Abstract
1. Evidence has been sought for crossed actions on midlumbar propriospinal neurones activated by ipsilateral group II muscle afferents, with particular emphasis on those neurones with projections to the ipsilateral hindlimb motor nuclei. 2. A large majority of group II-activated midlumbar neurones were influenced by stimulation of contralateral group II afferents. The most frequent and most powerful actions were from those nerves which most effectively influenced ipsilateral midlumbar neurones. Crossed actions from group I afferents were rare. 3. In the great majority of neurones the pattern of actions was similar from both limbs, the neurones being bilaterally excited, bilaterally inhibited or had both EPSPs and IPSPs from both sides. 4. The latencies of crossed actions suggest that the earliest crossed EPSPs from group II afferents were evoked disynaptically (i.e. via a single commissural neurone) and that the crossed IPSPs were evoked trisynaptically. 5. The pattern of crossed actions suggests a strong bilateral interaction between midlumbar neurones. The possible role of these neurones in postural control and the production of co-ordinated movements of the hindlimbs is discussed.
Full text
PDF


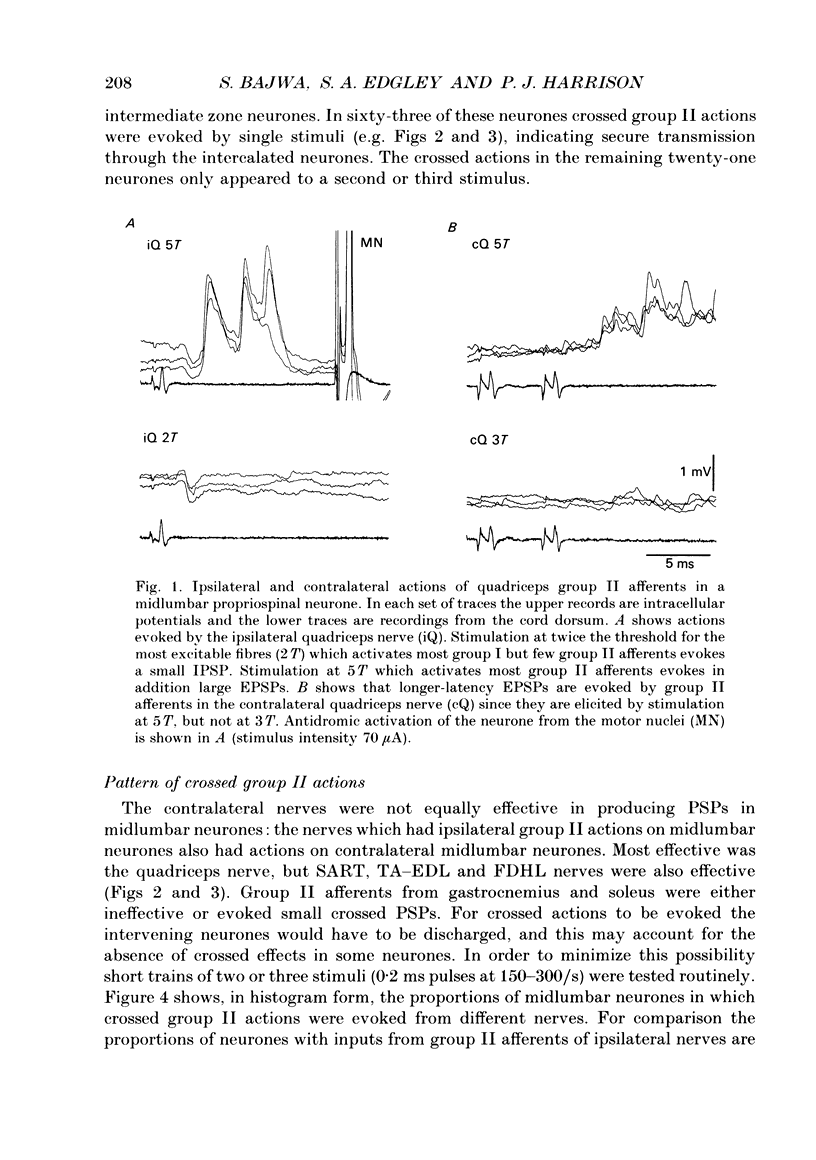
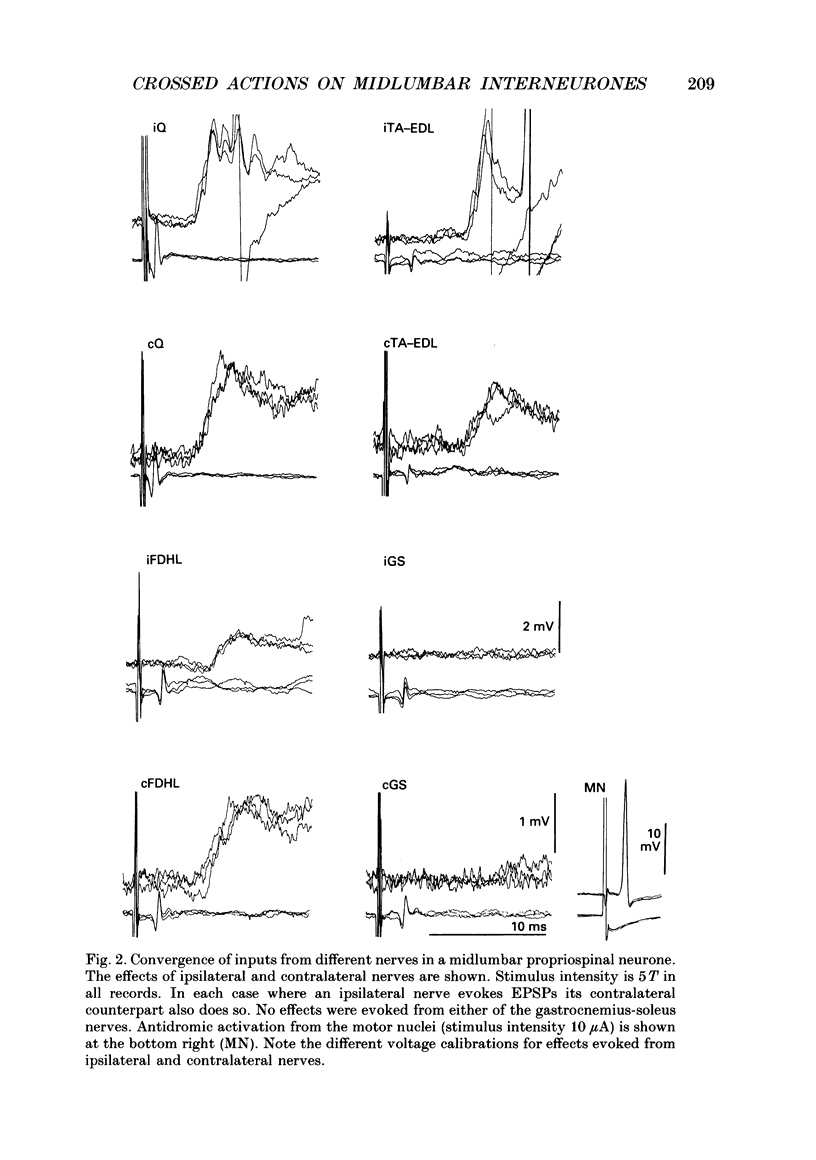
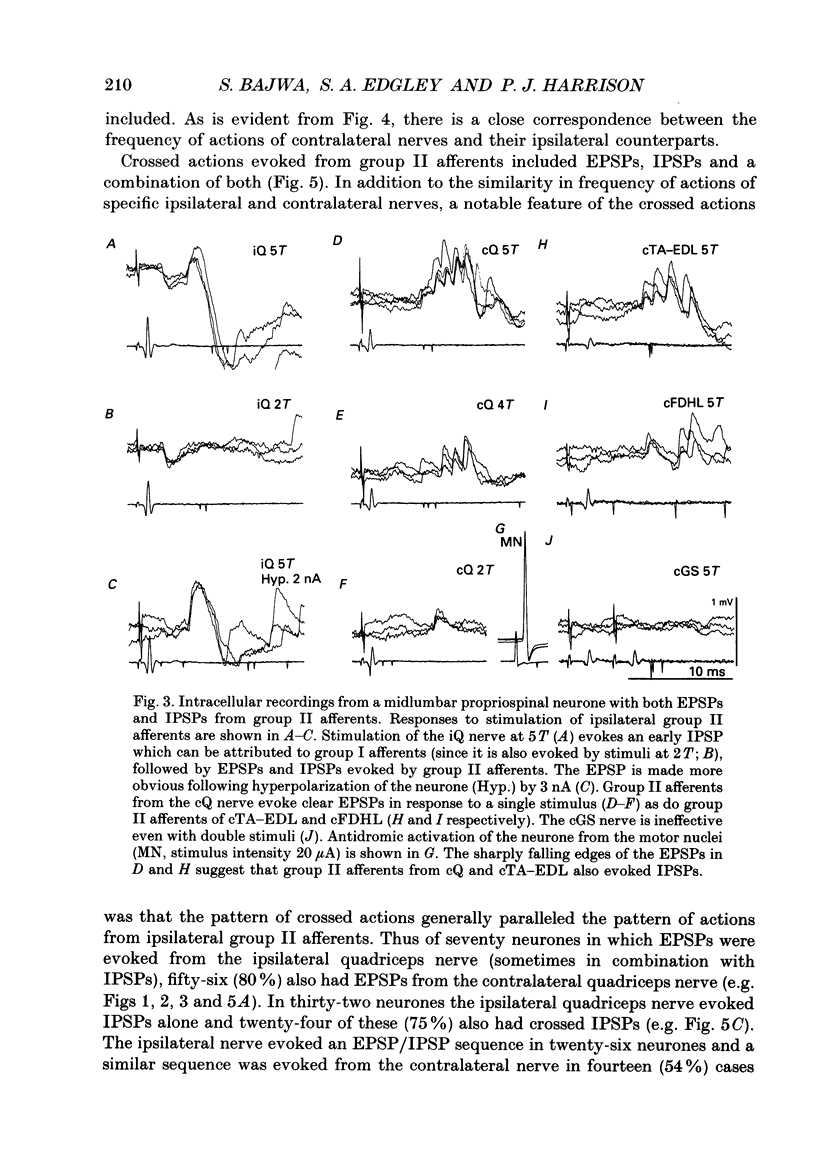
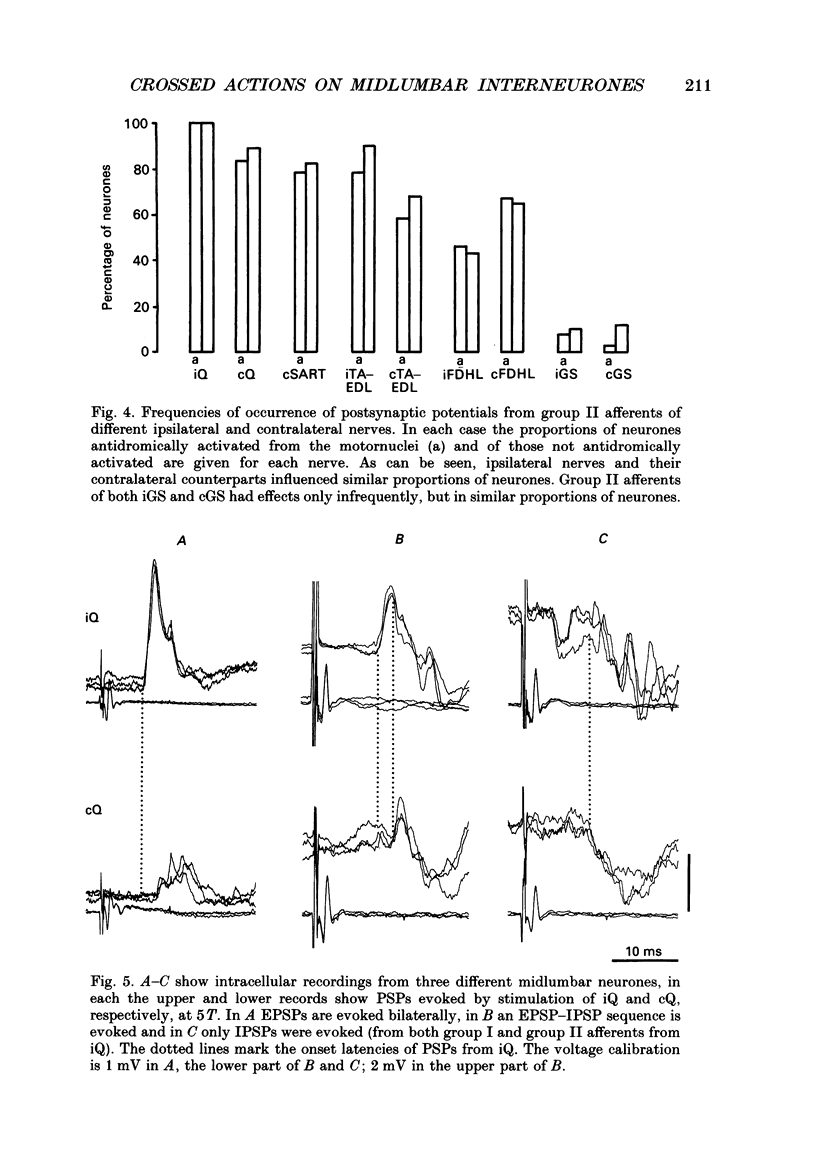





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arya T., Bajwa S., Edgley S. A. Crossed reflex actions from group II muscle afferents in the lumbar spinal cord of the anaesthetized cat. J Physiol. 1991 Dec;444:117–131. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bras H., Cavallari P., Jankowska E., Kubin L. Morphology of midlumbar interneurones relaying information from group II muscle afferents in the cat spinal cord. J Comp Neurol. 1989 Dec 1;290(1):1–15. doi: 10.1002/cne.902900102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgley S. A., Jankowska E. An interneuronal relay for group I and II muscle afferents in the midlumbar segments of the cat spinal cord. J Physiol. 1987 Aug;389:647–674. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgley S. A., Jankowska E. Field potentials generated by group II muscle afferents in the middle lumbar segments of the cat spinal cord. J Physiol. 1987 Apr;385:393–413. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgley S. A., Jankowska E., Shefchyk S. Evidence that mid-lumbar neurones in reflex pathways from group II afferents are involved in locomotion in the cat. J Physiol. 1988 Sep;403:57–71. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fern R., Harrison P. J., Riddell J. S. The dorsal column projection of muscle afferent fibres from the cat hindlimb. J Physiol. 1988 Jul;401:97–113. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu T. C., Schomburg E. D. Electrophysiological investigation of the projection of secondary muscle spindle afferents in the cat spinal cord. Acta Physiol Scand. 1974 Jul;91(3):314–329. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1974.tb05687.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyffe R. E. The morphology of group II muscle afferent fibre collaterals [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1979 Nov;296:39P–40P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grillner S., Rossignol S. On the initiation of the swing phase of locomotion in chronic spinal cats. Brain Res. 1978 May 12;146(2):269–277. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90973-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison P. J., Jami L., Jankowska E. Further evidence for synaptic actions of muscle spindle secondaries in the middle lumbar segments of the cat spinal cord. J Physiol. 1988 Aug;402:671–686. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison P. J., Jankowska E., Zytnicki D. Lamina VIII interneurones interposed in crossed reflex pathways in the cat. J Physiol. 1986 Feb;371:147–166. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp015965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison P. J., Riddell J. S. Group II-activated lumbosacral interneurones with an ascending projection to midlumbar segments of the cat spinal cord. J Physiol. 1989 Jan;408:561–570. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoheisel U., Lehmann-Willenbrock E., Mense S. Termination patterns of identified group II and III afferent fibres from deep tissues in the spinal cord of the cat. Neuroscience. 1989;28(2):495–507. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90195-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hongo T., Kudo N., Tanaka R. The vestibulospinal tract: crossed and uncrossed effects on hindlimb motoneurones in the cat. Exp Brain Res. 1975 Nov 28;24(1):37–55. doi: 10.1007/BF00236016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., Noga B. R. Contralaterally projecting lamina VIII interneurones in middle lumbar segments in the cat. Brain Res. 1990 Dec 10;535(2):327–330. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91618-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Light A. R., Perl E. R. Reexamination of the dorsal root projection to the spinal dorsal horn including observations on the differential termination of coarse and fine fibers. J Comp Neurol. 1979 Jul 15;186(2):117–131. doi: 10.1002/cne.901860202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg A., Malmgren K., Schomburg E. D. Reflex pathways from group II muscle afferents. 1. Distribution and linkage of reflex actions to alpha-motoneurones. Exp Brain Res. 1987;65(2):271–281. doi: 10.1007/BF00236299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg A., Malmgren K., Schomburg E. D. Reflex pathways from group II muscle afferents. 2. Functional characteristics of reflex pathways to alpha-motoneurones. Exp Brain Res. 1987;65(2):282–293. doi: 10.1007/BF00236300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson J. B., Sypert G. W., Zengel J. E., Lofton S. A., Fleshman J. W. Monosynaptic projections of individual spindle group II afferents to type-identified medial gastrocnemius motoneurons in the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1982 Nov;48(5):1164–1174. doi: 10.1152/jn.1982.48.5.1164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shefchyk S., McCrea D., Kriellaars D., Fortier P., Jordan L. Activity of interneurons within the L4 spinal segment of the cat during brainstem-evoked fictive locomotion. Exp Brain Res. 1990;80(2):290–295. doi: 10.1007/BF00228156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki I., Timerick S. J., Wilson V. J. Body position with respect to the head or body position in space is coded by lumbar interneurons. J Neurophysiol. 1985 Jul;54(1):123–133. doi: 10.1152/jn.1985.54.1.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates B. J., Kasper J., Wilson V. J. Effects of muscle and cutaneous hindlimb afferents on L4 neurons whose activity is modulated by neck rotation. Exp Brain Res. 1989;77(1):48–56. doi: 10.1007/BF00250566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


