Abstract
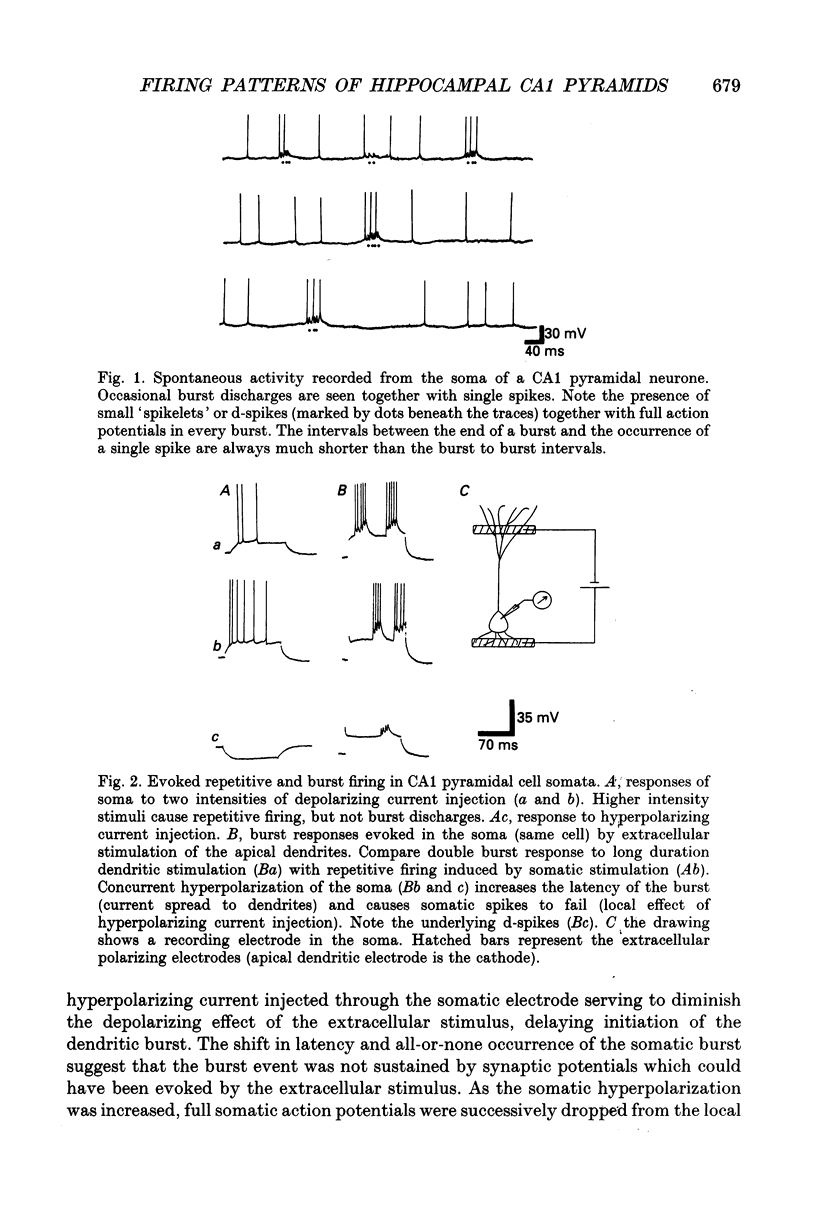
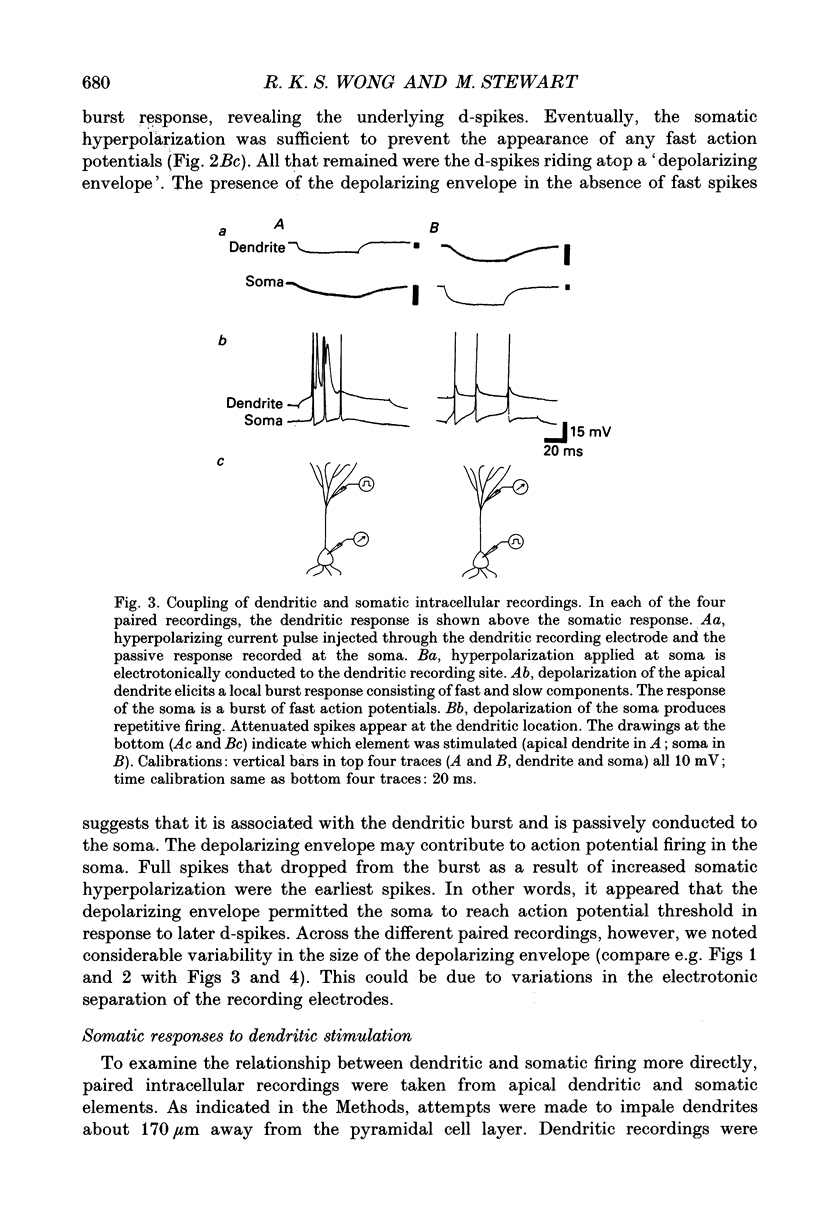
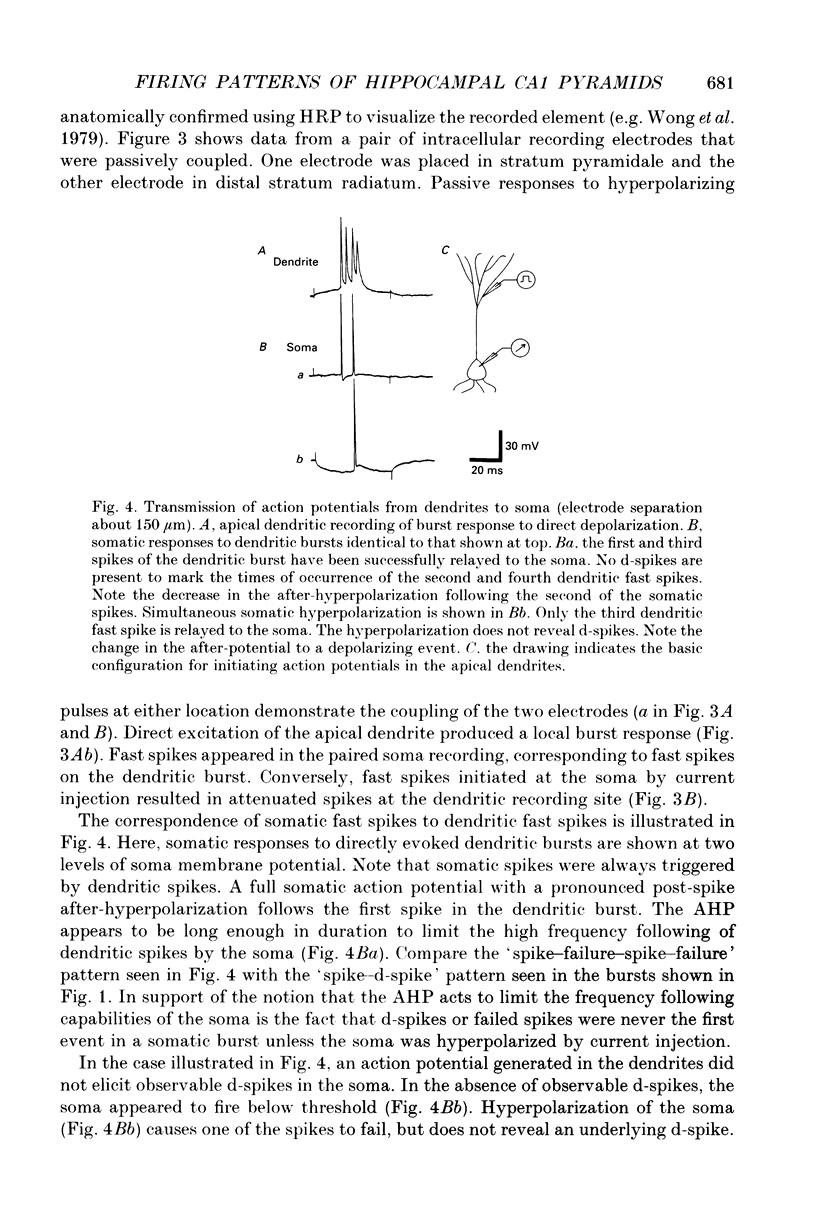
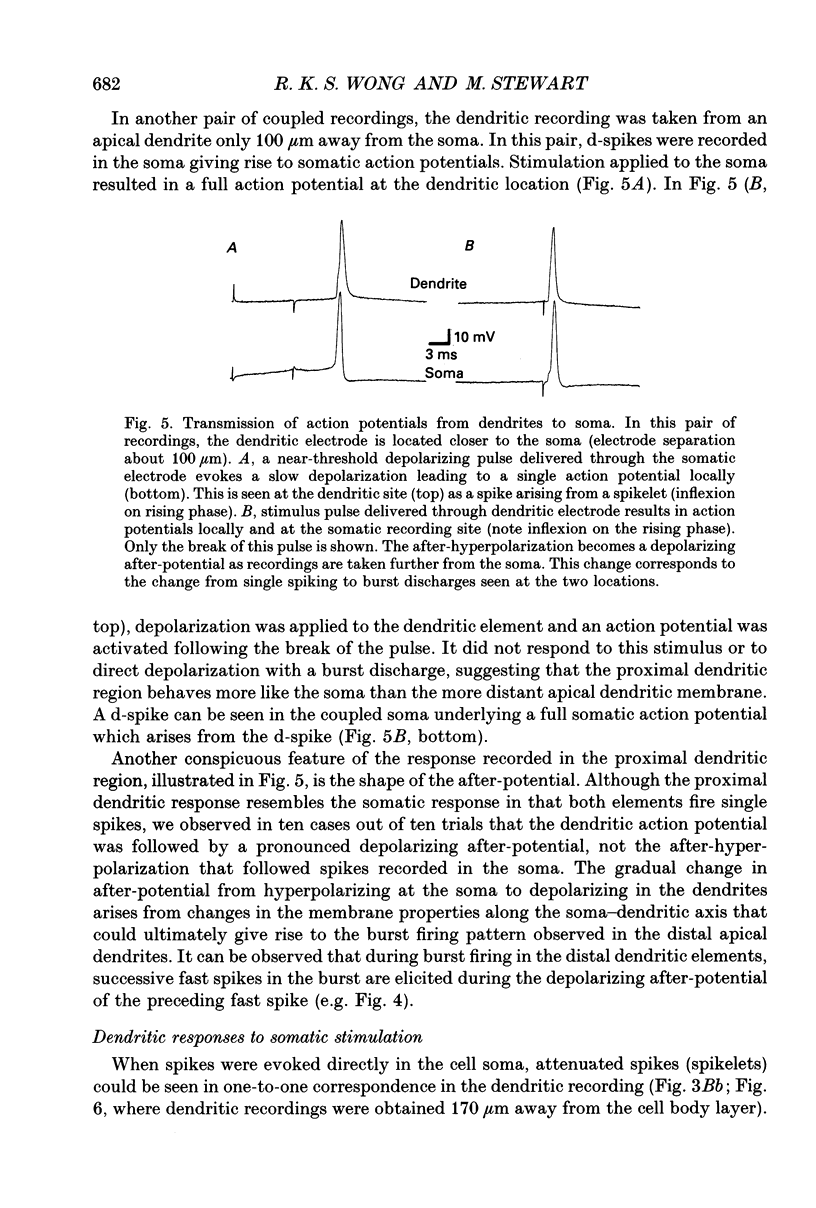
1. Intracellular recordings, taken from CA1 pyramidal cells in guinea-pig hippocampal slices, were used to examine the origins of repetitive and burst firing in these cells. Single action potentials were elicited by depolarizing current injection at somatic recording sites. In contrast, current injection during intradendritic recordings initiated burst firing in the dendrites. Burst firing could be elicited in the soma by direct depolarization of distal apical dendrites (> 150 microns from the cell body layer) with large extracellular polarizing electrodes. 2. Intracellular recordings were taken simultaneously from the apical dendrites and pyramidal cell somata with the intention of impaling the same neurone with both electrodes. Paired dendrite-soma recordings confirmed that rhythmic single action potentials were generated at the cell soma, whereas bursts of action potentials were initiated in the distal apical dendrites (> 150 microns from the cell body layer). Fast spikes in the dendrite often triggered fast spikes in the soma, but not all fast spikes in the dendritic burst were 'relayed' to the soma. 3. In paired recordings, when a dendritic action potential failed to elicit a full somatic action potential, a 'd-spike' was commonly recorded in the soma. Somatic d-spikes were uniform all-or-none responses that could be shown, in some cases, to trigger the full somatic action potentials. 4. Attenuated spikes could be recorded in the dendrites, triggered by action potentials initiated at the cell soma. Dendritic responses to somatic stimulation sometimes varied in amplitude, but always showed a direct correspondence with somatic action potentials. 5. Dendritic recordings taken closer to the pyramidal cell bodies (< 150 microns from the cell body layer) showed a 'transitional' region where single action potentials rather than burst discharges could be evoked. After-potentials of these single spikes differed from those associated with somatic spikes in that proximal dendritic spikes had depolarizing after-potentials. The observed shift from after-hyperpolarization to depolarizing after-potentials in intradendritic recordings taken progressively further from the cell body corresponds to the change from repetitive to burst firing. 6. The results indicate that activity of the CA1 pyramidal cell soma, presumably a reflection of its output, can be either burst or repetitive firing. Somatic 'bursts,' unlike the burst discharges seen in the apical dendrites or the burst discharges reported in CA3 cells, are not initiated locally. Rather, they appear to be simply a rapid spike-for-spike response by the soma to the fast spikes that form part of the apical dendritic burst.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
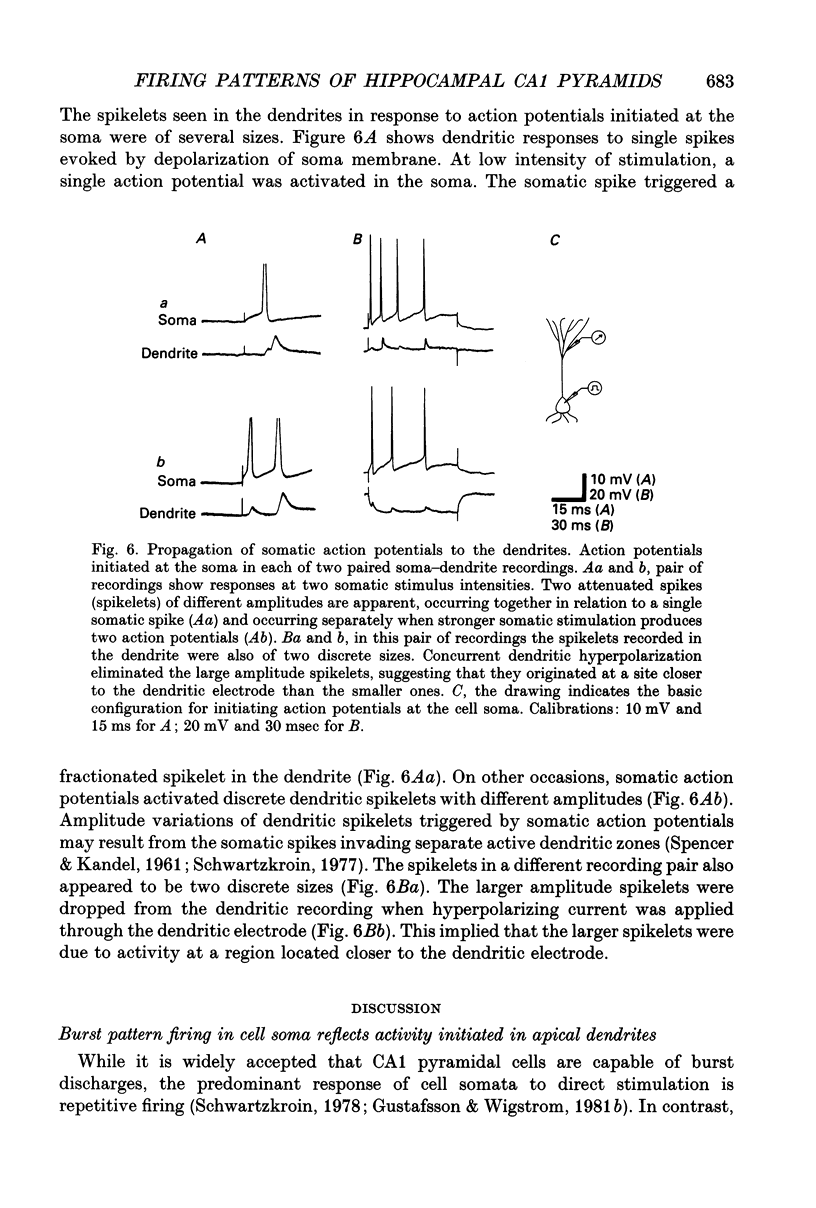
- Alger B. E., Williamson A. A transient calcium-dependent potassium component of the epileptiform burst after-hyperpolarization in rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1988 May;399:191–205. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrew R. D., Taylor C. P., Snow R. W., Dudek F. E. Coupling in rat hippocampal slices: dye transfer between CA1 pyramidal cells. Brain Res Bull. 1982 Feb;8(2):211–222. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(82)90048-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benardo L. S., Masukawa L. M., Prince D. A. Electrophysiology of isolated hippocampal pyramidal dendrites. J Neurosci. 1982 Nov;2(11):1614–1622. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.02-11-01614.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benardo L. S., Prince D. A. Cholinergic excitation of mammalian hippocampal pyramidal cells. Brain Res. 1982 Oct 14;249(2):315–331. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90066-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benardo L. S., Prince D. A. Cholinergic pharmacology of mammalian hippocampal pyramidal cells. Neuroscience. 1982 Jul;7(7):1703–1712. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90028-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colino A., Halliwell J. V. Differential modulation of three separate K-conductances in hippocampal CA1 neurons by serotonin. Nature. 1987 Jul 2;328(6125):73–77. doi: 10.1038/328073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox S. E., Ranck J. B., Jr Electrophysiological characteristics of hippocampal complex-spike cells and theta cells. Exp Brain Res. 1981;41(3-4):399–410. doi: 10.1007/BF00238898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson B., Wigström H. Evidence for two types of afterhyperpolarization in CA1 pyramidal cells in the hippocampus. Brain Res. 1981 Feb 16;206(2):462–468. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90548-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson B., Wigström H. Shape of frequency-current curves in CAI pyramidal cells in the hippocampus. Brain Res. 1981 Nov 2;223(2):417–421. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)91158-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas H. L., Greene R. W. Adenosine enhances afterhyperpolarization and accommodation in hippocampal pyramidal cells. Pflugers Arch. 1984 Nov;402(3):244–247. doi: 10.1007/BF00585506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas H. L., Greene R. W. Effects of histamine on hippocampal pyramidal cells of the rat in vitro. Exp Brain Res. 1986;62(1):123–130. doi: 10.1007/BF00237408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotson J. R., Prince D. A. A calcium-activated hyperpolarization follows repetitive firing in hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1980 Feb;43(2):409–419. doi: 10.1152/jn.1980.43.2.409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahnsen H., Llinás R. Electrophysiological properties of guinea-pig thalamic neurones: an in vitro study. J Physiol. 1984 Apr;349:205–226. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahnsen H., Llinás R. Ionic basis for the electro-responsiveness and oscillatory properties of guinea-pig thalamic neurones in vitro. J Physiol. 1984 Apr;349:227–247. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferys J. G. Influence of electric fields on the excitability of granule cells in guinea-pig hippocampal slices. J Physiol. 1981;319:143–152. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles W. D., Schwartzkroin P. A. Local circuit synaptic interactions in hippocampal brain slices. J Neurosci. 1981 Mar;1(3):318–322. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.01-03-00318.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster B., Adams P. R. Calcium-dependent current generating the afterhyperpolarization of hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1986 Jun;55(6):1268–1282. doi: 10.1152/jn.1986.55.6.1268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster B., Nicoll R. A. Properties of two calcium-activated hyperpolarizations in rat hippocampal neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Aug;389:187–203. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Jahnsen H. Electrophysiology of mammalian thalamic neurones in vitro. Nature. 1982 Jun 3;297(5865):406–408. doi: 10.1038/297406a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison D. V., Lancaster B., Nicoll R. A. Voltage clamp analysis of cholinergic action in the hippocampus. J Neurosci. 1987 Mar;7(3):733–741. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-03-00733.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison D. V., Nicoll R. A. Noradrenaline blocks accommodation of pyramidal cell discharge in the hippocampus. Nature. 1982 Oct 14;299(5884):636–638. doi: 10.1038/299636a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malenka R. C., Nicoll R. A. Dopamine decreases the calcium-activated afterhyperpolarization in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells. Brain Res. 1986 Aug 6;379(2):210–215. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90773-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick D. A., Prince D. A. Acetylcholine induces burst firing in thalamic reticular neurones by activating a potassium conductance. 1986 Jan 30-Feb 5Nature. 319(6052):402–405. doi: 10.1038/319402a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick D. A., Prince D. A. Mechanisms of action of acetylcholine in the guinea-pig cerebral cortex in vitro. J Physiol. 1986 Jun;375:169–194. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller R. U., Kubie J. L., Ranck J. B., Jr Spatial firing patterns of hippocampal complex-spike cells in a fixed environment. J Neurosci. 1987 Jul;7(7):1935–1950. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-07-01935.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Numann R. E., Wadman W. J., Wong R. K. Outward currents of single hippocampal cells obtained from the adult guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;393:331–353. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Keefe J., Dostrovsky J. The hippocampus as a spatial map. Preliminary evidence from unit activity in the freely-moving rat. Brain Res. 1971 Nov;34(1):171–175. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90358-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince D. A. Neurophysiology of epilepsy. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1978;1:395–415. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.01.030178.002143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranck J. B., Jr Studies on single neurons in dorsal hippocampal formation and septum in unrestrained rats. I. Behavioral correlates and firing repertoires. Exp Neurol. 1973 Nov;41(2):461–531. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(73)90290-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzkroin P. A. Characteristics of CA1 neurons recorded intracellularly in the hippocampal in vitro slice preparation. Brain Res. 1975 Mar 7;85(3):423–436. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90817-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzkroin P. A. Further characteristics of hippocampal CA1 cells in vitro. Brain Res. 1977 Jun 3;128(1):53–68. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90235-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzkroin P. A. Secondary range rhythmic spiking in hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. 1978 Jun 23;149(1):247–250. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90606-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storm J. F. Action potential repolarization and a fast after-hyperpolarization in rat hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Physiol. 1987 Apr;385:733–759. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storm J. F. An after-hyperpolarization of medium duration in rat hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Physiol. 1989 Feb;409:171–190. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. P., Dudek F. E. A physiological test for electrotonic coupling between CA1 pyramidal cells in rat hippocampal slices. Brain Res. 1982 Mar 11;235(2):351–357. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)91013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson A., Alger B. E. Characterization of an early afterhyperpolarization after a brief train of action potentials in rat hippocampal neurons in vitro. J Neurophysiol. 1990 Jan;63(1):72–81. doi: 10.1152/jn.1990.63.1.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong R. K., Prince D. A. Afterpotential generation in hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Neurophysiol. 1981 Jan;45(1):86–97. doi: 10.1152/jn.1981.45.1.86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong R. K., Prince D. A., Basbaum A. I. Intradendritic recordings from hippocampal neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):986–990. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong R. K., Prince D. A. Participation of calcium spikes during intrinsic burst firing in hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. 1978 Dec 29;159(2):385–390. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90544-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


