Abstract
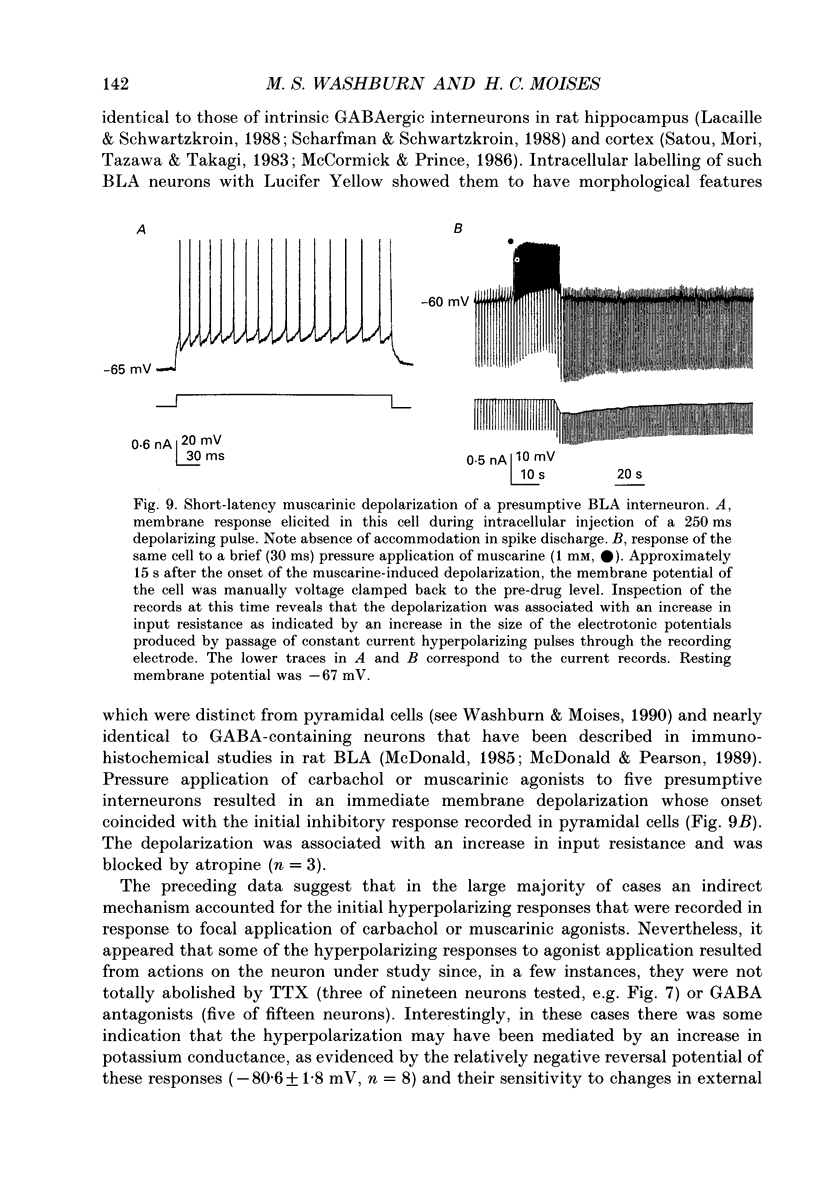
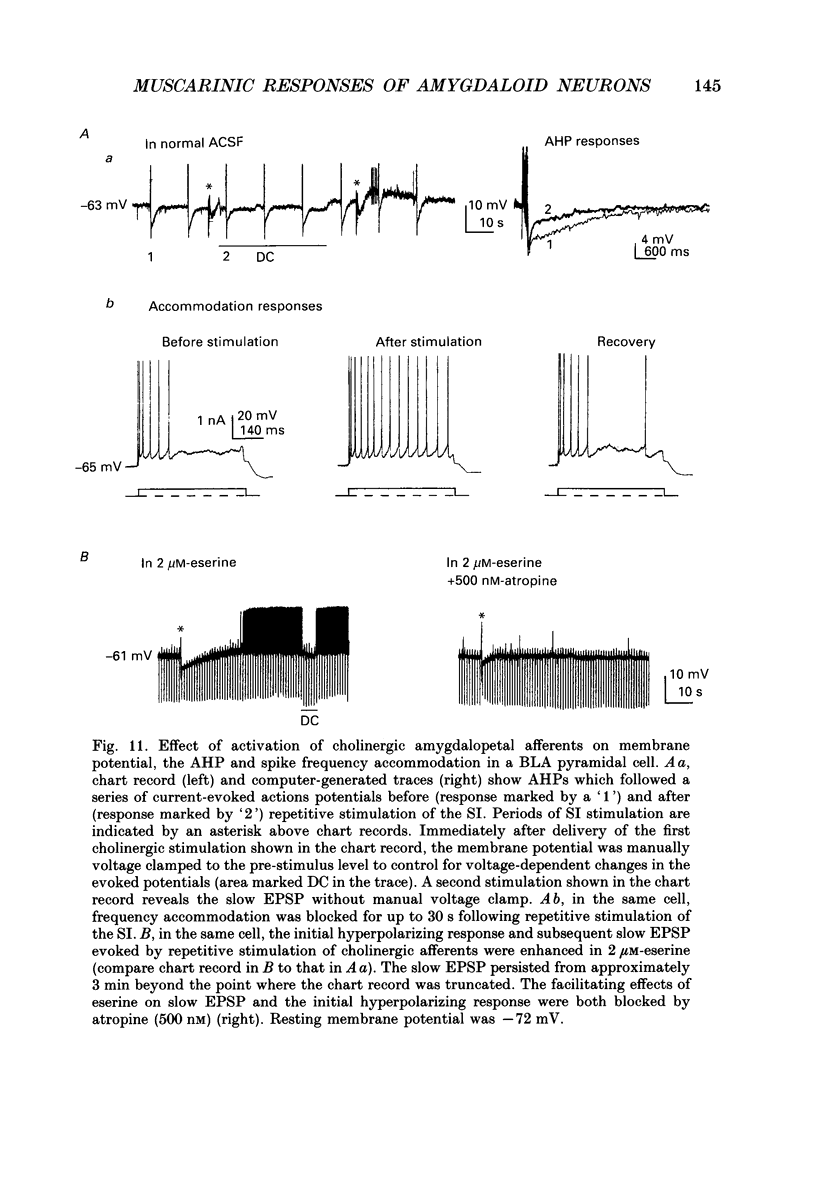
1. Intracellular recordings were obtained from pyramidal-type neurons in the basolateral amygdaloid nucleus (BLA) in slices of rat ventral forebrain and used to compare the actions of exogenously applied cholinomimetics to the effects produced by electrical stimulation of amygdalopetal cholinergic afferents from basal forebrain. 2. Bath application of carbachol depolarized pyramidal cells with an associated increase in input resistance (Ri), reduced the slow after-hyperpolarization (AHP) that followed a series of current-evoked action potentials and blocked spike frequency accommodation. All of these effects were reversed by the muscarinic antagonist atropine but not by the nicotinic antagonist hexamethonium. 3. Electrical stimulation of amygdaloid afferents within the external capsule evoked a series of synaptic potentials consisting of a non-cholinergic fast excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP), followed by early and late inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs). Each of these synaptic potentials was reduced by carbachol in an atropine-sensitive manner. 4. Local application of carbachol to pyramidal cells produced a short-latency hyperpolarization followed by a prolonged depolarization. The hyperpolarization and depolarization to carbachol were blocked by atropine but not hexamethonium. 5. The carbachol-induced hyperpolarization was associated with a decrease in Ri and had a reversal potential nearly identical to that of the early IPSP. The inhibitory response was blocked by perfusion of medium containing tetrodotoxin (TTX), bicuculline or picrotoxin, while the subsequent depolarization was unaffected. On the basis of these data, it is concluded that the muscarinic hyperpolarization is mediated through the rapid excitation of presynaptic GABAergic interneurons in the slice. 6. The findings that the carbachol-induced depolarization was associated with an increase in Ri, often had a reversal potential below -80 mV, was sensitive to changes in extracellular potassium concentration and was blocked by intracellular ionophoresis of the potassium channel blocker caesium suggest that it resulted from a muscarinic blockade of one or more potassium conductances. 7. Repetitive stimulation of sites within the slice containing cholinergic afferents evoked a series of fast EPSPs followed by IPSPs. These non-cholinergic potentials were followed by a slow EPSP that lasted from 10 s-4 min. The slow EPSP was enhanced by eserine and blocked by atropine. It was also blocked by TTX or cadmium, indicating that it was dependent on spike propagation and calcium-dependent release of acetylcholine (ACh). 8. Stimulation of cholinergic afferents in the slice mimicked other effects produced by carbachol including blockade of the slow AHP and accommodation of action potential discharge and these actions were potentiated by eserine and blocked by atropine.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
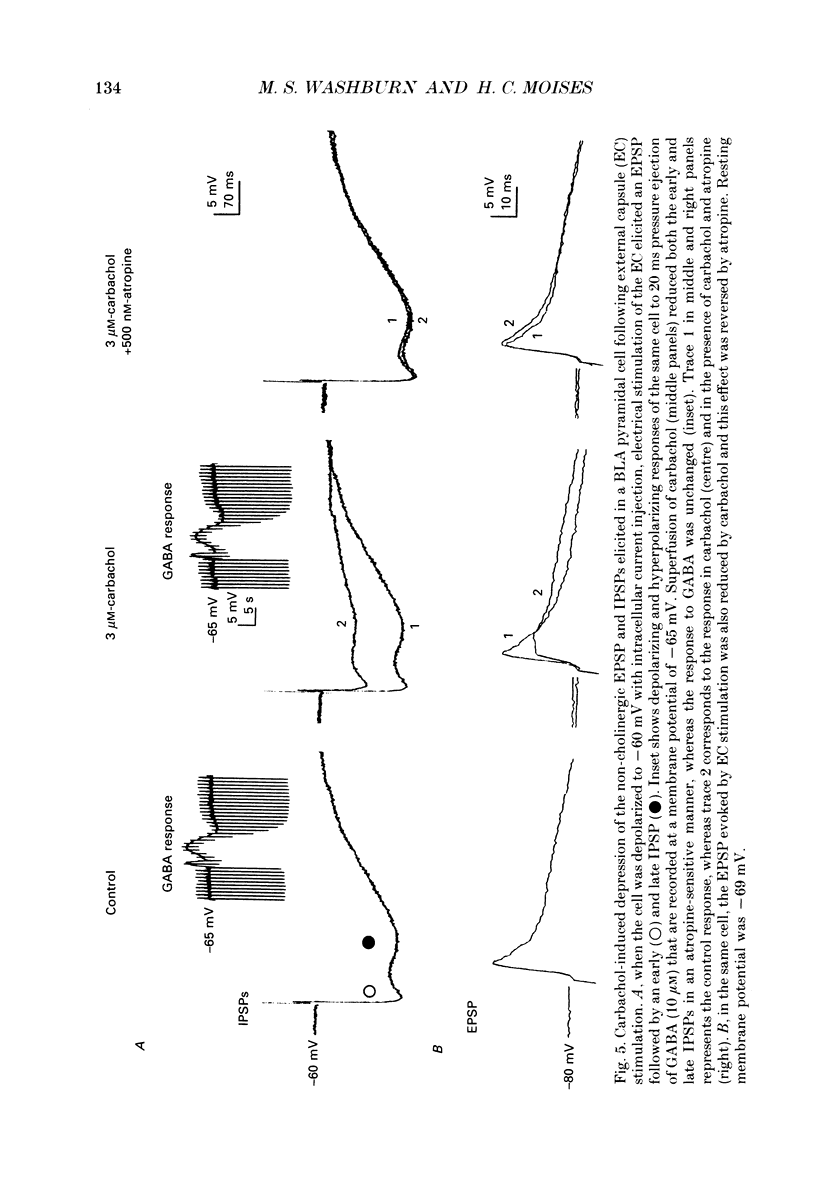
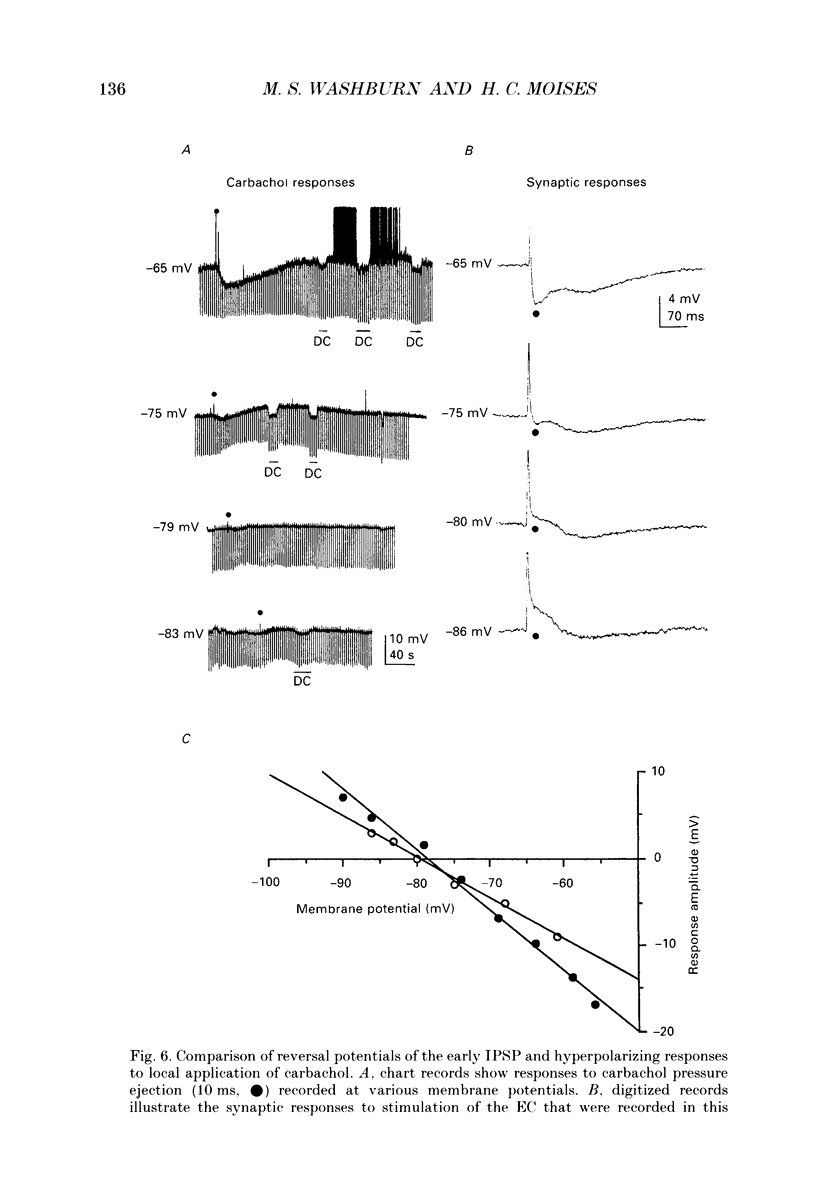
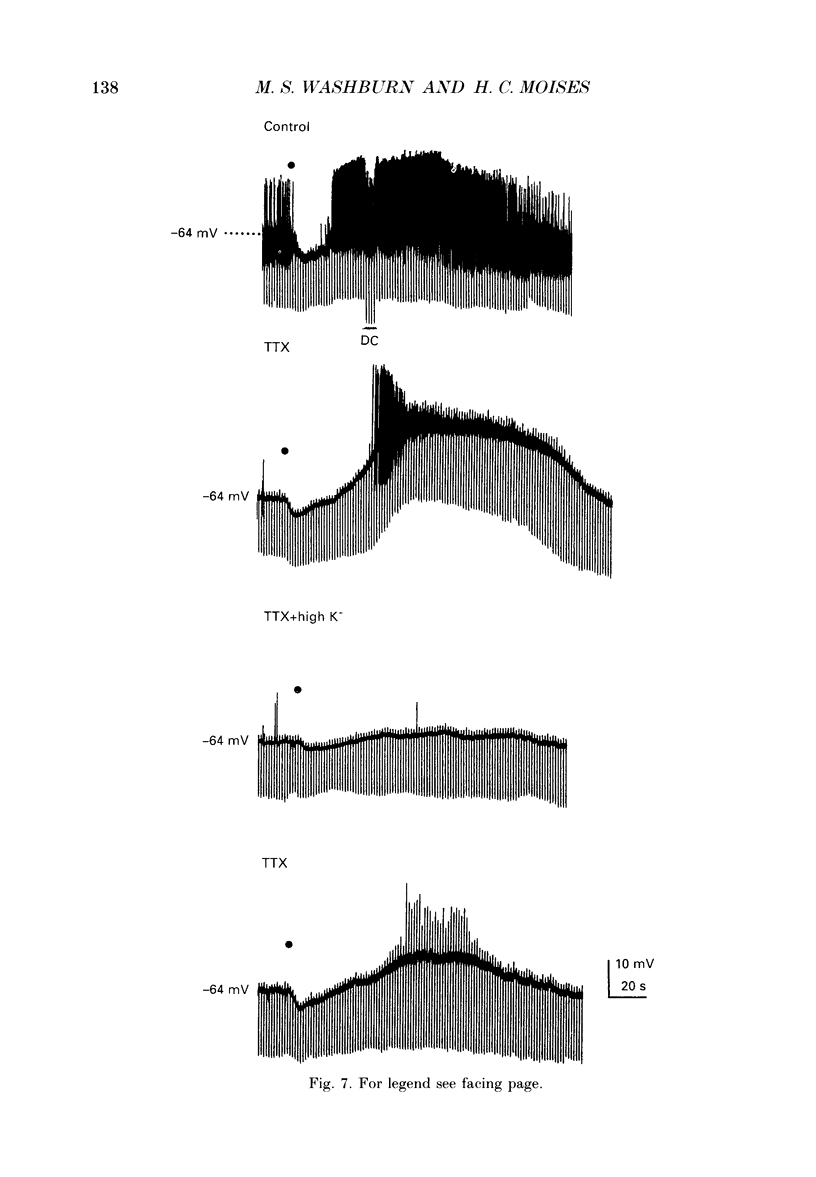
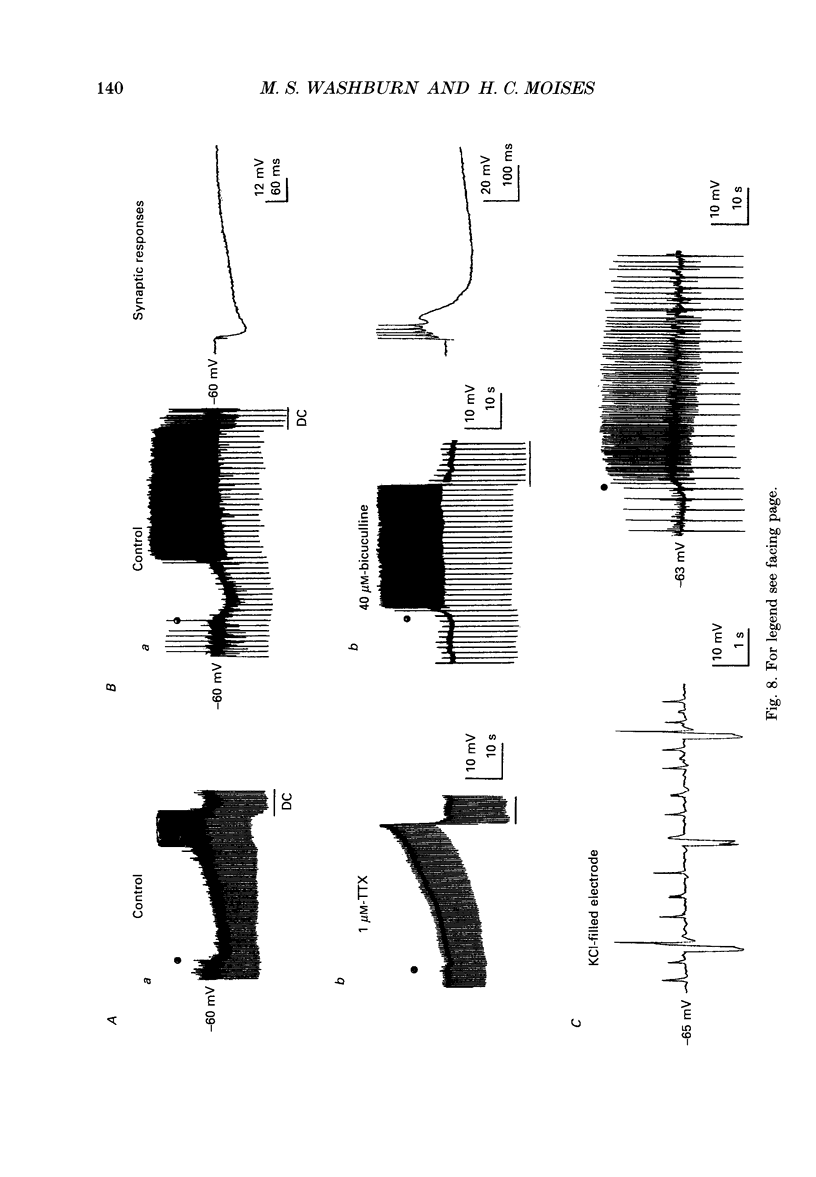
PDF






















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R., Brown D. A., Constanti A. Pharmacological inhibition of the M-current. J Physiol. 1982 Nov;332:223–262. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
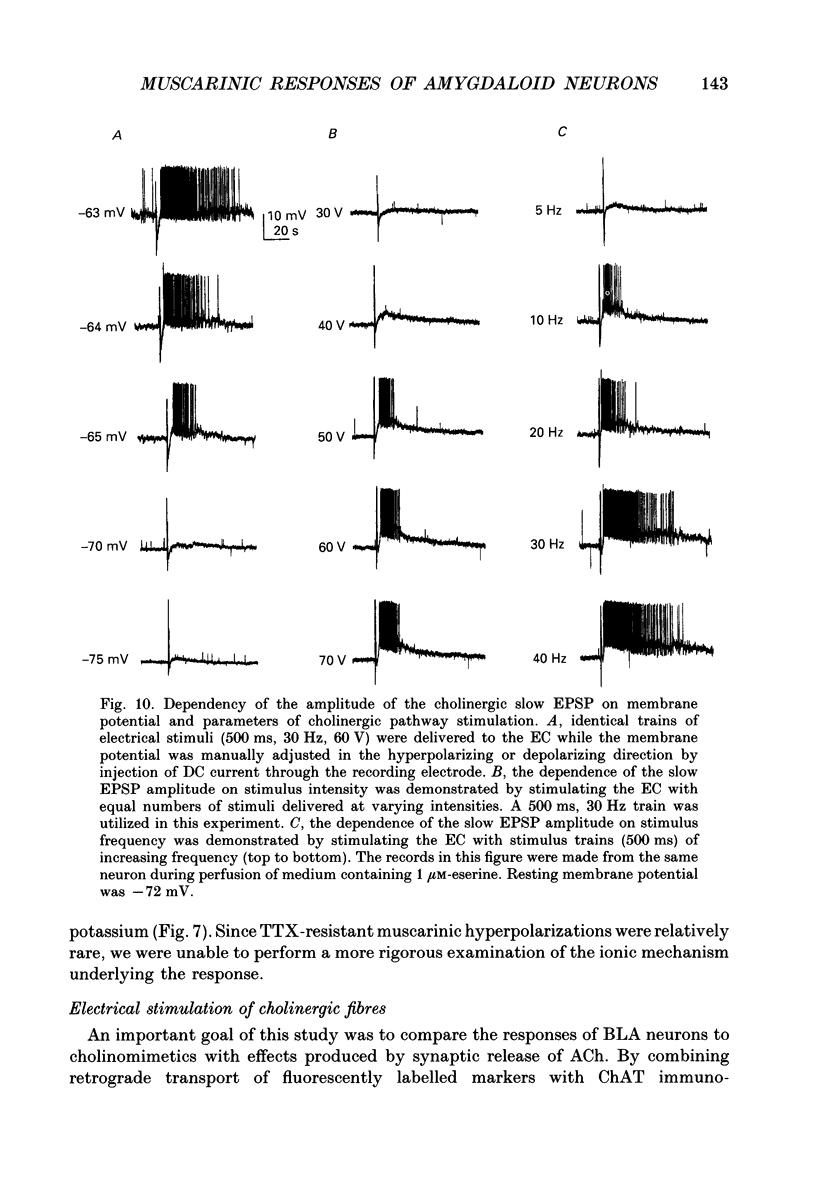
- Adams P. R., Brown D. A. Synaptic inhibition of the M-current: slow excitatory post-synaptic potential mechanism in bullfrog sympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1982 Nov;332:263–272. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belluzzi O., Sacchi O., Wanke E. Identification of delayed potassium and calcium currents in the rat sympathetic neurone under voltage clamp. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:109–129. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ari Y., Krnjević K., Reinhardt W., Ropert N. Intracellular observations on the disinhibitory action of acetylcholine in the hippocampus. Neuroscience. 1981;6(12):2475–2484. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90093-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ari Y., Zigmond R. E., Shute C. C., Lewis P. R. Regional distribution of choline acetyltransferase and acetylcholinesterase within the amygdaloid complex and stria terminalis system. Brain Res. 1977 Jan 28;120(3):435–444. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90397-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benardo L. S., Prince D. A. Cholinergic excitation of mammalian hippocampal pyramidal cells. Brain Res. 1982 Oct 14;249(2):315–331. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90066-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson D. M., Blitzer R. D., Landau E. M. An analysis of the depolarization produced in guinea-pig hippocampus by cholinergic receptor stimulation. J Physiol. 1988 Oct;404:479–496. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Selyanko A. A. Membrane currents underlying the cholinergic slow excitatory post-synaptic potential in the rat sympathetic ganglion. J Physiol. 1985 Aug;365:365–387. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Selyanko A. A. Two components of muscarine-sensitive membrane current in rat sympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:335–363. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsen J., Heimer L. A correlated light and electron microscopic immunocytochemical study of cholinergic terminals and neurons in the rat amygdaloid body with special emphasis on the basolateral amygdaloid nucleus. J Comp Neurol. 1986 Feb 1;244(1):121–136. doi: 10.1002/cne.902440110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsen J., Heimer L. The basolateral amygdaloid complex as a cortical-like structure. Brain Res. 1988 Feb 16;441(1-2):377–380. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)91418-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsen J. Immunocytochemical localization of glutamate decarboxylase in the rat basolateral amygdaloid nucleus, with special reference to GABAergic innervation of amygdalostriatal projection neurons. J Comp Neurol. 1988 Jul 22;273(4):513–526. doi: 10.1002/cne.902730407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsen J. New perspectives on the functional anatomical organization of the basolateral amygdala. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl. 1989;122:1–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1989.tb08018.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsen J., Záborszky L., Heimer L. Cholinergic projections from the basal forebrain to the basolateral amygdaloid complex: a combined retrograde fluorescent and immunohistochemical study. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Apr 8;234(2):155–167. doi: 10.1002/cne.902340203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassell J. F., McLachlan E. M. Muscarinic agonists block five different potassium conductances in guinea-pig sympathetic neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Jun;91(2):259–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb10279.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole A. E., Nicoll R. A. Characterization of a slow cholinergic post-synaptic potential recorded in vitro from rat hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Physiol. 1984 Jul;352:173–188. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constanti A., Sim J. A. Calcium-dependent potassium conductance in guinea-pig olfactory cortex neurones in vitro. J Physiol. 1987 Jun;387:173–194. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodd J., Dingledine R., Kelly J. S. The excitatory action of acetylcholine on hippocampal neurones of the guinea pig and rat maintained in vitro. Brain Res. 1981 Feb 23;207(1):109–127. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodt H. U., Misgeld U. Muscarinic slow excitation and muscarinic inhibition of synaptic transmission in the rat neostriatum. J Physiol. 1986 Nov;380:593–608. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutar P., Nicoll R. A. Classification of muscarinic responses in hippocampus in terms of receptor subtypes and second-messenger systems: electrophysiological studies in vitro. J Neurosci. 1988 Nov;8(11):4214–4224. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-11-04214.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emson P. C., Paxinos G., Le Gal La Salle G., Ben-Ari Y., Silver A. Choline acetyltransferase and acetylcholinesterase containing projections from the basal forebrain to the amygdaloid complex of the rat. Brain Res. 1979 Apr 13;165(2):271–282. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90559-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galligan J. J., North R. A., Tokimasa T. Muscarinic agonists and potassium currents in guinea-pig myenteric neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Jan;96(1):193–203. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11800.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gean P. W., Shinnick-Gallagher P. The transient potassium current, the A-current, is involved in spike frequency adaptation in rat amygdala neurons. Brain Res. 1989 Feb 20;480(1-2):160–169. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)91578-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gloor P., Olivier A., Quesney L. F., Andermann F., Horowitz S. The role of the limbic system in experiential phenomena of temporal lobe epilepsy. Ann Neurol. 1982 Aug;12(2):129–144. doi: 10.1002/ana.410120203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene R. W., Gerber U., McCarley R. W. Cholinergic activation of medial pontine reticular formation neurons in vitro. Brain Res. 1989 Jan 2;476(1):154–159. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)91549-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gähwiler B. H., Brown D. A. Muscarine affects calcium-currents in rat hippocampal pyramidal cells in vitro. Neurosci Lett. 1987 May 19;76(3):301–306. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90419-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas H. L. Cholinergic disinhibition in hippocampal slices of the rat. Brain Res. 1982 Feb 4;233(1):200–204. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90942-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliwell J. V., Adams P. R. Voltage-clamp analysis of muscarinic excitation in hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. 1982 Oct 28;250(1):71–92. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90954-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasuo H., Gallagher J. P., Shinnick-Gallagher P. Disinhibition in the rat septum mediated by M1 muscarinic receptors. Brain Res. 1988 Jan 12;438(1-2):323–327. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)91356-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellendall R. P., Godfrey D. A., Ross C. D., Armstrong D. M., Price J. L. The distribution of choline acetyltransferase in the rat amygdaloid complex and adjacent cortical areas, as determined by quantitative micro-assay and immunohistochemistry. J Comp Neurol. 1986 Jul 22;249(4):486–498. doi: 10.1002/cne.902490405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hounsgaard J. Presynaptic inhibitory action of acetylcholine in area CA1 of the hippocampus. Exp Neurol. 1978 Dec;62(3):787–797. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(78)90284-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa T., Hirata Y. Organization of choline acetyltransferase-containing structures in the forebrain of the rat. J Neurosci. 1986 Jan;6(1):281–292. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-01-00281.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knöpfel T., Vranesic I., Gähwiler B. H., Brown D. A. Muscarinic and beta-adrenergic depression of the slow Ca2(+)-activated potassium conductance in hippocampal CA3 pyramidal cells is not mediated by a reduction of depolarization-induced cytosolic Ca2+ transients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4083–4087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacaille J. C., Schwartzkroin P. A. Stratum lacunosum-moleculare interneurons of hippocampal CA1 region. I. Intracellular response characteristics, synaptic responses, and morphology. J Neurosci. 1988 Apr;8(4):1400–1410. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-04-01400.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster B., Nicoll R. A. Properties of two calcium-activated hyperpolarizations in rat hippocampal neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Aug;389:187–203. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis P. R., Shute C. C. The cholinergic limbic system: projections to hippocampal formation, medial cortex, nuclei of the ascending cholinergic reticular system, and the subfornical organ and supra-optic crest. Brain. 1967 Sep;90(3):521–540. doi: 10.1093/brain/90.3.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison D. V., Lancaster B., Nicoll R. A. Voltage clamp analysis of cholinergic action in the hippocampus. J Neurosci. 1987 Mar;7(3):733–741. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-03-00733.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison D. V., Nicoll R. A. Control of the repetitive discharge of rat CA 1 pyramidal neurones in vitro. J Physiol. 1984 Sep;354:319–331. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick D. A., Prince D. A. Mechanisms of action of acetylcholine in the guinea-pig cerebral cortex in vitro. J Physiol. 1986 Jun;375:169–194. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald A. J. Immunohistochemical identification of gamma-aminobutyric acid-containing neurons in the rat basolateral amygdala. Neurosci Lett. 1985 Jan 21;53(2):203–207. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90186-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald A. J. Neuronal organization of the lateral and basolateral amygdaloid nuclei in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1984 Feb 1;222(4):589–606. doi: 10.1002/cne.902220410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald A. J. Neurons of the lateral and basolateral amygdaloid nuclei: a Golgi study in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1982 Dec 10;212(3):293–312. doi: 10.1002/cne.902120307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald A. J., Pearson J. C. Coexistence of GABA and peptide immunoreactivity in non-pyramidal neurons of the basolateral amygdala. Neurosci Lett. 1989 May 22;100(1-3):53–58. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90659-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mesulam M. M., Mufson E. J., Levey A. I., Wainer B. H. Cholinergic innervation of cortex by the basal forebrain: cytochemistry and cortical connections of the septal area, diagonal band nuclei, nucleus basalis (substantia innominata), and hypothalamus in the rhesus monkey. J Comp Neurol. 1983 Feb 20;214(2):170–197. doi: 10.1002/cne.902140206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millhouse O. E., DeOlmos J. Neuronal configurations in lateral and basolateral amygdala. Neuroscience. 1983 Dec;10(4):1269–1300. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90112-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misgeld U., Calabresi P., Dodt H. U. Muscarinic modulation of calcium dependent plateau potentials in rat neostriatal neurons. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Nov;407(5):482–487. doi: 10.1007/BF00657504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misgeld U., Müller W., Polder H. R. Potentiation and suppression by eserine of muscarinic synaptic transmission in the guinea-pig hippocampal slice. J Physiol. 1989 Feb;409:191–206. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita K., North R. A., Tokimasa T. Muscarinic presynaptic inhibition of synaptic transmission in myenteric plexus of guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1982 Dec;333:141–149. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W., Misgeld U. Slow cholinergic excitation of guinea pig hippocampal neurons is mediated by two muscarinic receptor subtypes. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Jun 18;67(2):107–112. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90381-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai T., Kimura H., Maeda T., McGeer P. L., Peng F., McGeer E. G. Cholinergic projections from the basal forebrain of rat to the amygdala. J Neurosci. 1982 Apr;2(4):513–520. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.02-04-00513.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitecka L., Ben-Ari Y. Distribution of GABA-like immunoreactivity in the rat amygdaloid complex. J Comp Neurol. 1987 Dec 1;266(1):45–55. doi: 10.1002/cne.902660105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitecka L., Frotscher M. Organization and synaptic interconnections of GABAergic and cholinergic elements in the rat amygdaloid nuclei: single- and double-immunolabeling studies. J Comp Neurol. 1989 Jan 15;279(3):470–488. doi: 10.1002/cne.902790311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Slack B. E., Surprenant A. Muscarinic M1 and M2 receptors mediate depolarization and presynaptic inhibition in guinea-pig enteric nervous system. J Physiol. 1985 Nov;368:435–452. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Tokimasa T. Depression of calcium-dependent potassium conductance of guinea-pig myenteric neurones by muscarinic agonists. J Physiol. 1983 Sep;342:253–266. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Tokimasa T. The time course of muscarinic depolarization of guinea-pig myenteric neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 May;82(1):85–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb16444.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitler T. A., Alger B. E. Activation of the pharmacologically defined M3 muscarinic receptor depolarizes hippocampal pyramidal cells. Brain Res. 1990 Nov 26;534(1-2):257–262. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90137-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarter M., Markowitsch H. J. The amygdala's role in human mnemonic processing. Cortex. 1985 Mar;21(1):7–24. doi: 10.1016/s0010-9452(85)80013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satou M., Mori K., Tazawa Y., Takagi S. F. Interneurons mediating fast postsynaptic inhibition in pyriform cortex of the rabbit. J Neurophysiol. 1983 Jul;50(1):89–101. doi: 10.1152/jn.1983.50.1.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharfman H. E., Schwartzkroin P. A. Electrophysiology of morphologically identified mossy cells of the dentate hilus recorded in guinea pig hippocampal slices. J Neurosci. 1988 Oct;8(10):3812–3821. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-10-03812.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal M. Synaptic activation of a cholinergic receptor in rat hippocampus. Brain Res. 1988 Jun 14;452(1-2):79–86. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storm J. F. An after-hyperpolarization of medium duration in rat hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Physiol. 1989 Feb;409:171–190. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentino R. J., Dingledine R. Presynaptic inhibitory effect of acetylcholine in the hippocampus. J Neurosci. 1981 Jul;1(7):784–792. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.01-07-00784.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanke E., Ferroni A., Malgaroli A., Ambrosini A., Pozzan T., Meldolesi J. Activation of a muscarinic receptor selectively inhibits a rapidly inactivated Ca2+ current in rat sympathetic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4313–4317. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson A., Alger B. E. Characterization of an early afterhyperpolarization after a brief train of action potentials in rat hippocampal neurons in vitro. J Neurophysiol. 1990 Jan;63(1):72–81. doi: 10.1152/jn.1990.63.1.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolf N. J., Butcher L. L. Cholinergic projections to the basolateral amygdala: a combined Evans Blue and acetylcholinesterase analysis. Brain Res Bull. 1982 Jun;8(6):751–763. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(82)90102-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


