Abstract
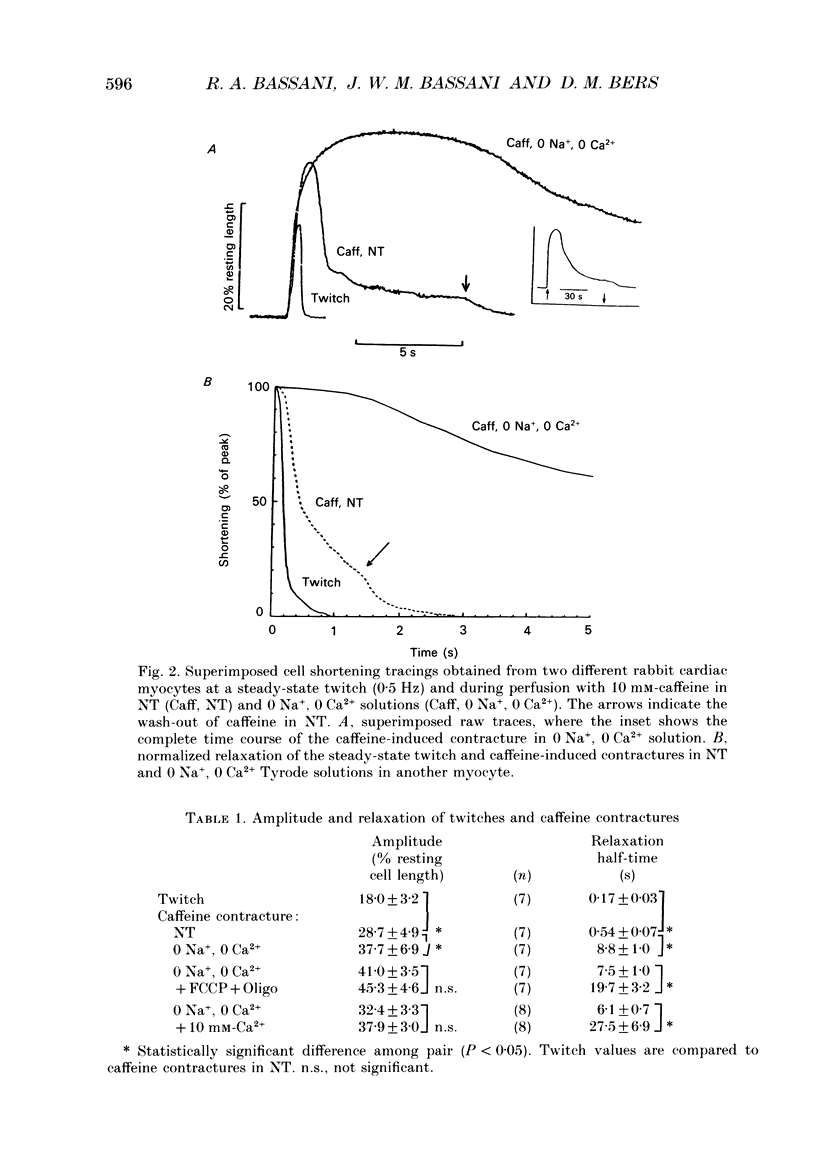
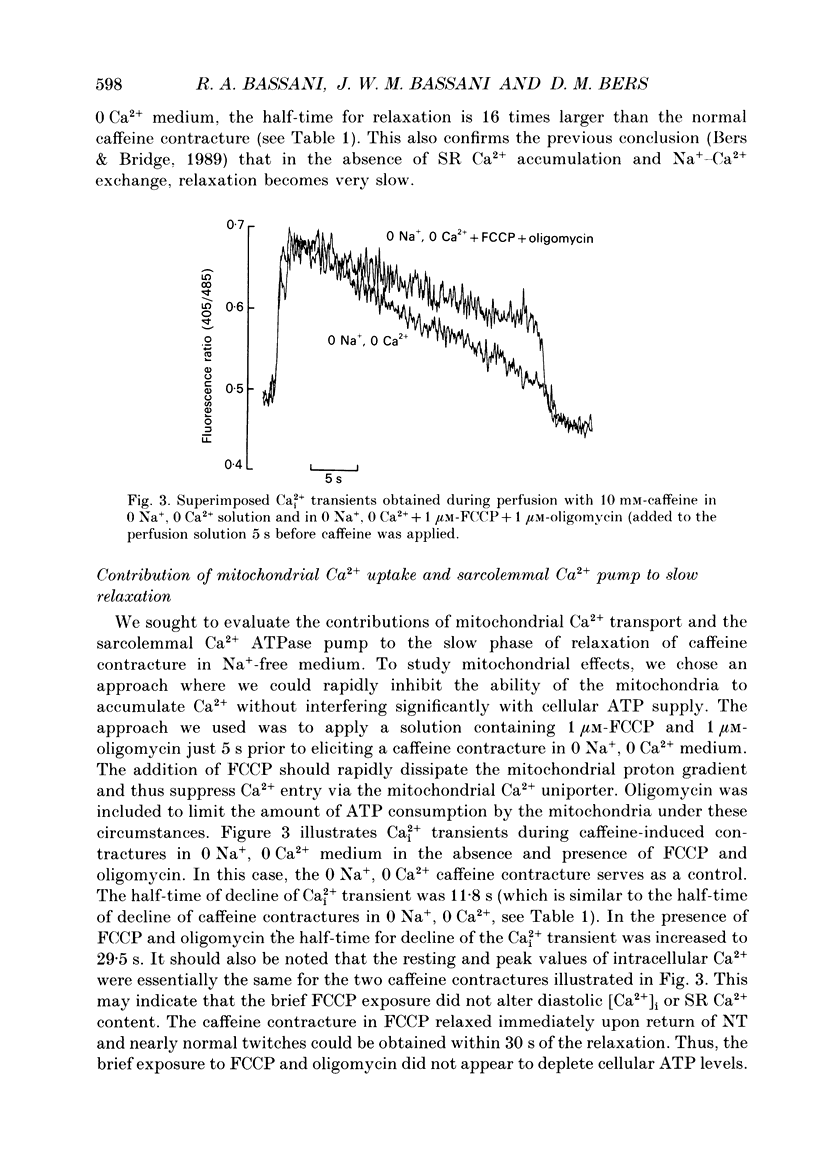
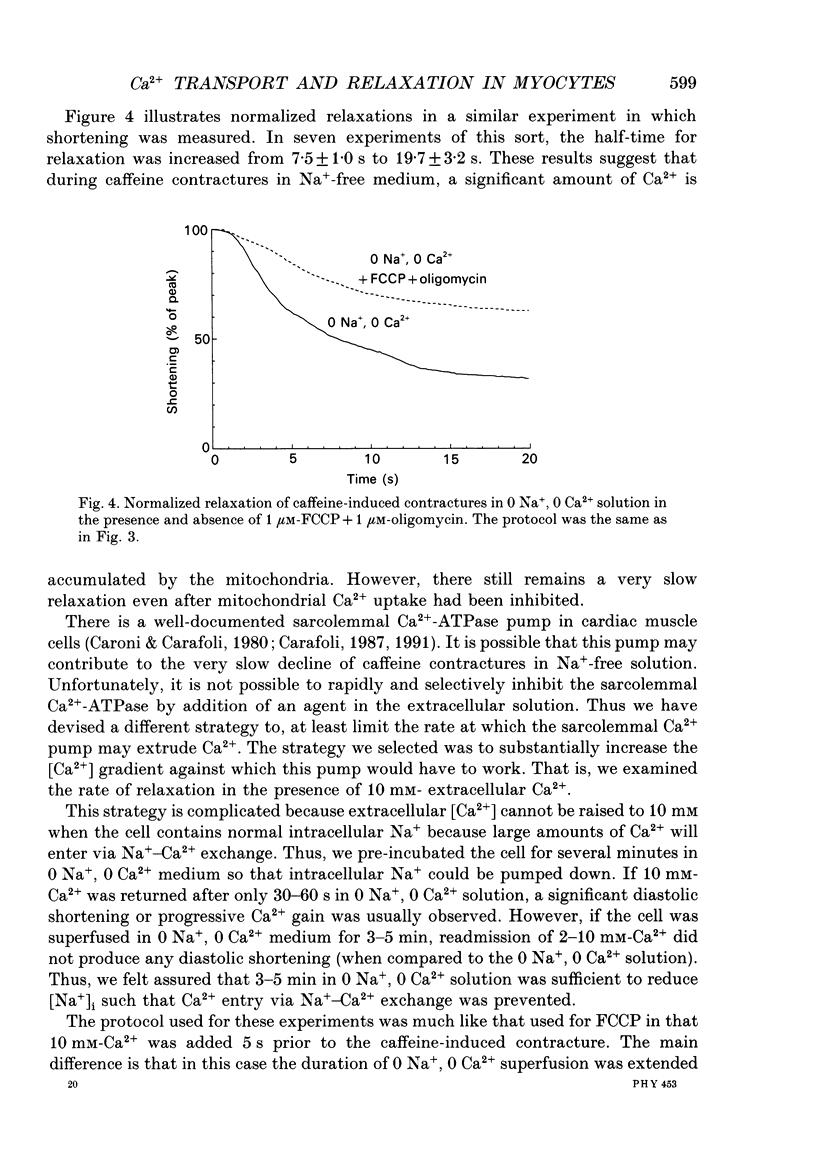
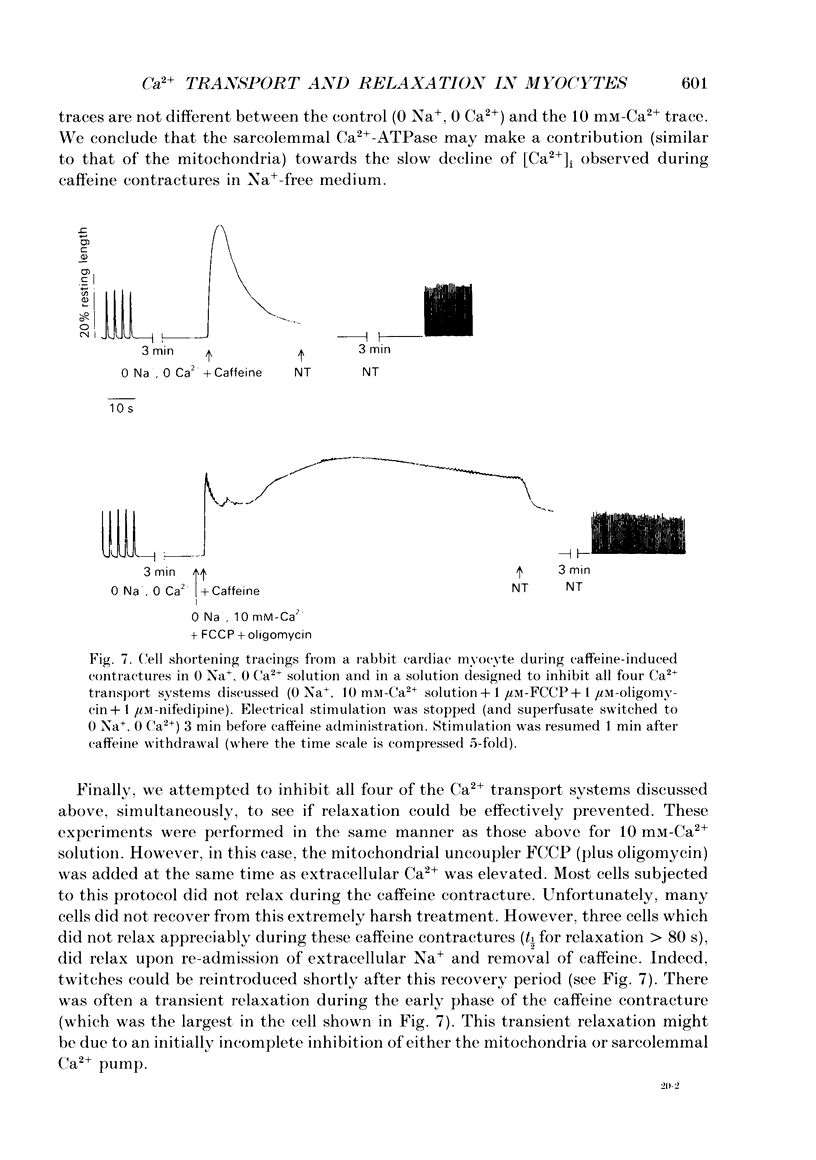
1. Contraction and intracellular Ca2+ (Ca2+i) transients were measured in isolated rabbit ventricular myocytes during twitches and contractures induced by rapid application of 10 mM-caffeine. 2. The amplitude of caffeine-induced contractures and the accompanying Ca2+i transients were larger than during normal twitches and also declined more slowly. This may be because only a fraction of sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) Ca2+ is released during a normal twitch, or because of a temporal overlap of SR Ca2+ release and uptake during the twitch. 3. When a caffeine contracture was initiated in Na(+)-free, Ca(2+)-free medium (to prevent sarcolemmal Na(+)-Ca2+ exchange) the contracture and Ca2+i transient were larger and decreased much more slowly. Thus, Ca2+ extrusion via Na(+)-Ca2+ exchange may limit the amplitude of caffeine-induced contractures. 4. Relaxation half-time (t1/2) for the twitch (0.17 +/- 0.03 s) was increased to 0.54 +/- 0.07 s for caffeine contractures in control solution and 8.8 +/- 1 s for caffeine-induced contractures in Na(+)-free, Ca(2+)-free solution. These results confirm that the SR Ca2+ pump and Na(+)-Ca2+ exchange are the predominant mechanisms for cytoplasmic Ca2+ removal during relaxation. However slower mechanisms can still reduce intracellular [Ca2+]. 5. Relaxation of caffeine contractures in Na(+)-free solution was further slowed when (a) mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake was inhibited with the oxidative phosphorylation uncoupler, FCCP (t1/2 = 19.7 +/- 3.2 s), or (b) the sarcolemmal Ca(2+)-ATPase pumping ability was depressed by a large transmembrane [Ca2+] gradient (t1/2 = 27.5 +/- 6.9 s). 6. When the four Ca2+ transport systems were simultaneously inhibited (i.e. SR Ca2+ pump, Na(+)-Ca2+ exchange, mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake and sarcolemmal Ca2+ pump), relaxation was practically abolished, but the cell could recover quickly when Na+ was reintroduced and caffeine removed. 7. We conclude that, under our experimental conditions, the sarcolemmal Ca2+ pump and mitochondria are approximately 37- and 50-fold slower than the Na(+)-Ca2+ exchange at removing Ca2+ from the cytoplasm. Additionally, the SR Ca2+ pump is about 3-4 times faster than Na(+)-Ca2+ exchange.
Full text
PDF













Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen D. G., Morris P. G., Orchard C. H., Pirolo J. S. A nuclear magnetic resonance study of metabolism in the ferret heart during hypoxia and inhibition of glycolysis. J Physiol. 1985 Apr;361:185–204. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry W. H., Rasmussen C. A., Jr, Ishida H., Bridge J. H. External Na-independent Ca extrusion in cultured ventricular cells. Magnitude and functional significance. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Sep;88(3):393–411. doi: 10.1085/jgp.88.3.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bers D. M., Bridge J. H., MacLeod K. T. The mechanism of ryanodine action in rabbit ventricular muscle evaluated with Ca-selective microelectrodes and rapid cooling contractures. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1987 Apr;65(4):610–618. doi: 10.1139/y87-103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bers D. M., Bridge J. H. Relaxation of rabbit ventricular muscle by Na-Ca exchange and sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium pump. Ryanodine and voltage sensitivity. Circ Res. 1989 Aug;65(2):334–342. doi: 10.1161/01.res.65.2.334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bers D. M., Bridge J. H., Spitzer K. W. Intracellular Ca2+ transients during rapid cooling contractures in guinea-pig ventricular myocytes. J Physiol. 1989 Oct;417:537–553. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bers D. M. Ca influx and sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca release in cardiac muscle activation during postrest recovery. Am J Physiol. 1985 Mar;248(3 Pt 2):H366–H381. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1985.248.3.H366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bers D. M., Lederer W. J., Berlin J. R. Intracellular Ca transients in rat cardiac myocytes: role of Na-Ca exchange in excitation-contraction coupling. Am J Physiol. 1990 May;258(5 Pt 1):C944–C954. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.258.5.C944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bers D. M. Ryanodine and the calcium content of cardiac SR assessed by caffeine and rapid cooling contractures. Am J Physiol. 1987 Sep;253(3 Pt 1):C408–C415. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.3.C408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bers D. M. SR Ca loading in cardiac muscle preparations based on rapid-cooling contractures. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jan;256(1 Pt 1):C109–C120. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.1.C109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beuckelmann D. J., Wier W. G. Mechanism of release of calcium from sarcoplasmic reticulum of guinea-pig cardiac cells. J Physiol. 1988 Nov;405:233–255. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridge J. H. Relationships between the sarcoplasmic reticulum and sarcolemmal calcium transport revealed by rapidly cooling rabbit ventricular muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Oct;88(4):437–473. doi: 10.1085/jgp.88.4.437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridge J. H., Spitzer K. W., Ershler P. R. Relaxation of isolated ventricular cardiomyocytes by a voltage-dependent process. Science. 1988 Aug 12;241(4867):823–825. doi: 10.1126/science.3406740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carafoli E. Calcium pump of the plasma membrane. Physiol Rev. 1991 Jan;71(1):129–153. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1991.71.1.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carafoli E. Intracellular calcium homeostasis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:395–433. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caroni P., Carafoli E. An ATP-dependent Ca2+-pumping system in dog heart sarcolemma. Nature. 1980 Feb 21;283(5749):765–767. doi: 10.1038/283765a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman R. A., Léoty C. The time-dependent and dose-dependent effects of caffeine on the contraction of the ferret heart. J Physiol. 1976 Apr;256(2):287–314. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clusin W. T., Fischmeister R., DeHaan R. L. Caffeine-induced current in embryonic heart cells: time course and voltage dependence. Am J Physiol. 1983 Sep;245(3):H528–H532. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1983.245.3.H528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crespo L. M., Grantham C. J., Cannell M. B. Kinetics, stoichiometry and role of the Na-Ca exchange mechanism in isolated cardiac myocytes. Nature. 1990 Jun 14;345(6276):618–621. doi: 10.1038/345618a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton R. M., McCormack J. G. Ca2+ as a second messenger within mitochondria of the heart and other tissues. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:451–466. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.002315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisner D. A., Valdeolmillos M. The mechanism of the increase of tonic tension produced by caffeine in sheep cardiac Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1985 Jul;364:313–326. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A. Calcium-induced release of calcium from the cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jul;245(1):C1–14. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1983.245.1.C1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A., Fabiato F. Contractions induced by a calcium-triggered release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of single skinned cardiac cells. J Physiol. 1975 Aug;249(3):469–495. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A. Time and calcium dependence of activation and inactivation of calcium-induced release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of a skinned canine cardiac Purkinje cell. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Feb;85(2):247–289. doi: 10.1085/jgp.85.2.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunter T. E., Pfeiffer D. R. Mechanisms by which mitochondria transport calcium. Am J Physiol. 1990 May;258(5 Pt 1):C755–C786. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.258.5.C755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansford R. G. Relation between mitochondrial calcium transport and control of energy metabolism. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1985;102:1–72. doi: 10.1007/BFb0034084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hryshko L. V., Stiffel V., Bers D. M. Rapid cooling contractures as an index of sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium content in rabbit ventricular myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1989 Nov;257(5 Pt 2):H1369–H1377. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1989.257.5.H1369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitazawa T. Caffeine contracture in guinea-pig ventricular muscle and the effect of extracellular sodium ions. J Physiol. 1988 Aug;402:703–729. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewartowski B., Hansford R. G., Langer G. A., Lakatta E. G. Contraction and sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ content in single myocytes of guinea pig heart: effect of ryanodine. Am J Physiol. 1990 Oct;259(4 Pt 2):H1222–H1229. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.259.4.H1222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Q., Hohl C. M., Altschuld R. A., Stokes B. T. Energy depletion-repletion and calcium transients in single cardiomyocytes. Am J Physiol. 1989 Sep;257(3 Pt 1):C427–C434. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.257.3.C427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipp P., Pott L. Transient inward current in guinea-pig atrial myocytes reflects a change of sodium-calcium exchange current. J Physiol. 1988 Mar;397:601–630. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Näbauer M., Callewaert G., Cleemann L., Morad M. Regulation of calcium release is gated by calcium current, not gating charge, in cardiac myocytes. Science. 1989 May 19;244(4906):800–803. doi: 10.1126/science.2543067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill S. C., Donoso P., Eisner D. A. The role of [Ca2+]i and [Ca2+] sensitization in the caffeine contracture of rat myocytes: measurement of [Ca2+]i and [caffeine]i. J Physiol. 1990 Jun;425:55–70. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sipido K. R., Wier W. G. Flux of Ca2+ across the sarcoplasmic reticulum of guinea-pig cardiac cells during excitation-contraction coupling. J Physiol. 1991 Apr;435:605–630. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. L., Valdeolmillos M., Eisner D. A., Allen D. G. Effects of rapid application of caffeine on intracellular calcium concentration in ferret papillary muscles. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Sep;92(3):351–368. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.3.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solaro R. J., Wise R. M., Shiner J. S., Briggs F. N. Calcium requirements for cardiac myofibrillar activation. Circ Res. 1974 Apr;34(4):525–530. doi: 10.1161/01.res.34.4.525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurgeon H. A., Stern M. D., Baartz G., Raffaeli S., Hansford R. G., Talo A., Lakatta E. G., Capogrossi M. C. Simultaneous measurement of Ca2+, contraction, and potential in cardiac myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1990 Feb;258(2 Pt 2):H574–H586. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.258.2.H574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wendt I. R., Stephenson D. G. Effects of caffeine on Ca-activated force production in skinned cardiac and skeletal muscle fibres of the rat. Pflugers Arch. 1983 Aug;398(3):210–216. doi: 10.1007/BF00657153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolska B. M., Lewartowski B. Calcium in the in situ mitochondria of rested and stimulated myocardium. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1991 Feb;23(2):217–226. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(91)90108-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


