Abstract
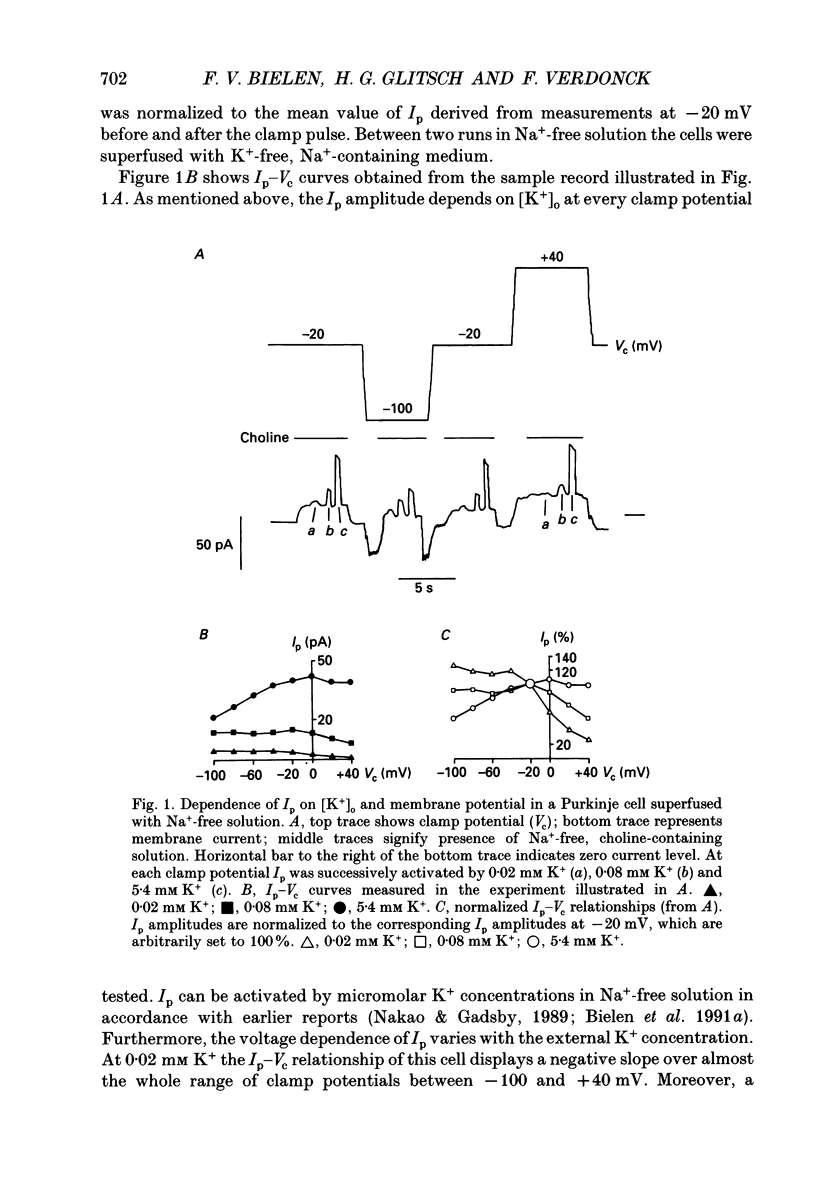
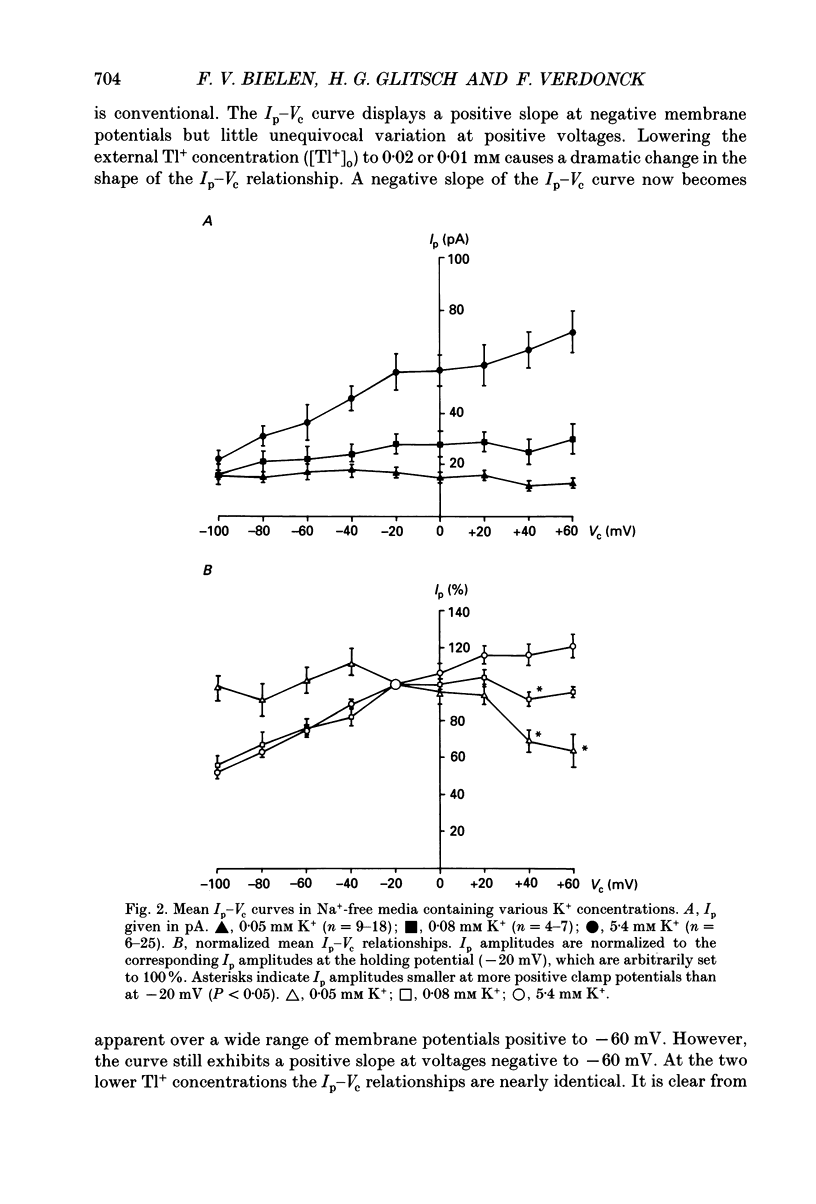
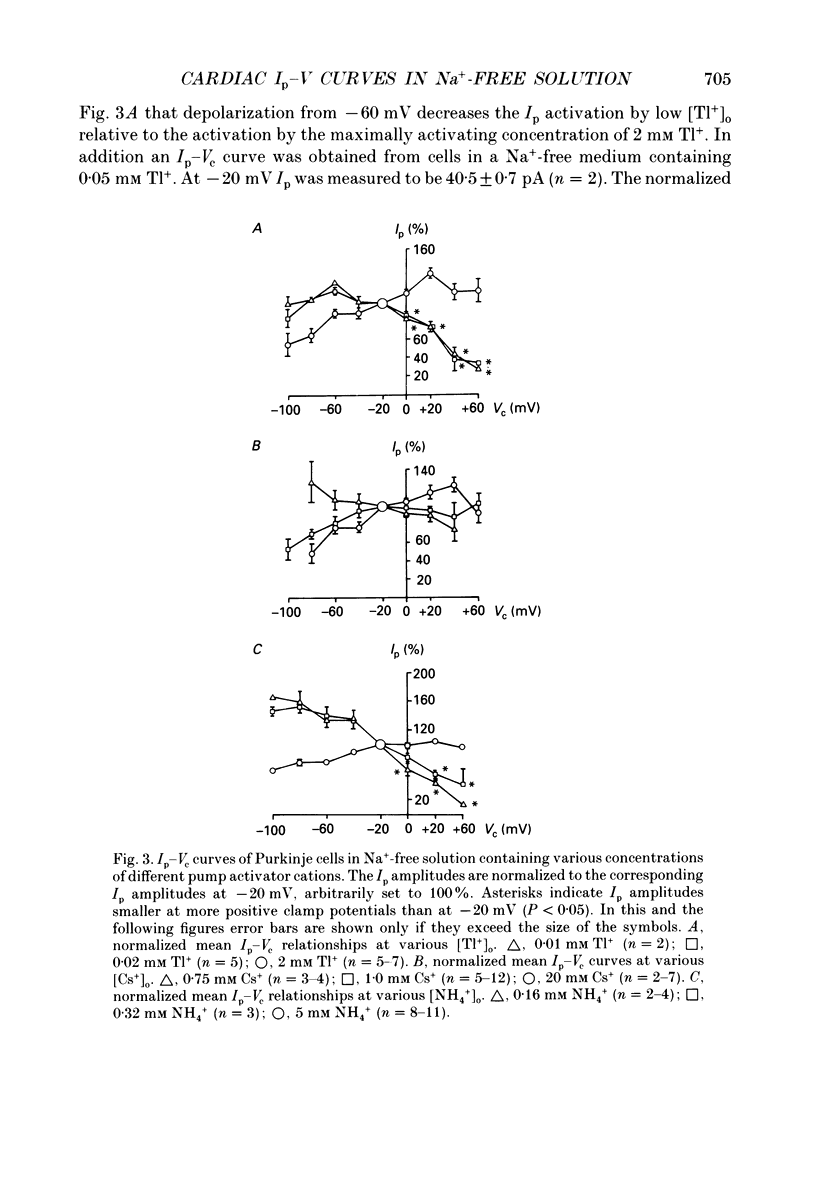
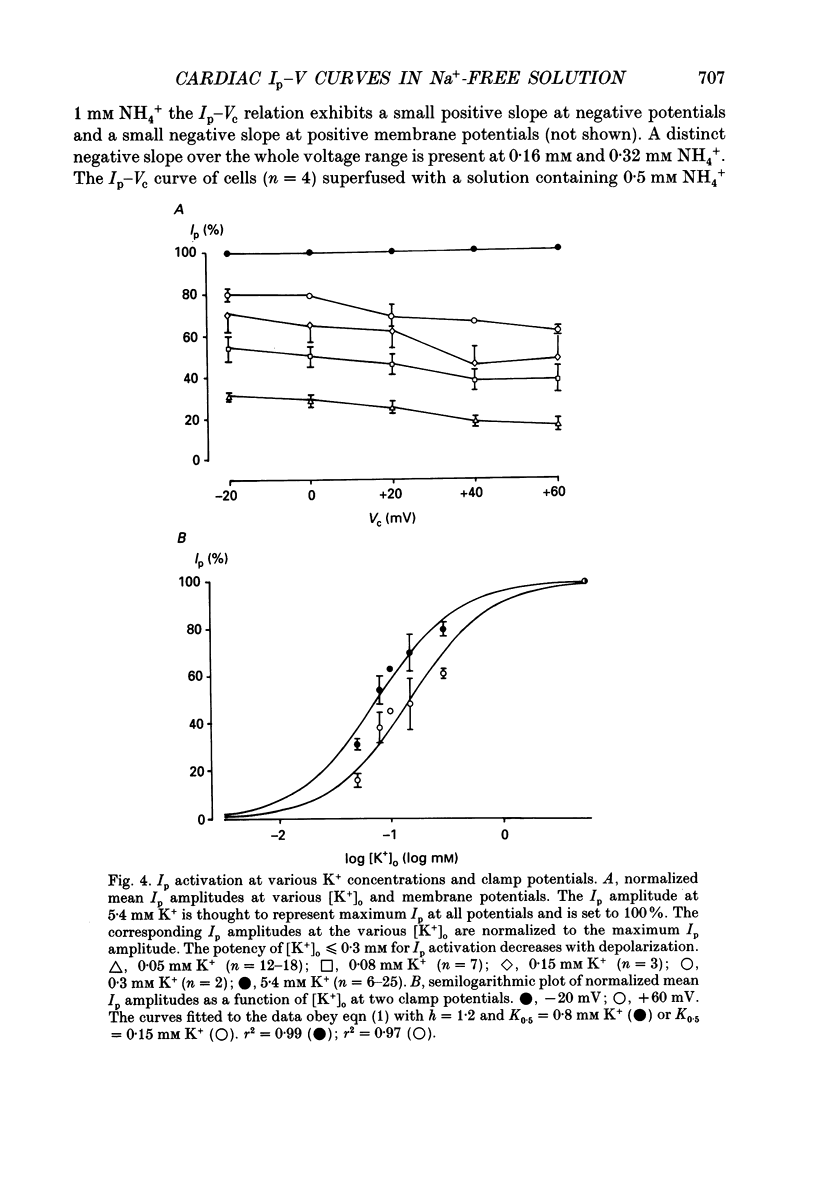
1. The Na+ pump current (Ip) of isolated, single rabbit cardiac Purkinje cells in Na(+)-free solution was measured at 32-34 degrees C by means of whole-cell recording. 2. The Ip amplitude was studied as a function of clamp potential (Vc) and external concentration of various monovalent cations known to activate the Na(+)-K+ pump. 3. Under conditions which strongly activated Ip the Ip-Vc curve of the cells displayed a positive slope at membrane potentials negative to -20 mV and little variation at more positive potentials. 4. The Ip-Vc relationship showed an extended region of negative slope at positive and negative potentials in solutions containing low concentrations of activator cations which caused little Ip activation. A positive slope of the Ip-Vc curve was occasionally observed at clamp potentials negative to -60 mV under these conditions. 5. The shape of the Ip-Vc relation was independent of the cation species used as external Ip activator. 6. At zero membrane potential half-maximum Ip activation (K0.5(Vc = 0 mV) occurred at 0.05 mM Tl+, 0.08 mM K+, 0.4 mM NH4+ and 1.5 mM Cs+. The Hill coefficient derived amounted to 0.9 for Tl+, 1.2 for K+, 1.04 for NH4+ and 1.5 for Cs+. 7. The concentrations of external activator cations required for half-maximum Ip activation increased with depolarization. The voltage dependence of the K0.5 values could be described by a single exponential function for clamp potentials positive to -40 mV. 8. The steepness of the function is determined by a factor alpha, indicating the apparent fraction of an elementary charge which moves in the electrical field across the sarcolemma when external monovalent cations bind to the Na(+)-K+ pump. 9. The alpha values were calculated to be 0.32 for Tl+, 0.24 for K+, 0.29 for NH4+ and 0.18 for Cs+. Possible interpretations of the alpha values are considered. 10. It is suggested that binding of external monovalent activator cations to the Na(+)-K+ pump (or a process related to the binding) is voltage dependent. This potential-dependent process determines mainly the shape of the Ip-Vc curve in cardiac Purkinje cells superfused with Na(+)-free media containing low concentrations (< K0.5(Vc = 0 mV)) of K+ or its congeners.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
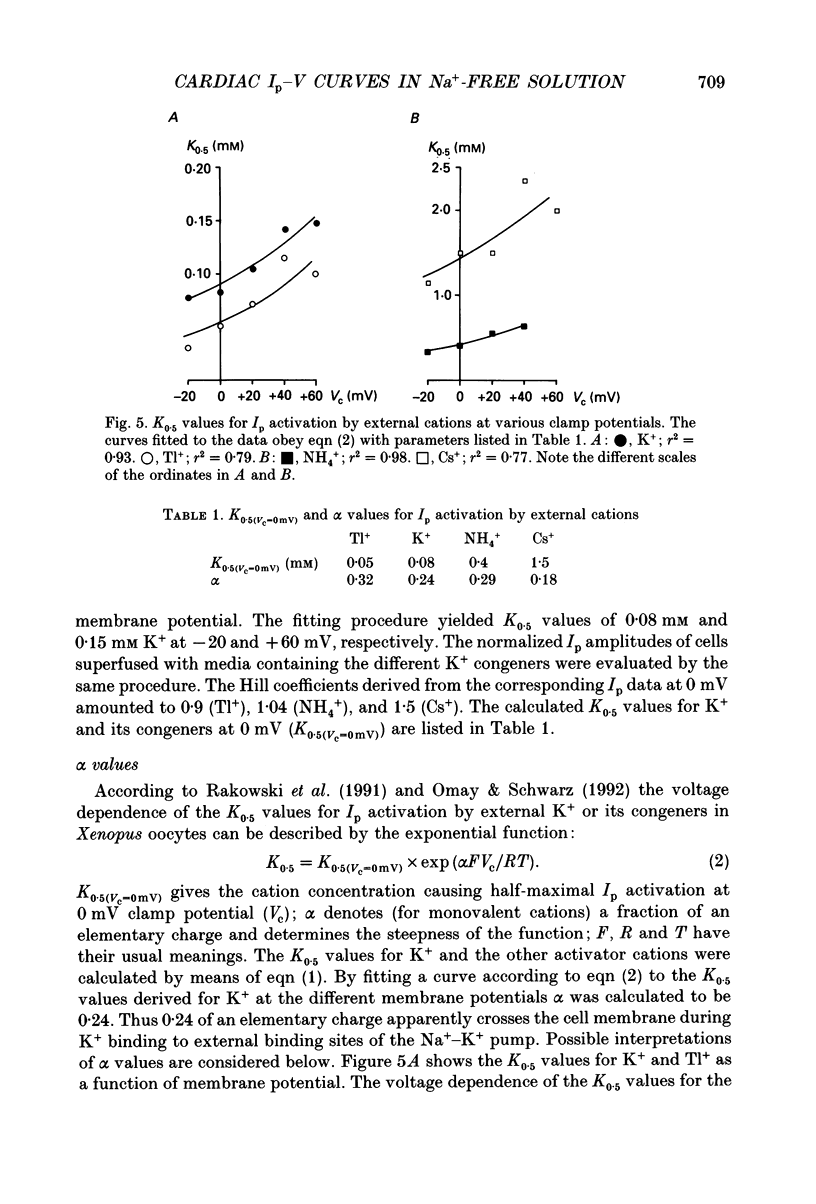
- Apell H. J. Electrogenic properties of the Na,K pump. J Membr Biol. 1989 Sep;110(2):103–114. doi: 10.1007/BF01869466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bahinski A., Nakao M., Gadsby D. C. Potassium translocation by the Na+/K+ pump is voltage insensitive. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3412–3416. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bielen F. V., Glitsch H. G., Verdonck F. Changes of the subsarcolemmal Na+ concentration in internally perfused cardiac cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jun 18;1065(2):269–271. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90239-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bielen F. V., Glitsch H. G., Verdonck F. Dependence of Na+ pump current on external monovalent cations and membrane potential in rabbit cardiac Purkinje cells. J Physiol. 1991 Oct;442:169–189. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Weer P., Gadsby D. C., Rakowski R. F. Voltage dependence of the Na-K pump. Annu Rev Physiol. 1988;50:225–241. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.50.030188.001301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisner D. A., Lederer W. J. The relationship between sodium pump activity and twitch tension in cardiac Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1980 Jun;303:475–494. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisner D. A., Lederer W. J. The role of the sodium pump in the effects of potassium-depleted solutions on mammalian cardiac muscle. J Physiol. 1979 Sep;294:279–301. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadsby D. C., Kimura J., Noma A. Voltage dependence of Na/K pump current in isolated heart cells. Nature. 1985 May 2;315(6014):63–65. doi: 10.1038/315063a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadsby D. C., Nakao M. Steady-state current-voltage relationship of the Na/K pump in guinea pig ventricular myocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Sep;94(3):511–537. doi: 10.1085/jgp.94.3.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadsby D. C. The Na/K pump of cardiac cells. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1984;13:373–398. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.13.060184.002105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glitsch H. G., Krahn T., Pusch H. The dependence of sodium pump current on internal Na concentration and membrane potential in cardioballs from sheep Purkinje fibres. Pflugers Arch. 1989 May;414(1):52–58. doi: 10.1007/BF00585626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldshlegger R., Karlish S. J., Rephaeli A., Stein W. D. The effect of membrane potential on the mammalian sodium-potassium pump reconstituted into phospholipid vesicles. J Physiol. 1987 Jun;387:331–355. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafaire A. V., Schwarz W. Voltage dependence of the rheogenic Na+/K+ ATPase in the membrane of oocytes of Xenopus laevis. J Membr Biol. 1986;91(1):43–51. doi: 10.1007/BF01870213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao M., Gadsby D. C. [Na] and [K] dependence of the Na/K pump current-voltage relationship in guinea pig ventricular myocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Sep;94(3):539–565. doi: 10.1085/jgp.94.3.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omay H. S., Schwarz W. Voltage-dependent stimulation of Na+/K(+)-pump current by external cations: selectivity of different K+ congeners. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Feb 17;1104(1):167–173. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(92)90146-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POST R. L., MERRITT C. R., KINSOLVING C. R., ALBRIGHT C. D. Membrane adenosine triphosphatase as a participant in the active transport of sodium and potassium in the human erythrocyte. J Biol Chem. 1960 Jun;235:1796–1802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakowski R. F., Gadsby D. C., De Weer P. Stoichiometry and voltage dependence of the sodium pump in voltage-clamped, internally dialyzed squid giant axon. J Gen Physiol. 1989 May;93(5):903–941. doi: 10.1085/jgp.93.5.903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakowski R. F., Vasilets L. A., LaTona J., Schwarz W. A negative slope in the current-voltage relationship of the Na+/K+ pump in Xenopus oocytes produced by reduction of external [K+]. J Membr Biol. 1991 Apr;121(2):177–187. doi: 10.1007/BF01870531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz W., Gu Q. B. Characteristics of the Na+/K+-ATPase from Torpedo californica expressed in Xenopus oocytes: a combination of tracer flux measurements with electrophysiological measurements. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Nov 22;945(2):167–174. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90479-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweigert B., Lafaire A. V., Schwarz W. Voltage dependence of the Na-K ATPase: measurements of ouabain-dependent membrane current and ouabain binding in oocytes of Xenopus laevis. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Oct;412(6):579–588. doi: 10.1007/BF00583758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stürmer W., Bühler R., Apell H. J., Läuger P. Charge translocation by the Na,K-pump: II. Ion binding and release at the extracellular face. J Membr Biol. 1991 Apr;121(2):163–176. doi: 10.1007/BF01870530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasilets L. A., Schwarz W. Regulation of endogenous and expressed Na+/K+ pumps in Xenopus oocytes by membrane potential and stimulation of protein kinases. J Membr Biol. 1992 Jan;125(2):119–132. doi: 10.1007/BF00233352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


