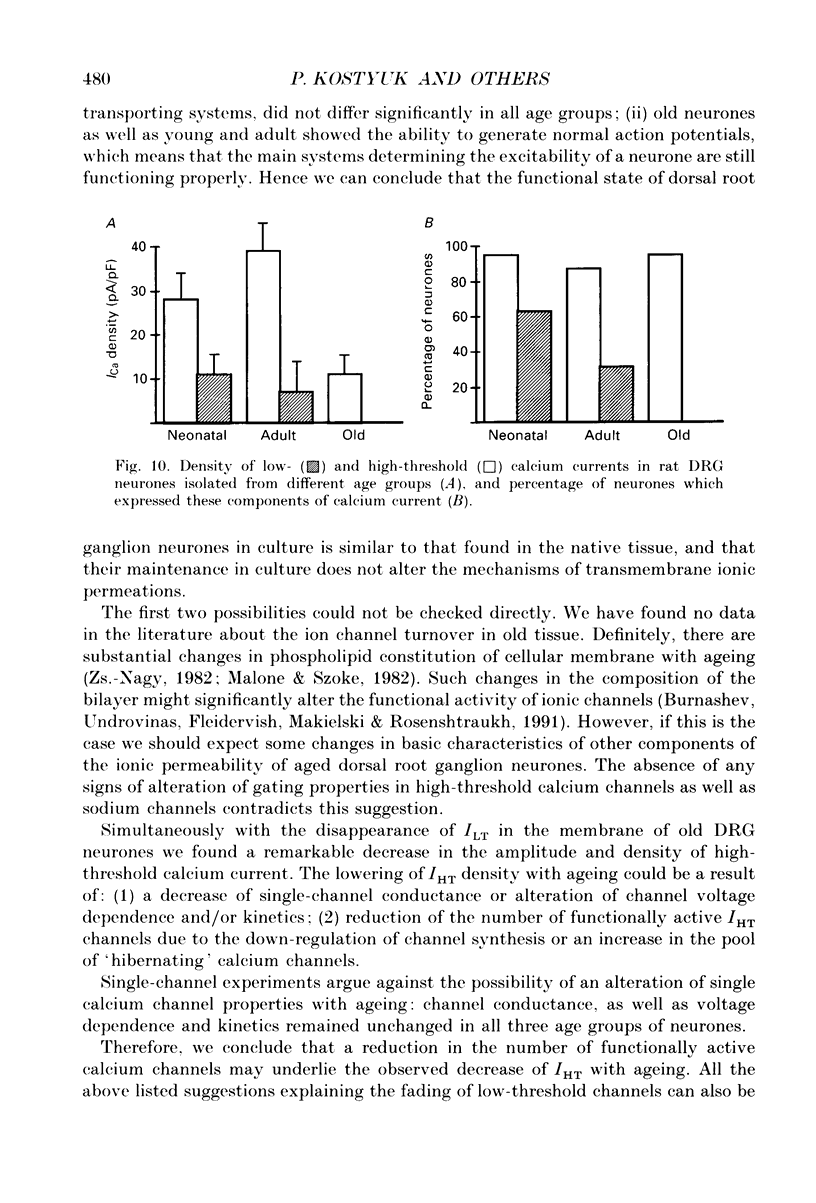



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bean B. P. Classes of calcium channels in vertebrate cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:367–384. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.51.030189.002055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belles B., Malécot C. O., Hescheler J., Trautwein W. "Run-down" of the Ca current during long whole-cell recordings in guinea pig heart cells: role of phosphorylation and intracellular calcium. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Apr;411(4):353–360. doi: 10.1007/BF00587713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnashev N. A., Undrovinas A. I., Fleidervish I. A., Makielski J. C., Rosenshtraukh L. V. Modulation of cardiac sodium channel gating by lysophosphatidylcholine. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1991 Feb;23 (Suppl 1):23–30. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(91)90020-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone E., Swandulla D. Neuronal calcium channels: kinetics, blockade and modulation. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1989;54(1):31–58. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(89)90008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLorme E. M., Rabe C. S., McGee R., Jr Regulation of the number of functional voltage-sensitive Ca++ channels on PC12 cells by chronic changes in membrane potential. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Mar;244(3):838–843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert R., Chad J. E. Inactivation of Ca channels. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1984;44(3):215–267. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(84)90009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedulova S. A., Kostyuk P. G., Veselovsky N. S. Calcium channels in the somatic membrane of the rat dorsal root ganglion neurons, effect of cAMP. Brain Res. 1981 Jun 9;214(1):210–214. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90457-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedulova S. A., Kostyuk P. G., Veselovsky N. S. Ionic mechanisms of electrical excitability in rat sensory neurons during postnatal ontogenesis. Neuroscience. 1991;41(1):303–309. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(91)90219-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fifková E., Cullen-Dockstader K. Calcium distribution in dendritic spines of the dentate fascia varies with age. Brain Res. 1986 Jun 25;376(2):357–362. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90199-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frolkis V. V., Martynenko O. A., Timchenko A. N. Potential-dependent Ca channels of neurons in the mollusc Lymnaea stagnalis in aging: effect of norepinephrine. Mech Ageing Dev. 1991 Apr 1;58(1):75–83. doi: 10.1016/0047-6374(91)90121-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frolkis V. V., Stupina A. S., Martinenko O. A., Tòth S., Timchenko A. I. Aging of neurons in the mollusc Lymnaea stagnalis. Structure, function and sensitivity to transmitters. Mech Ageing Dev. 1984 Apr-May;25(1-2):91–102. doi: 10.1016/0047-6374(84)90132-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson G. E., Peterson C. Calcium and the aging nervous system. Neurobiol Aging. 1987 Jul-Aug;8(4):329–343. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(87)90072-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess P. Calcium channels in vertebrate cells. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1990;13:337–356. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.13.030190.002005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G. Calcium channels in the cell membrane. Neurosci Behav Physiol. 1986 Sep-Oct;16(5):401–410. doi: 10.1007/BF01185371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G. Diversity of calcium ion channels in cellular membranes. Neuroscience. 1989;28(2):253–261. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90177-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G., Krishtal O. A. Effects of calcium and calcium-chelating agents on the inward and outward current in the membrane of mollusc neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;270(3):569–580. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G., Veselovsky N. S., Fedulova S. A. Ionic currents in the somatic membrane of rat dorsal root ganglion neurons-II. Calcium currents. Neuroscience. 1981;6(12):2431–2437. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90089-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G., Veselovsky N. S., Fedulova S. A., Tsyndrenko A. Y. Ionic currents in the somatic membrane of rat dorsal root ganglion neurons-III. Potassium currents. Neuroscience. 1981;6(12):2439–2444. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90090-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G., Veselovsky N. S., Tsyndrenko A. Y. Ionic currents in the somatic membrane of rat dorsal root ganglion neurons-I. Sodium currents. Neuroscience. 1981;6(12):2423–2430. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90088-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landfield P. W., Campbell L. W., Hao S. Y., Kerr D. S. Aging-related increases in voltage-sensitive, inactivating calcium currents in rat hippocampus. Implications for mechanisms of brain aging and Alzheimer's disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;568:95–105. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb12495.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malone M. J., Szoke M. C. Neurochemical studies in aging brain. I. Structural changes in myelin lipids. J Gerontol. 1982 May;37(3):262–267. doi: 10.1093/geronj/37.3.262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez A., Vitórica J., Satrústegui J. Cytosolic free calcium levels increase with age in rat brain synaptosomes. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Jun 7;88(3):336–342. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90234-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez A., Vitórica J., Bogónez E., Satrústegui J. Differential effects of age on the pathways of calcium influx into nerve terminals. Brain Res. 1987 Dec 1;435(1-2):249–257. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)91608-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. J. Multiple calcium channels and neuronal function. Science. 1987 Jan 2;235(4784):46–52. doi: 10.1126/science.2432656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morales F. R., Boxer P. A., Fung S. J., Chase M. H. Basic electrophysiological properties of spinal cord motoneurons during old age in the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1987 Jul;58(1):180–194. doi: 10.1152/jn.1987.58.1.180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C., Ratan R., Shelanski M., Goldman J. Changes in calcium homeostasis during aging and Alzheimer's disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;568:262–270. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb12515.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. N., Carlen P. L. Diminished calcium currents in aged hippocampal dentate gyrus granule neurones. Brain Res. 1989 Feb 13;479(2):384–390. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)91646-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott B., Leu J., Cinader B. Effects of aging on neuronal electrical membrane properties. Mech Ageing Dev. 1988 Sep;44(3):203–214. doi: 10.1016/0047-6374(88)90022-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W. Calcium channels in excitable cell membranes. Annu Rev Physiol. 1983;45:341–358. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.45.030183.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zs-Nagy I. Rol' kletochnoi membrany v starenii kletok. Zh Obshch Biol. 1982 May-Jun;43(3):335–345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]