Abstract
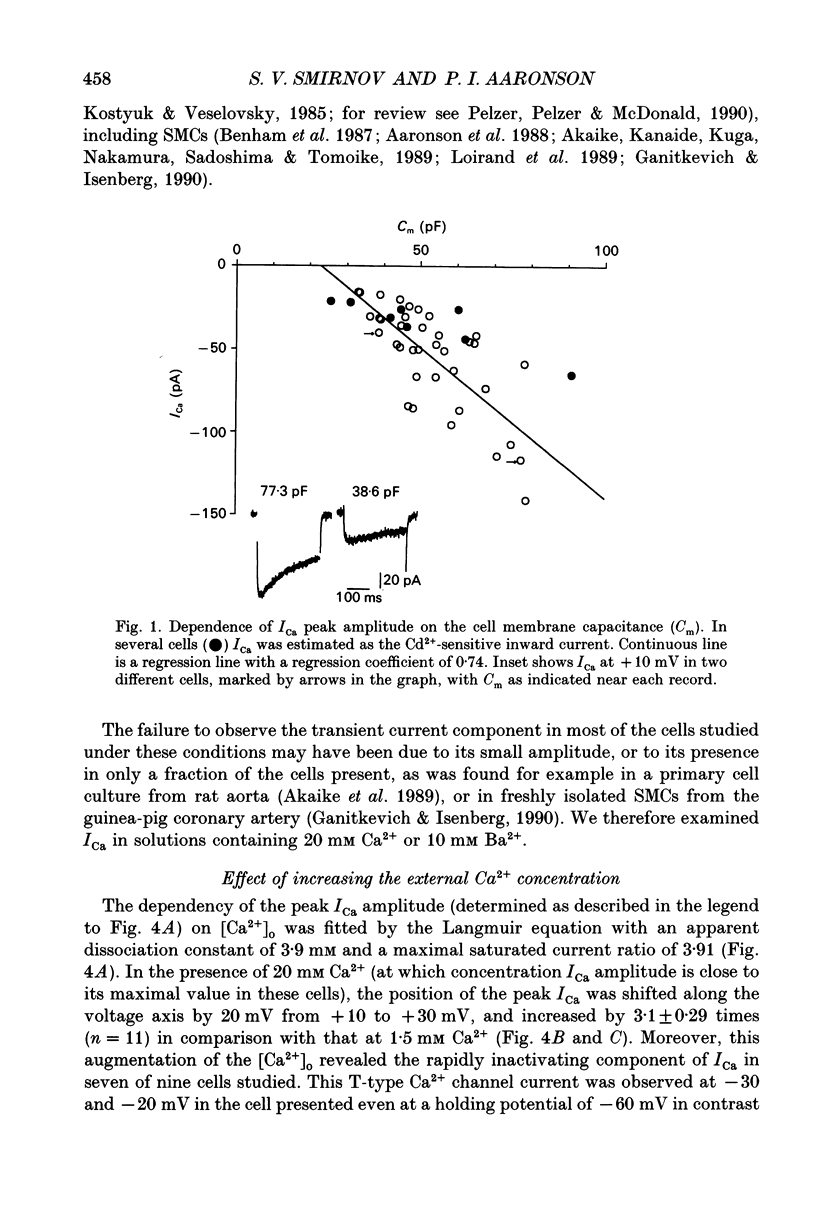
1. Voltage-gated Ca2+ currents (ICa) in isolated human mesenteric arterial cells were characterized in solutions containing normal (1.5 mM) Ca2+ and elevated concentrations of divalent cations using the conventional whole-cell patch clamp technique. 2. In normal Ca2+ solution, depolarization beyond -40 mV elicited a slowly decaying ICa which reached a maximum at +10 mV and appeared to reverse between +40 and +50 mV. The amplitude of this current in a group of cells correlated with cell membrane capacitance. 3. In two of thirty-three cells a small transient component of inward current was detected in the voltage range between -40 and -10 mV when cells were held at -80 mV. This current was abolished at a holding potential of -40 mV, while the current at 10 mV was not affected. These currents were referred to as T- and L-type Ca2+ respectively. 4. Elevation of the extracellular Ca2+ concentration to 20 mM shifted the voltage dependencies of Ca2+ current activation and inactivation by approximately +20 mV; a small T-current component was then observed in seven of nine cells held at -60 mV. 5. Replacement of 1.5 mM Ca2+ with 10 mM Ba2+ increased the amplitude of the current elicited at +10 mV by a factor of 3.7 and a small barium current (IBa) through T-type Ca2+ channels was also observed in most cells studied. Activation and steady-state inactivation curves for L-type current were found to be almost identical in both solutions. The steady-state inactivation for the T-type IBa was, however, more than 30 mV more negative (half-inactivation potential of -62.6 mV) of that for L-current in 1.5 mM Ca2+ and 10 mM Ba2+ solutions (-30.4 and -24.9 mV respectively). 6. A sustained inward Ca2+ channel current was recorded in the presence of normal Ca2+ and high divalent cation concentrations during 30 s depolarizations. The amplitude of this sustained current was found to be similar to the theoretical 'window current' predicted by the overlap of the activation and inactivation functions in these solutions. 7. Examination of the inactivation of the L-type current using a two-pulse protocol with a 240 ms prepulse revealed a U-shaped potential dependency for ICa, but not for IBa, suggesting the presence of a Ca(2+)-dependent component of the inactivation process. 8. These cells resemble other arterial smooth muscle cells previously studied in that they demonstrate both T- and L-components of ICa.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
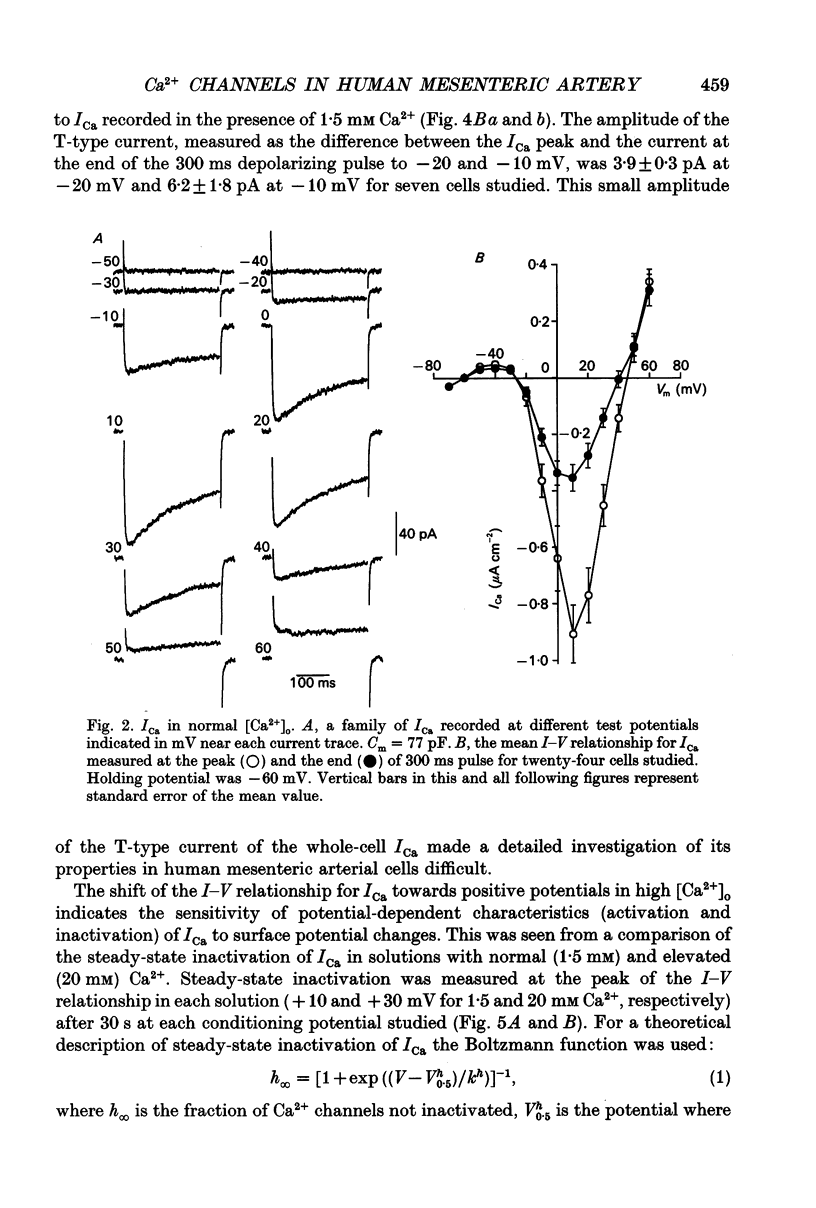
Full text
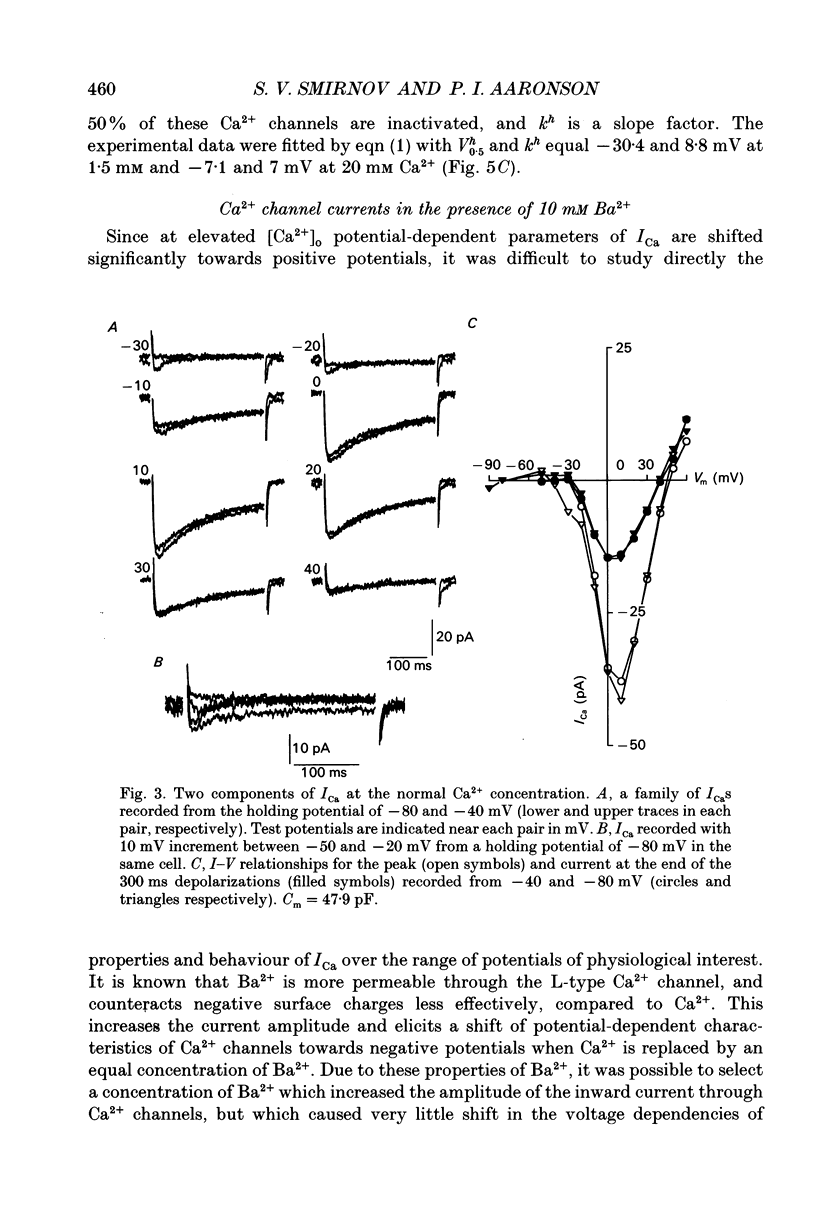
PDF


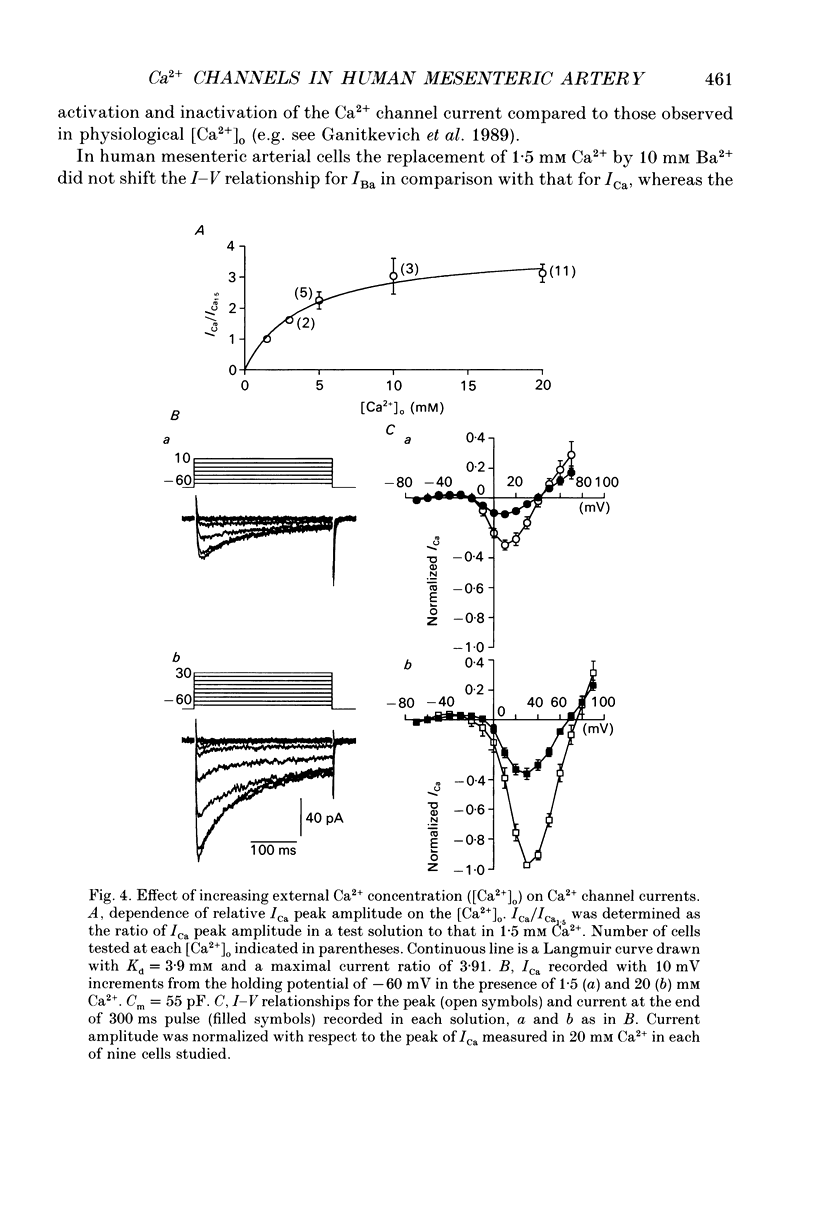







Selected References
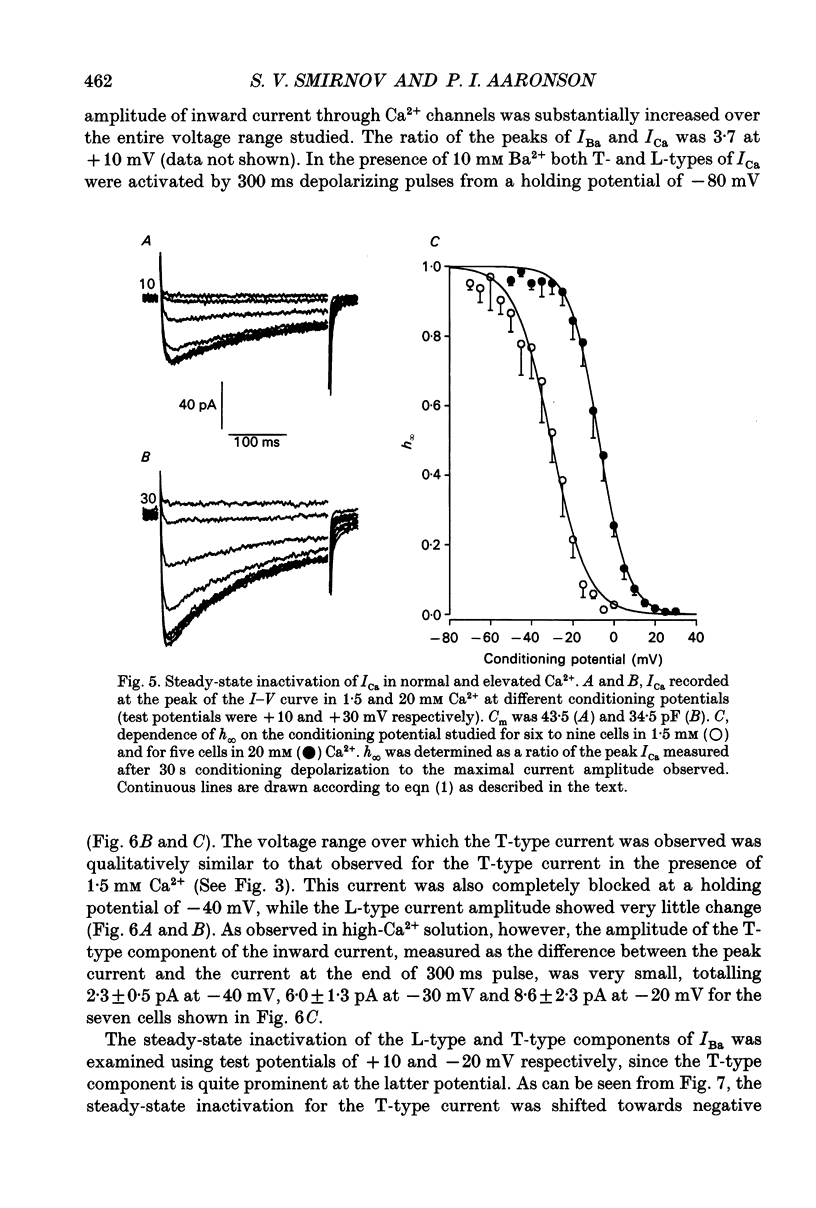
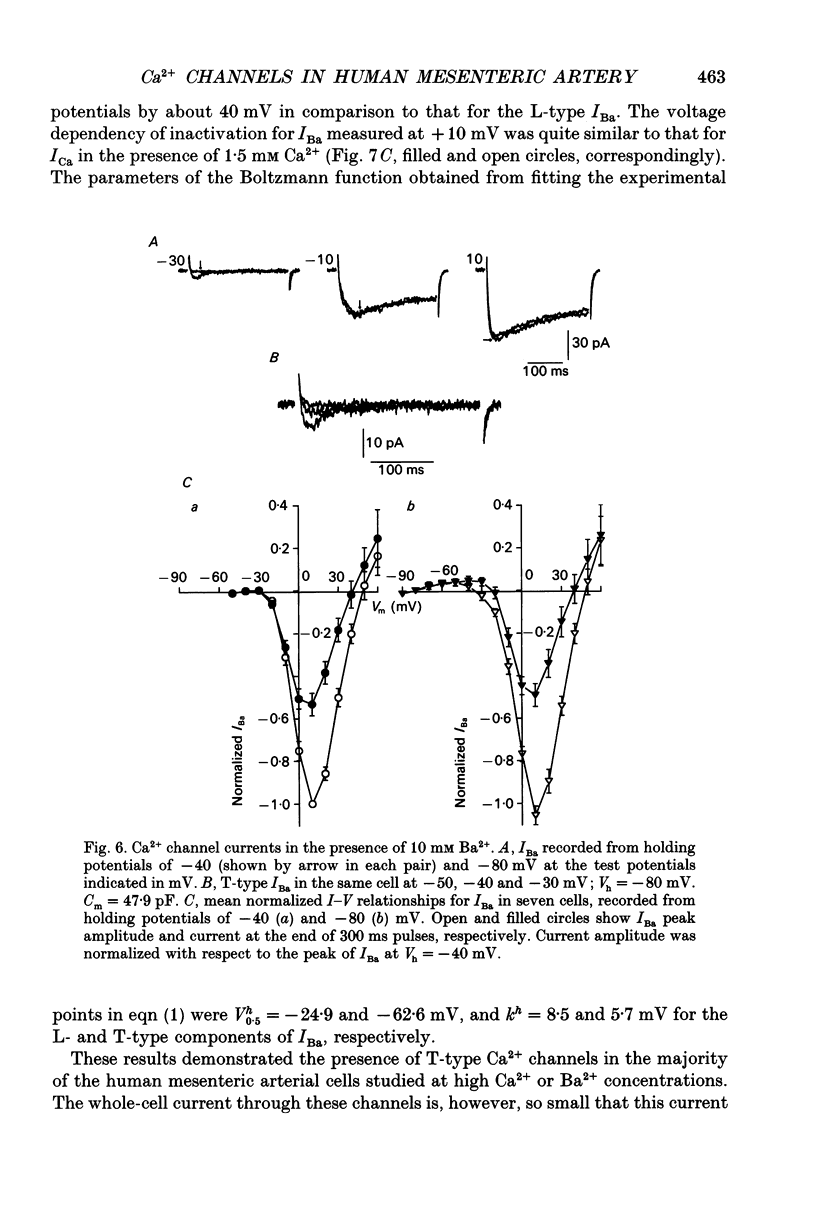
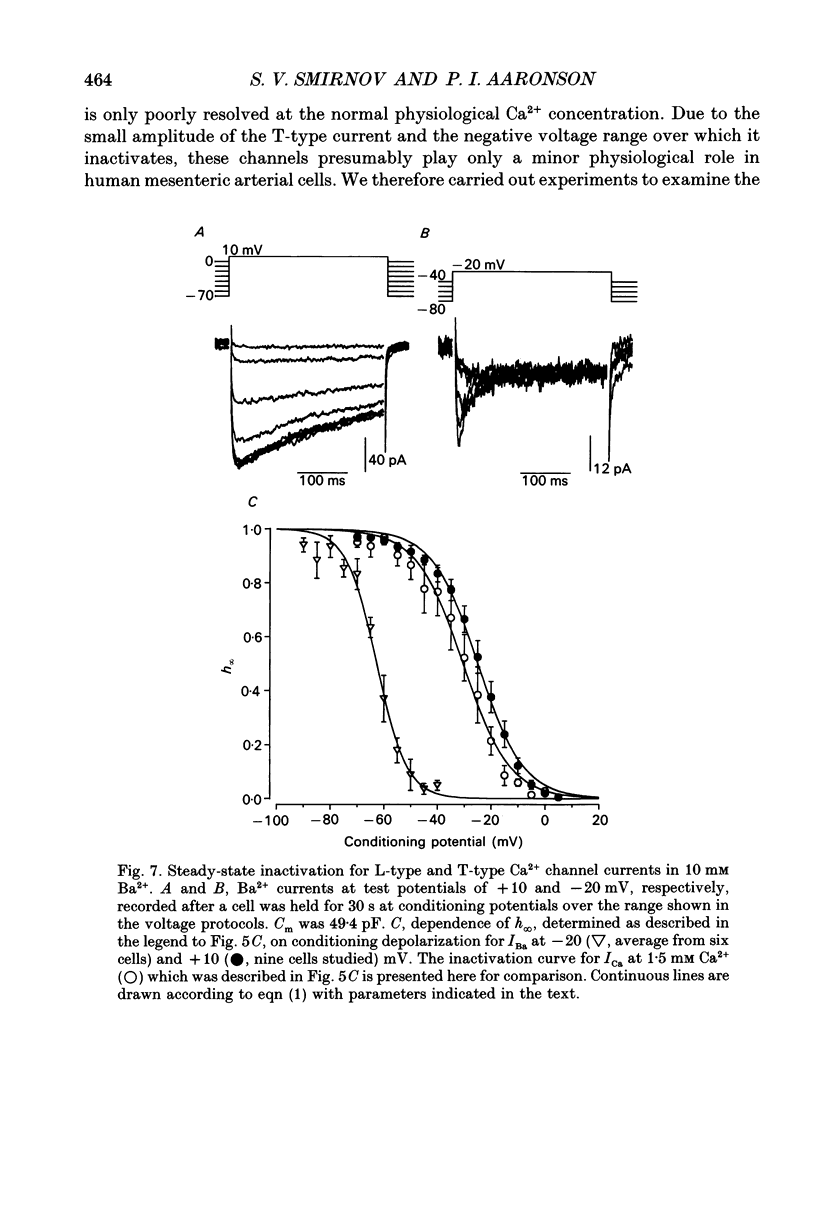
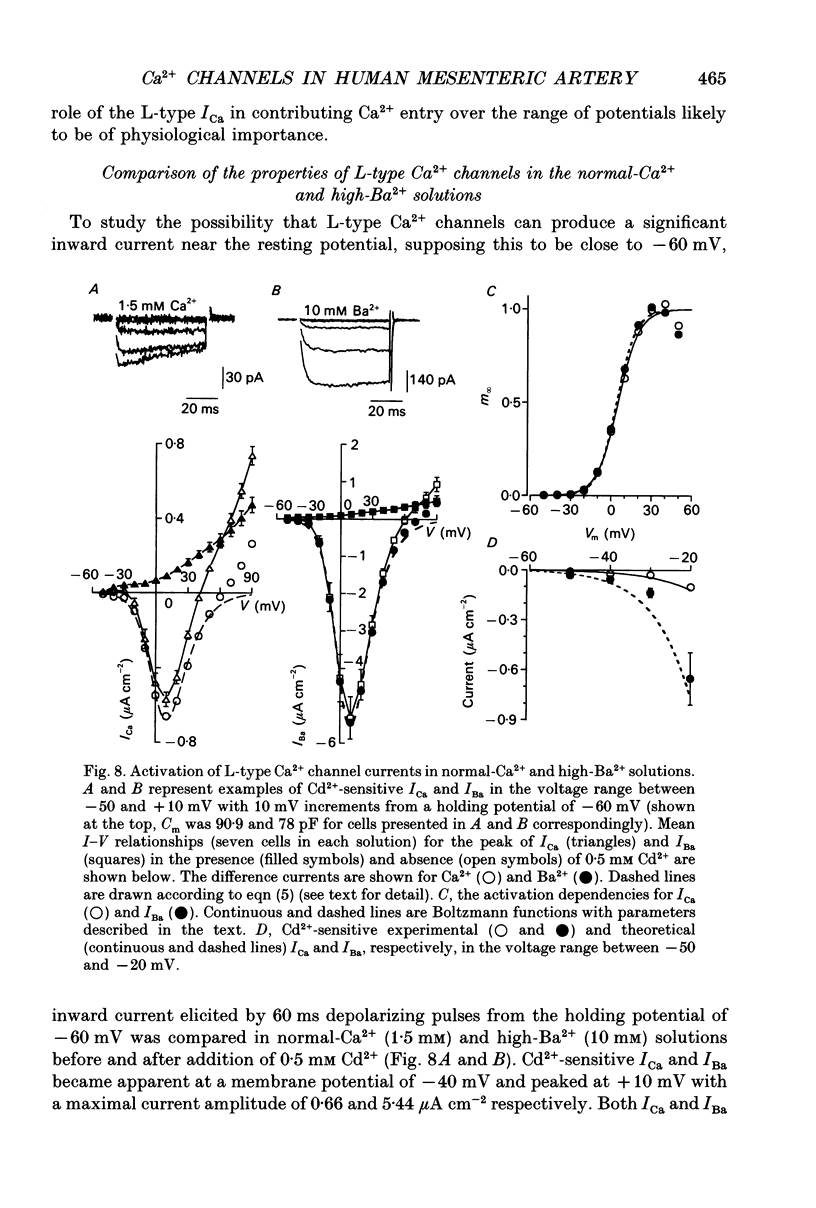
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
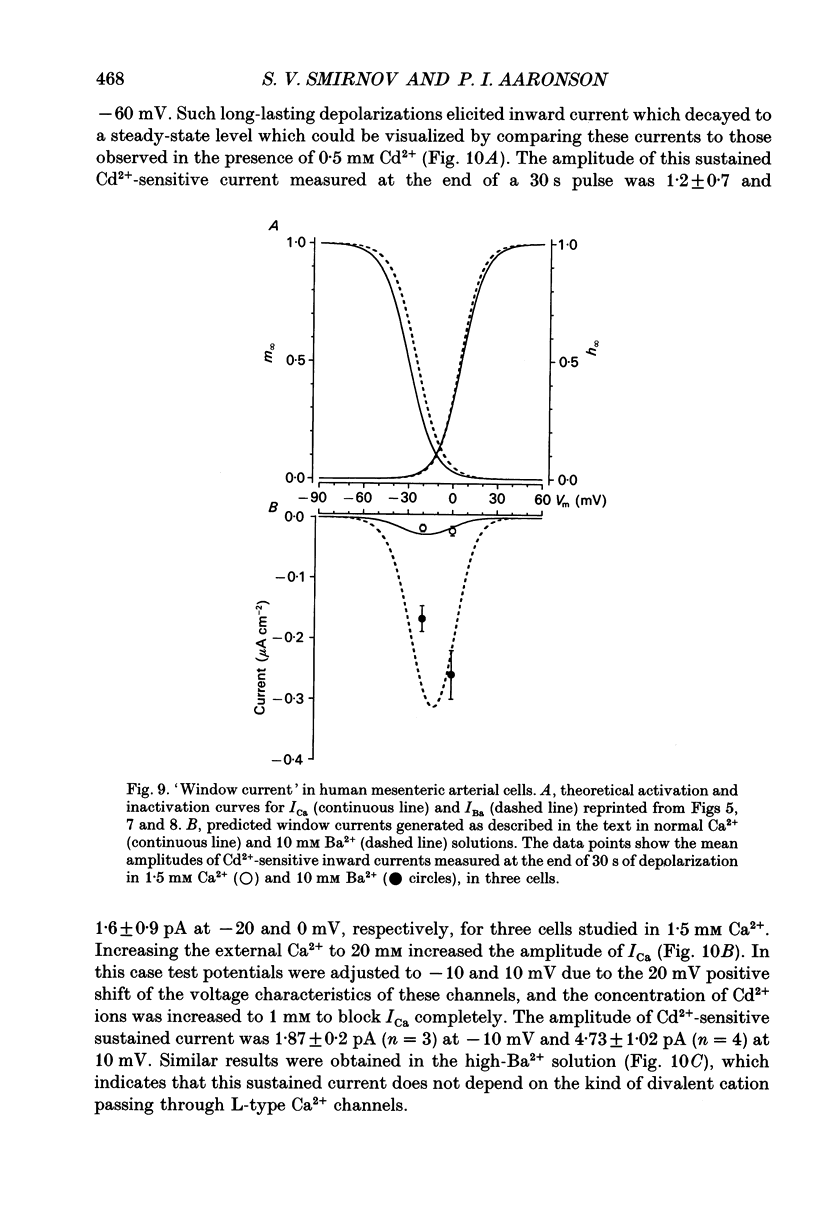
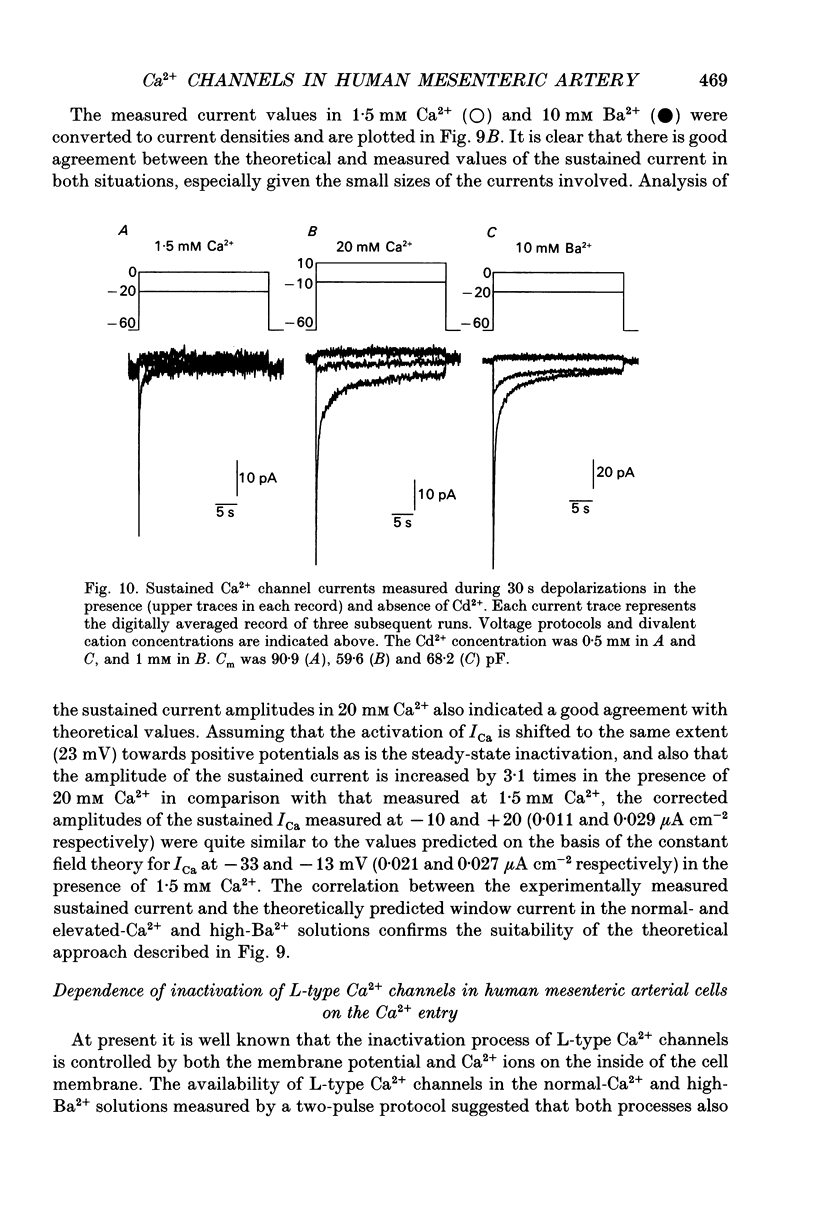
- Aaronson P. I., Bolton T. B., Lang R. J., MacKenzie I. Calcium currents in single isolated smooth muscle cells from the rabbit ear artery in normal-calcium and high-barium solutions. J Physiol. 1988 Nov;405:57–75. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
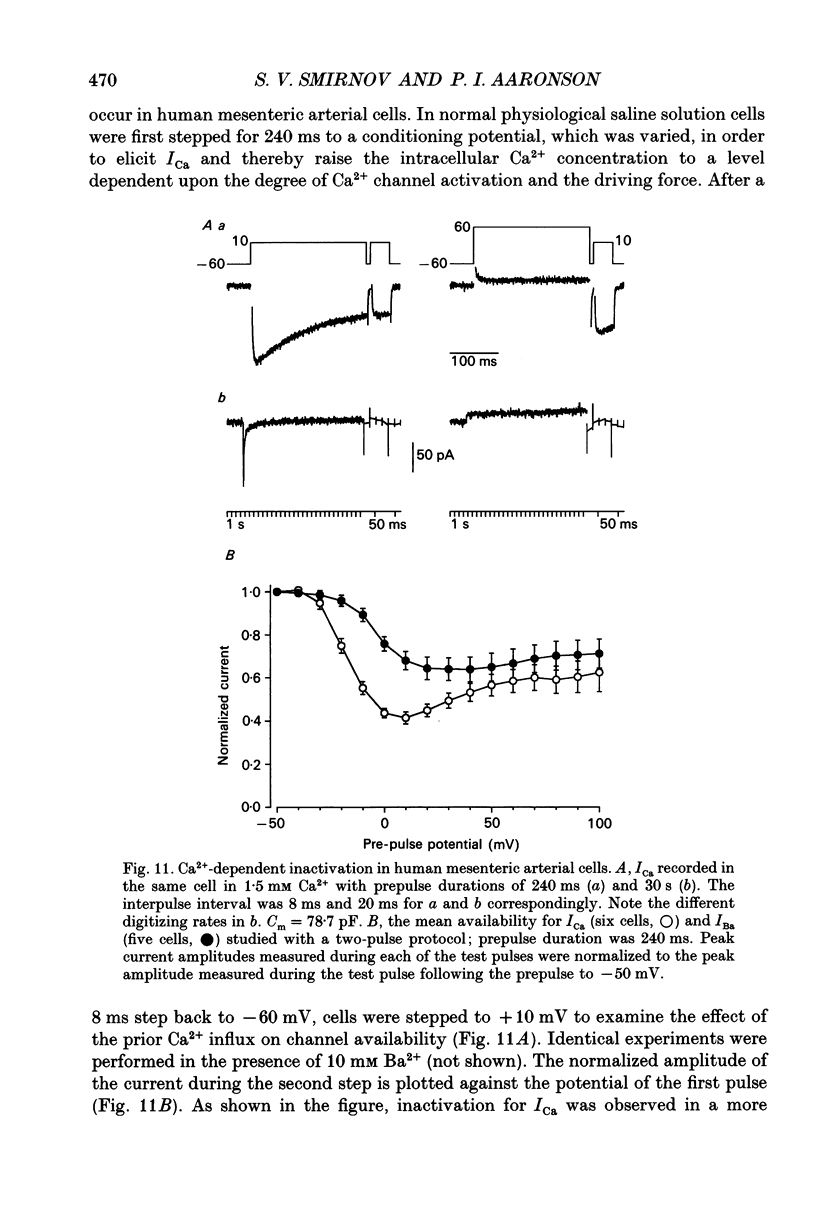
- Akaike N., Kanaide H., Kuga T., Nakamura M., Sadoshima J., Tomoike H. Low-voltage-activated calcium current in rat aorta smooth muscle cells in primary culture. J Physiol. 1989 Sep;416:141–160. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean B. P., Sturek M., Puga A., Hermsmeyer K. Calcium channels in muscle cells isolated from rat mesenteric arteries: modulation by dihydropyridine drugs. Circ Res. 1986 Aug;59(2):229–235. doi: 10.1161/01.res.59.2.229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean B. P. Two kinds of calcium channels in canine atrial cells. Differences in kinetics, selectivity, and pharmacology. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Jul;86(1):1–30. doi: 10.1085/jgp.86.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton T. B. Mechanisms of action of transmitters and other substances on smooth muscle. Physiol Rev. 1979 Jul;59(3):606–718. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.3.606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byerly L., Chase P. B., Stimers J. R. Permeation and interaction of divalent cations in calcium channels of snail neurons. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Apr;85(4):491–518. doi: 10.1085/jgp.85.4.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Droogmans G., Raeymaekers L., Casteels R. Electro- and pharmacomechanical coupling in the smooth muscle cells of the rabbit ear artery. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Aug;70(2):129–148. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.2.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert R., Chad J. E. Inactivation of Ca channels. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1984;44(3):215–267. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(84)90009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedulova S. A., Kostyuk P. G., Veselovsky N. S. Two types of calcium channels in the somatic membrane of new-born rat dorsal root ganglion neurones. J Physiol. 1985 Feb;359:431–446. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick E. M., Marty A., Neher E. Sodium and calcium channels in bovine chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:599–635. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman M. E., Suarez-Kurtz G., Kaczorowski G. J., Katz G. M., Reuben J. P. Two calcium currents in a smooth muscle cell line. Am J Physiol. 1986 Apr;250(4 Pt 2):H699–H703. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1986.250.4.H699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganitkevich VYa, Isenberg G. Contribution of two types of calcium channels to membrane conductance of single myocytes from guinea-pig coronary artery. J Physiol. 1990 Jul;426:19–42. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganitkevich VYa, Shuba M. F., Smirnov S. V. Calcium-dependent inactivation of potential-dependent calcium inward current in an isolated guinea-pig smooth muscle cell. J Physiol. 1987 Nov;392:431–449. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganitkevich VYa, Shuba M. F., Smirnov S. V. Inactivation of calcium channels in single vascular and visceral smooth muscle cells of the guinea-pig. Gen Physiol Biophys. 1991 Apr;10(2):137–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganitkevich VYa, Shuba M. F., Smirnov S. V. Potential-dependent calcium inward current in a single isolated smooth muscle cell of the guinea-pig taenia caeci. J Physiol. 1986 Nov;380:1–16. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Byerly L. Calcium channel. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1981;4:69–125. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.04.030181.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imaizumi Y., Muraki K., Takeda M., Watanabe M. Measurement and simulation of noninactivating Ca current in smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 1989 Apr;256(4 Pt 1):C880–C885. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.4.C880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jmari K., Mironneau C., Mironneau J. Inactivation of calcium channel current in rat uterine smooth muscle: evidence for calcium- and voltage-mediated mechanisms. J Physiol. 1986 Nov;380:111–126. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jmari K., Mironneau C., Mironneau J. Selectivity of calcium channels in rat uterine smooth muscle: interactions between sodium, calcium and barium ions. J Physiol. 1987 Mar;384:247–261. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klöckner U., Isenberg G. Calcium currents of cesium loaded isolated smooth muscle cells (urinary bladder of the guinea pig). Pflugers Arch. 1985 Dec;405(4):340–348. doi: 10.1007/BF00595686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. S., Tsien R. W. High selectivity of calcium channels in single dialysed heart cells of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1984 Sep;354:253–272. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loirand G., Mironneau C., Mironneau J., Pacaud P. Two types of calcium currents in single smooth muscle cells from rat portal vein. J Physiol. 1989 May;412:333–349. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda J. J., Volk K. A., Shibata E. F. Calcium currents in isolated rabbit coronary arterial smooth muscle myocytes. J Physiol. 1990 Aug;427:657–680. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisheri K. D., van Breemen C. Effects of beta-adrenergic stimulation on calcium movements in rabbit aortic smooth muscle: relationship with cyclic AMP. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:429–441. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meves H., Vogel W. Calcium inward currents in internally perfused giant axons. J Physiol. 1973 Nov;235(1):225–265. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M. T., Patlak J. B., Worley J. F., Standen N. B. Calcium channels, potassium channels, and voltage dependence of arterial smooth muscle tone. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jul;259(1 Pt 1):C3–18. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.259.1.C3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowycky M. C., Fox A. P., Tsien R. W. Three types of neuronal calcium channel with different calcium agonist sensitivity. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):440–443. doi: 10.1038/316440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohya Y., Kitamura K., Kuriyama H. Regulation of calcium current by intracellular calcium in smooth muscle cells of rabbit portal vein. Circ Res. 1988 Feb;62(2):375–383. doi: 10.1161/01.res.62.2.375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohya Y., Terada K., Kitamura K., Kuriyama H. Membrane currents recorded from a fragment of rabbit intestinal smooth muscle cell. Am J Physiol. 1986 Sep;251(3 Pt 1):C335–C346. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.251.3.C335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelzer D., Pelzer S., McDonald T. F. Properties and regulation of calcium channels in muscle cells. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1990;114:107–207. doi: 10.1007/BFb0031019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H., Scholz H. A study of the ion selectivity and the kinetic properties of the calcium dependent slow inward current in mammalian cardiac muscle. J Physiol. 1977 Jan;264(1):17–47. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smirnov S. V., Aaronson P. I. Ca(2+)-activated and voltage-gated K+ currents in smooth muscle cells isolated from human mesenteric arteries. J Physiol. 1992 Nov;457:431–454. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez J. A., Stefani E. Kinetic properties of calcium channels of twitch muscle fibres of the frog. J Physiol. 1983 Apr;337:1–17. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


