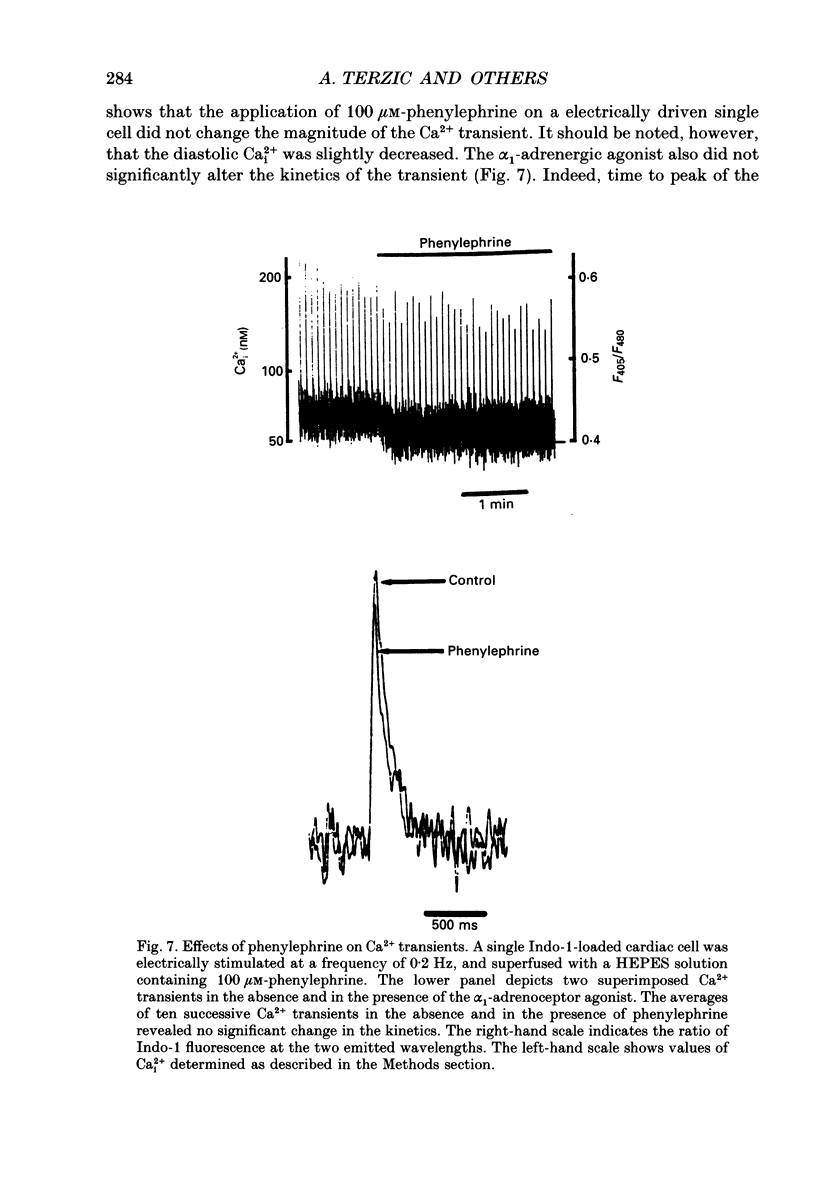
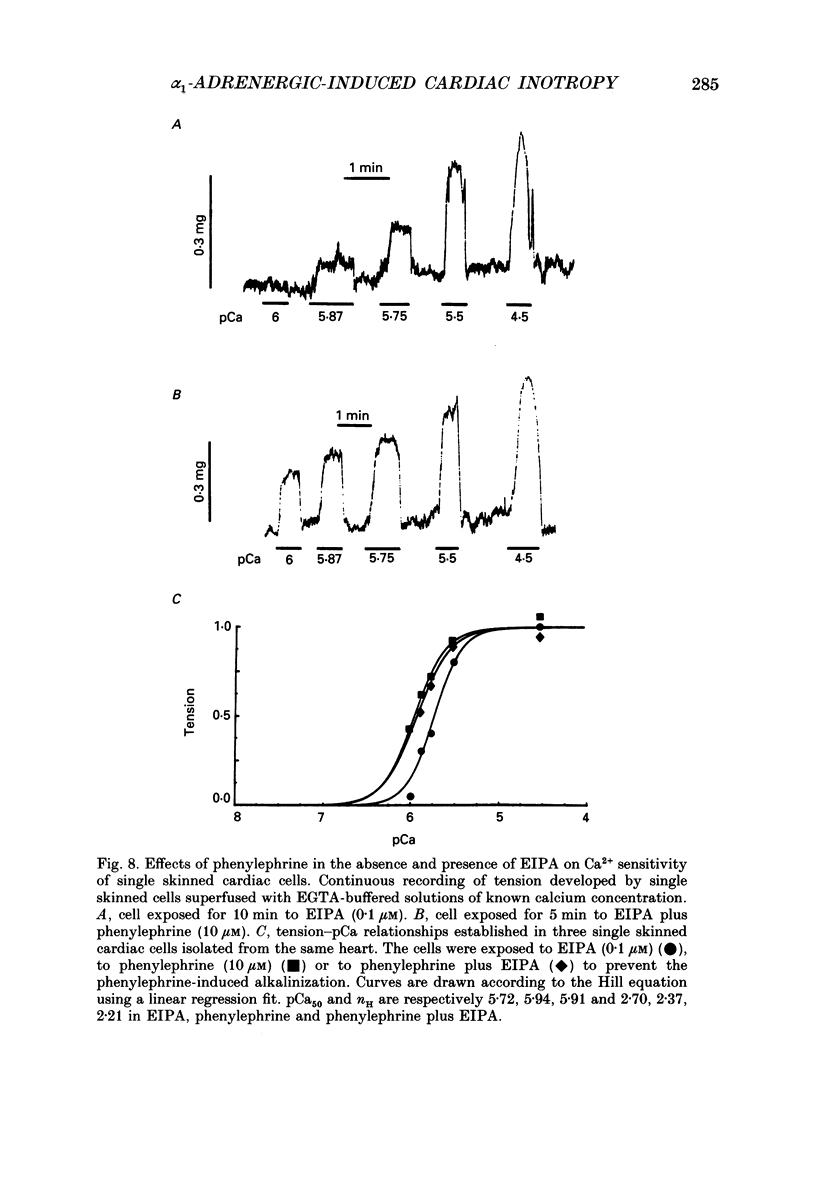
Abstract
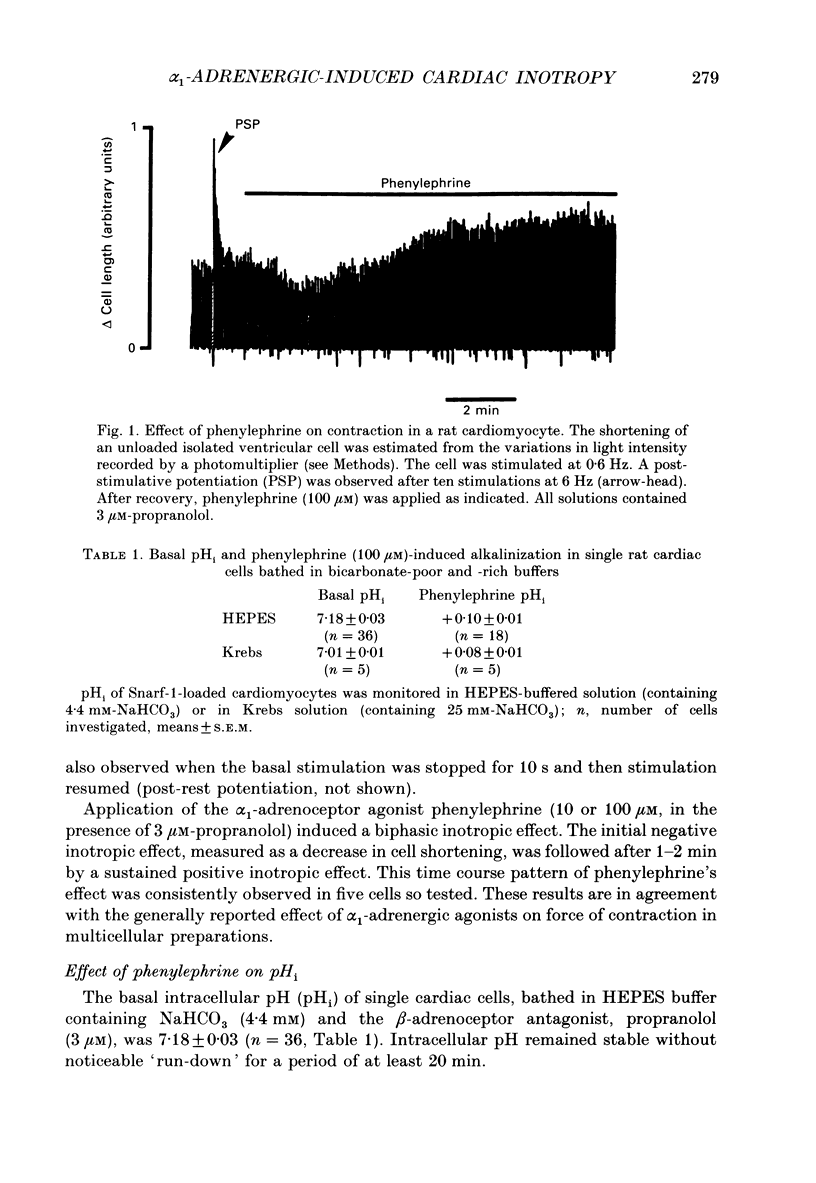
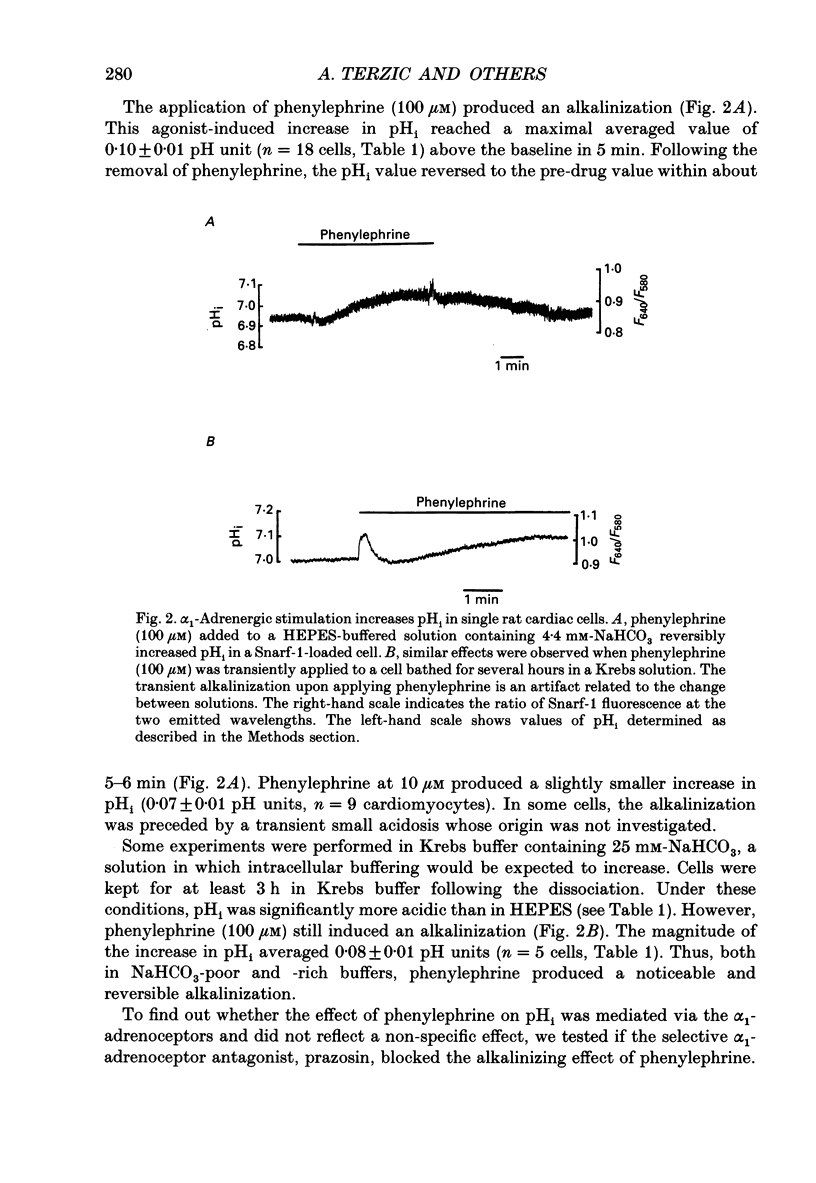
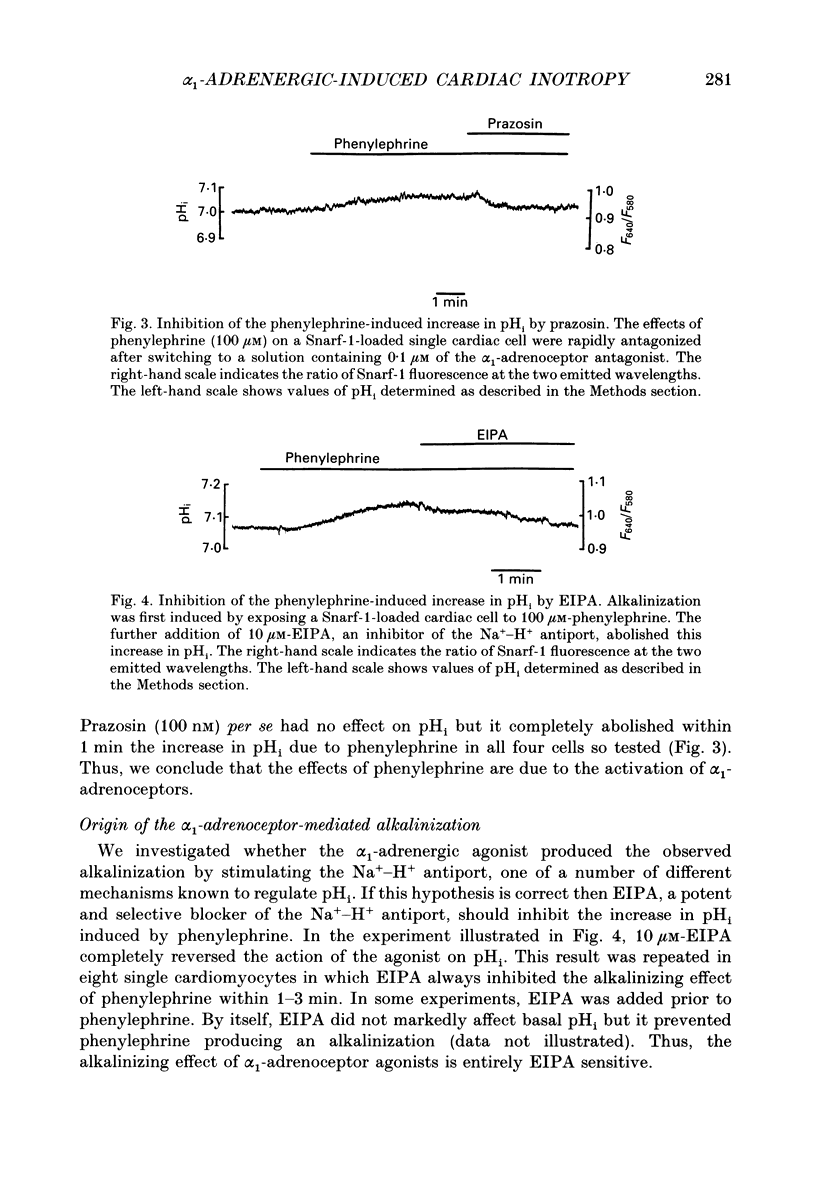
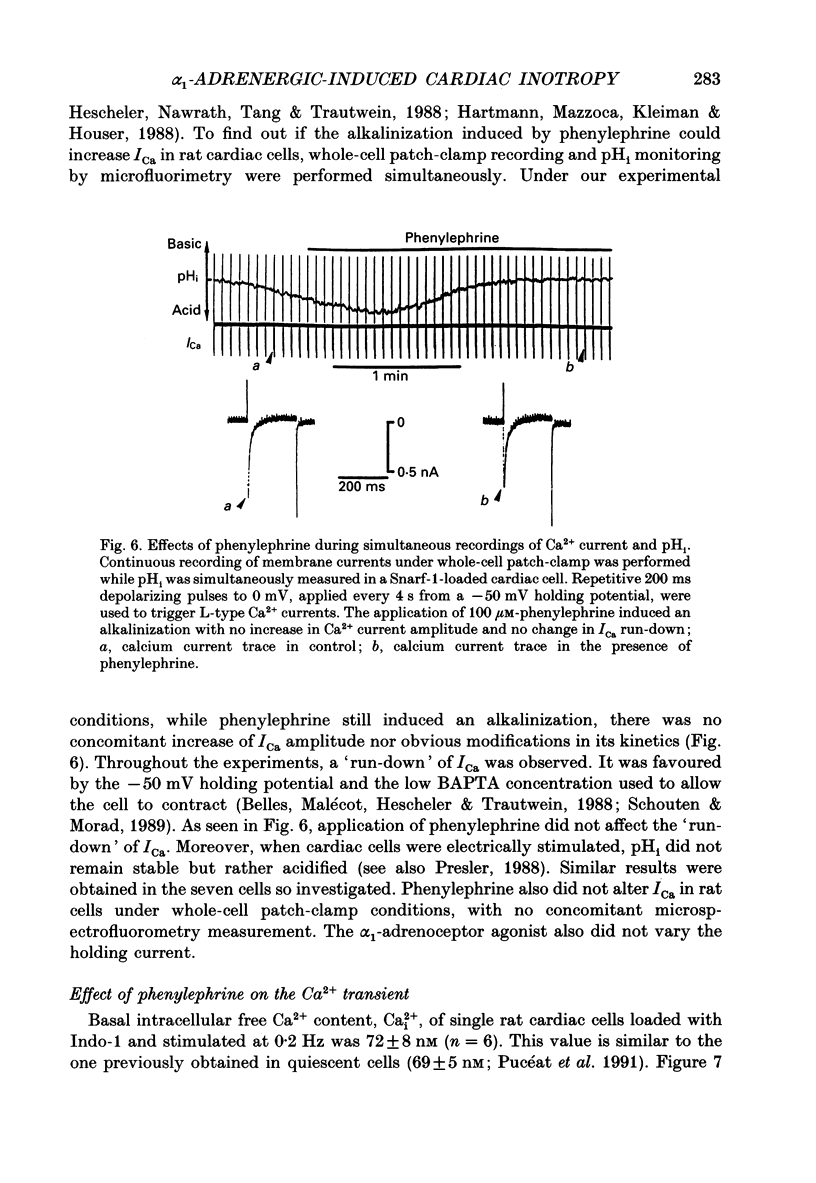
1. The cellular effects of alpha 1-adrenoceptor stimulation by phenylephrine were studied in the presence of propranolol in single cells isolated from the ventricles of rat hearts. 2. Phenylephrine (10-100 microM) induced a biphasic pattern of inotropism in these cells: a transient negative followed by a sustained positive inotropic effect as usually observed in cardiac tissues. 3. In Snarf-1-loaded cells, phenylephrine induced an alkalinization. This effect was reversible on wash-out and inhibited by prazosin, an alpha 1-adrenoceptor antagonist. 4. The alpha 1-adrenoceptor-mediated increase in intracellular pH (pHi) was 0.1 pH unit in HEPES buffer containing 4.4 mM-NaHCO3 and in Krebs buffer containing 25 mM-NaHCO3. 5. The alkalinization was blocked by the Na(+)-H+ antiport blocker, ethylisopropylamiloride (EIPA). 6. The recovery from an acidosis induced by a NH4Cl pre-pulse was accelerated by phenylephrine. The phenylephrine-induced alkalinization was attributed to activation of the Na(+)-H+ antiport. 7. Despite its ability to increase pHi, phenylephrine did not alter Ca2+ current amplitude and kinetics. 8. Ca2+ transients recorded in Indo-1-loaded cells were not augmented by phenylephrine. Diastolic calcium level was decreased. 9. In single skinned cells, the Ca2+ sensitivity of the contractile proteins was increased by a pre-treatment with phenylephrine even when the alpha 1-adrenoceptor-mediated alkalinizing effect had been prevented by EIPA. 10. These results lead us to propose that the alpha 1-adrenergic-induced positive inotropic response of heart muscle could result from an increased sensitivity of the myofilaments to Ca2+ ions. This alpha 1-adrenoceptor-mediated Ca2+ sensitization could result both from an intracellular alkalinization and from a direct effect on contractile proteins.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belles B., Malécot C. O., Hescheler J., Trautwein W. "Run-down" of the Ca current during long whole-cell recordings in guinea pig heart cells: role of phosphorylation and intracellular calcium. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Apr;411(4):353–360. doi: 10.1007/BF00587713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol as second messengers. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):345–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2200345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brückner R., Scholz H. Effects of alpha-adrenoceptor stimulation with phenylephrine in the presence of propranolol on force of contraction, slow inward current and cyclic AMP content in the bovine heart. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 May;82(1):223–232. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb16462.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capogrossi M. C., Kaku T., Filburn C. R., Pelto D. J., Hansford R. G., Spurgeon H. A., Lakatta E. G. Phorbol ester and dioctanoylglycerol stimulate membrane association of protein kinase C and have a negative inotropic effect mediated by changes in cytosolic Ca2+ in adult rat cardiac myocytes. Circ Res. 1990 Apr;66(4):1143–1155. doi: 10.1161/01.res.66.4.1143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crompton M., Kessar P., Al-Nasser I. The alpha-adrenergic-mediated activation of the cardiac mitochondrial Ca2+ uniporter and its role in the control of intramitochondrial Ca2+ in vivo. Biochem J. 1983 Nov 15;216(2):333–342. doi: 10.1042/bj2160333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endoh M., Blinks J. R. Actions of sympathomimetic amines on the Ca2+ transients and contractions of rabbit myocardium: reciprocal changes in myofibrillar responsiveness to Ca2+ mediated through alpha- and beta-adrenoceptors. Circ Res. 1988 Feb;62(2):247–265. doi: 10.1161/01.res.62.2.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endoh M., Hiramoto T., Ishihata A., Takanashi M., Inui J. Myocardial alpha 1-adrenoceptors mediate positive inotropic effect and changes in phosphatidylinositol metabolism. Species differences in receptor distribution and the intracellular coupling process in mammalian ventricular myocardium. Circ Res. 1991 May;68(5):1179–1190. doi: 10.1161/01.res.68.5.1179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A., Fabiato F. Effects of pH on the myofilaments and the sarcoplasmic reticulum of skinned cells from cardiace and skeletal muscles. J Physiol. 1978 Mar;276:233–255. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedida D., Shimoni Y., Giles W. R. A novel effect of norepinephrine on cardiac cells is mediated by alpha 1-adrenoceptors. Am J Physiol. 1989 May;256(5 Pt 2):H1500–H1504. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1989.256.5.H1500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frelin C., Vigne P., Ladoux A., Lazdunski M. The regulation of the intracellular pH in cells from vertebrates. Eur J Biochem. 1988 May 16;174(1):3–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14055.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann H. A., Mazzocca N. J., Kleiman R. B., Houser S. R. Effects of phenylephrine on calcium current and contractility of feline ventricular myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1988 Nov;255(5 Pt 2):H1173–H1180. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1988.255.5.H1173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hescheler J., Nawrath H., Tang M., Trautwein W. Adrenoceptor-mediated changes of excitation and contraction in ventricular heart muscle from guinea-pigs and rabbits. J Physiol. 1988 Mar;397:657–670. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahnel U., Nawrath H., Carmeliet E., Vereecke J. Depolarization-induced influx of sodium in response to phenylephrine in rat atrial heart muscle. J Physiol. 1991 Jan;432:621–637. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurachi Y. The effects of intracellular protons on the electrical activity of single ventricular cells. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Sep;394(3):264–270. doi: 10.1007/BF00589102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacerda A. E., Rampe D., Brown A. M. Effects of protein kinase C activators on cardiac Ca2+ channels. Nature. 1988 Sep 15;335(6187):249–251. doi: 10.1038/335249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledda F., Marchetti P., Mugelli A. Studies on the positive inotropic effect of phenylephrine: a comparison with isoprenaline. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 May;54(1):83–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07413.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Movsesian M. A., Nishikawa M., Adelstein R. S. Phosphorylation of phospholamban by calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase. Stimulation of cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium uptake. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8029–8032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Movsesian M. A., Thomas A. P., Selak M., Williamson J. R. Inositol trisphosphate does not release Ca2+ from permeabilized cardiac myocytes and sarcoplasmic reticulum. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jun 17;185(2):328–332. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80932-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orchard C. H., Kentish J. C. Effects of changes of pH on the contractile function of cardiac muscle. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jun;258(6 Pt 1):C967–C981. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.258.6.C967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otani H., Otani H., Das D. K. Alpha 1-adrenoceptor-mediated phosphoinositide breakdown and inotropic response in rat left ventricular papillary muscles. Circ Res. 1988 Jan;62(1):8–17. doi: 10.1161/01.res.62.1.8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otani H., Otani H., Uriu T., Hara M., Inoue M., Omori K., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Inagaki C. Effects of inhibitors of protein kinase C and Na+/H+ exchange on alpha 1-adrenoceptor-mediated inotropic responses in the rat left ventricular papillary muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Jun;100(2):207–210. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb15783.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipson K. D., Bersohn M. M., Nishimoto A. Y. Effects of pH on Na+-Ca2+ exchange in canine cardiac sarcolemmal vesicles. Circ Res. 1982 Feb;50(2):287–293. doi: 10.1161/01.res.50.2.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poggioli J., Sulpice J. C., Vassort G. Inositol phosphate production following alpha 1-adrenergic, muscarinic or electrical stimulation in isolated rat heart. FEBS Lett. 1986 Oct 6;206(2):292–298. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80999-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pressler M. L. Phasic changes in intracellular pH during action potentials of sheep Purkinje fibres. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Jan;411(1):69–75. doi: 10.1007/BF00581648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puceat M., Clement O., Lechene P., Pelosin J. M., Ventura-Clapier R., Vassort G. Neurohormonal control of calcium sensitivity of myofilaments in rat single heart cells. Circ Res. 1990 Aug;67(2):517–524. doi: 10.1161/01.res.67.2.517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pucéat M., Clément O., Scamps F., Vassort G. Extracellular ATP-induced acidification leads to cytosolic calcium transient rise in single rat cardiac myocytes. Biochem J. 1991 Feb 15;274(Pt 1):55–62. doi: 10.1042/bj2740055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravens U., Wang X. L., Wettwer E. Alpha adrenoceptor stimulation reduces outward currents in rat ventricular myocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Jul;250(1):364–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter M. Calcium mobilization and cardiac inotropic mechanisms. Pharmacol Rev. 1988 Sep;40(3):189–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos A., Boron W. F. Intracellular pH. Physiol Rev. 1981 Apr;61(2):296–434. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.2.296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scamps F., Legssyer A., Mayoux E., Vassort G. The mechanism of positive inotropy induced by adenosine triphosphate in rat heart. Circ Res. 1990 Oct;67(4):1007–1016. doi: 10.1161/01.res.67.4.1007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholz J., Schaefer B., Schmitz W., Scholz H., Steinfath M., Lohse M., Schwabe U., Puurunen J. Alpha-1 adrenoceptor-mediated positive inotropic effect and inositol trisphosphate increase in mammalian heart. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Apr;245(1):327–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schouten V. J., Morad M. Regulation of Ca2+ current in frog ventricular myocytes by the holding potential, c-AMP and frequency. Pflugers Arch. 1989 Oct;415(1):1–11. doi: 10.1007/BF00373135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schümann H. J., Endoh S., Brodde O. E. The time course of the effects of beta- and alpha-adrenoceptor stimulation by isoprenaline and methoxamine on the contractile force and cAMP level of the isolated rabbit papillary muscle. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1975;289(3):291–302. doi: 10.1007/BF00499982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen L., Liang B. T., Colucci W. S., Smith T. W. Enhanced alpha 1-adrenergic responsiveness in cardiomyopathic hamster cardiac myocytes. Relation to the expression of pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein and alpha 1-adrenergic receptors. Circ Res. 1990 Nov;67(5):1182–1192. doi: 10.1161/01.res.67.5.1182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skomedal T., Osnes J. B., Oye I. Differences between alpha-adrenergic and beta-adrenergic inotropic effects in rat heart papillary muscles. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1982 Jan;50(1):1–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1982.tb00932.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terzic A., Anagnostopoulos T., Vogel S. M. Opposite modulation of ouabain cardiotoxicity by hexamethyleneamiloride and phenylephrine. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1991 May;343(5):511–518. doi: 10.1007/BF00169554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terzic A., Vogel S. M. Amiloride-sensitive actions of an alpha-adrenoceptor agonist and ouabain in rat atria. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1990 Apr;22(4):391–402. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(90)91475-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terzic A., Vogel S. M. On the mechanism of the positive inotropic action of the alpha adrenoceptor agonist, phenylephrine, in isolated rat left atria. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Apr;257(1):520–529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan-Jones R. D., Eisner D. A., Lederer W. J. Effects of changes of intracellular pH on contraction in sheep cardiac Purkinje fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Jun;89(6):1015–1032. doi: 10.1085/jgp.89.6.1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan-Jones R. D. Regulation of intracellular pH in cardiac muscle. Ciba Found Symp. 1988;139:23–46. doi: 10.1002/9780470513699.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigne P., Frelin C., Lazdunski M. The Na+/H+ antiport is activated by serum and phorbol esters in proliferating myoblasts but not in differentiated myotubes. Properties of the activation process. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):8008–8013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vites A. M., Pappano A. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate releases intracellular Ca2+ in permeabilized chick atria. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jun;258(6 Pt 2):H1745–H1752. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.258.6.H1745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel S. M., Terzic A. Alpha-adrenergic regulation of action potentials in isolated rat cardiomyocytes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 May 19;164(2):231–239. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90463-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner J., Brodde O. E. On the presence and distribution of alpha-adrenoceptors in the heart of various mammalian species. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1978 May;302(3):239–254. doi: 10.1007/BF00508293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. S., Lefkowitz R. J. Alpha-adrenergic receptors in rat myocardium. Identification by binding of [3H]dihydroergocryptine. Circ Res. 1978 Nov;43(5):721–727. doi: 10.1161/01.res.43.5.721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaza A., Kline R. P., Rosen M. R. Effects of alpha-adrenergic stimulation on intracellular sodium activity and automaticity in canine Purkinje fibers. Circ Res. 1990 Feb;66(2):416–426. doi: 10.1161/01.res.66.2.416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


