Abstract
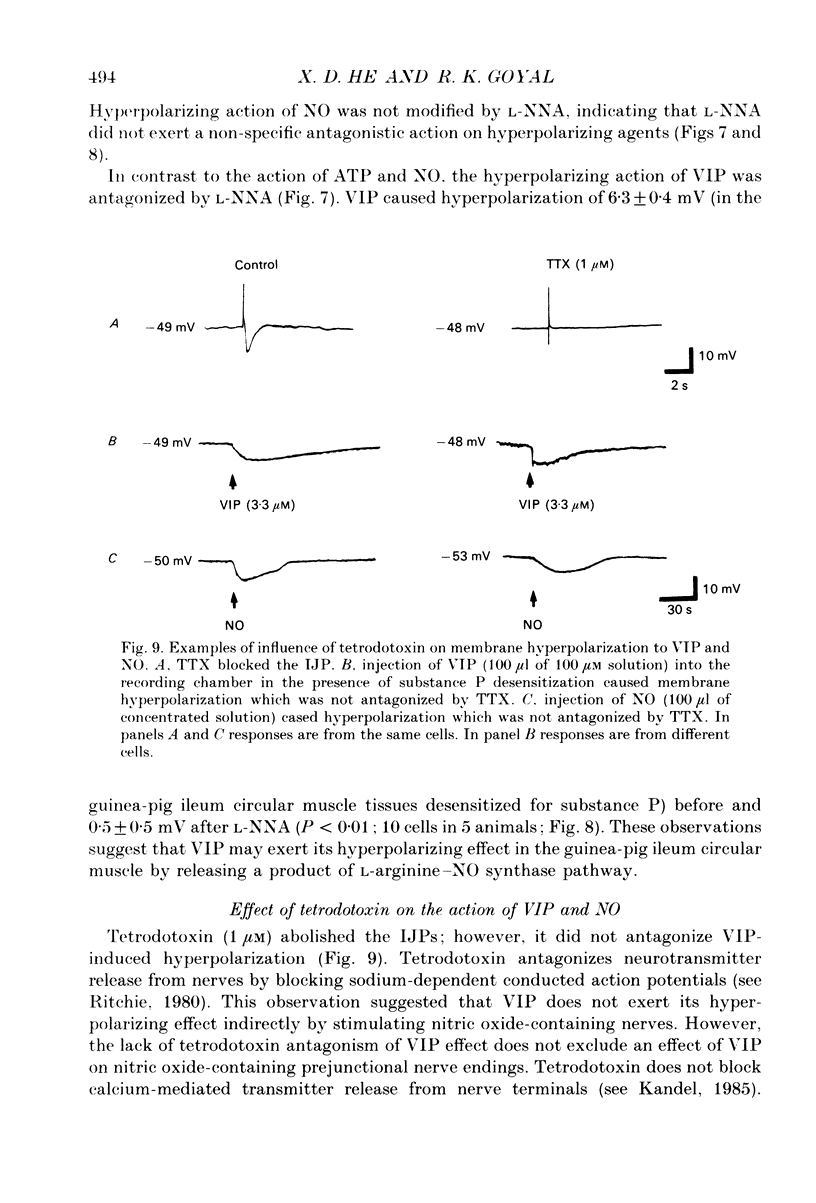
1. Intracellular membrane potential recordings were made from circular smooth muscle cells of the guinea-pig ileum in the presence of atropine (1 microM) and nifedipine (0.1 microM) at 30 degrees C. 2. Electrical field stimulation with one or four pulses produced a fast inhibitory junction potential (IJP) which lasted around 1 s. It was abolished by tetrodotoxin (1 microM), apamin (0.3 microM), and alpha, beta-methylene ATP tachyphylaxis. 3. Nitric oxide synthase inhibitor N-nitro-L-arginine (L-NNA; 200 microM) had no effect on the resting membrane potential or the fast IJP. 4. Electrical field stimulation in the presence of apamin and substance P desensitization produced a slow IJP which was abolished by tetrodotoxin (1 microM). 5. L-NNA significantly reduced the amplitude of the slow IJP (P < 0.01). The antagonistic effect of L-NNA was reversed by L-arginine but not by D-arginine. 6. Injections of alpha, beta-methylene ATP, nitric oxide (NO), and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) into the recording chamber caused tetrodotoxin-resistant hyperpolarizations of the smooth muscle membrane. Substance P desensitization did not modify the amplitudes of the hyperpolarizing response to ATP or NO, but increased the VIP hyperpolarization by 150% (P < 0.01). 7. L-NNA did not modify the amplitude of hyperpolarization due to ATP or NO; however, it antagonized VIP-induced hyperpolarization (P < 0.01). 8. These studies show that in the guinea-pig ileum circular muscle: (a) NO is not involved in the fast IJP which is mediated by ATP; (b) NO is involved in the slow IJP which is mediated by VIP and NO acting in series, and (c) the hyperpolarizing effects of VIP and the slow IJP are normally masked by overlapping depolarization due to concomitant release of substance P by the peptide VIP.
Full text
PDF













Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer V., Kuriyama H. The nature of non-cholinergic, non-adrenergic transmission in longitudinal and circular muscles of the guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1982 Nov;332:375–391. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behar J., Guenard V., Walsh J. H., Biancani P. VIP and acetylcholine: neurotransmitters in esophageal circular smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1989 Sep;257(3 Pt 1):G380–G385. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1989.257.3.G380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeckxstaens G. E., Pelckmans P. A., Bult H., De Man J. G., Herman A. G., van Maercke Y. M. Evidence for nitric oxide as mediator of non-adrenergic non-cholinergic relaxations induced by ATP and GABA in the canine gut. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Feb;102(2):434–438. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12191.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Hwang P. M., Snyder S. H. Localization of nitric oxide synthase indicating a neural role for nitric oxide. Nature. 1990 Oct 25;347(6295):768–770. doi: 10.1038/347768a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bult H., Boeckxstaens G. E., Pelckmans P. A., Jordaens F. H., Van Maercke Y. M., Herman A. G. Nitric oxide as an inhibitory non-adrenergic non-cholinergic neurotransmitter. Nature. 1990 May 24;345(6273):346–347. doi: 10.1038/345346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bywater R. A., Holman M. E., Taylor G. S. Atropine-resistant depolarization in the guinea-pig small intestine. J Physiol. 1981 Jul;316:369–378. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bywater R. A., Taylor G. S. Non-cholinergic excitatory and inhibitory junction potentials in the circular smooth muscle of the guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1986 May;374:153–164. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bülbring E., Tomita T. Properties of the inhibitory potential of smooth muscle as observed in the response to field stimulation of the guinea-pig taenia coli. J Physiol. 1967 Apr;189(2):299–315. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castle N. A., Haylett D. G., Jenkinson D. H. Toxins in the characterization of potassium channels. Trends Neurosci. 1989 Feb;12(2):59–65. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(89)90137-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christinck F., Jury J., Cayabyab F., Daniel E. E. Nitric oxide may be the final mediator of nonadrenergic, noncholinergic inhibitory junction potentials in the gut. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1991 Oct;69(10):1448–1458. doi: 10.1139/y91-217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa M., Furness J. B., Humphreys C. M. Apamin distinguishes two types of relaxation mediated by enteric nerves in the guinea-pig gastrointestinal tract. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1986 Jan;332(1):79–88. doi: 10.1007/BF00633202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crist J. R., He X. D., Goyal R. K. Both ATP and the peptide VIP are inhibitory neurotransmitters in guinea-pig ileum circular muscle. J Physiol. 1992 Feb;447:119–131. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp018994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crist J. R., He X. D., Goyal R. K. Chloride-mediated inhibitory junction potentials in opossum esophageal circular smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1991 Nov;261(5 Pt 1):G752–G762. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1991.261.5.G752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crist J. R., He X. D., Goyal R. K. Chloride-mediated junction potentials in circular muscle of the guinea pig ileum. Am J Physiol. 1991 Nov;261(5 Pt 1):G742–G751. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1991.261.5.G742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crist J. R., He X. D., Goyal R. K. The nature of noncholinergic membrane potential responses to transmural stimulation in guinea pig ileum. Gastroenterology. 1991 Apr;100(4):1006–1015. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90276-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalziel H. H., Thornbury K. D., Ward S. M., Sanders K. M. Involvement of nitric oxide synthetic pathway in inhibitory junction potentials in canine proximal colon. Am J Physiol. 1991 May;260(5 Pt 1):G789–G792. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1991.260.5.G789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel E. E., Helmy-Elkholy A., Jager L. P., Kannan M. S. Neither a purine nor VIP is the mediator of inhibitory nerves of opossum oesophageal smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1983 Mar;336:243–260. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desai K. M., Sessa W. C., Vane J. R. Involvement of nitric oxide in the reflex relaxation of the stomach to accommodate food or fluid. Nature. 1991 Jun 6;351(6326):477–479. doi: 10.1038/351477a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frew R., Lundy P. M. Evidence against ATP being the nonadrenergic, noncholinergic inhibitory transmitter in guinea pig stomach. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Jul 9;81(2):333–336. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90453-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furness J. B., Bornstein J. C., Murphy R., Pompolo S. Roles of peptides in transmission in the enteric nervous system. Trends Neurosci. 1992 Feb;15(2):66–71. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(92)90029-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaw A. J., Aberdeen J., Humphrey P. P., Wadsworth R. M., Burnstock G. Relaxation of sheep cerebral arteries by vasoactive intestinal polypeptide and neurogenic stimulation: inhibition by L-NG-monomethyl arginine in endothelium-denuded vessels. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;102(3):567–572. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12213.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie J. S., Liu X. R., Martin W. The effects of L-arginine and NG-monomethyl L-arginine on the response of the rat anococcygeus muscle to NANC nerve stimulation. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;98(4):1080–1082. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12650.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyal R. K., Rattan S., Said S. I. VIP as a possible neurotransmitter of non-cholinergic non-adrenergic inhibitory neurones. Nature. 1980 Nov 27;288(5789):378–380. doi: 10.1038/288378a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grider J. R., Makhlouf G. M. Vasoactive intestinal peptide. Transmitter of inhibitory motor neurons of the gut. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;527:369–377. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb26993.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grider J. R., Murthy K. S., Jin J. G., Makhlouf G. M. Stimulation of nitric oxide from muscle cells by VIP: prejunctional enhancement of VIP release. Am J Physiol. 1992 Apr;262(4 Pt 1):G774–G778. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1992.262.4.G774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J., Byrns R. E., Buga G. M., Wood K. S. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor from pulmonary artery and vein possesses pharmacologic and chemical properties identical to those of nitric oxide radical. Circ Res. 1987 Dec;61(6):866–879. doi: 10.1161/01.res.61.6.866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J. Nitric oxide. A novel signal transduction mechanism for transcellular communication. Hypertension. 1990 Nov;16(5):477–483. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.16.5.477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles R. G., Salter M., Brooks S. L., Moncada S. Anti-inflammatory glucocorticoids inhibit the induction by endotoxin of nitric oxide synthase in the lung, liver and aorta of the rat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Nov 15;172(3):1042–1048. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91551-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert L. E., Whitten J. P., Baron B. M., Cheng H. C., Doherty N. S., McDonald I. A. Nitric oxide synthesis in the CNS endothelium and macrophages differs in its sensitivity to inhibition by arginine analogues. Life Sci. 1991;48(1):69–75. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(91)90426-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maas A. J., Den Hertog A., Ras R., Van den Akker J. The action of apamin on guinea-pig taenia caeci. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Oct 17;67(2-3):265–274. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90507-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao Y. K., Barnett W., Coy D. H., Tougas G., Daniel E. E. Distribution of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) binding in circular muscle and characterization of VIP binding in canine small intestinal mucosa. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Sep;258(3):986–991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niel J. P., Bywater R. A., Taylor G. S. Apamin-resistant post-stimulus hyperpolarization in the circular muscle of the guinea-pig ileum. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1983 Nov;9(2-3):565–569. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(83)90014-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rattan S., Chakder S. Role of nitric oxide as a mediator of internal anal sphincter relaxation. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jan;262(1 Pt 1):G107–G112. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1992.262.1.G107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rattan S., Goyal R. K. Evidence against purinergic inhibitory nerves in the vagal pathway to the opossum lower esophageal sphincter. Gastroenterology. 1980 May;78(5 Pt 1):898–904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. D., Palmer R. M., Schulz R., Hodson H. F., Moncada S. Characterization of three inhibitors of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in vitro and in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;101(3):746–752. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14151.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders K. M., Ward S. M. Nitric oxide as a mediator of nonadrenergic noncholinergic neurotransmission. Am J Physiol. 1992 Mar;262(3 Pt 1):G379–G392. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1992.262.3.G379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark M. E., Bauer A. J., Szurszewski J. H. Effect of nitric oxide on circular muscle of the canine small intestine. J Physiol. 1991 Dec;444:743–761. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tøttrup A., Svane D., Forman A. Nitric oxide mediating NANC inhibition in opossum lower esophageal sphincter. Am J Physiol. 1991 Mar;260(3 Pt 1):G385–G389. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1991.260.3.G385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamato S., Saha J. K., Goyal R. K. Role of nitric oxide in lower esophageal sphincter relaxation to swallowing. Life Sci. 1992;50(17):1263–1272. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(92)90326-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


