Abstract
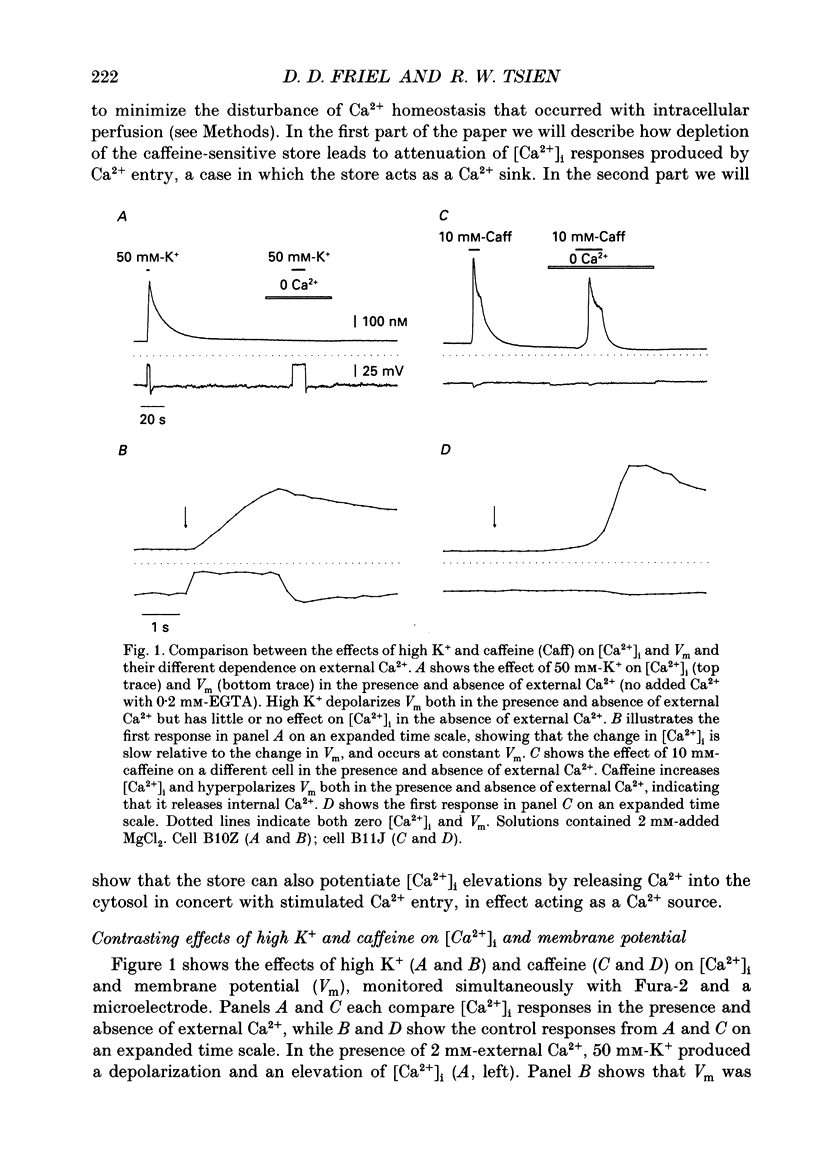
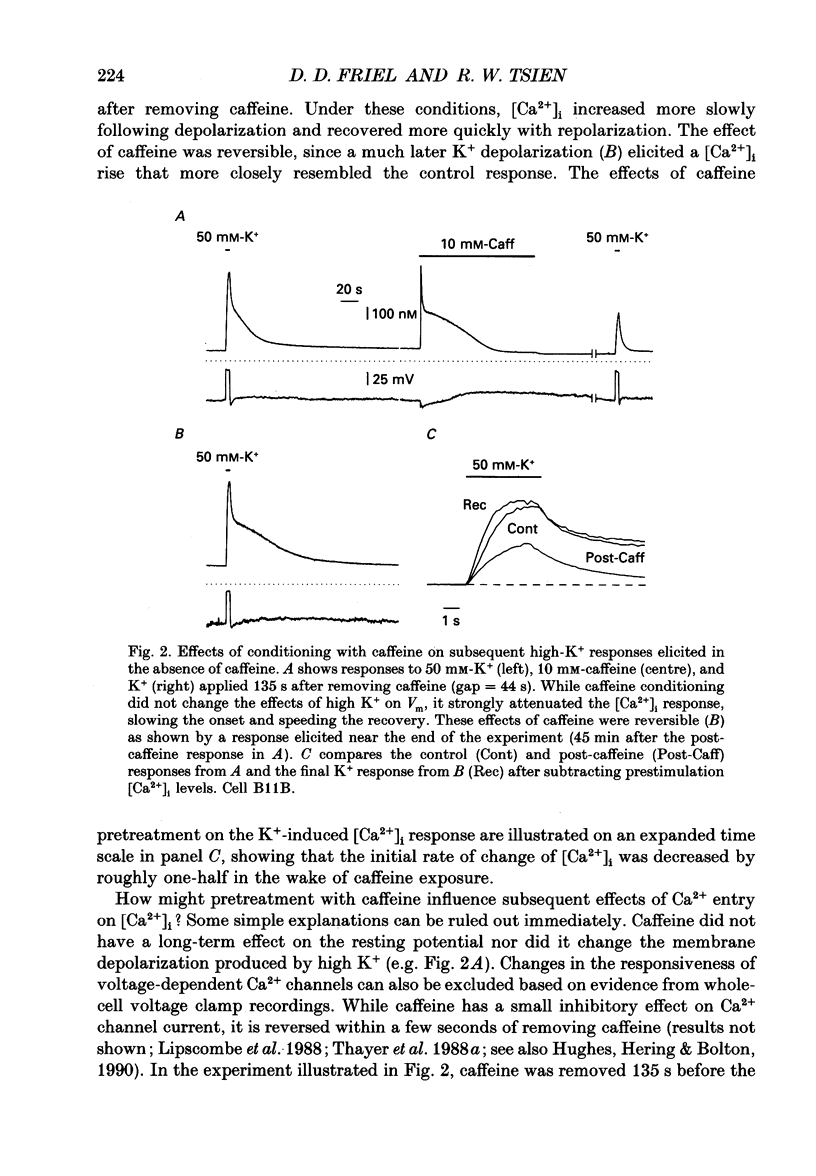
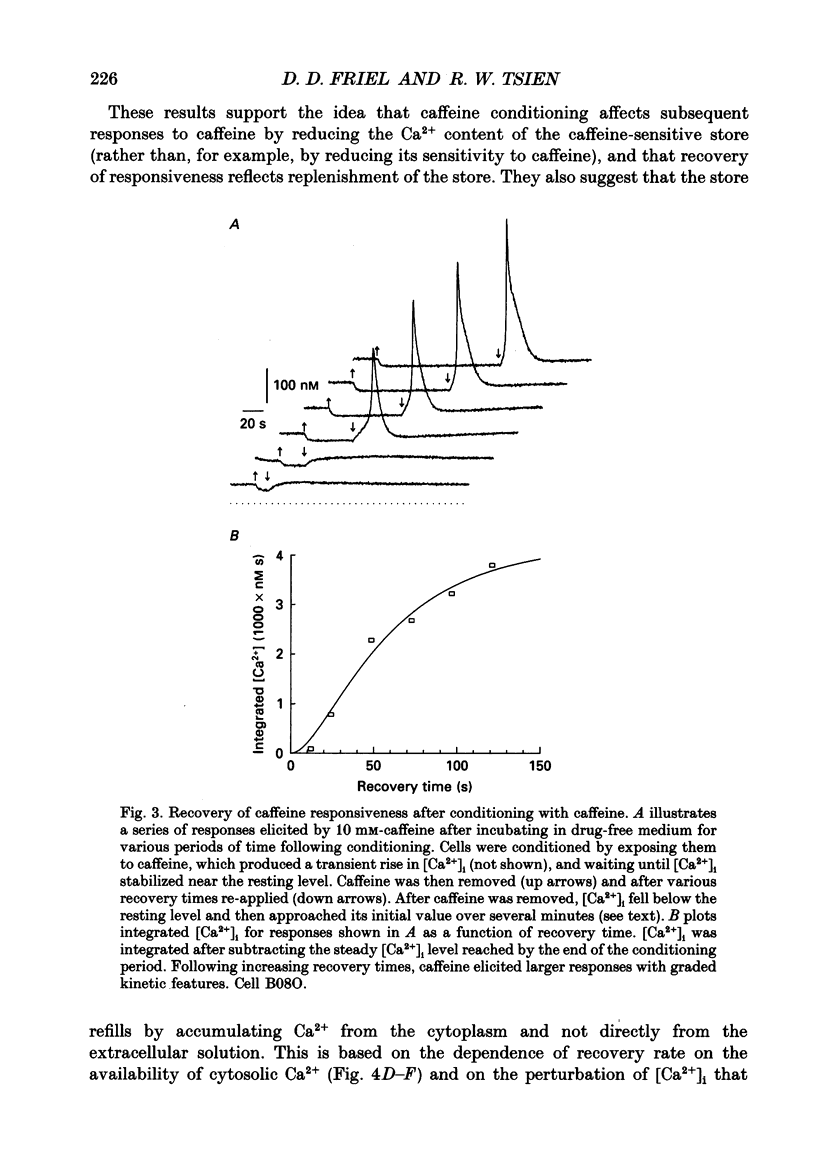
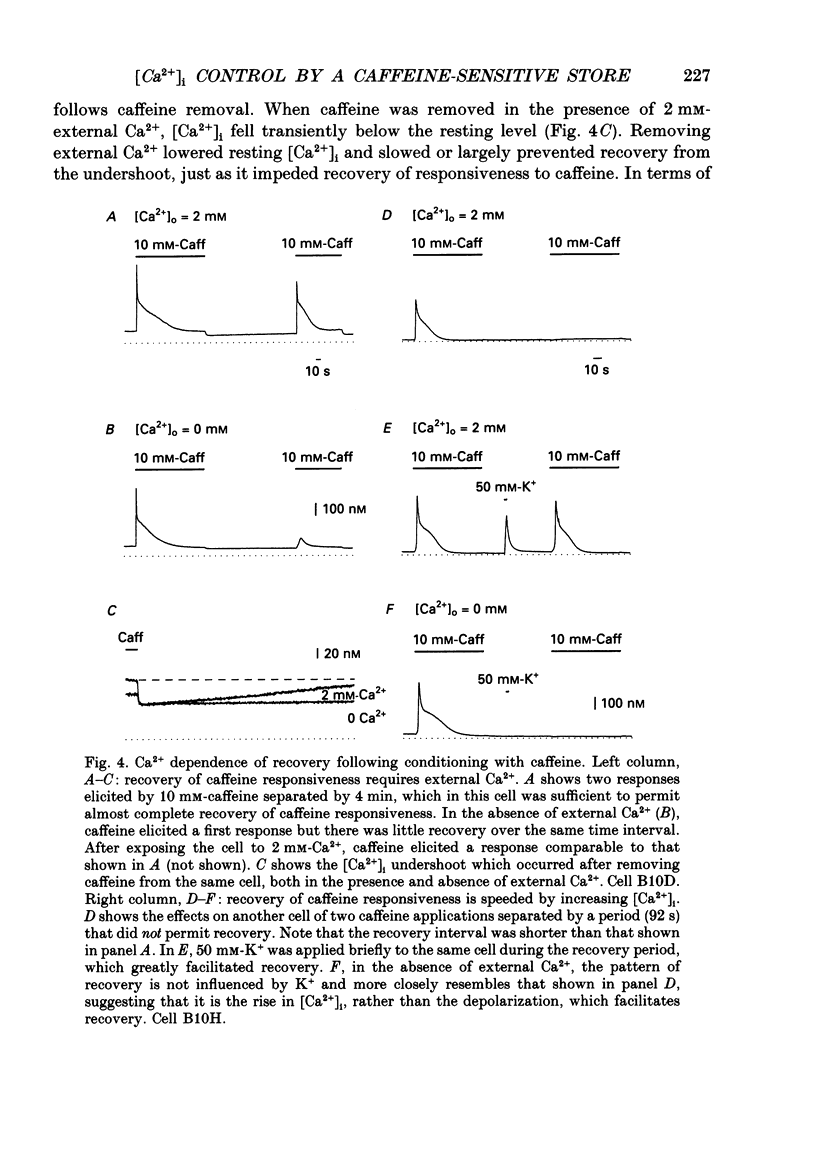
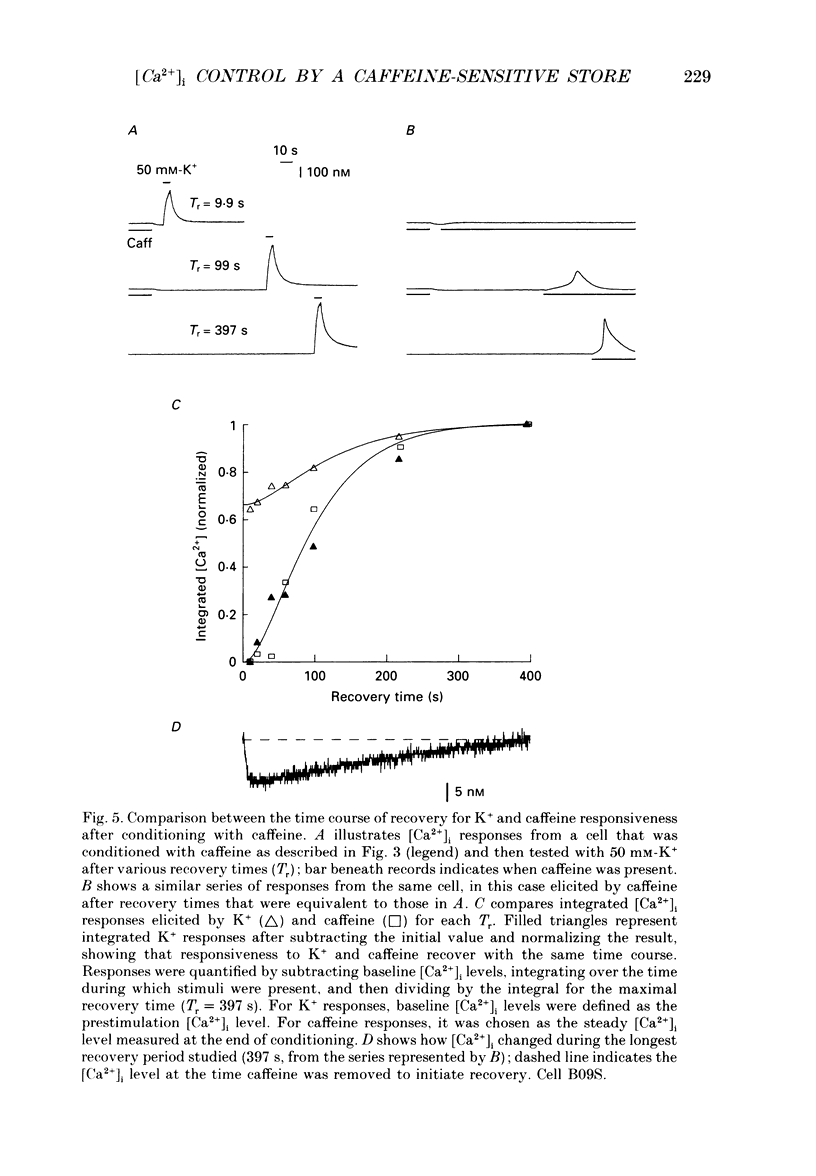
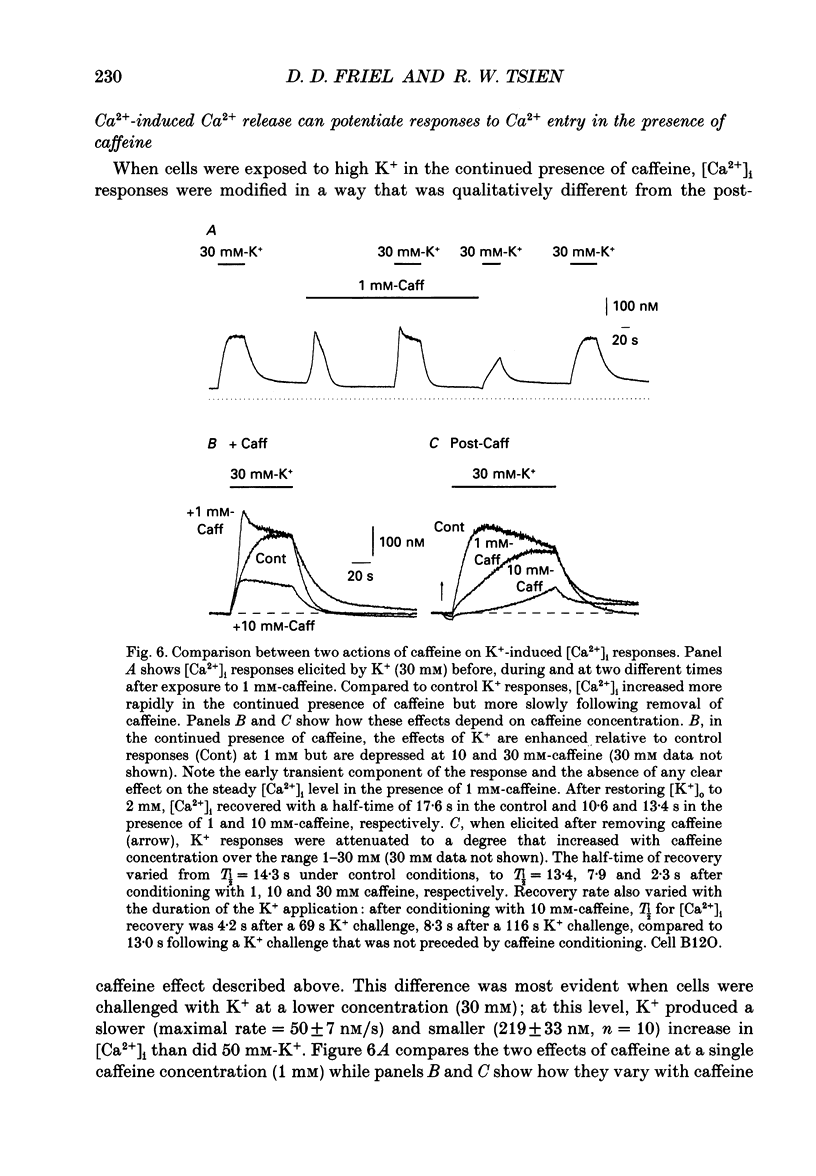
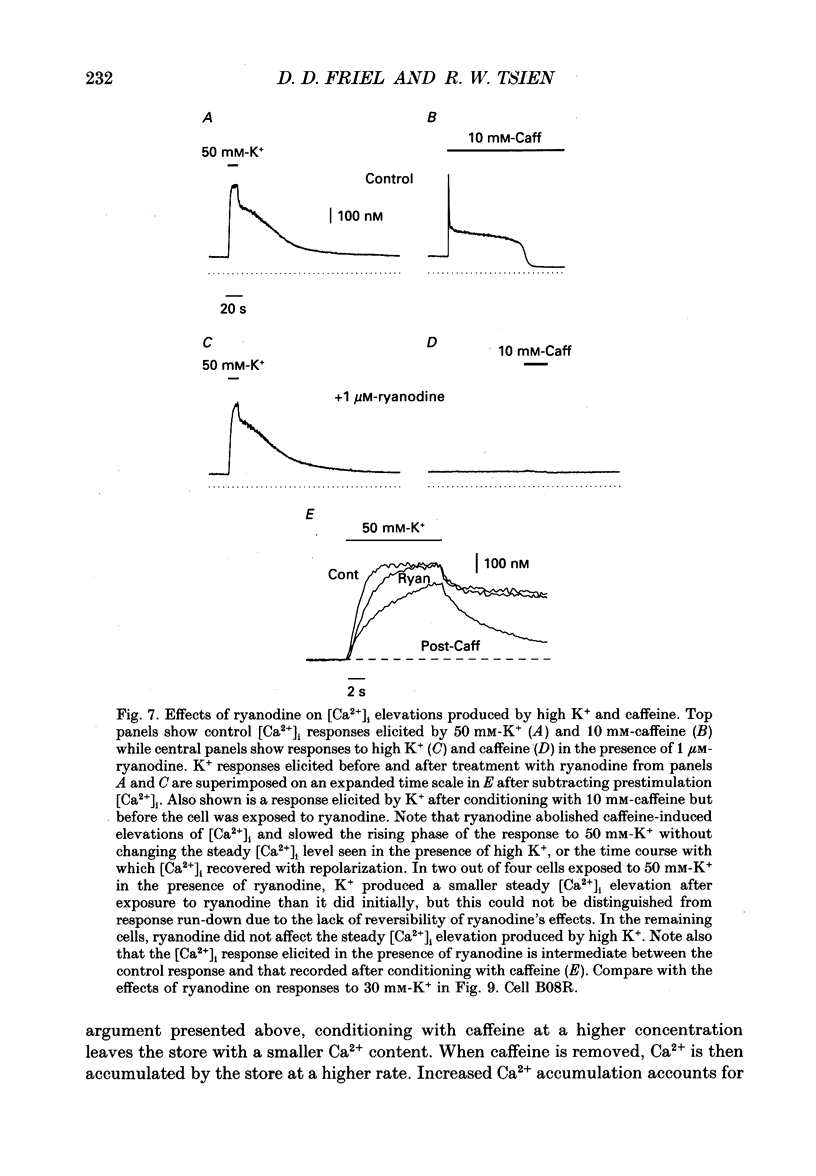
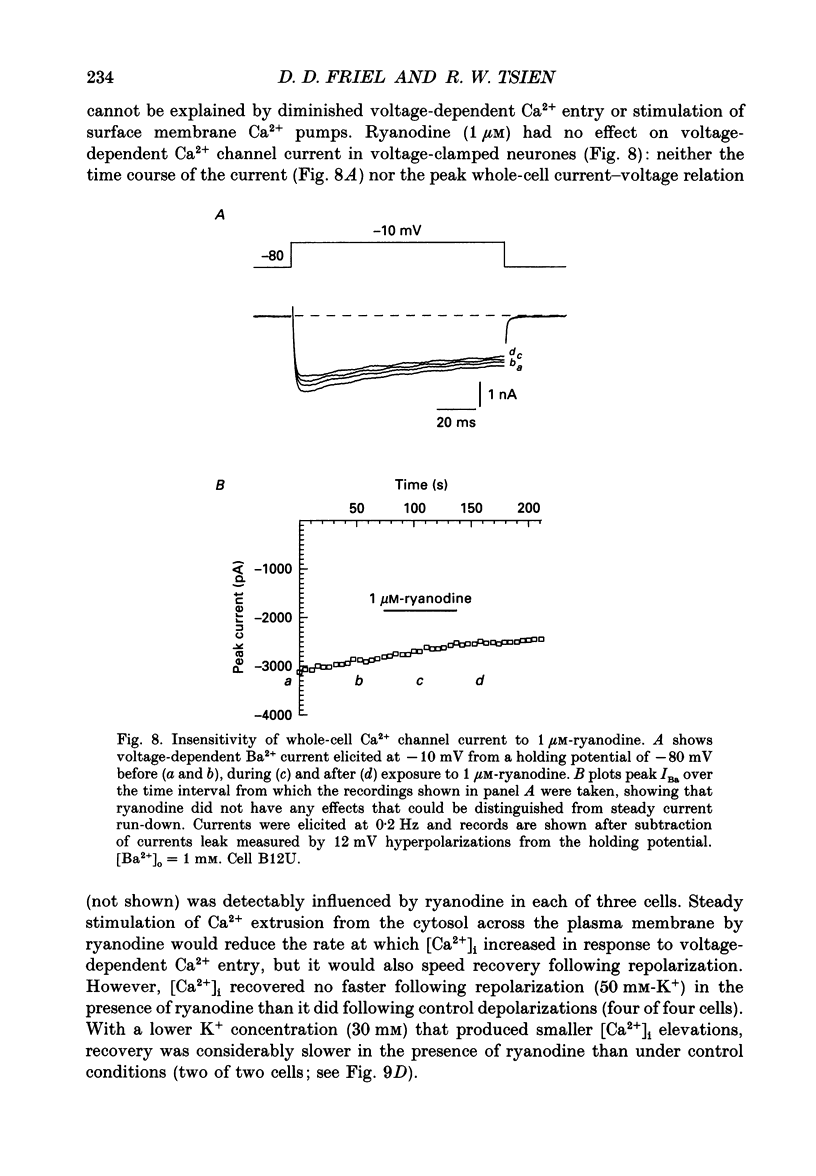
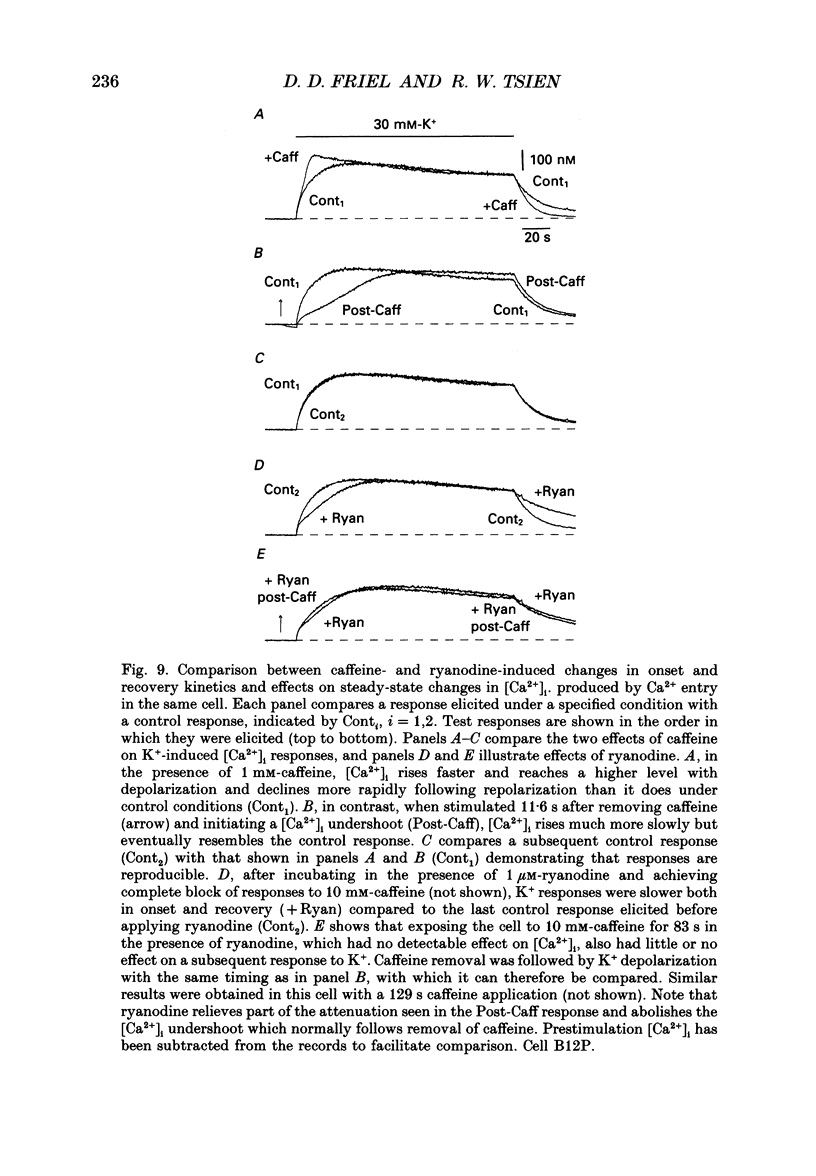
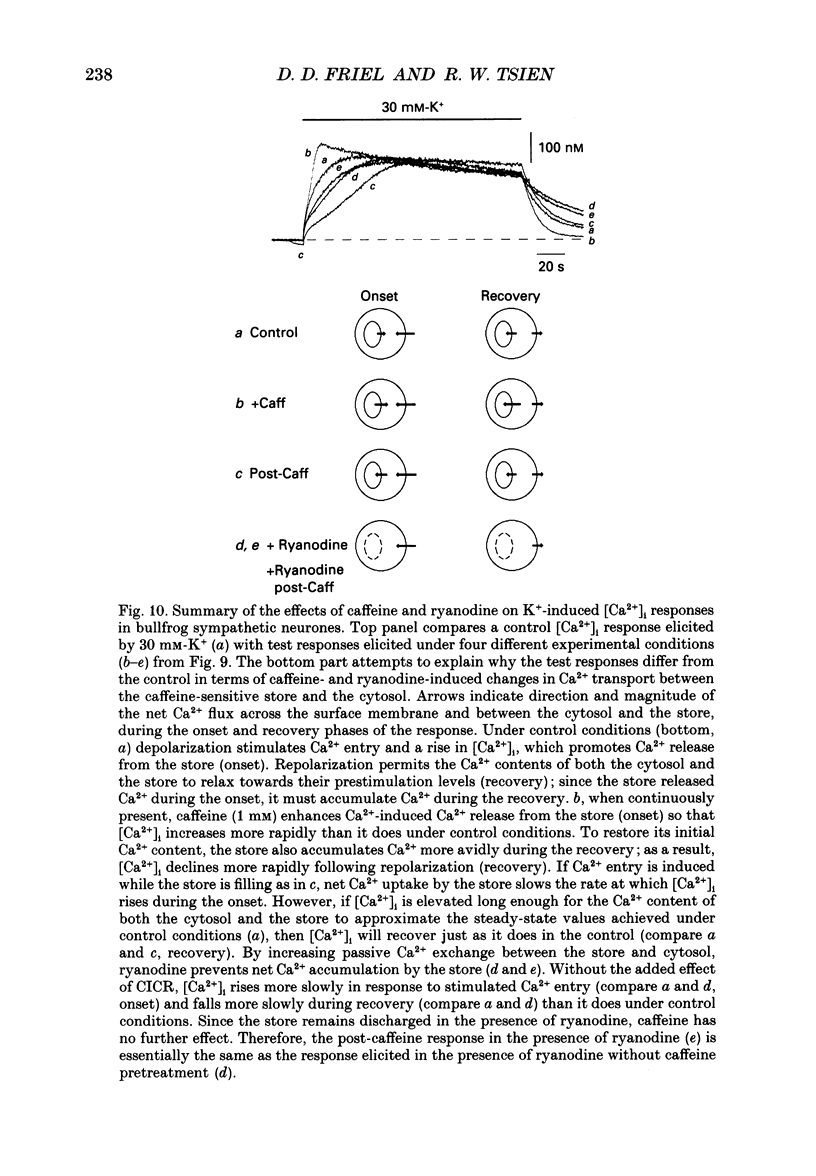
1. We studied how in changes in cytosolic free Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) produced by voltage-dependent Ca2+ entry are influenced by a caffeine-sensitive Ca2+ store in bullfrog sympathetic neurones. Ca2+ influx was elicited by K+ depolarization and the store was manipulated with either caffeine or ryanodine. 2. For a time after discharging the store with caffeine and switching to a caffeine-free medium: (a) [Ca2+]i was depressed by up to 40-50 nM below the resting level, (b) caffeine responsiveness was diminished, and (c) brief K+ applications elicited [Ca2+]i responses with slower onset and faster recovery than controls. These effects were more pronounced as the conditioning caffeine concentration was increased over the range 1-30 mM. 3. [Ca2+]i, caffeine and K+ responsiveness recovered in parallel with a half-time of approximately 2 min. Recovery required external Ca2+ and was speeded by increasing the availability of cytosolic Ca2+, suggesting that it reflected replenishment of the store at the expense of cytosolic Ca2+. 4. During recovery, Ca2+ entry stimulated by depolarization had the least effect on [Ca2+]i when the store was filling most rapidly. This suggests that the effect of Ca2+ entry on [Ca2+]i is modified, at least in part, because some of the Ca2+ which enters the cytosol during stimulation is taken up by the store as it refills. 5. Further experiments were carried out to investigate whether the store can also release Ca2+ in response to stimulated Ca2+ entry. In the continued presence of caffeine at a low concentration (1 mM), high K+ elicited a faster and larger [Ca2+]i response compared to controls; at higher concentrations of caffeine (10 and 30 mM) responses were depressed. 6. Ryanodine (1 microM) reduced the rate at which [Ca2+]i increased with Ca2+ entry, but not to the degree observed after discharging the store. At this concentration, ryanodine completely blocked responses to caffeine but had no detectable effect on Ca2+ channel current or the steady [Ca2+]i level achieved during depolarization. 7. We propose that, depending on its Ca2+ content, the caffeine-sensitive store can either attenuate or potentiate responses to depolarization. When depleted and in the process of refilling, the store reduces the impact of Ca2+ entry as some of the Ca2+ entering the cytosol during stimulation is captured by the store.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R., Jones S. W., Pennefather P., Brown D. A., Koch C., Lancaster B. Slow synaptic transmission in frog sympathetic ganglia. J Exp Biol. 1986 Sep;124:259–285. doi: 10.1242/jeb.124.1.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akaike N., Sadoshima J. Caffeine affects four different ionic currents in the bull-frog sympathetic neurone. J Physiol. 1989 May;412:221–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezprozvanny I., Watras J., Ehrlich B. E. Bell-shaped calcium-response curves of Ins(1,4,5)P3- and calcium-gated channels from endoplasmic reticulum of cerebellum. Nature. 1991 Jun 27;351(6329):751–754. doi: 10.1038/351751a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carafoli E. Intracellular calcium homeostasis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:395–433. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo M., Tanaka M., Ogawa Y. Calcium induced release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of skinned skeletal muscle fibres. Nature. 1970 Oct 3;228(5266):34–36. doi: 10.1038/228034a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A. Calcium-induced release of calcium from the cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jul;245(1):C1–14. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1983.245.1.C1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fill M., Coronado R. Ryanodine receptor channel of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Oct;11(10):453–457. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90198-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford L. E., Podolsky R. J. Regenerative calcium release within muscle cells. Science. 1970 Jan 2;167(3914):58–59. doi: 10.1126/science.167.3914.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friel D. D., Bean B. P. Two ATP-activated conductances in bullfrog atrial cells. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Jan;91(1):1–27. doi: 10.1085/jgp.91.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galione A., Lee H. C., Busa W. B. Ca(2+)-induced Ca2+ release in sea urchin egg homogenates: modulation by cyclic ADP-ribose. Science. 1991 Sep 6;253(5024):1143–1146. doi: 10.1126/science.1909457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Cruz A., Sala F., Adams P. R. Subcellular calcium transients visualized by confocal microscopy in a voltage-clamped vertebrate neuron. Science. 1990 Feb 16;247(4944):858–862. doi: 10.1126/science.2154851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashida H., Brown D. A. Membrane current responses to intracellular injections of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate and inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate in NG108-15 hybrid cells. FEBS Lett. 1986 Nov 24;208(2):283–286. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81033-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes A. D., Hering S., Bolton T. B. The action of caffeine on inward barium current through voltage-dependent calcium channels in single rabbit ear artery cells. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Jun;416(4):462–466. doi: 10.1007/BF00370755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino M. Calcium-induced calcium release mechanism in guinea pig taenia caeci. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Aug;94(2):363–383. doi: 10.1085/jgp.94.2.363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa T., Smith J. S., Coronado R., Campbell K. P. Purified ryanodine receptor from skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum is the Ca2+-permeable pore of the calcium release channel. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16636–16643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. W., Marks T. N. Calcium currents in bullfrog sympathetic neurons. I. Activation kinetics and pharmacology. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Jul;94(1):151–167. doi: 10.1085/jgp.94.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein M. G., Simon B. J., Schneider M. F. Effects of caffeine on calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum in frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1990 Jun;425:599–626. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuba K., Nishi S. Rhythmic hyperpolarizations and depolarization of sympathetic ganglion cells induced by caffeine. J Neurophysiol. 1976 May;39(3):547–563. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.3.547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuba K. Release of calcium ions linked to the activation of potassium conductance in a caffeine-treated sympathetic neurone. J Physiol. 1980 Jan;298:251–269. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai F. A., Erickson H. P., Rousseau E., Liu Q. Y., Meissner G. Purification and reconstitution of the calcium release channel from skeletal muscle. Nature. 1988 Jan 28;331(6154):315–319. doi: 10.1038/331315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipscombe D., Madison D. V., Poenie M., Reuter H., Tsien R. W., Tsien R. Y. Imaging of cytosolic Ca2+ transients arising from Ca2+ stores and Ca2+ channels in sympathetic neurons. Neuron. 1988 Jul;1(5):355–365. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90185-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mains R. E., Patterson P. H. Primary cultures of dissociated sympathetic neurons. I. Establishment of long-term growth in culture and studies of differentiated properties. J Cell Biol. 1973 Nov;59(2 Pt 1):329–345. doi: 10.1083/jcb.59.2.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson P. S., Kim Y. K., Valdivia H., Knudson C. M., Takekura H., Franzini-Armstrong C., Coronado R., Campbell K. P. The brain ryanodine receptor: a caffeine-sensitive calcium release channel. Neuron. 1991 Jul;7(1):17–25. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90070-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. J. Calcium signalling in neurons. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Oct;11(10):415–419. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90191-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagasaki K., Kasai M. Channel selectivity and gating specificity of calcium-induced calcium release channel in isolated sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biochem. 1984 Dec;96(6):1769–1775. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neering I. R., McBurney R. N. Role for microsomal Ca storage in mammalian neurones? Nature. 1984 May 10;309(5964):158–160. doi: 10.1038/309158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nohmi M., Kuba K., Ogura A., Kudo Y. Measurement of intracellular Ca2+ in the bullfrog sympathetic ganglion cells using fura-2 fluorescence. Brain Res. 1988 Jan 12;438(1-2):175–181. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)91336-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaffinger P. J., Leibowitz M. D., Subers E. M., Nathanson N. M., Almers W., Hille B. Agonists that suppress M-current elicit phosphoinositide turnover and Ca2+ transients, but these events do not explain M-current suppression. Neuron. 1988 Aug;1(6):477–484. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90178-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau E., Ladine J., Liu Q. Y., Meissner G. Activation of the Ca2+ release channel of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum by caffeine and related compounds. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Nov 15;267(1):75–86. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau E., Smith J. S., Henderson J. S., Meissner G. Single channel and 45Ca2+ flux measurements of the cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium channel. Biophys J. 1986 Nov;50(5):1009–1014. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83543-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau E., Smith J. S., Meissner G. Ryanodine modifies conductance and gating behavior of single Ca2+ release channel. Am J Physiol. 1987 Sep;253(3 Pt 1):C364–C368. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.3.C364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sah P., McLachlan E. M. Ca(2+)-activated K+ currents underlying the afterhyperpolarization in guinea pig vagal neurons: a role for Ca(2+)-activated Ca2+ release. Neuron. 1991 Aug;7(2):257–264. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90264-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. J., MacDermott A. B., Weight F. F. Detection of intracellular Ca2+ transients in sympathetic neurones using arsenazo III. 1983 Jul 28-Aug 3Nature. 304(5924):350–352. doi: 10.1038/304350a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutko J. L., Ito K., Kenyon J. L. Ryanodine: a modifier of sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium release in striated muscle. Fed Proc. 1985 Dec;44(15):2984–2988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer S. A., Hirning L. D., Miller R. J. The role of caffeine-sensitive calcium stores in the regulation of the intracellular free calcium concentration in rat sympathetic neurons in vitro. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Nov;34(5):664–673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer S. A., Miller R. J. Regulation of the intracellular free calcium concentration in single rat dorsal root ganglion neurones in vitro. J Physiol. 1990 Jun;425:85–115. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer S. A., Perney T. M., Miller R. J. Regulation of calcium homeostasis in sensory neurons by bradykinin. J Neurosci. 1988 Nov;8(11):4089–4097. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-11-04089.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W., Tsien R. Y. Calcium channels, stores, and oscillations. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:715–760. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.003435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdivia H. H., Coronado R. Inhibition of dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channels by the plant alkaloid ryanodine. FEBS Lett. 1989 Feb 27;244(2):333–337. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80557-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


