Abstract
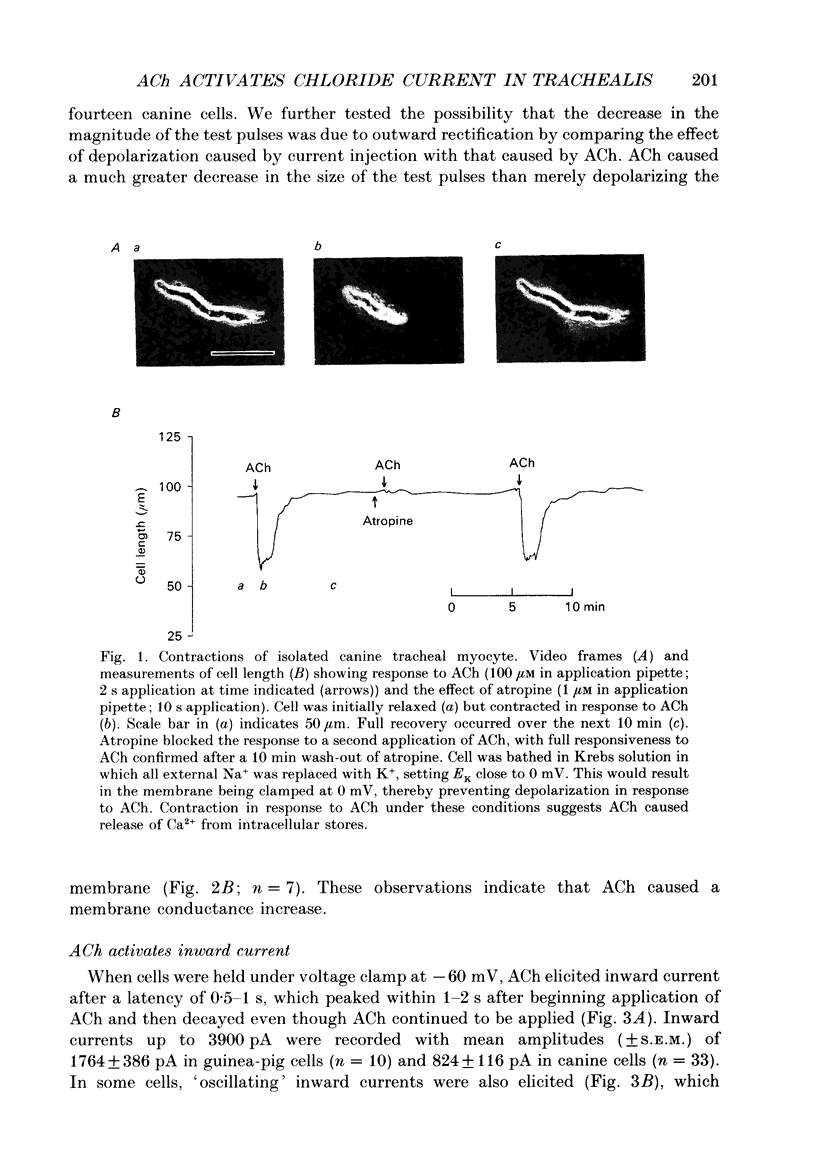
1. Membrane currents activated by acetylcholine (ACh) were investigated in isolated canine and guinea-pig tracheal myocytes using the nystatin perforated patch configuration of whole-cell recording. ACh caused depolarization accompanied by a membrane conductance increase. 2. When cells were held under voltage clamp (holding potential, Vh = -60 mV), ACh elicited inward current (IACh) of up to 3900 pA, with a reversal potential (Erev) of approximately -20 mV. 3. Removal of extracellular Na+ (Na+o) reduced but did not eliminate IACh. IACh remaining in the absence of Na+ reversed direction close to the predicted equilibrium potential for Cl-. Erev shifted 32 +/- 4 mV per 10-fold change of [Cl-]i. Increasing external [K+] caused Erev to shift in the positive direction. These results suggest that ACh activated chloride and non-selective cation conductances. 4. In the absence of Na+o, the Cl- channel blockers SITS or niflumic acid reversibly antagonized IACh. 5. Caffeine and ryanodine elicited currents both in the presence and absence of Na+o; these currents had a reversal potential similar to that of IACh. Caffeine applied before ACh occluded the response to ACh. 6. We also observed two types of spontaneous membrane currents. Spontaneous transient outward currents (STOCs) may represent Ca(2+)-activated K+ currents. Spontaneous inward currents were also observed which were reduced in magnitude (but not eliminated) by removal of Na+o and reversed direction at approximately the Cl- equilibrium potential. The spontaneous inward currents and STOCs were coincident and were reversibly suppressed by ACh. 7. ACh elicited contractions of cells under voltage clamp at -60 mV, an effect also observed in the absence of extracellular Ca2+ or when IACh was reduced by omission of Na+o and exposure to Cl- channel blockers. The number of cells which did contract in response to ACh decreased, however, when the concentration of internal Cl- decreased. 8. All effects of ACh on contraction and membrane currents were antagonized by atropine. 9. We conclude that activation of muscarinic receptors in mammalian tracheal myocytes causes release of Ca2+ from intracellular stores and subsequent activation of Cl- and non-selective cation conductances. This is the first direct demonstration of these conductances in tracheal smooth muscle cells. Activation of these conductances does not appear to be required for contraction. However, regulation of cytosolic Cl- levels may be important for release and uptake of Ca2+ from internal stores.
Full text
PDF




















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aickin C. C., Vermuë N. A. Microelectrode measurement of intracellular chloride activity in smooth muscle cells of guinea-pig ureter. Pflugers Arch. 1983 Apr;397(1):25–28. doi: 10.1007/BF00585163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amédée T., Benham C. D., Bolton T. B., Byrne N. G., Large W. A. Potassium, chloride and non-selective cation conductances opened by noradrenaline in rabbit ear artery cells. J Physiol. 1990 Apr;423:551–568. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amédée T., Large W. A., Wang Q. Characteristics of chloride currents activated by noradrenaline in rabbit ear artery cells. J Physiol. 1990 Sep;428:501–516. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baba K., Baron C. B., Coburn R. F. Phorbol ester effects on coupling mechanisms during cholinergic contraction of swine tracheal smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1989 May;412:23–42. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benham C. D., Bolton T. B., Lang R. J. Acetylcholine activates an inward current in single mammalian smooth muscle cells. Nature. 1985 Jul 25;316(6026):345–347. doi: 10.1038/316345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benham C. D., Bolton T. B. Spontaneous transient outward currents in single visceral and vascular smooth muscle cells of the rabbit. J Physiol. 1986 Dec;381:385–406. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton T. B., Large W. A. Are junction potentials essential? Dual mechanism of smooth muscle cell activation by transmitter released from autonomic nerves. Q J Exp Physiol. 1986 Jan;71(1):1–28. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1986.sp002960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne N. G., Large W. A. Action of noradrenaline on single smooth muscle cells freshly dispersed from the rat anococcygeus muscle. J Physiol. 1987 Aug;389:513–525. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coburn R. F. Electromechanical coupling in canine trachealis muscle: acetylcholine contractions. Am J Physiol. 1979 Mar;236(3):C177–C184. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1979.236.3.C177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel E. E., Jury J., Serio R., Jager L. P. Role of depolarization and calcium in contractions of canine trachealis from endogenous or exogenous acetylcholine. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1991 Apr;69(4):518–525. doi: 10.1139/y91-078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farley J. M., Miles P. R. Role of depolarization in acetylcholine-induced contractions of dog trachealis muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1977 Apr;201(1):199–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch E. A., Turner T. J., Goldin S. M. Calcium as a coagonist of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced calcium release. Science. 1991 Apr 19;252(5004):443–446. doi: 10.1126/science.2017683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerstheimer F. P., Mühleisen M., Nehring D., Kreye V. A. A chloride-bicarbonate exchanging anion carrier in vascular smooth muscle of the rabbit. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Jun;409(1-2):60–66. doi: 10.1007/BF00584750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gies J. P., Bertrand C., Vanderheyden P., Waeldele F., Dumont P., Pauli G., Landry Y. Characterization of muscarinic receptors in human, guinea pig and rat lung. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Jul;250(1):309–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. T., Ritchie J. M. A voltage-gated chloride conductance in rat cultured astrocytes. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1986 Aug 22;228(1252):267–288. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1986.0055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hals G. D., Stein P. G., Palade P. T. Single channel characteristics of a high conductance anion channel in "sarcoballs". J Gen Physiol. 1989 Mar;93(3):385–410. doi: 10.1085/jgp.93.3.385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hisada T., Kurachi Y., Sugimoto T. Properties of membrane currents in isolated smooth muscle cells from guinea-pig trachea. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Apr;416(1-2):151–161. doi: 10.1007/BF00370237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hisayama T., Takayanagi I. Ryanodine: its possible mechanism of action in the caffeine-sensitive calcium store of smooth muscle. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Sep;412(4):376–381. doi: 10.1007/BF01907555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg S. R., Williams A. J. Single channel recordings from human cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. Circ Res. 1989 Nov;65(5):1445–1449. doi: 10.1161/01.res.65.5.1445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn R., Marty A. Muscarinic activation of ionic currents measured by a new whole-cell recording method. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Aug;92(2):145–159. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.2.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inesi G. Mechanism of calcium transport. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:573–601. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.003041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue R., Isenberg G. Effect of membrane potential on acetylcholine-induced inward current in guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1990 May;424:57–71. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue R., Isenberg G. Intracellular calcium ions modulate acetylcholine-induced inward current in guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1990 May;424:73–92. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen L. J., Daniel E. E. Depolarizing agents induce oscillations in canine bronchial smooth muscle membrane potential: possible mechanisms. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Oct;259(1):110–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen L. J., Daniel E. E. Pre- and postjunctional muscarinic receptors in canine bronchi. Am J Physiol. 1990 Oct;259(4 Pt 1):L304–L314. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1990.259.4.L304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komori S., Bolton T. B. Role of G-proteins in muscarinic receptor inward and outward currents in rabbit jejunal smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1990 Aug;427:395–419. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn S. J., Horn R. Influence of sodium-calcium exchange on calcium current rundown and the duration of calcium-dependent chloride currents in pituitary cells, studied with whole cell and perforated patch recording. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Nov;94(5):789–812. doi: 10.1085/jgp.94.5.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotlikoff M. I. Calcium currents in isolated canine airway smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 1988 Jun;254(6 Pt 1):C793–C801. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.254.6.C793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotlikoff M. I. Potassium currents in canine airway smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 1990 Dec;259(6 Pt 1):L384–L395. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1990.259.6.L384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechleiter J., Girard S., Clapham D., Peralta E. Subcellular patterns of calcium release determined by G protein-specific residues of muscarinic receptors. Nature. 1991 Apr 11;350(6318):505–508. doi: 10.1038/350505a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loirand G., Pacaud P., Baron A., Mironneau C., Mironneau J. Large conductance calcium-activated non-selective cation channel in smooth muscle cells isolated from rat portal vein. J Physiol. 1991 Jun;437:461–475. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCann J. D., Welsh M. J. Calcium-activated potassium channels in canine airway smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1986 Mar;372:113–127. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T., Stryer L. Molecular model for receptor-stimulated calcium spiking. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5051–5055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muraki K., Imaizumi Y., Kojima T., Kawai T., Watanabe M. Effects of tetraethylammonium and 4-aminopyridine on outward currents and excitability in canine tracheal smooth muscle cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Jul;100(3):507–515. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb15838.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacaud P., Bolton T. B. Relation between muscarinic receptor cationic current and internal calcium in guinea-pig jejunal smooth muscle cells. J Physiol. 1991 Sep;441:477–499. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacaud P., Loirand G., Lavie J. L., Mironneau C., Mironneau J. Calcium-activated chloride current in rat vascular smooth muscle cells in short-term primary culture. Pflugers Arch. 1989 Apr;413(6):629–636. doi: 10.1007/BF00581813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen O. H., Wakui M. Oscillating intracellular Ca2+ signals evoked by activation of receptors linked to inositol lipid hydrolysis: mechanism of generation. J Membr Biol. 1990 Nov;118(2):93–105. doi: 10.1007/BF01868467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims S. M. Cholinergic activation of a non-selective cation current in canine gastric smooth muscle is associated with contraction. J Physiol. 1992 Apr;449:377–398. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims S. M., Vivaudou M. B., Hillemeier C., Biancani P., Walsh J. V., Jr, Singer J. J. Membrane currents and cholinergic regulation of K+ current in esophageal smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 1990 May;258(5 Pt 1):G794–G802. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1990.258.5.G794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Morita K., Kuriyama H. Innervation and properties of the smooth muscle of the dog trachea. Jpn J Physiol. 1976;26(3):303–320. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.26.303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swillens S., Mercan D. Computer simulation of a cytosolic calcium oscillator. Biochem J. 1990 Nov 1;271(3):835–838. doi: 10.1042/bj2710835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Q., Large W. A. Noradrenaline-evoked cation conductance recorded with the nystatin whole-cell method in rabbit portal vein cells. J Physiol. 1991 Apr;435:21–39. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



