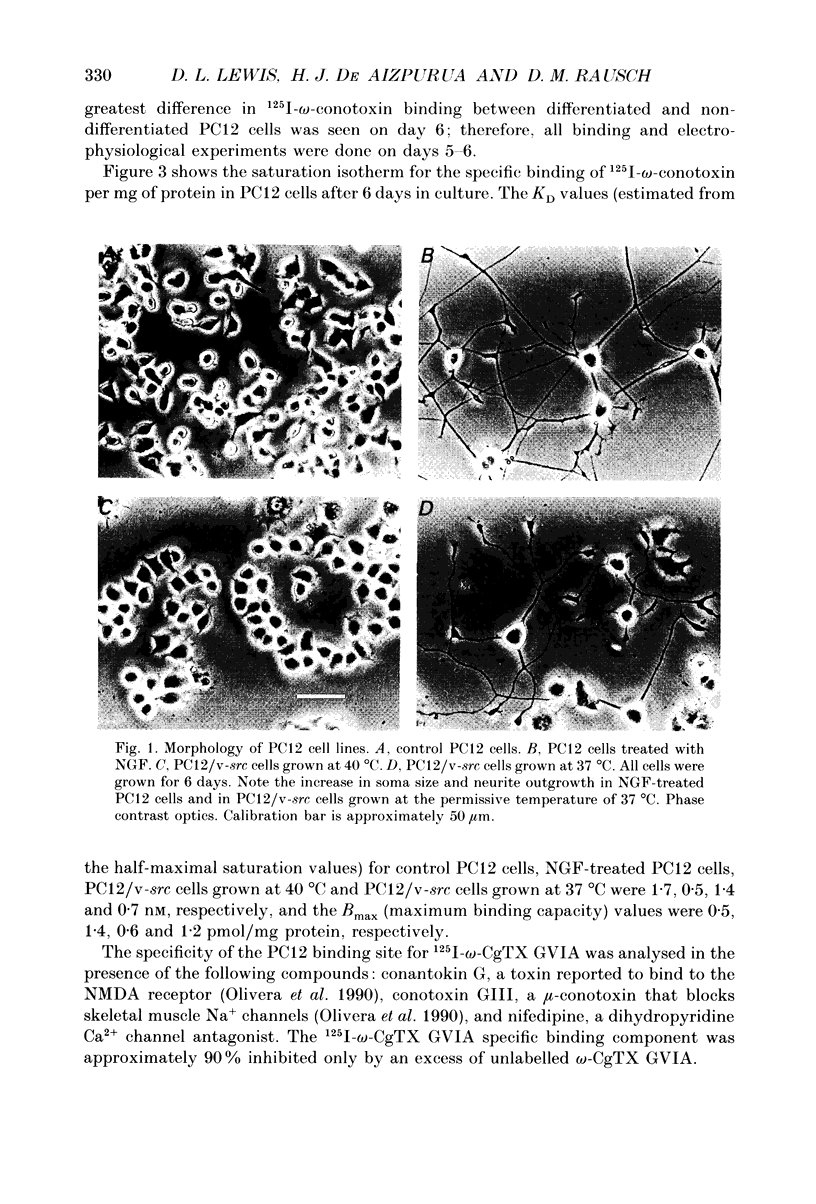
Abstract
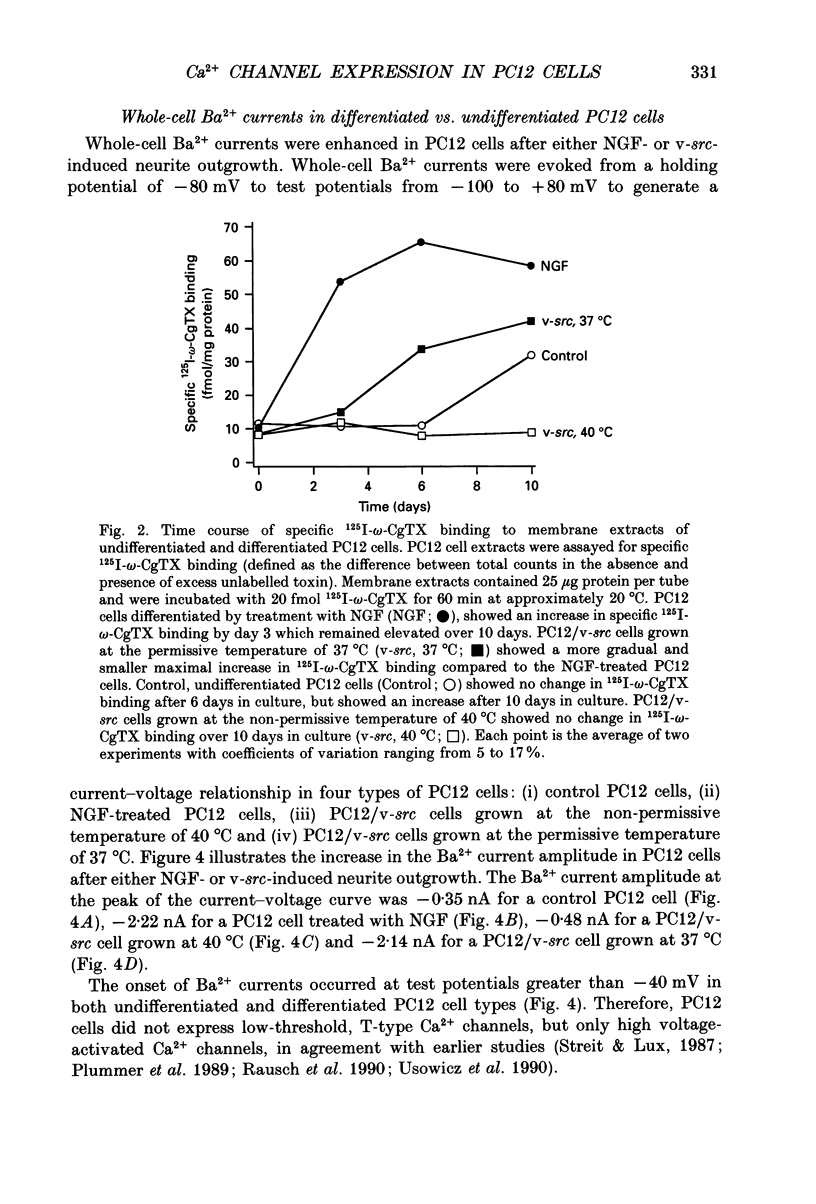
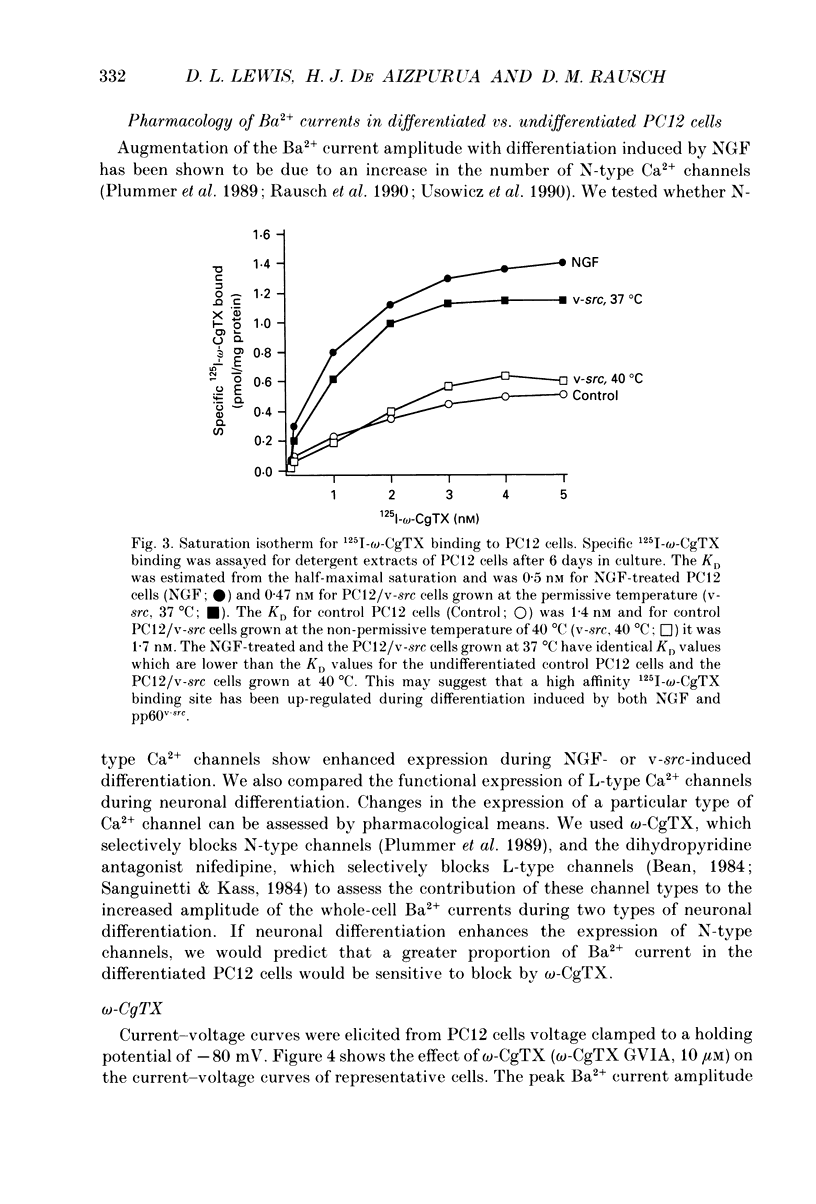
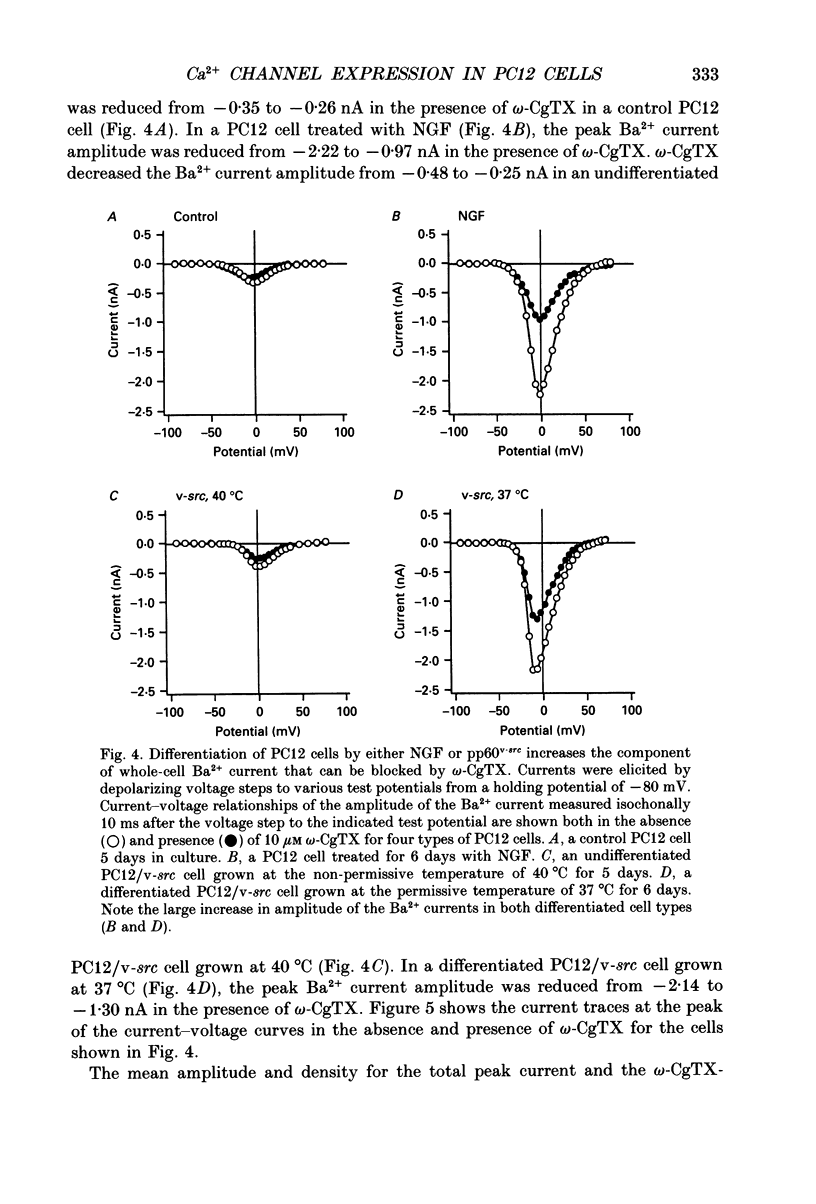
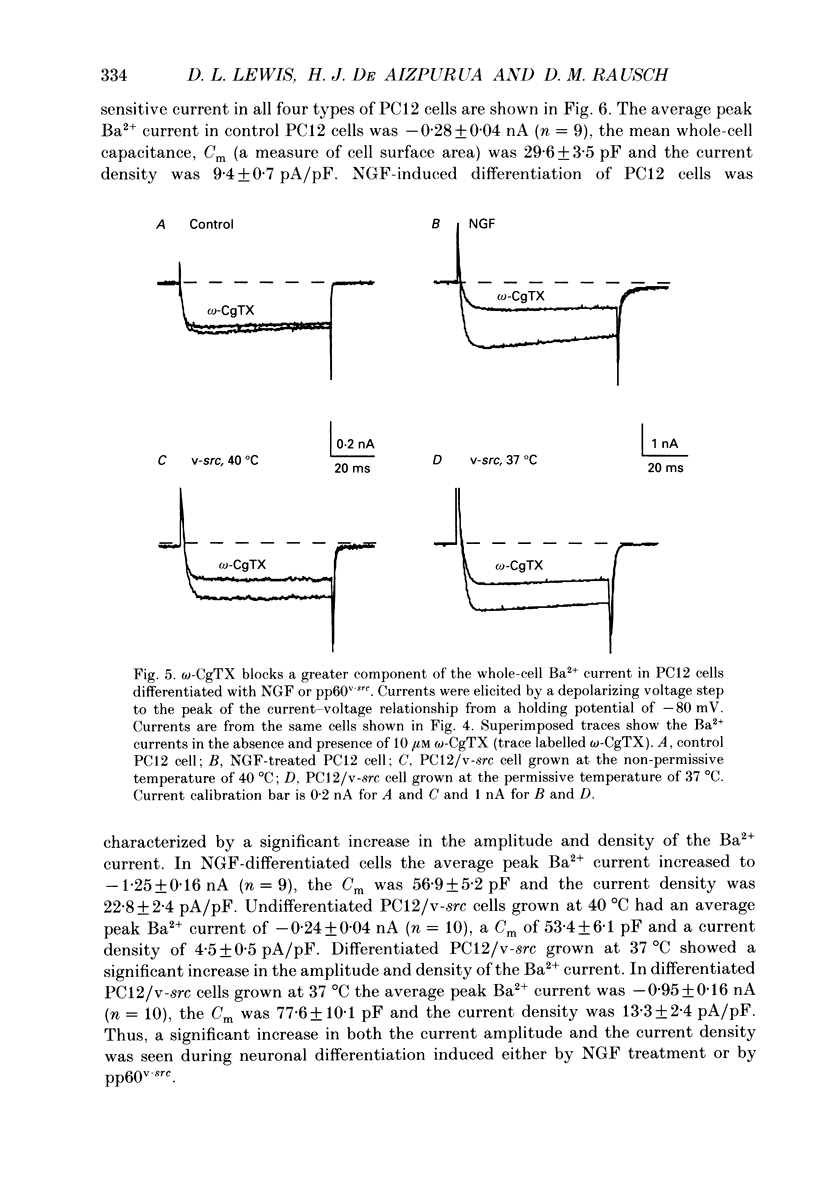
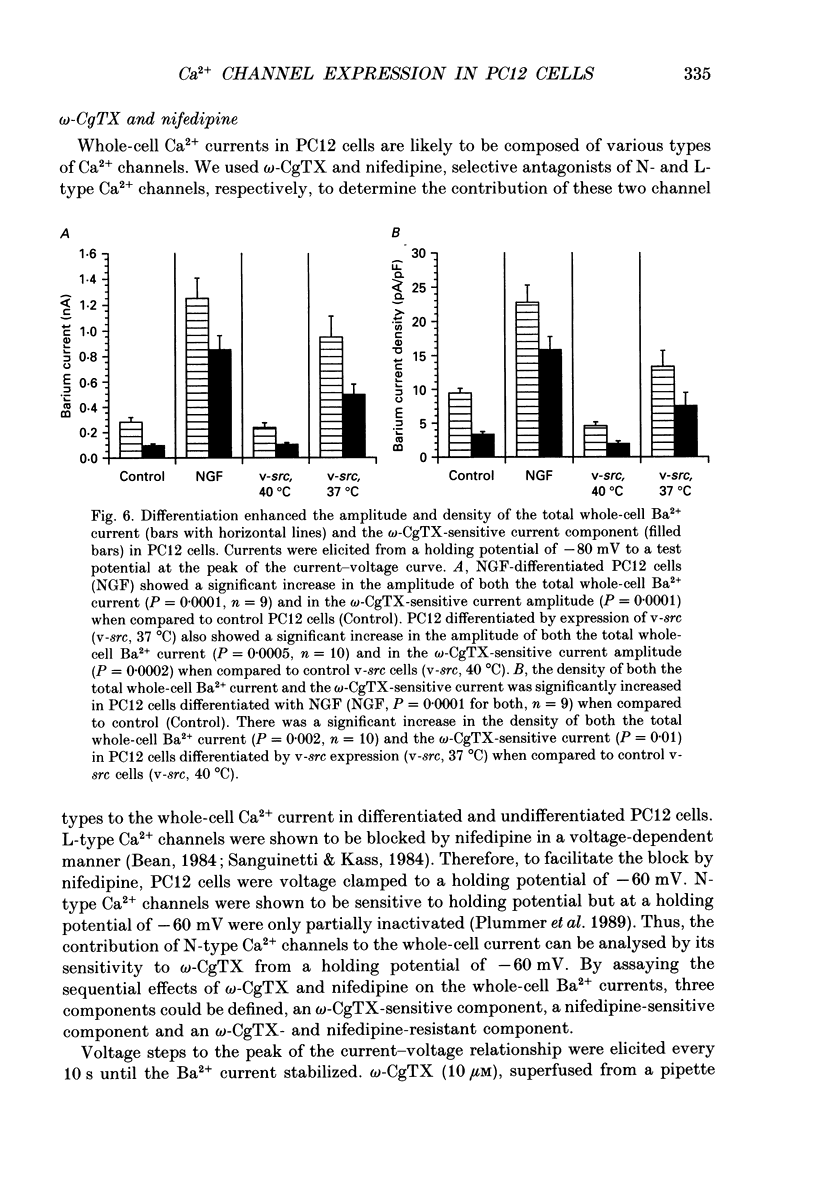
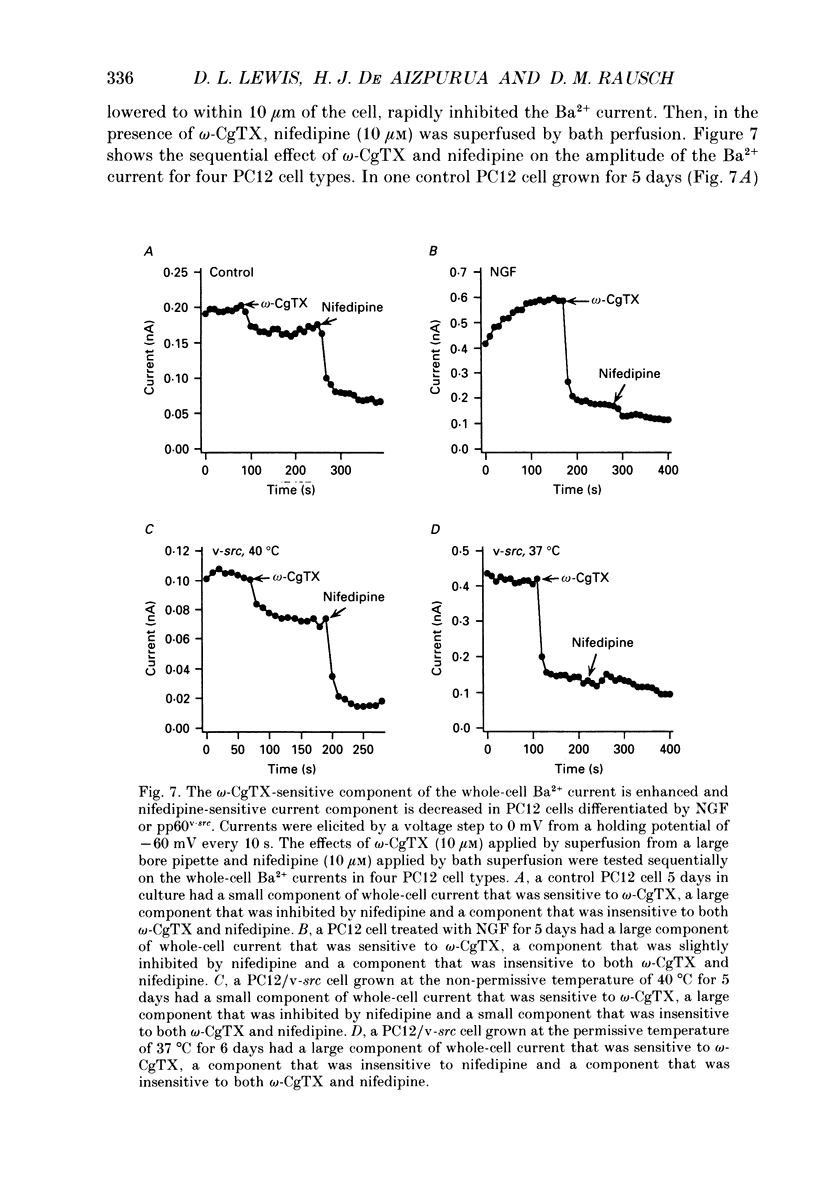
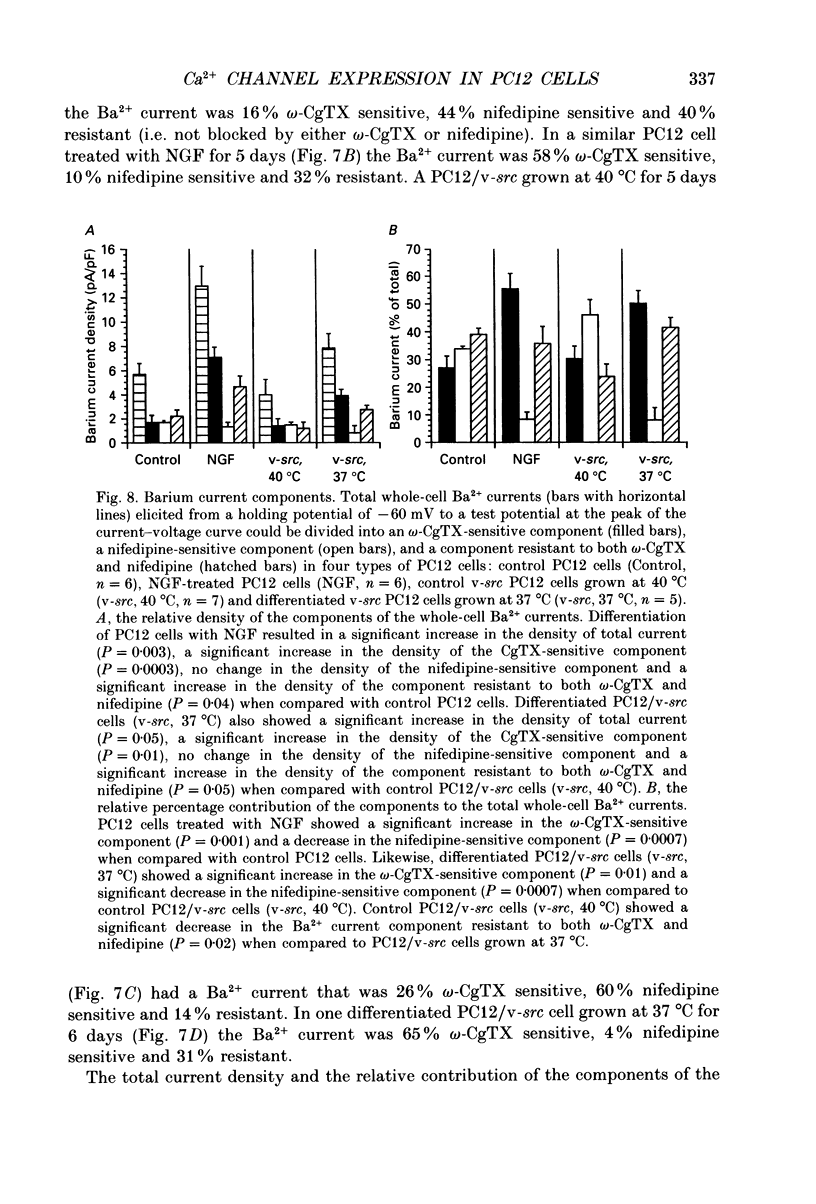
1. Rat phaeochromocytoma (PC12) cells were used to investigate the expression of Ca2+ channel types during neuronal differentiation. Neuronal differentiation was induced by treatment with nerve growth factor (NGF) or by activation of a temperature-sensitive tyrosine kinase (pp60v-src) in genetically modified PC12 (PC12/v-src) cells. PC12 cells differentiated morphologically in the presence of NGF. When grown at the permissive temperature of 37 degrees C which activates the kinase activity of pp60v-src, PC12/v-src cells differentiated morphologically with the extension of neurites. In contrast, PC12/v-src cells grown at the non-permissive temperature of 40 degrees C continued to divide and were morphologically indistinguishable from control PC12 cells. 2. Whole-cell Ca2+ currents were measured in PC12 cells using Ba2+ as the charge carrier. Ba2+ currents measured at the peak of the current-voltage curve from a holding potential of -80 mV were -0.28 +/- 0.04 nA (mean +/- S.E.M.) in control PC12 cells compared to -1.25 +/- 0.16 nA in NGF-differentiated cells. The current density increased from 9.4 +/- 0.7 pA/pF in control PC12 cells to 22.8 +/- 2.4 pA/pF in NGF-differentiated PC12 cells. Ba2+ currents were -0.24 +/- 0.04 nA in undifferentiated PC12/v-src cells grown at the non-permissive temperature of 40 degrees C compared to -0.95 +/- 0.16 nA in differentiated PC12/v-src cells grown at the permissive temperature of 37 degrees C. The current density increased from 4.5 +/- 0.5 pA/pF in PC12/v-src cells grown at the non-permissive temperature of 40 degrees C to 13.3 +/- 2.4 pA/pF in PC12/v-src cells grown at the permissive temperature of 37 degrees C. 3. The sensitivity of Ba2+ currents to omega-conotoxin GVIA (omega-CgTX) was determined for currents measured at the peak of the current-voltage curve (0 mV in 10 mM Ba2+) from a holding potential of -80 mV. In NGF-differentiated PC12 cells, 10 microM omega-CgTx inhibited 68.1 +/- 3.2% of the total Ba2+ current compared to 35.9 +/- 4.1% in control cells. The density of the omega-CgTX-sensitive current increased from 3.3 +/- 0.4 pA/pF in control cells to 15.7 +/- 2.0 pA/pF in NGF-differentiated cells. In differentiated PC12/v-src cells grown at 37 degrees C, omega-CgTX inhibited 52.2 +/- 4.2% of total Ba2+ current compared to 41.1 +/- 3.8% in PC12/v-src cells grown at 40 degrees C. The density of the omega-CgTX-sensitive current increased from 1.9 +/- 0.3 to 7.4 +/- 2.0 pA/pF with v-src-mediated differentiation.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alemà S., Casalbore P., Agostini E., Tatò F. Differentiation of PC12 phaeochromocytoma cells induced by v-src oncogene. Nature. 1985 Aug 8;316(6028):557–559. doi: 10.1038/316557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean B. P. Nitrendipine block of cardiac calcium channels: high-affinity binding to the inactivated state. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6388–6392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bocchini V., Angeletti P. U. The nerve growth factor: purification as a 30,000-molecular-weight protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Oct;64(2):787–794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.2.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Cotton P. C., Queral A. E., Barrett J. N., Nonner D., Keane R. W. Neurones express high levels of a structurally modified, activated form of pp60c-src. Nature. 1985 Aug 8;316(6028):554–557. doi: 10.1038/316554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dichter M. A., Tischler A. S., Greene L. A. Nerve growth factor-induced increase in electrical excitability and acetylcholine sensitivity of a rat pheochromocytoma cell line. Nature. 1977 Aug 11;268(5620):501–504. doi: 10.1038/268501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Hunter T. Platelet-derived growth factor induces multisite phosphorylation of pp60c-src and increases its protein-tyrosine kinase activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3345–3356. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto S. K-252a, a potent protein kinase inhibitor, blocks nerve growth factor-induced neurite outgrowth and changes in the phosphorylation of proteins in PC12h cells. J Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;107(4):1531–1539. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.4.1531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempstead B. L., Martin-Zanca D., Kaplan D. R., Parada L. F., Chao M. V. High-affinity NGF binding requires coexpression of the trk proto-oncogene and the low-affinity NGF receptor. Nature. 1991 Apr 25;350(6320):678–683. doi: 10.1038/350678a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirning L. D., Fox A. P., McCleskey E. W., Olivera B. M., Thayer S. A., Miller R. J., Tsien R. W. Dominant role of N-type Ca2+ channels in evoked release of norepinephrine from sympathetic neurons. Science. 1988 Jan 1;239(4835):57–61. doi: 10.1126/science.2447647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda S. R. Double-pulse calcium channel current facilitation in adult rat sympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1991 Aug;439:181–214. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. W., Jacobs L. S. Dihydropyridine actions on calcium currents of frog sympathetic neurons. J Neurosci. 1990 Jul;10(7):2261–2267. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-07-02261.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Hempstead B. L., Martin-Zanca D., Chao M. V., Parada L. F. The trk proto-oncogene product: a signal transducing receptor for nerve growth factor. Science. 1991 Apr 26;252(5005):554–558. doi: 10.1126/science.1850549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Martin-Zanca D., Parada L. F. Tyrosine phosphorylation and tyrosine kinase activity of the trk proto-oncogene product induced by NGF. Nature. 1991 Mar 14;350(6314):158–160. doi: 10.1038/350158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai S., Hanafusa H. The effects of reciprocal changes in temperature on the transformed state of cells infected with a rous sarcoma virus mutant. Virology. 1971 Nov;46(2):470–479. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90047-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koizumi S., Contreras M. L., Matsuda Y., Hama T., Lazarovici P., Guroff G. K-252a: a specific inhibitor of the action of nerve growth factor on PC 12 cells. J Neurosci. 1988 Feb;8(2):715–721. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-02-00715.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kongsamut S., Miller R. J. Nerve growth factor modulates the drug sensitivity of neurotransmitter release from PC-12 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2243–2247. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kypta R. M., Goldberg Y., Ulug E. T., Courtneidge S. A. Association between the PDGF receptor and members of the src family of tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):481–492. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarovici P., Levi B. Z., Lelkes P. I., Koizumi S., Fujita K., Matsuda Y., Ozato K., Guroff G. K-252a inhibits the increase in c-fos transcription and the increase in intracellular calcium produced by nerve growth factor in PC12 cells. J Neurosci Res. 1989 May;23(1):1–8. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490230102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R. The nerve growth factor 35 years later. Science. 1987 Sep 4;237(4819):1154–1162. doi: 10.1126/science.3306916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. B., Dorai T., Wang L. H., Brugge J. S. The structurally distinct form of pp60c-src detected in neuronal cells is encoded by a unique c-src mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):4142–4145. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.4142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Sugimori M., Lin J. W., Cherksey B. Blocking and isolation of a calcium channel from neurons in mammals and cephalopods utilizing a toxin fraction (FTX) from funnel-web spider poison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1689–1693. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb D. M., Maragos J., Martin-Zanca D., Chao M. V., Parada L. F., Greene L. A. The trk proto-oncogene rescues NGF responsiveness in mutant NGF-nonresponsive PC12 cell lines. Cell. 1991 Sep 6;66(5):961–966. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90441-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher P. A. Nerve growth factor induces protein-tyrosine phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6788–6791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher P. A. Role of protein tyrosine phosphorylation in the NGF response. J Neurosci Res. 1989 Sep;24(1):29–37. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490240106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel G., Cooperman S. S., Maue R. A., Goodman R. H., Brehm P. Selective induction of brain type II Na+ channels by nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):924–928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez R., Mathey-Prevot B., Bernards A., Baltimore D. Neuronal pp60c-src contains a six-amino acid insertion relative to its non-neuronal counterpart. Science. 1987 Jul 24;237(4813):411–415. doi: 10.1126/science.2440106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. J. Receptor-mediated regulation of calcium channels and neurotransmitter release. FASEB J. 1990 Dec;4(15):3291–3299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mintz I. M., Venema V. J., Swiderek K. M., Lee T. D., Bean B. P., Adams M. E. P-type calcium channels blocked by the spider toxin omega-Aga-IVA. Nature. 1992 Feb 27;355(6363):827–829. doi: 10.1038/355827a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. I., Curran T. Role of ion flux in the control of c-fos expression. Nature. 1986 Aug 7;322(6079):552–555. doi: 10.1038/322552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowycky M. C., Fox A. P., Tsien R. W. Three types of neuronal calcium channel with different calcium agonist sensitivity. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):440–443. doi: 10.1038/316440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivera B. M., Rivier J., Clark C., Ramilo C. A., Corpuz G. P., Abogadie F. C., Mena E. E., Woodward S. R., Hillyard D. R., Cruz L. J. Diversity of Conus neuropeptides. Science. 1990 Jul 20;249(4966):257–263. doi: 10.1126/science.2165278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plummer M. R., Logothetis D. E., Hess P. Elementary properties and pharmacological sensitivities of calcium channels in mammalian peripheral neurons. Neuron. 1989 May;2(5):1453–1463. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90191-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qiu M. S., Green S. H. NGF and EGF rapidly activate p21ras in PC12 cells by distinct, convergent pathways involving tyrosine phosphorylation. Neuron. 1991 Dec;7(6):937–946. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90339-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralston R., Bishop J. M. The product of the protooncogene c-src is modified during the cellular response to platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7845–7849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rausch D. M., Dickens G., Doll S., Fujita K., Koizumi S., Rudkin B. B., Tocco M., Eiden L. E., Guroff G. Differentiation of PC12 cells with v-src: comparison with nerve growth factor. J Neurosci Res. 1989 Sep;24(1):49–58. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490240108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rausch D. M., Lewis D. L., Barker J. L., Eiden L. E. Functional expression of dihydropyridine-insensitive calcium channels during PC12 cell differentiation by nerve growth factor (NGF), oncogenic ras, or src tyrosine kinase. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 1990 Jun;10(2):237–255. doi: 10.1007/BF00734577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudy B., Kirschenbaum B., Rukenstein A., Greene L. A. Nerve growth factor increases the number of functional Na channels and induces TTX-resistant Na channels in PC12 pheochromocytoma cells. J Neurosci. 1987 Jun;7(6):1613–1625. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-06-01613.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanguinetti M. C., Kass R. S. Voltage-dependent block of calcium channel current in the calf cardiac Purkinje fiber by dihydropyridine calcium channel antagonists. Circ Res. 1984 Sep;55(3):336–348. doi: 10.1161/01.res.55.3.336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorge L. K., Levy B. T., Maness P. F. pp60c-src is developmentally regulated in the neural retina. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):249–257. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90218-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley E. F., Goping G. Characterization of a calcium current in a vertebrate cholinergic presynaptic nerve terminal. J Neurosci. 1991 Apr;11(4):985–993. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-04-00985.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streit J., Lux H. D. Voltage dependent calcium currents in PC12 growth cones and cells during NGF-induced cell growth. Pflugers Arch. 1987 May;408(6):634–641. doi: 10.1007/BF00581167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Tsukui H., Hatanaka H. Neuronal differentiation of Ca2+ channel by nerve growth factor. Brain Res. 1985 Aug 26;341(2):381–384. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91079-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoenen H. The changing scene of neurotrophic factors. Trends Neurosci. 1991 May;14(5):165–170. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(91)90097-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas S. M., Hayes M., D'Arcangelo G., Armstrong R. C., Meyer B. E., Zilberstein A., Brugge J. S., Halegoua S. Induction of neurite outgrowth by v-src mimics critical aspects of nerve growth factor-induced differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4739–4750. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usowicz M. M., Porzig H., Becker C., Reuter H. Differential expression by nerve growth factor of two types of Ca2+ channels in rat phaeochromocytoma cell lines. J Physiol. 1990 Jul;426:95–116. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]