Abstract
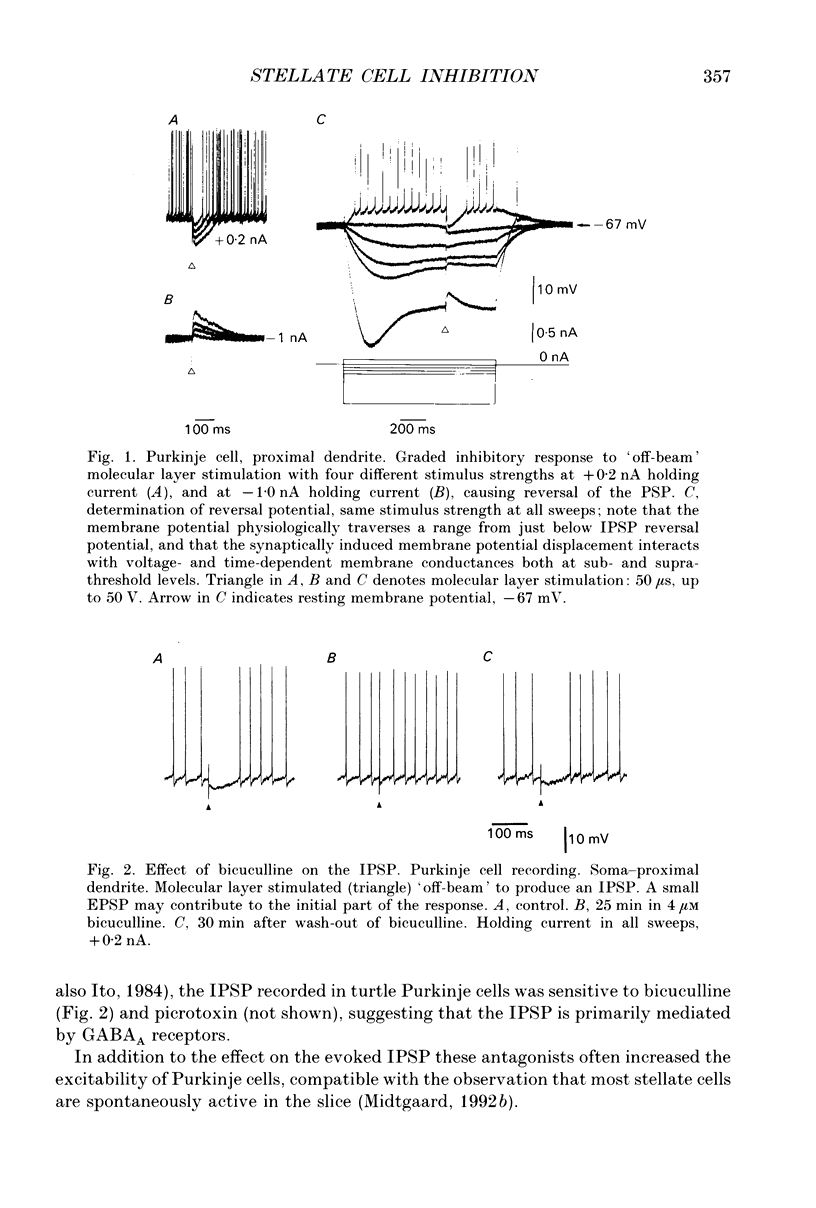
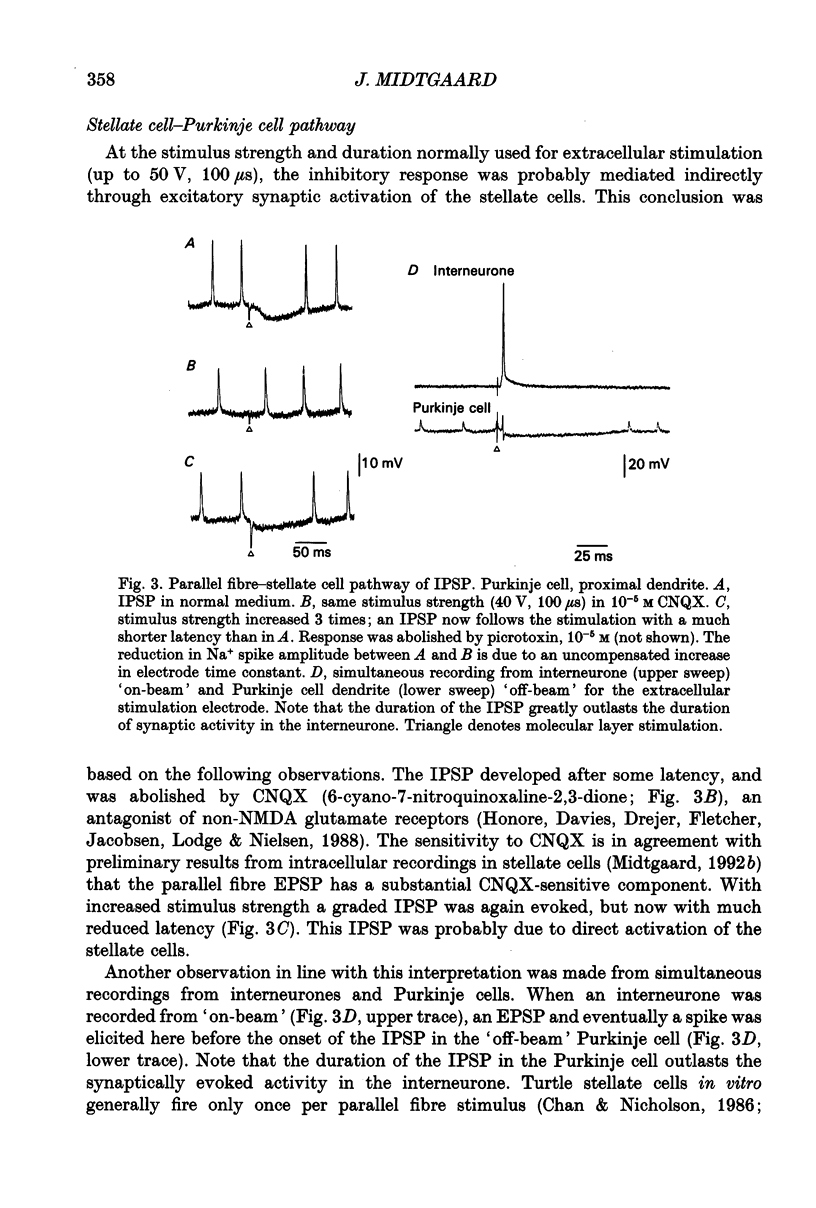
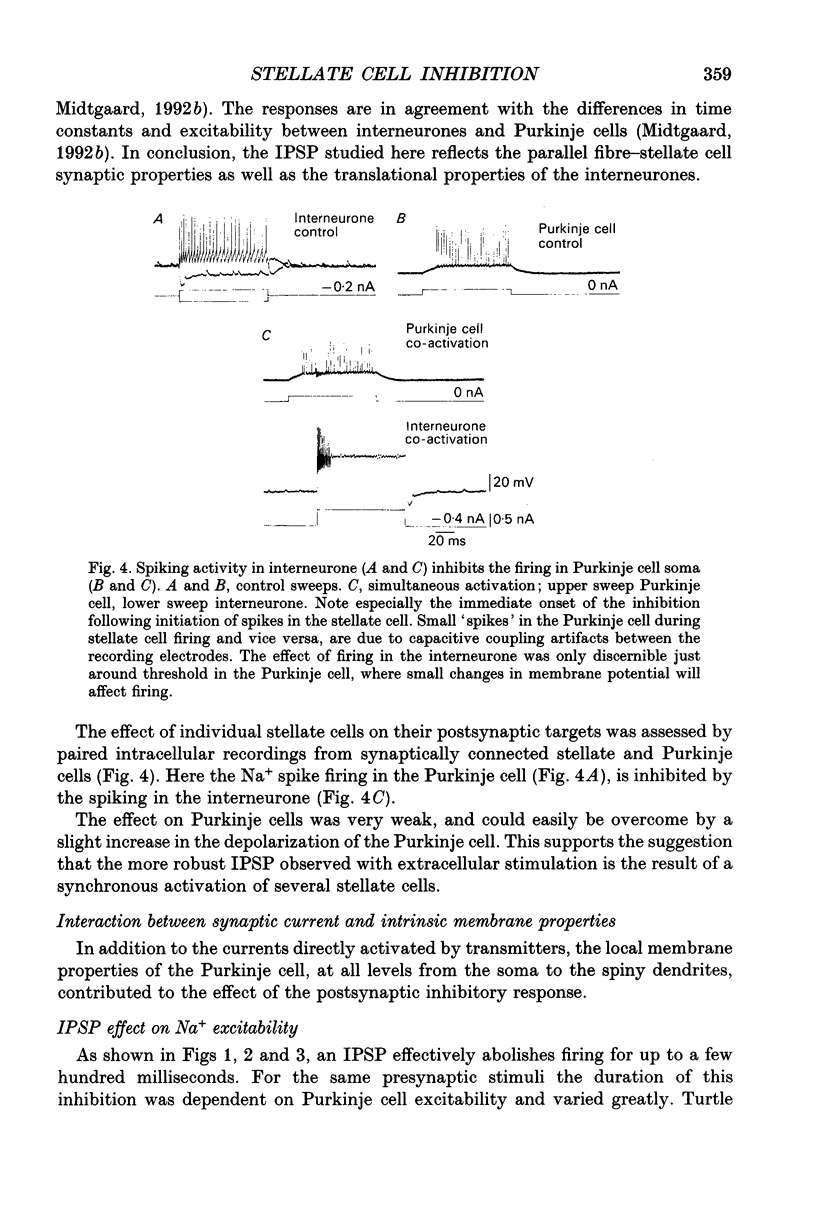
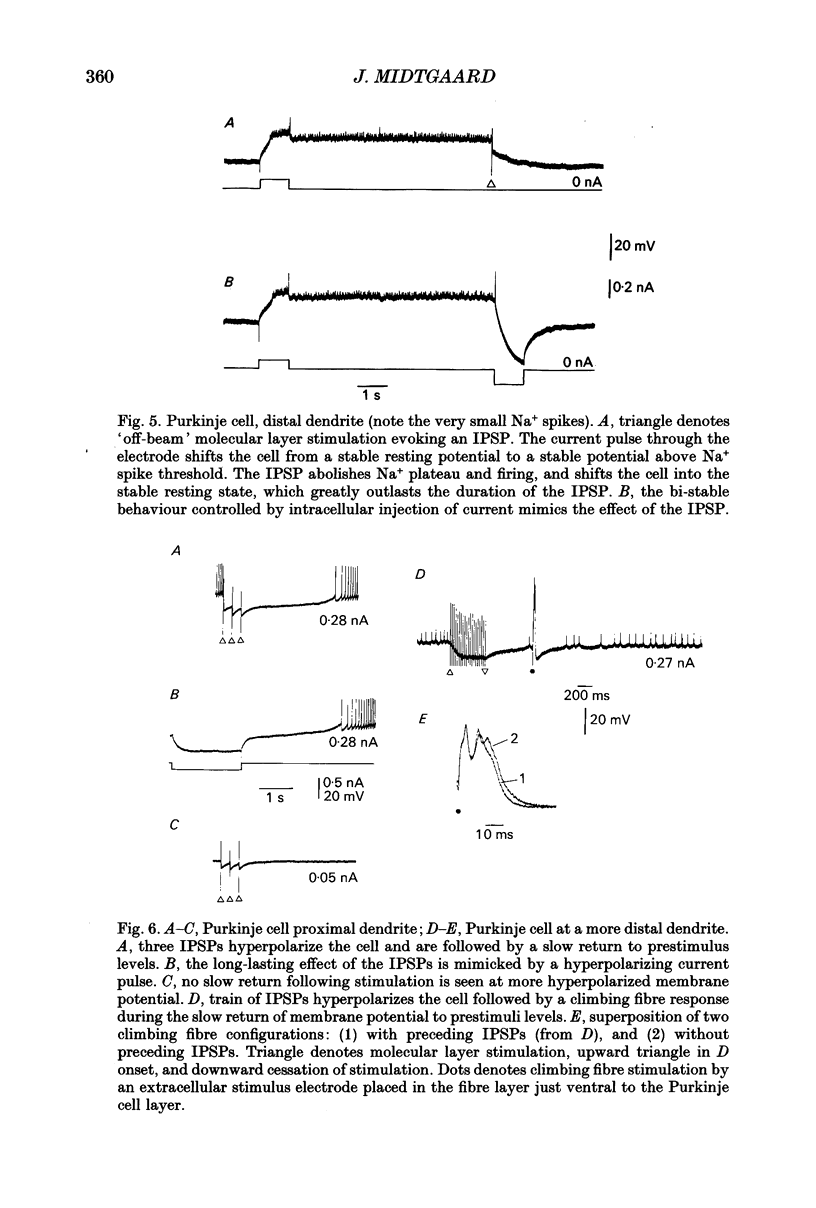
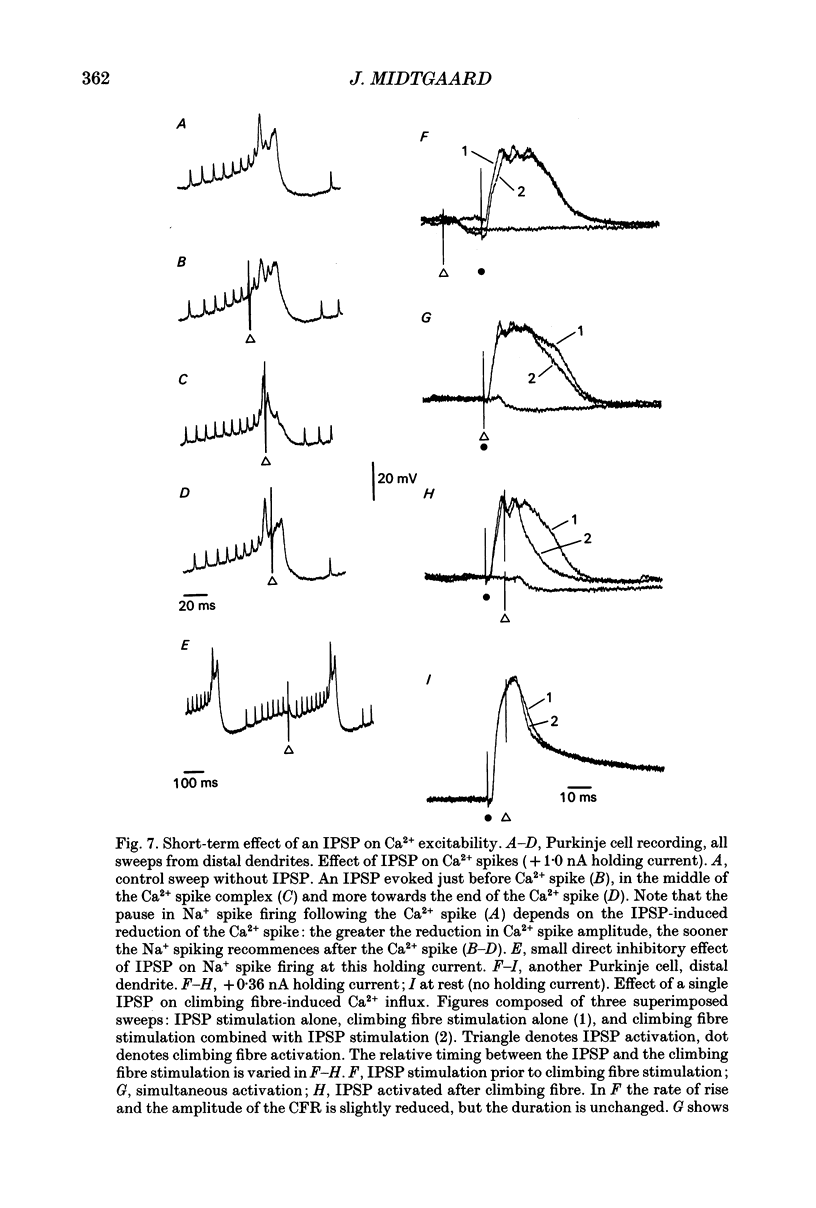
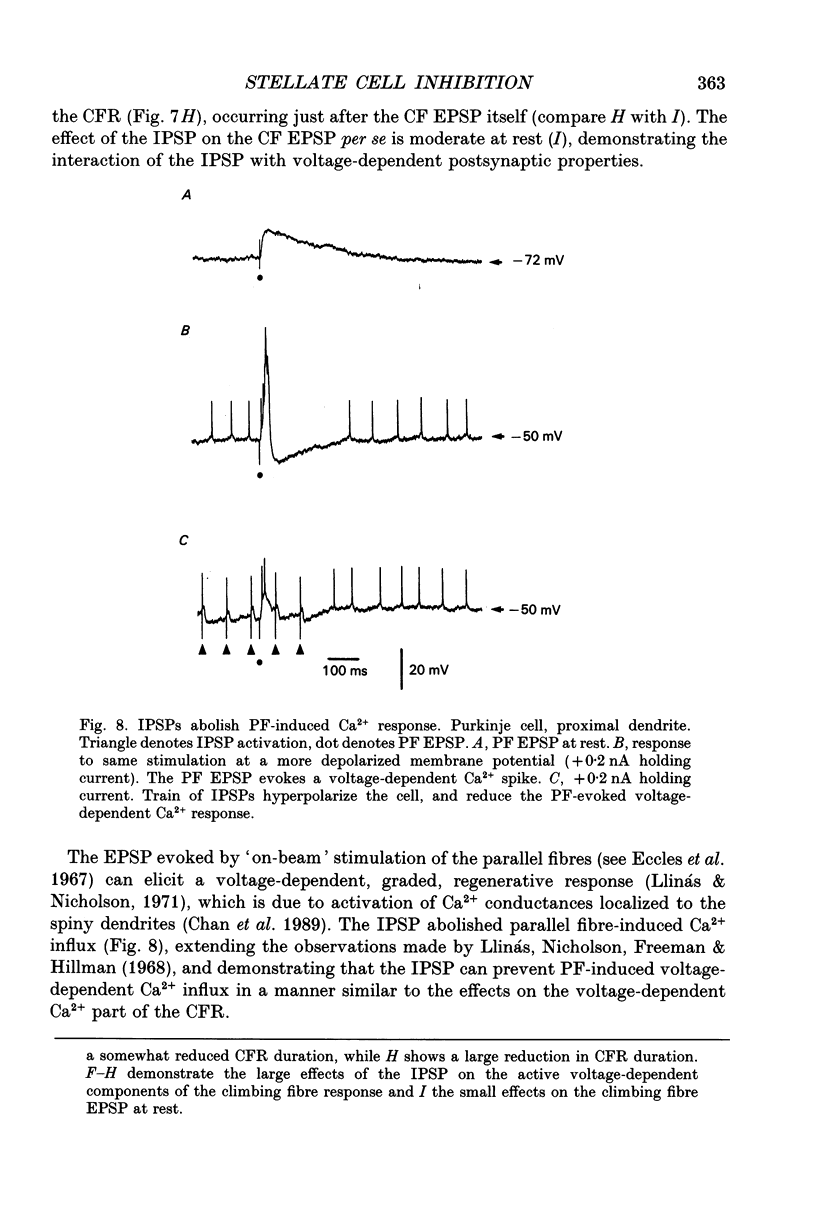
1. The stellate cell-mediated inhibition of Purkinje cells was studied by intracellular recordings in an in vitro slice preparation of the turtle cerebellar cortex. A graded inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP) was recorded in Purkinje cells upon stimulation of the parallel fibre-stellate cell pathway. 2. The IPSP was abolished by bicuculline, and had a reversal potential around -75 mV, consistent with a GABAA receptor-operated Cl- conductance dominating the response investigated here. 3. Paired recordings from synaptically coupled stellate cells and Purkinje cells demonstrated that the inhibitory input from a single stellate cell is sufficient to reduce the firing in a Purkinje cell. 4. The extracellular-evoked IPSP interacted with the active postsynaptic membrane properties in the Purkinje cell. Interaction with both the Na+ plateau and the IA prolonged the responses to an IPSP, making the net effect of the inhibitory response dependent on the membrane potential in each postsynaptic neurone. 5. A precisely timed IPSP was particularly efficient in reducing dendritic Ca2+ influx. 6. The voltage-dependent Ca2+ component of a climbing fibre response (CFR) as well as of a parallel fibre (PF) input was reduced by the IPSP. 7. It is suggested that Ca2+ spike-mediated reduction in Purkinje cell excitability may be prevented by the stellate cell IPSP-mediated reduction in Ca2+ influx.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen P., Dingledine R., Gjerstad L., Langmoen I. A., Laursen A. M. Two different responses of hippocampal pyramidal cells to application of gamma-amino butyric acid. J Physiol. 1980 Aug;305:279–296. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batini C. Cerebellar localization and colocalization of GABA and calcium binding protein-D28K. Arch Ital Biol. 1990 Jul;128(2-4):127–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisti S., Iosif G., Marchesi G. F., Strata P. Pharmacological properties of inhibitions in the cerebellar cortex. Exp Brain Res. 1971;14(1):24–37. doi: 10.1007/BF00234908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan C. Y., Hounsgaard J., Midtgaard J. Excitatory synaptic responses in turtle cerebellar Purkinje cells. J Physiol. 1989 Feb;409:143–156. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan C. Y., Nicholson C. Modulation by applied electric fields of Purkinje and stellate cell activity in the isolated turtle cerebellum. J Physiol. 1986 Feb;371:89–114. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp015963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eccles J. C., Llinás R., Sasaki K. Intracellularly recorded responses of the cerebellar Purkinje cells. Exp Brain Res. 1966;1(2):161–183. doi: 10.1007/BF00236869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frederickson R. C., Neuss M., Morzorati S. L., McBride W. J. A comparison of the inhibitory effects of taurine and GABA on identified Purkinje cells and other neurons in the cerebellar cortex of the rat. Brain Res. 1978 Apr 21;145(1):117–126. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90800-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honoré T., Davies S. N., Drejer J., Fletcher E. J., Jacobsen P., Lodge D., Nielsen F. E. Quinoxalinediones: potent competitive non-NMDA glutamate receptor antagonists. Science. 1988 Aug 5;241(4866):701–703. doi: 10.1126/science.2899909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi T., Asanuma A., Yanagisawa K., Anzai K., Goto S. Taurine and beta-alanine act on both GABA and glycine receptors in Xenopus oocyte injected with mouse brain messenger RNA. Brain Res. 1988 Sep;464(2):97–105. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(88)90002-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hounsgaard J., Midtgaard J. Intrinsic determinants of firing pattern in Purkinje cells of the turtle cerebellum in vitro. J Physiol. 1988 Aug;402:731–749. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hounsgaard J., Midtgaard J. Synaptic control of excitability in turtle cerebellar Purkinje cells. J Physiol. 1989 Feb;409:157–170. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneda M., Wakamori M., Akaike N. GABA-induced chloride current in rat isolated Purkinje cells. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jun;256(6 Pt 1):C1153–C1159. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.6.C1153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinas R., Nicholson C. Electrophysiological properties of dendrites and somata in alligator Purkinje cells. J Neurophysiol. 1971 Jul;34(4):532–551. doi: 10.1152/jn.1971.34.4.532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Nicholson C., Freeman J. A., Hillman D. E. Dendritic spikes and their inhibition in alligator Purkinje cells. Science. 1968 Jun 7;160(3832):1132–1135. doi: 10.1126/science.160.3832.1132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Sugimori M. Electrophysiological properties of in vitro Purkinje cell somata in mammalian cerebellar slices. J Physiol. 1980 Aug;305:171–195. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson K. R., Madl J. E., Clements J. R., Wu J. Y., Larson A. A., Beitz A. J. Colocalization of taurine- and cysteine sulfinic acid decarboxylase-like immunoreactivity in the cerebellum of the rat with monoclonal antibodies against taurine. J Neurosci. 1988 Dec;8(12):4551–4564. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-12-04551.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midtgaard J. Membrane properties and synaptic responses of Golgi cells and stellate cells in the turtle cerebellum in vitro. J Physiol. 1992 Nov;457:329–354. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson C., Llinás R. Inhibition of Purkinje cells in the cerebellum of elasmobranch fishes. Brain Res. 1969 Feb;12(2):477–481. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(69)90018-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottersen O. P., Madsen S., Storm-Mathisen J., Somogyi P., Scopsi L., Larsson L. I. Immunocytochemical evidence suggests that taurine is colocalized with GABA in the Purkinje cell terminals, but that the stellate cell terminals predominantly contain GABA: a light- and electronmicroscopic study of the rat cerebellum. Exp Brain Res. 1988;72(2):407–416. doi: 10.1007/BF00250262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottersen O. P. Quantitative assessment of taurine-like immunoreactivity in different cell types and processes in rat cerebellum: an electronmicroscopic study based on a postembedding immunogold labelling procedure. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1988;178(5):407–421. doi: 10.1007/BF00306047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


