Abstract
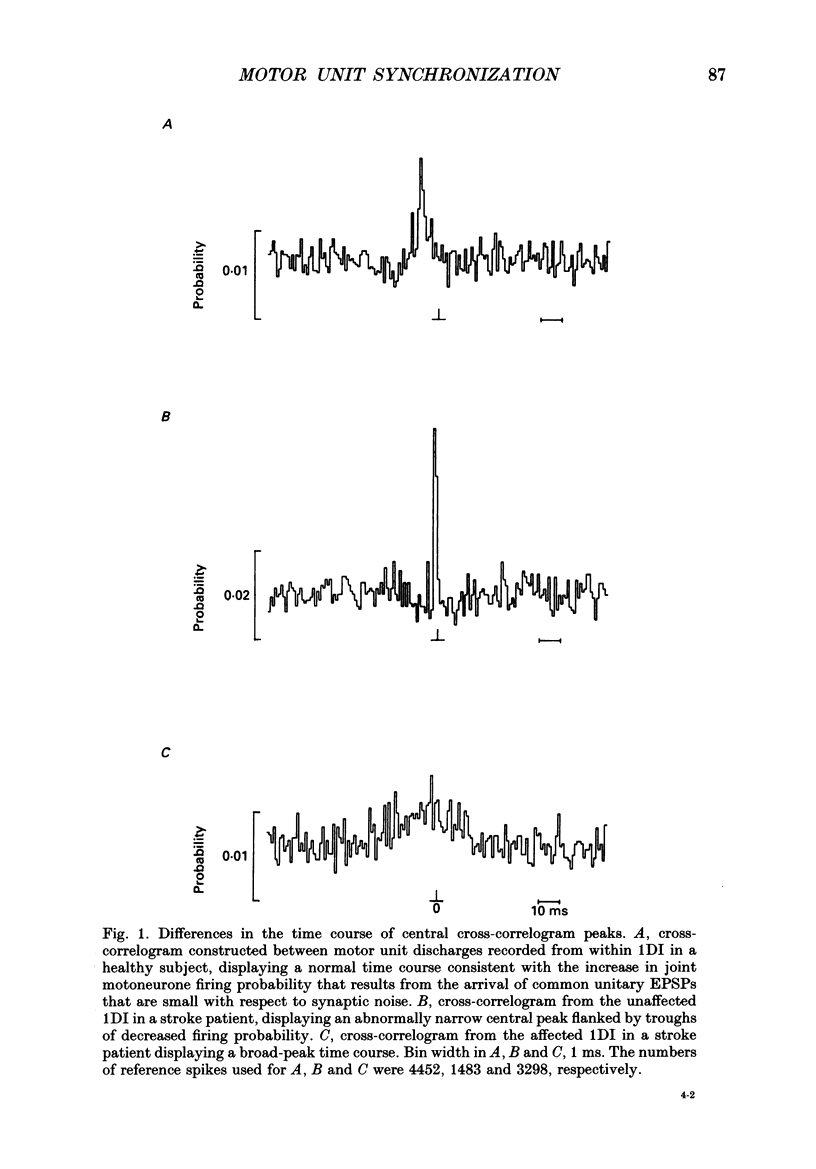
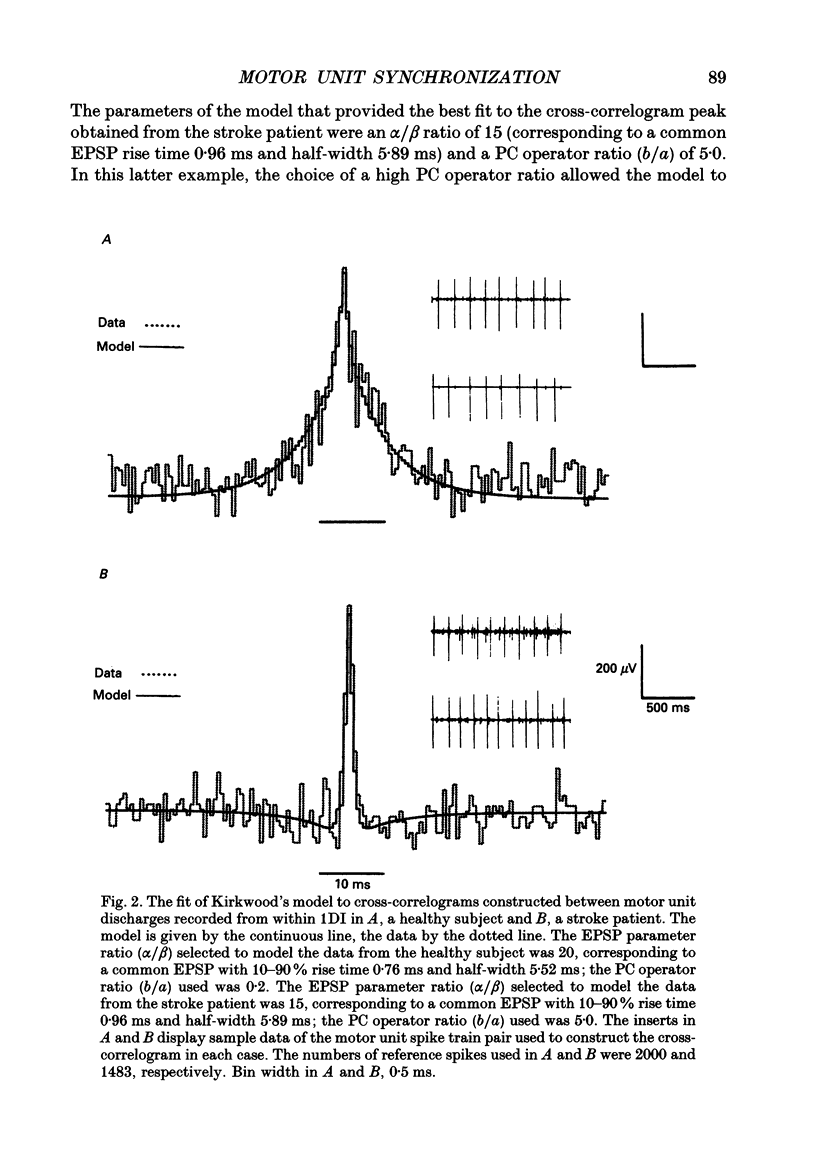
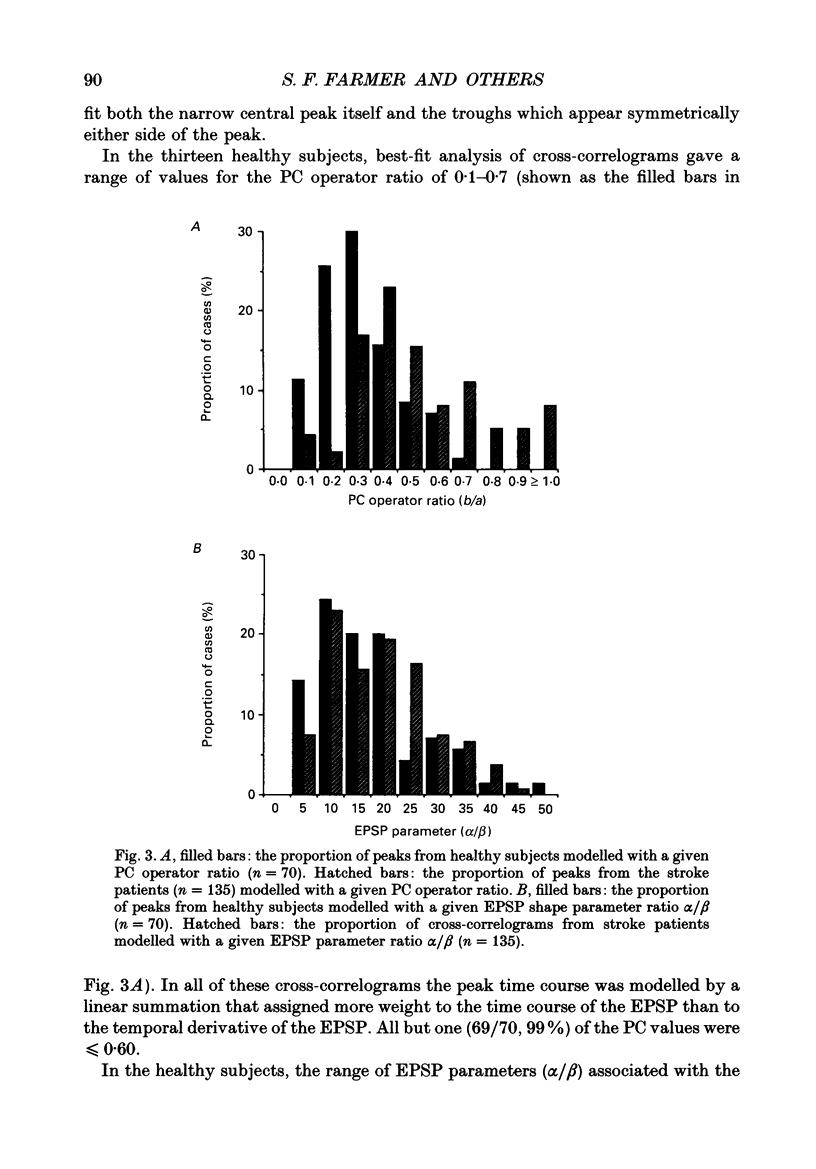
1. Single motor unit spike trains have been recorded during voluntary isometric contraction of the affected intrinsic hand muscles of patients with unilateral central nervous lesions. These have been compared with similar recordings made from the patients' unaffected hand muscles and with recordings made from the hand muscles of healthy subjects. 2. Cross-correlation analysis was performed between the times of occurrence of the motor unit spike trains. The time course of central cross-correlogram peaks constructed for normal subjects and stroke patients was used to infer properties of the underlying common EPSPs and the impulse-generating properties of the motoneurones. The results of this analysis were compared between the two groups. In addition, the size and time course of cross-correlogram peaks obtained from the patients were related both to the patients' clinical state and to their hand and fine finger function. 3. Central nervous lesions were found to result in either a narrowing or broadening of the time course of motor unit synchronization. These changes were attributed either to an increase in the size of common EPSPs with respect to synaptic noise, or to the effects of presynaptic synchronization of motoneurone inputs. 4. Longitudinal studies of motor unit discharges in the year following the stroke demonstrated, in some patients, differences in the level of motor unit synchronization. These paralleled improvements in the patients' fine motor control. Pooled data from patients with varying deficits of fine motor control confirmed that loss or reduction of motor unit synchronization was associated with a corresponding slowing in the performance of rapidly alternating finger movements. 5. The results of the present study suggest that the branched common presynaptic inputs that generate motor unit synchronization are either of corticospinal tract origin or are intimately dependent on its function. Differences in the strength and time course of motor unit synchronization are demonstrated that may reflect the altered behaviour of presynaptic inputs to motoneurones following central nervous damage in man.
Full text
PDF





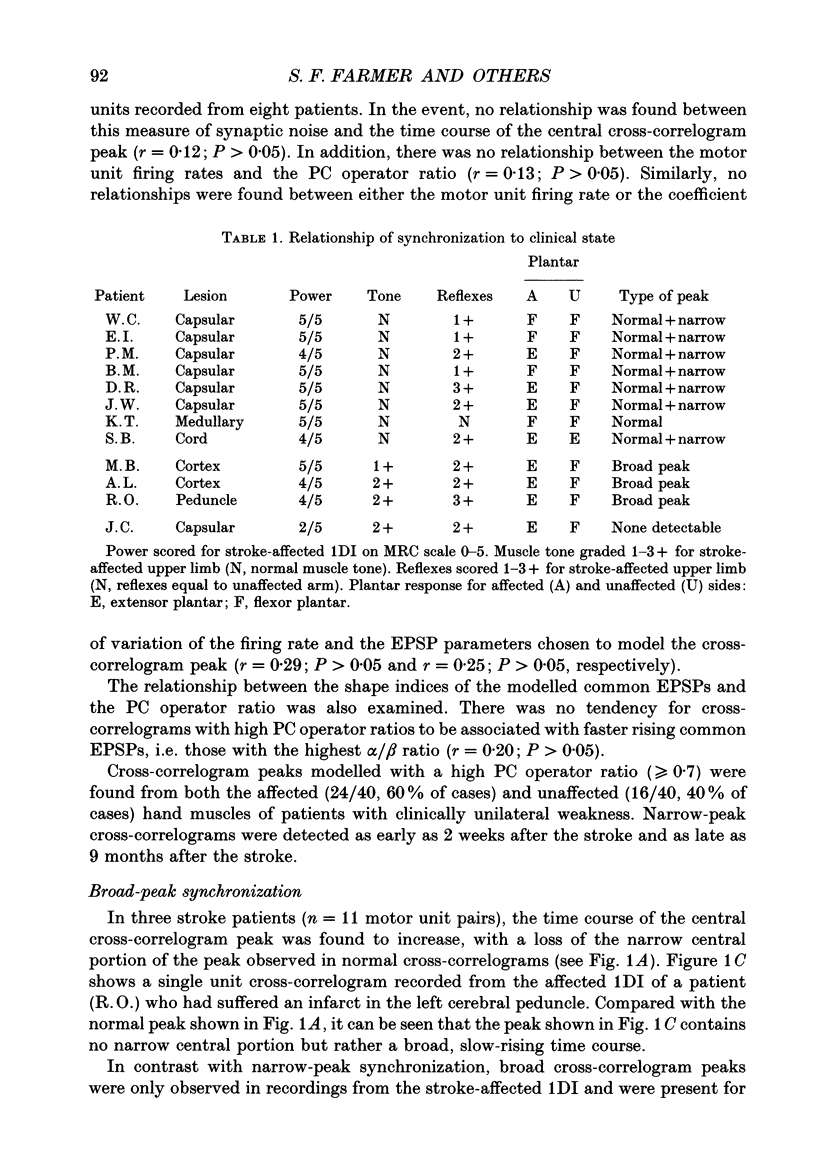


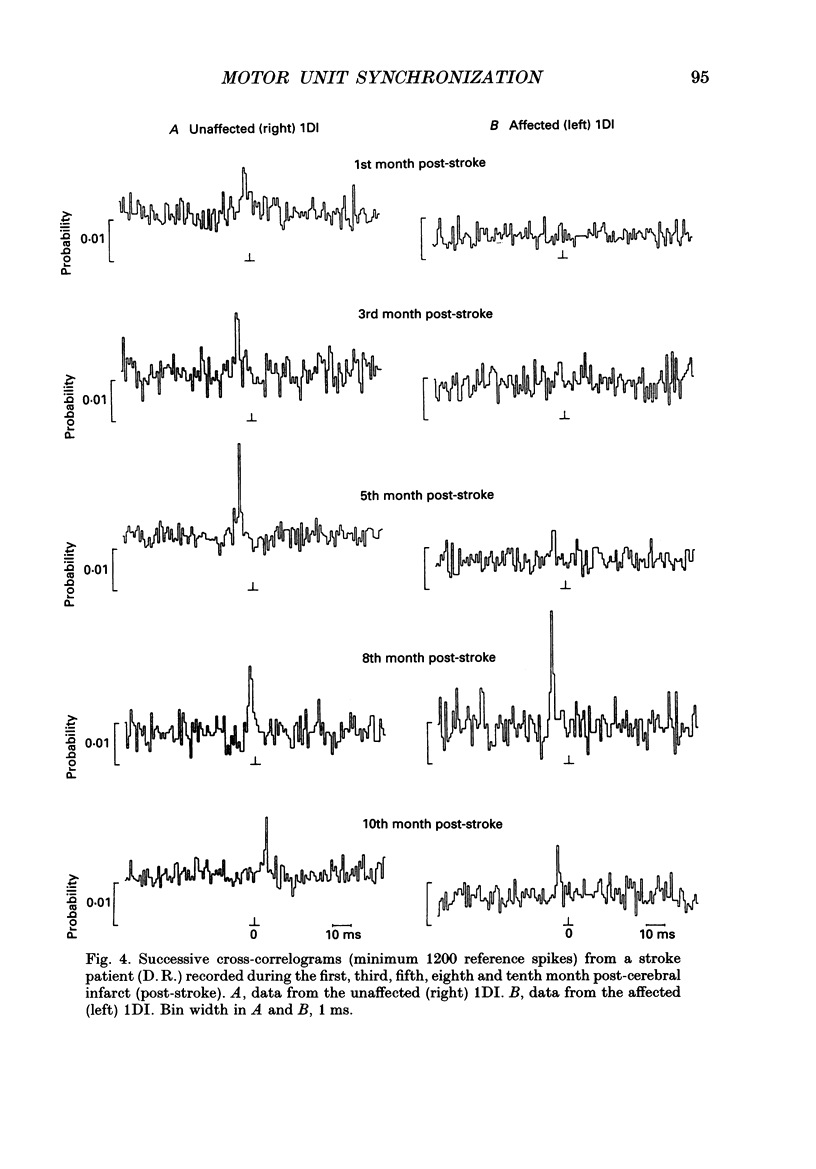
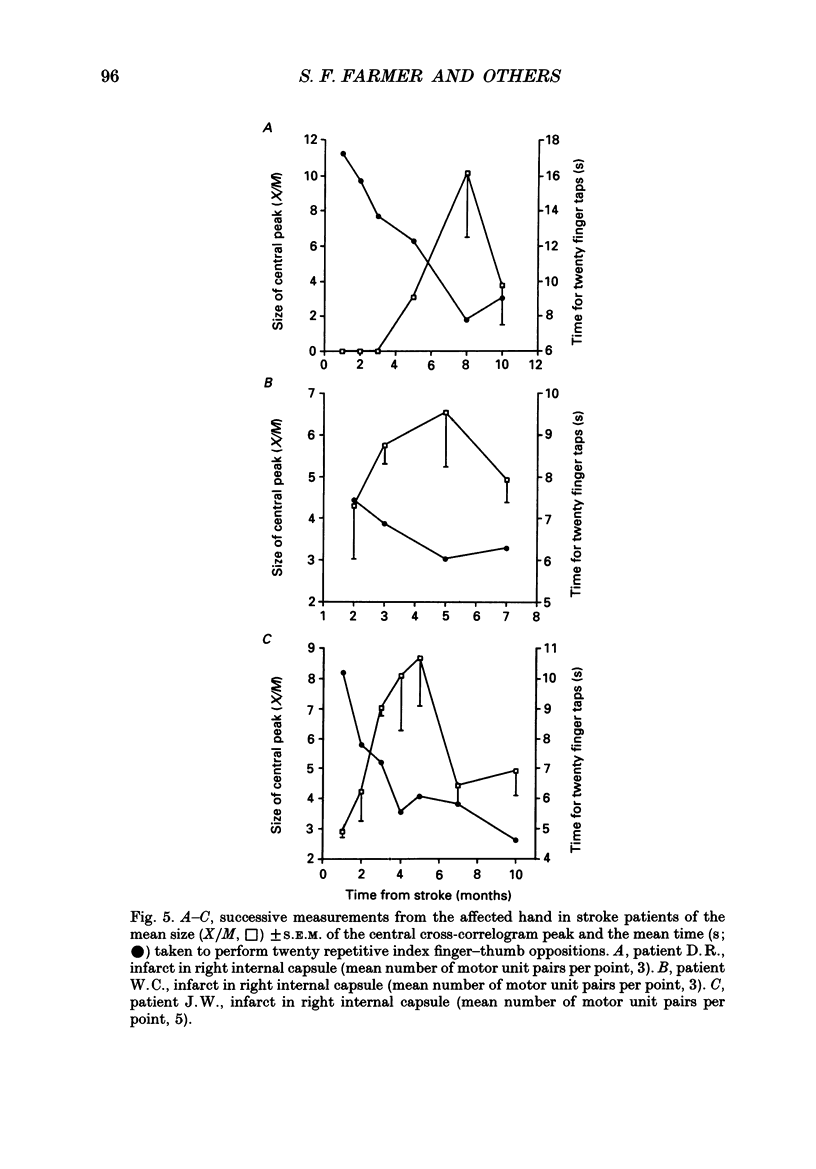
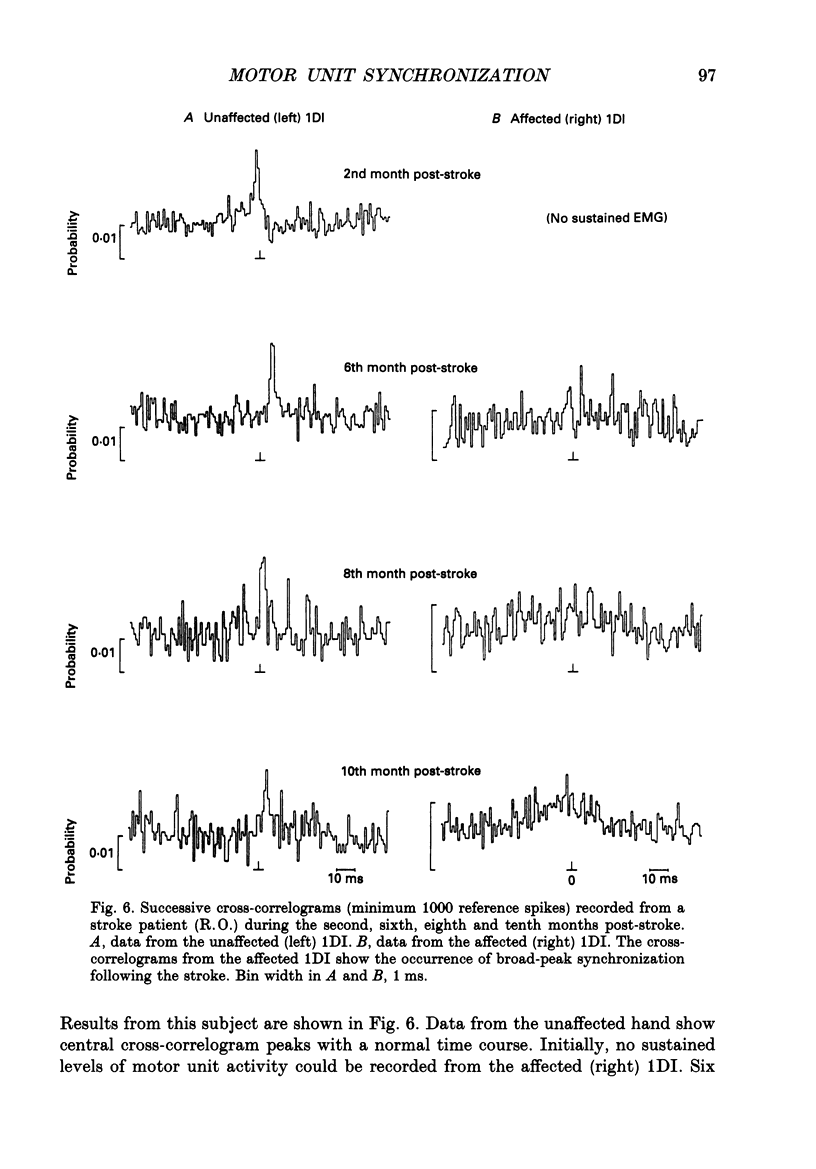
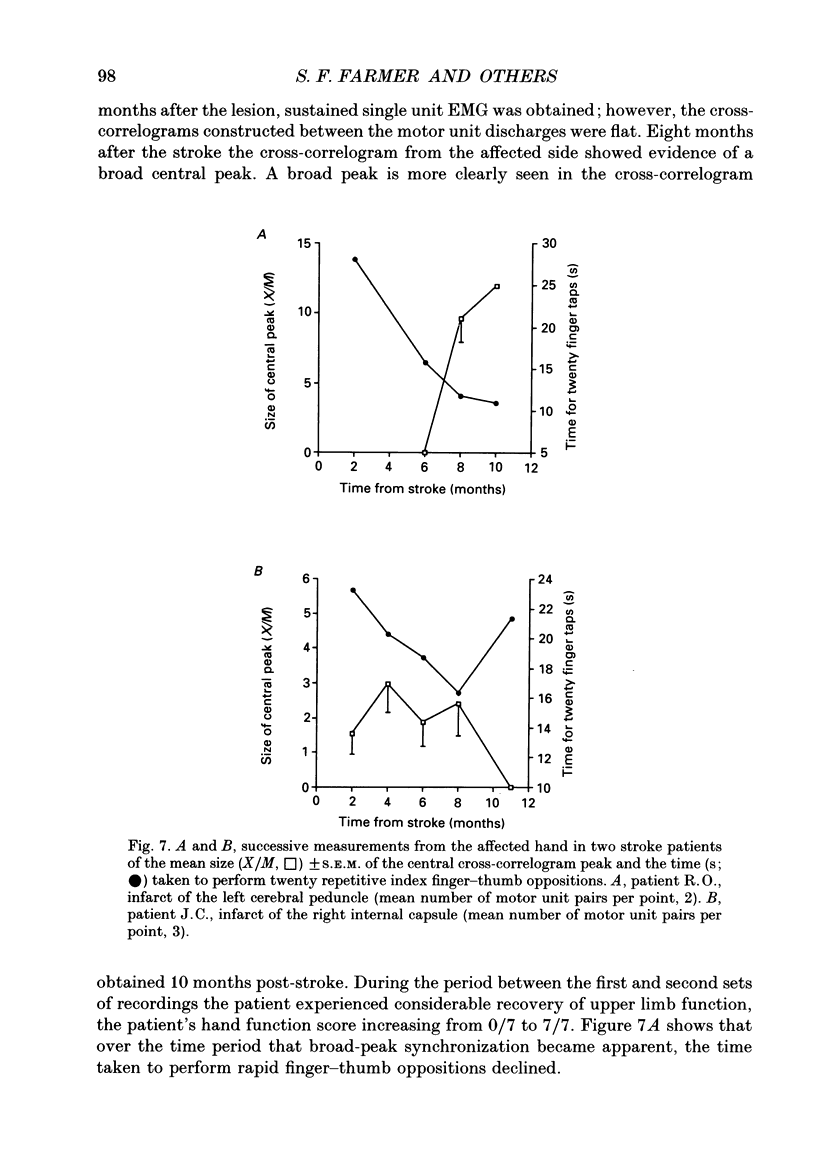
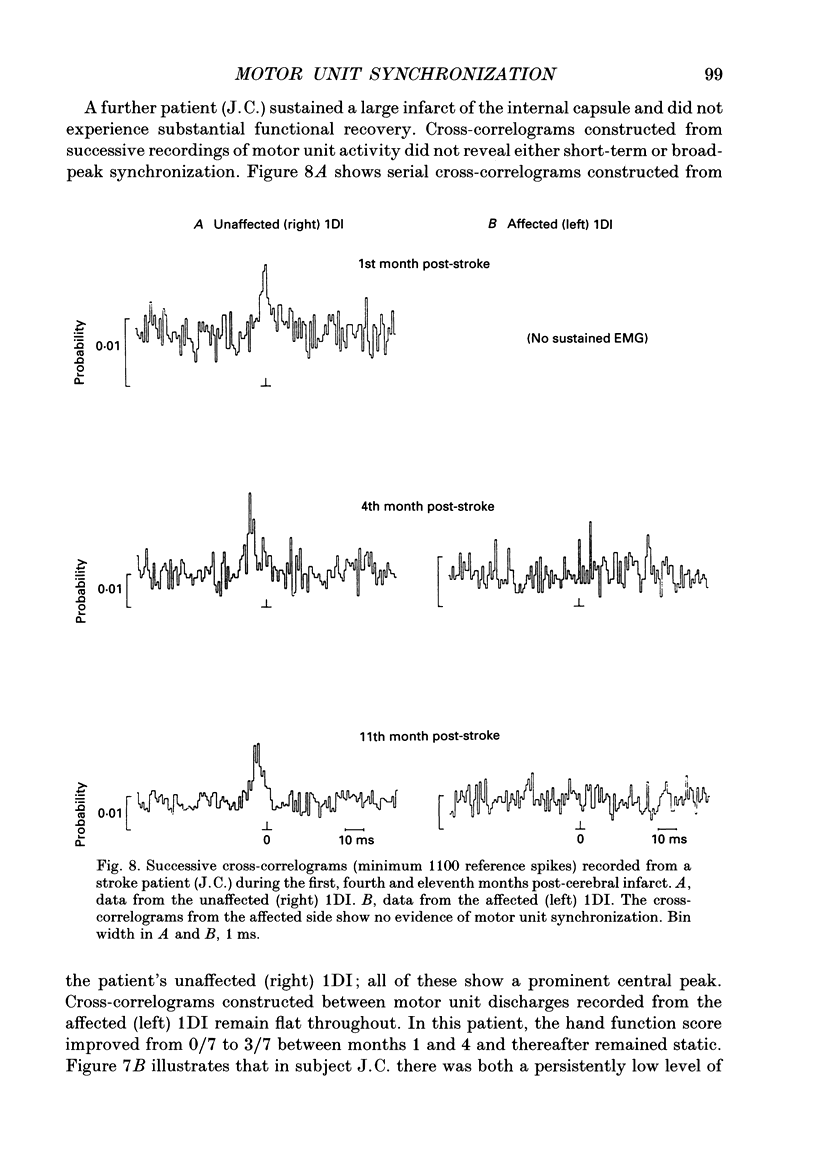
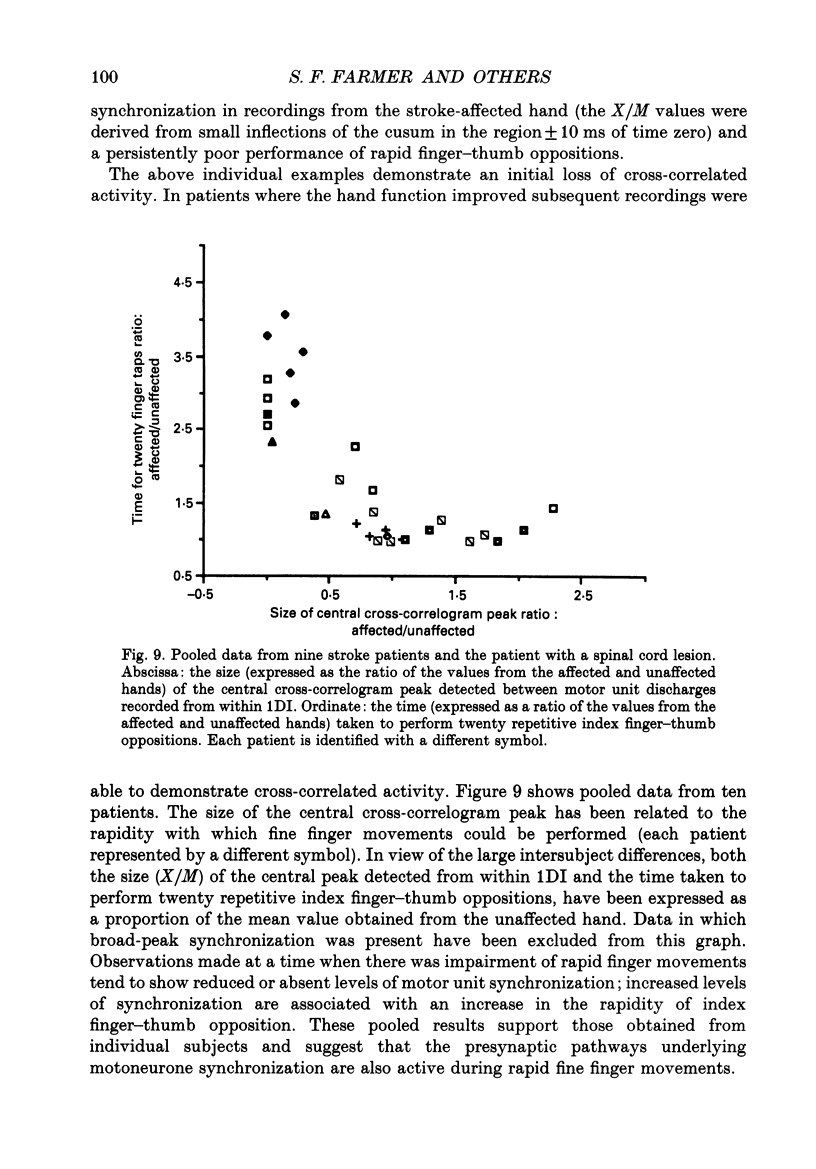





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam D., Windhorst U., Inbar G. F. The effects of recurrent inhibition on the cross-correlated firing patterns of motoneurones (and their relation to signal transmission in the spinal cord-muscle channel). Biol Cybern. 1978 Jun 21;29(4):229–235. doi: 10.1007/BF00337280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUCHTHAL F., MADSEN A. Synchronous activity in normal and atrophic muscle. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1950 Nov;2(4):425–444. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(50)90079-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremner F. D., Baker J. R., Stephens J. A. Correlation between the discharges of motor units recorded from the same and from different finger muscles in man. J Physiol. 1991 Jan;432:355–380. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremner F. D., Baker J. R., Stephens J. A. Variation in the degree of synchronization exhibited by motor units lying in different finger muscles in man. J Physiol. 1991 Jan;432:381–399. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvin W. H., Stevens C. F. Synaptic noise and other sources of randomness in motoneuron interspike intervals. J Neurophysiol. 1968 Jul;31(4):574–587. doi: 10.1152/jn.1968.31.4.574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cope T. C., Fetz E. E., Matsumura M. Cross-correlation assessment of synaptic strength of single Ia fibre connections with triceps surae motoneurones in cats. J Physiol. 1987 Sep;390:161–188. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cope T. C., Nelson S. G., Mendell L. M. Factors outside neuraxis mediate "acute" increase in EPSP amplitude caudal to spinal cord transection. J Neurophysiol. 1980 Jul;44(1):174–183. doi: 10.1152/jn.1980.44.1.174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta A. K., Farmer S. F., Stephens J. A. Central nervous pathways underlying synchronization of human motor unit firing studied during voluntary contractions. J Physiol. 1991 Jan;432:401–425. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta A. K., Stephens J. A. Synchronization of motor unit activity during voluntary contraction in man. J Physiol. 1990 Mar;422:397–419. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp017991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey N. J., Ellaway P. H., Stein R. B. Statistical limits for detecting change in the cumulative sum derivative of the peristimulus time histogram. J Neurosci Methods. 1986 Aug;17(2-3):153–166. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(86)90068-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denckla M. B. Development of speed in repetitive and successive finger-movements in normal children. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1973 Oct;15(5):635–645. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1973.tb05174.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietz V., Bischofberger E., Wita C., Freund H. J. Correlation between the dischanges of two simultaneously recorded motor units and physiological tremor. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1976 Jan;40(1):97–105. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(76)90183-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards F. R., Hirst G. D., Silinsky E. M. Interaction between inhibitory and excitatory synaptic potentials at a peripheral neurone. J Physiol. 1976 Aug;259(3):647–663. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellaway P. H., Murthy K. S. The origins and characteristics of cross-correlated activity between gamma-motoneurones in the cat. Q J Exp Physiol. 1985 Apr;70(2):219–232. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1985.sp002905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer S. F., Ingram D. A., Stephens J. A. Mirror movements studied in a patient with Klippel-Feil syndrome. J Physiol. 1990 Sep;428:467–484. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fetz E. E., Gustafsson B. Relation between shapes of post-synaptic potentials and changes in firing probability of cat motoneurones. J Physiol. 1983 Aug;341:387–410. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson B., McCrea D. Influence of stretch-evoked synaptic potentials on firing probability of cat spinal motoneurones. J Physiol. 1984 Feb;347:431–451. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison L. M., Ironton R., Stephens J. A. Cross-correlation analysis of multi-unit EMG recordings in man. J Neurosci Methods. 1991 Dec;40(2-3):171–179. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(91)90066-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepp-Reymond M. C., Wiesendanger M. Unilateral pyramidotomy in monkeys: effect on force and speed of a conditioned precision grip. Brain Res. 1972 Jan 14;36(1):117–131. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90770-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkwood P. A., Sears T. A. The synaptic connexions to intercostal motoneurones as revealed by the average common excitation potential. J Physiol. 1978 Feb;275:103–134. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkwood P. A., Sears T. A., Tuck D. L., Westgaard R. H. Variations in the time course of the synchronization of intercostal motoneurones in the cat. J Physiol. 1982 Jun;327:105–135. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkwood P. A., Sears T. A., Westgaard R. H. Restoration of function in external intercostal motoneurones of the cat following partial central deafferentation. J Physiol. 1984 May;350:225–251. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagrèze H. L., Levine R. L., Pedula K. L., Nickles R. J., Sunderland J. S., Rowe B. R. Contralateral flow reduction in unilateral stroke: evidence for transhemispheric diaschisis. Stroke. 1987 Sep-Oct;18(5):882–886. doi: 10.1161/01.str.18.5.882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner-Brown H. S., Stein R. B., Yemm R. The contractile properties of human motor units during voluntary isometric contractions. J Physiol. 1973 Jan;228(2):285–306. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson S. G., Mendell L. M. Enhancement in Ia-motoneuron synaptic transmission caudal to chronic spinal cord transection. J Neurophysiol. 1979 May;42(3):642–654. doi: 10.1152/jn.1979.42.3.642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers R. K., Rymer W. Z. Effects of acute dorsal spinal hemisection on motoneuron discharge in the medial gastrocnemius of the decerebrate cat. J Neurophysiol. 1988 May;59(5):1540–1556. doi: 10.1152/jn.1988.59.5.1540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears T. A., Stagg D. Short-term synchronization of intercostal motoneurone activity. J Physiol. 1976 Dec;263(3):357–381. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


