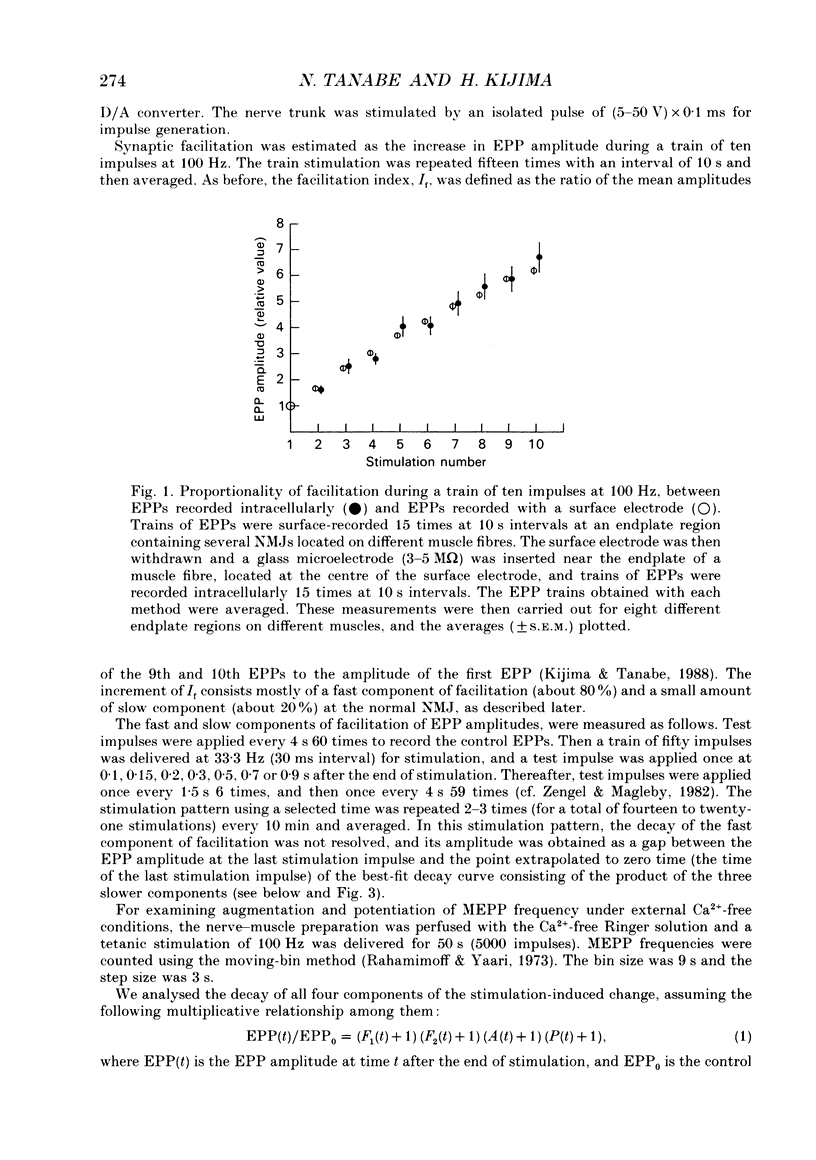
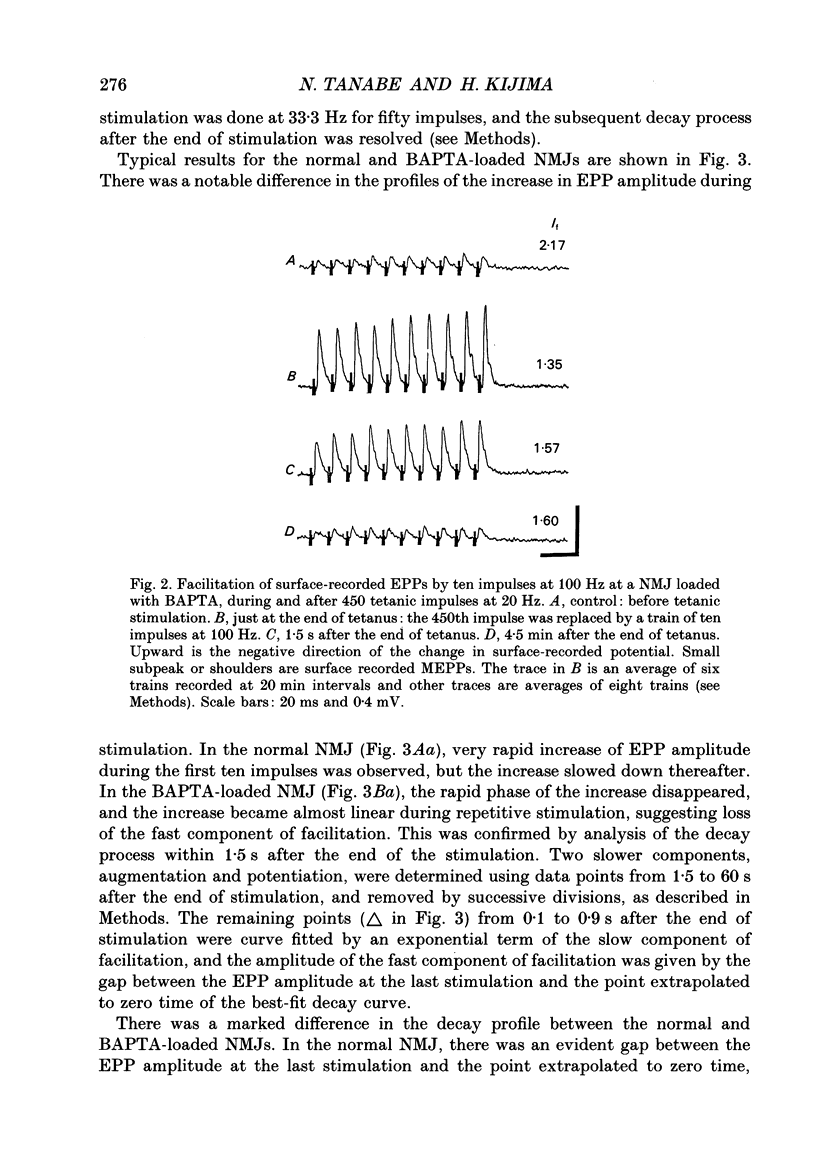
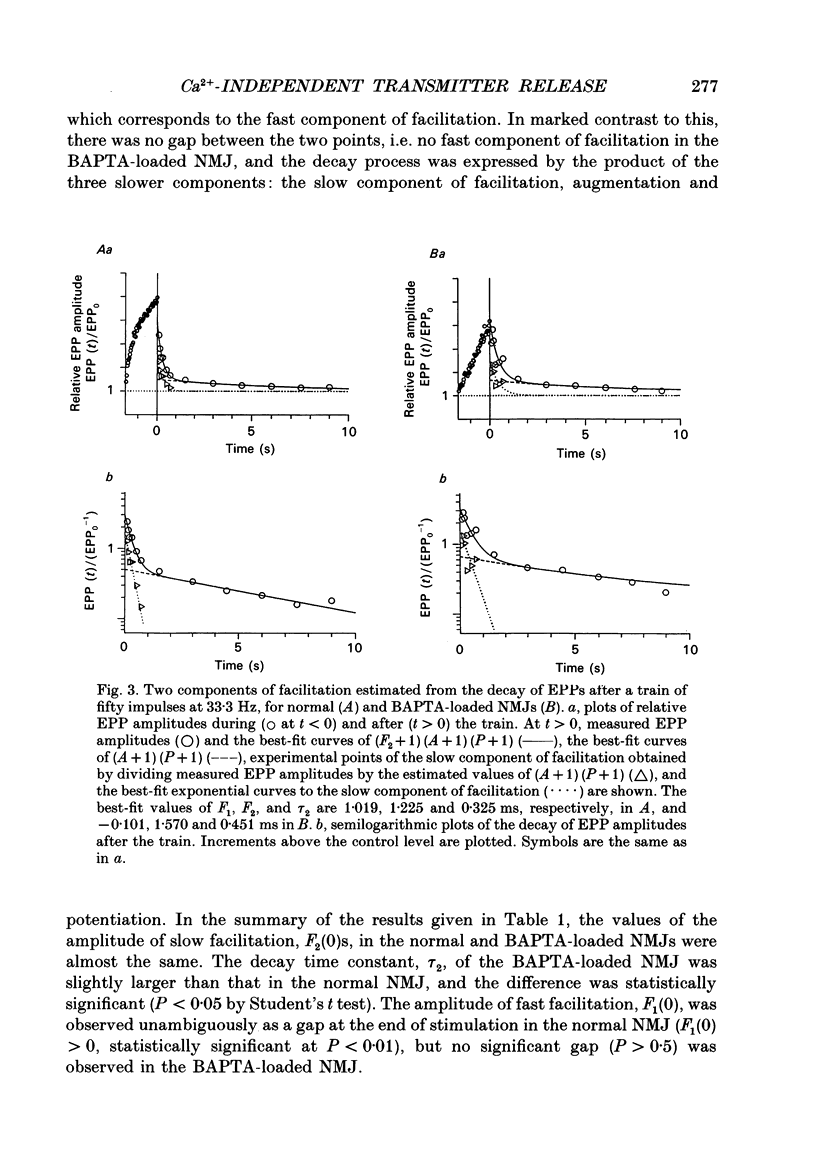
Abstract
1. When a Ca2+ chelator, bis (O-aminophenoxy)ethane-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid (BAPTA), was loaded into the presynaptic nerve terminal of the frog neuromuscular junction (NMJ), facilitation, measured as an increase in endplate potential (EPP) amplitudes during a train of ten stimulations at 100 Hz, was greatly decreased within 20 min of BAPTA-AM (the acetoxymethyl ester of BAPTA) perfusion, and remained at a constant low level thereafter, suggesting that [Ca2+]i at the presynaptic nerve terminal was buffered by BAPTA. 2. Detailed examination of the two components of facilitation of EPP amplitude in the BAPTA-loaded NMJs showed that the fast component was lost almost completely, while the slow component was unaffected by loaded BAPTA. Augmentation and potentiation were also unaffected by BAPTA. 3. Under external Ca(2+)-free conditions (with 1 mM-EGTA), both augmentation and potentiation of miniature endplate potential (MEPP) frequency were clearly observed after tetanic stimulation in the normal NMJ, and were also unaffected by loaded BAPTA. 4. The above findings strongly support the residual Ca2+ hypothesis for the fast component of facilitation, and suggest that the three slower processes (the slow component of facilitation, augmentation and potentiation) occur independently of [Ca2+]i. This Ca2+ independence was supported by the fact that facilitation and potentiation have multiplicative effects on the amount of release. 5. The quantal content of the first EPP in the train remained unchanged throughout the time course of BAPTA loading for most NMJs. This suggests that [Ca2+]i immediately adjacent to Ca2+ channels at the active zone triggers transmitter release and is little affected by loaded BAPTA. 6. MEPP frequency was almost unchanged during BAPTA loading, suggesting that the basal [Ca2+]i remained unchanged close to the dissociation constant of BAPTA for Ca2+ (108 nM). 7. The slow component of facilitation had a multiplicative relationship with augmentation and potentiation, suggesting that the underlying mechanism for the slow component of facilitation differs from that for augmentation and potentiation.
Full text
PDF



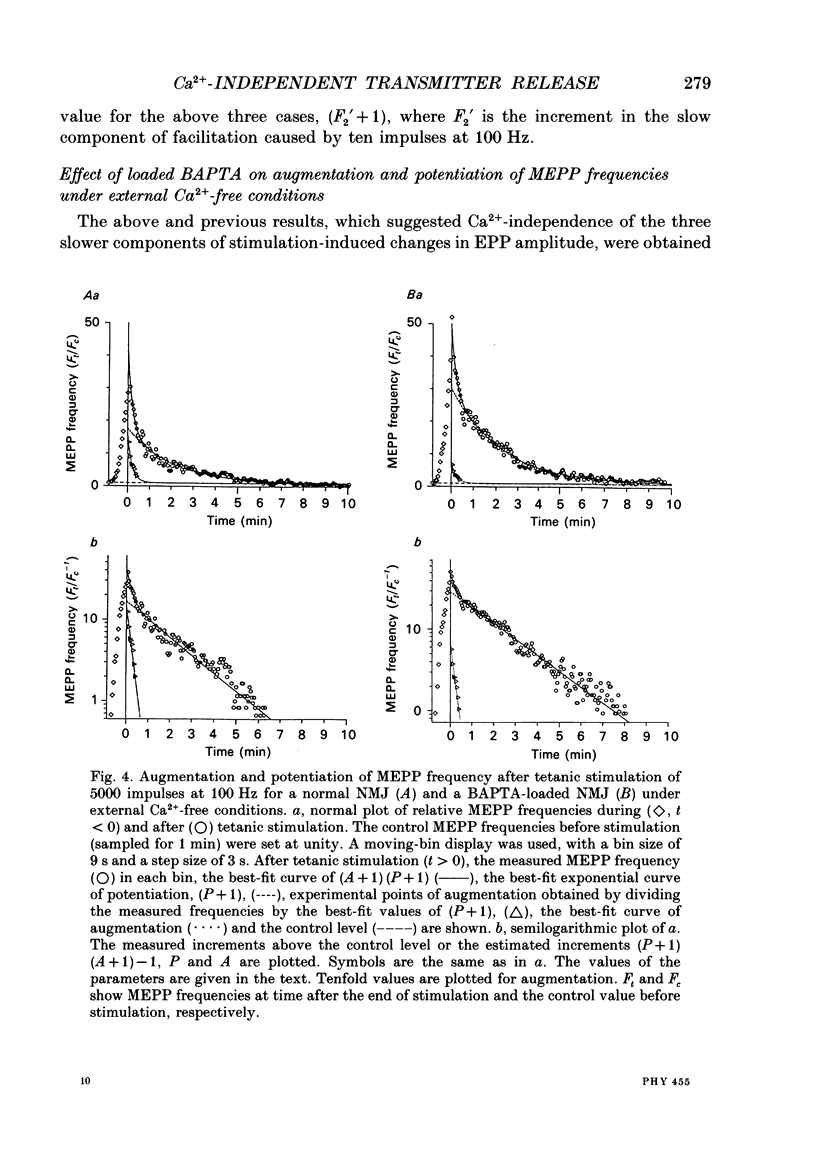

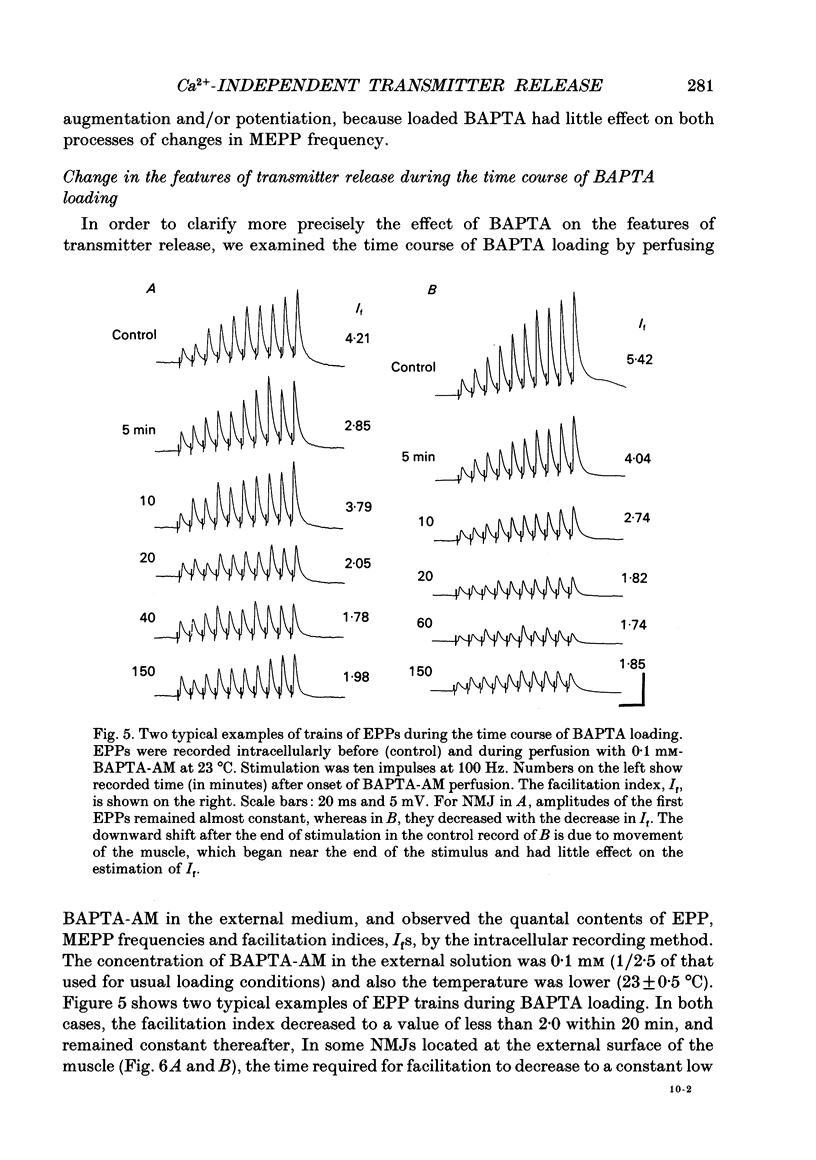
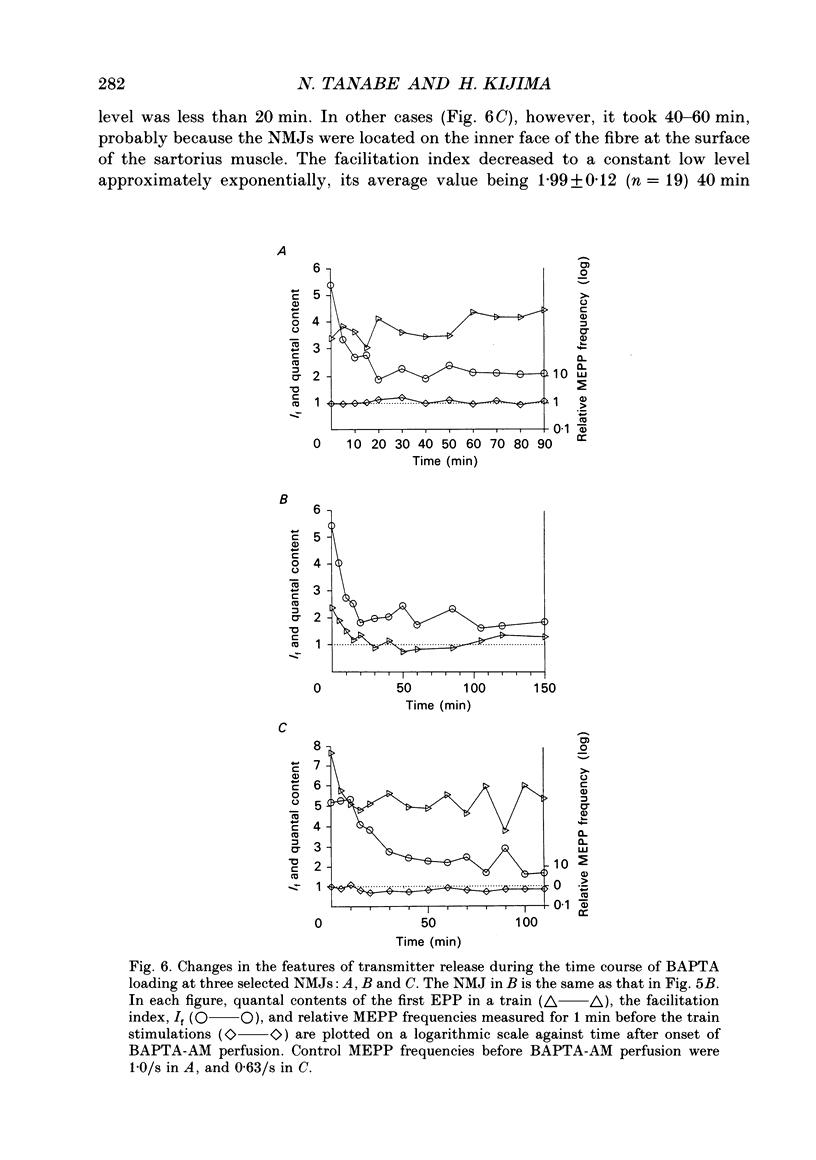

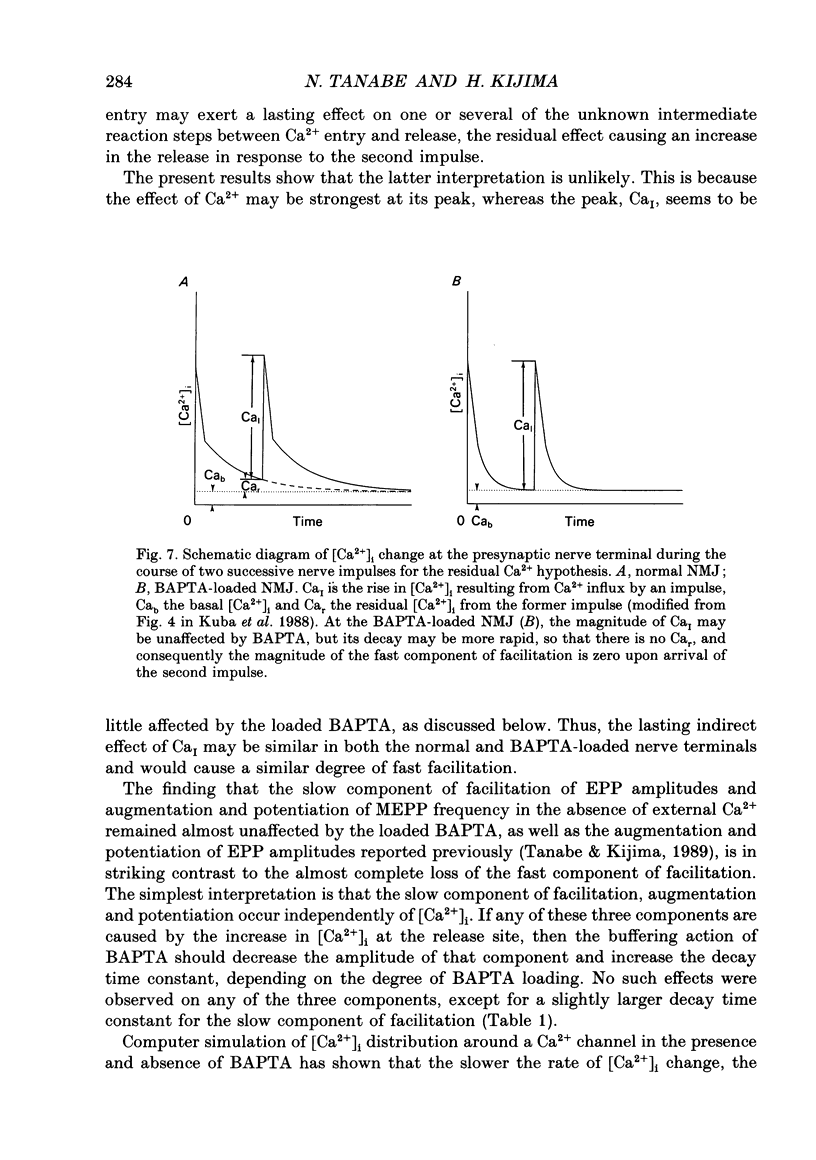





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrams T. W., Kandel E. R. Is contiguity detection in classical conditioning a system or a cellular property? Learning in Aplysia suggests a possible molecular site. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Apr;11(4):128–135. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90137-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams D. J., Takeda K., Umbach J. A. Inhibitors of calcium buffering depress evoked transmitter release at the squid giant synapse. J Physiol. 1985 Dec;369:145–159. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton S. B., Cohen I. S., van der Kloot W. The calcium dependence of spontaneous and evoked quantal release at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1983 Apr;337:735–751. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlton M. P., Smith S. J., Zucker R. S. Role of presynaptic calcium ions and channels in synaptic facilitation and depression at the squid giant synapse. J Physiol. 1982 Feb;323:173–193. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale N., Kandel E. R. Facilitatory and inhibitory transmitters modulate spontaneous transmitter release at cultured Aplysia sensorimotor synapses. J Physiol. 1990 Feb;421:203–222. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp017941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delaney K. R., Zucker R. S., Tank D. W. Calcium in motor nerve terminals associated with posttetanic potentiation. J Neurosci. 1989 Oct;9(10):3558–3567. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-10-03558.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodge F. A., Jr, Rahamimoff R. Co-operative action a calcium ions in transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(2):419–432. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erulkar S. D., Rahamimoff R. The role of calcium ions in tetanic and post-tetanic increase of miniature end-plate potential frequency. J Physiol. 1978 May;278:501–511. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogelson A. L., Zucker R. S. Presynaptic calcium diffusion from various arrays of single channels. Implications for transmitter release and synaptic facilitation. Biophys J. 1985 Dec;48(6):1003–1017. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83863-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The role of calcium in neuromuscular facilitation. J Physiol. 1968 Mar;195(2):481–492. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kijima H., Tanabe N. Calcium-independent increase of transmitter release at frog end-plate by trinitrobenzene sulphonic acid. J Physiol. 1988 Sep;403:135–149. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kita H., Van Der Kloot W. Effects of the ionophore X-537A on acetylcholine release at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1976 Jul;259(1):177–198. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight D. E., von Grafenstein H., Athayde C. M. Calcium-dependent and calcium-independent exocytosis. Trends Neurosci. 1989 Nov;12(11):451–458. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(89)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuba K., Kumamoto E. Long-term potentiation of transmitter release induced by adrenaline in bull-frog sympathetic ganglia. J Physiol. 1986 May;374:515–530. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landau E. M., Smolinsky A., Lass Y. Post-tetanic potentiation and facilitation do not share a common calcium-dependent mechanism. Nat New Biol. 1973 Aug 1;244(135):155–157. doi: 10.1038/newbio244155a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeno T., Hara N. Ca-independent augmentation of endplate potential during repetitive stimulation. Acta Physiol Pharmacol Latinoam. 1989;39(4):375–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Stevens C. F. A quantitative description of end-plate currents. J Physiol. 1972 May;223(1):173–197. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L. The effect of repetitive stimulation on facilitation of transmitter release at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1973 Oct;234(2):327–352. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L. The effect of tetanic and post-tetanic potentiation on facilitation of transmitter release at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1973 Oct;234(2):353–371. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Zengel J. E. A quantitative description of stimulation-induced changes in transmitter release at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Oct;80(4):613–638. doi: 10.1085/jgp.80.4.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Zengel J. E. Augmentation: A process that acts to increase transmitter release at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1976 May;257(2):449–470. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meiri H., Erulkar S. D., Lerman T., Rahamimoff R. The action of the sodium ionophore, monensin, or transmitter release at the frog neuromuscular junction. Brain Res. 1981 Jan 5;204(1):204–208. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90665-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner R., Neher E. The role of calcium in stimulus-secretion coupling in excitable and non-excitable cells. J Exp Biol. 1988 Sep;139:329–345. doi: 10.1242/jeb.139.1.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahamimoff R., Lev-Tov A., Meiri H. Primary and secondary regulation of quantal transmitter release: calcium and sodium. J Exp Biol. 1980 Dec;89:5–18. doi: 10.1242/jeb.89.1.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahamimoff R., Meiri H., Erulkar S. D., Barenholz Y. Changes in transmitter release induced by ion-containing liposomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5214–5216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahamimoff R., Yaari Y. Delayed release of transmitter at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1973 Jan;228(1):241–257. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon S. M., Llinás R. R. Compartmentalization of the submembrane calcium activity during calcium influx and its significance in transmitter release. Biophys J. 1985 Sep;48(3):485–498. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83804-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe N., Kijima H. Both augmentation and potentiation occur independently of internal Ca2+ at the frog neuromuscular junction. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Apr 24;99(1-2):147–152. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90280-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe N., Kijima H. Transmitter release at frog end-plate loaded with a Ca2+-chelator, BAPTA: hypertonicity and erythrosin B augment the release independently of internal Ca2+. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Sep 23;92(1):52–57. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90741-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y. New calcium indicators and buffers with high selectivity against magnesium and protons: design, synthesis, and properties of prototype structures. Biochemistry. 1980 May 27;19(11):2396–2404. doi: 10.1021/bi00552a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinreich D. Ionic mechanism of post-tetanic potentiation at the neuromuscular junction of the frog. J Physiol. 1971 Jan;212(2):431–446. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zengel J. E., Magleby K. L. Augmentation and facilitation of transmitter release. A quantitative description at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Oct;80(4):583–611. doi: 10.1085/jgp.80.4.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zengel J. E., Magleby K. L. Changes in miniature endplate potential frequency during repetitive nerve stimulation in the presence of Ca2+, Ba2+, and Sr2+ at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Gen Physiol. 1981 May;77(5):503–529. doi: 10.1085/jgp.77.5.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zengel J. E., Magleby K. L. Differential effects of Ba2+, Sr2+, and Ca2+ on stimulation-induced changes in transmitter release at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Aug;76(2):175–211. doi: 10.1085/jgp.76.2.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


