Abstract
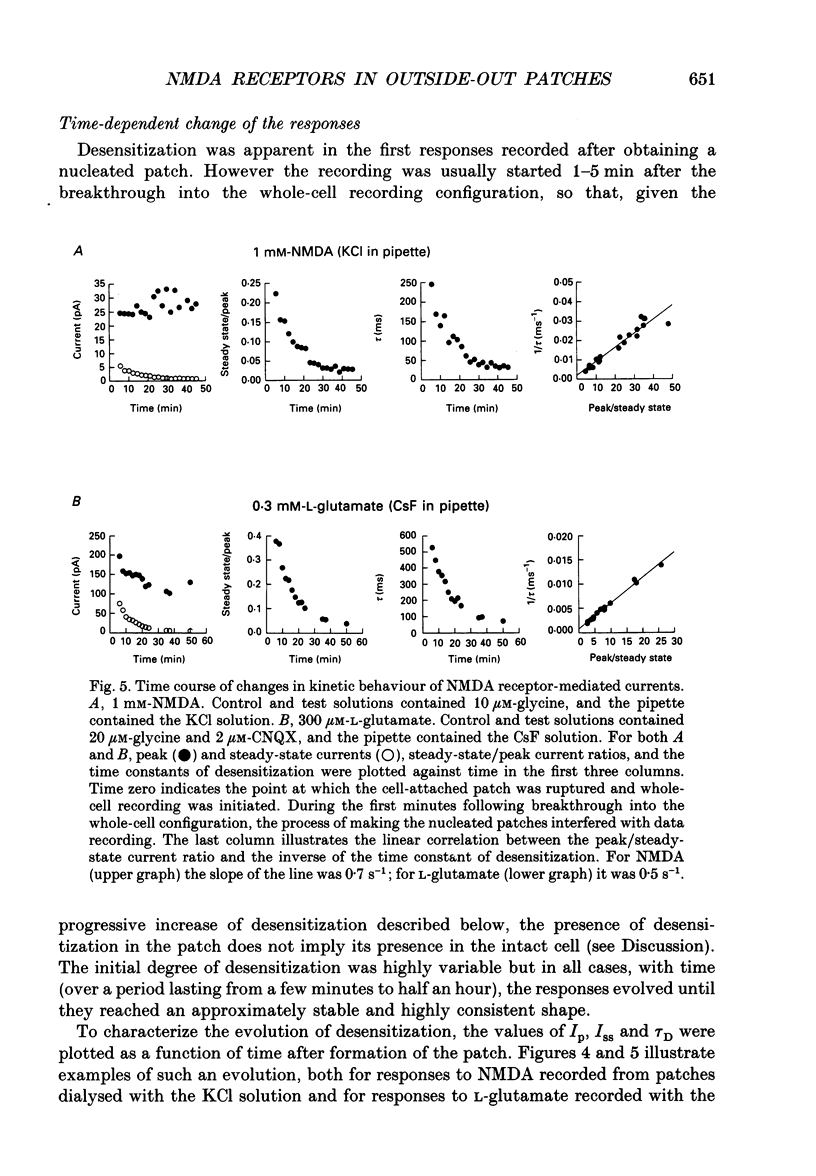
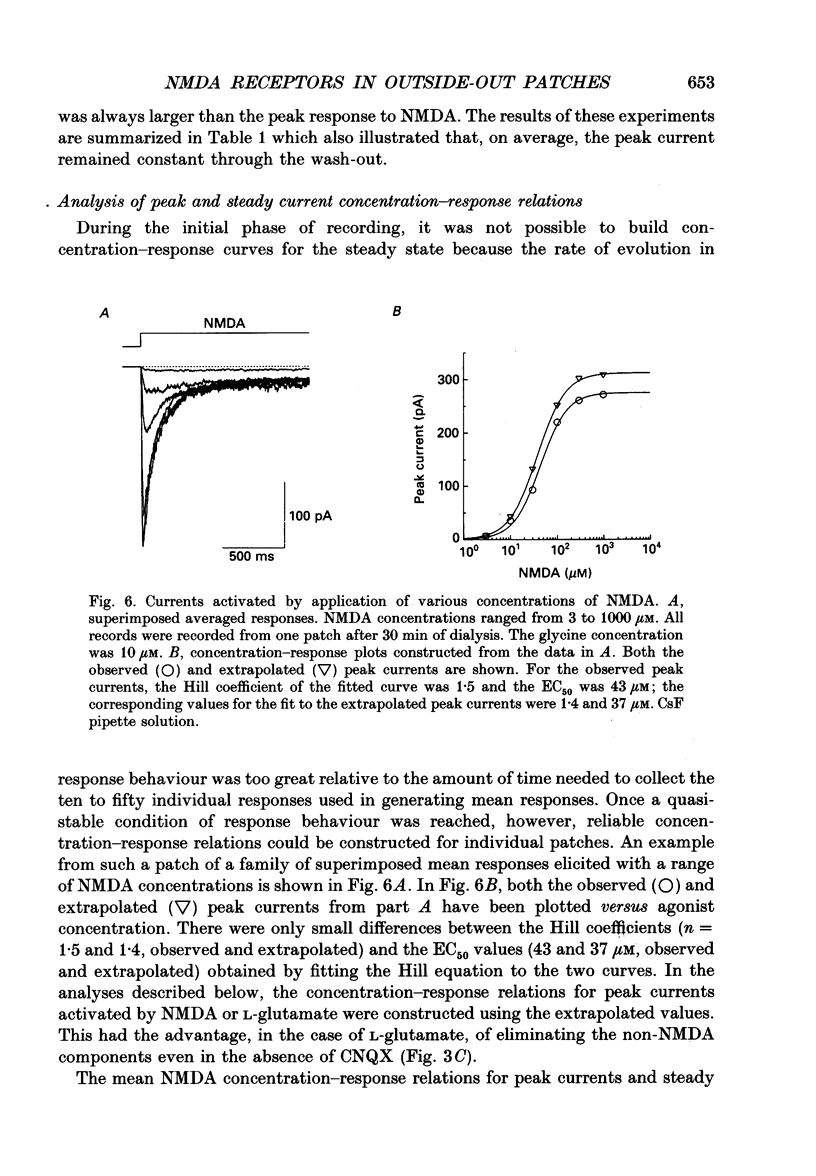
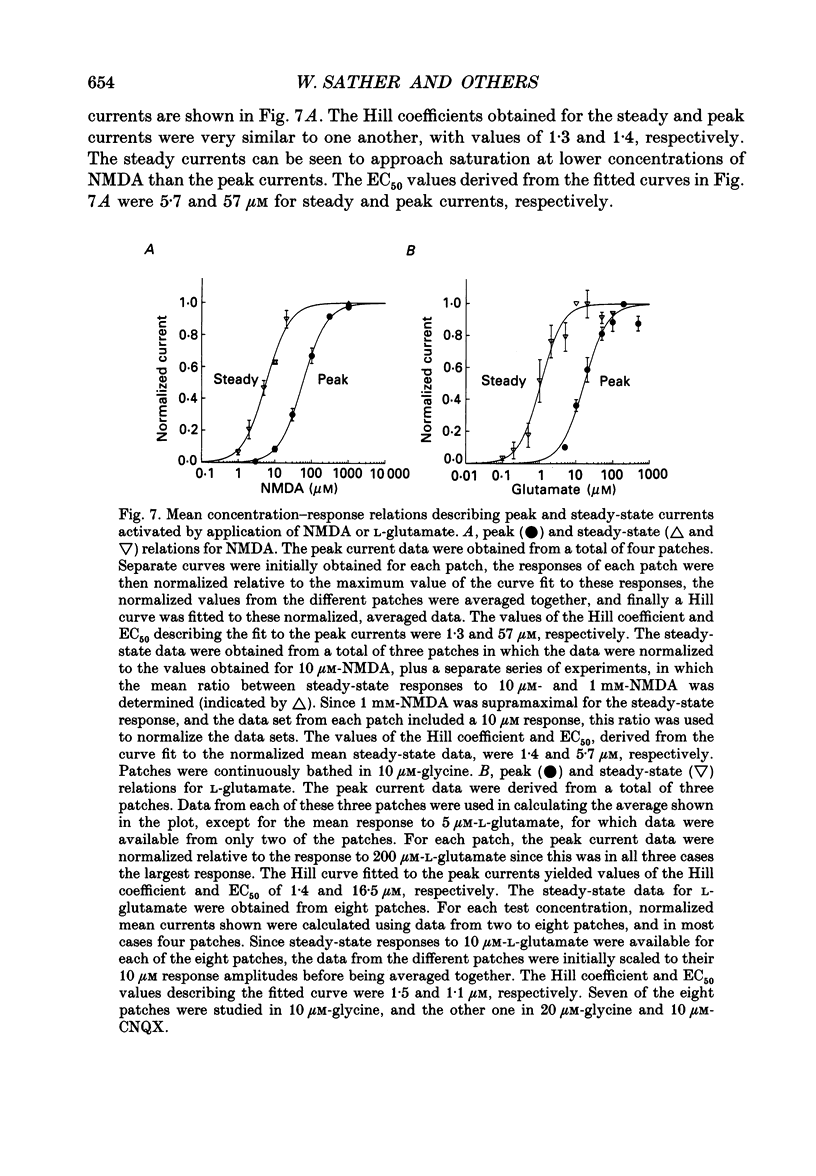
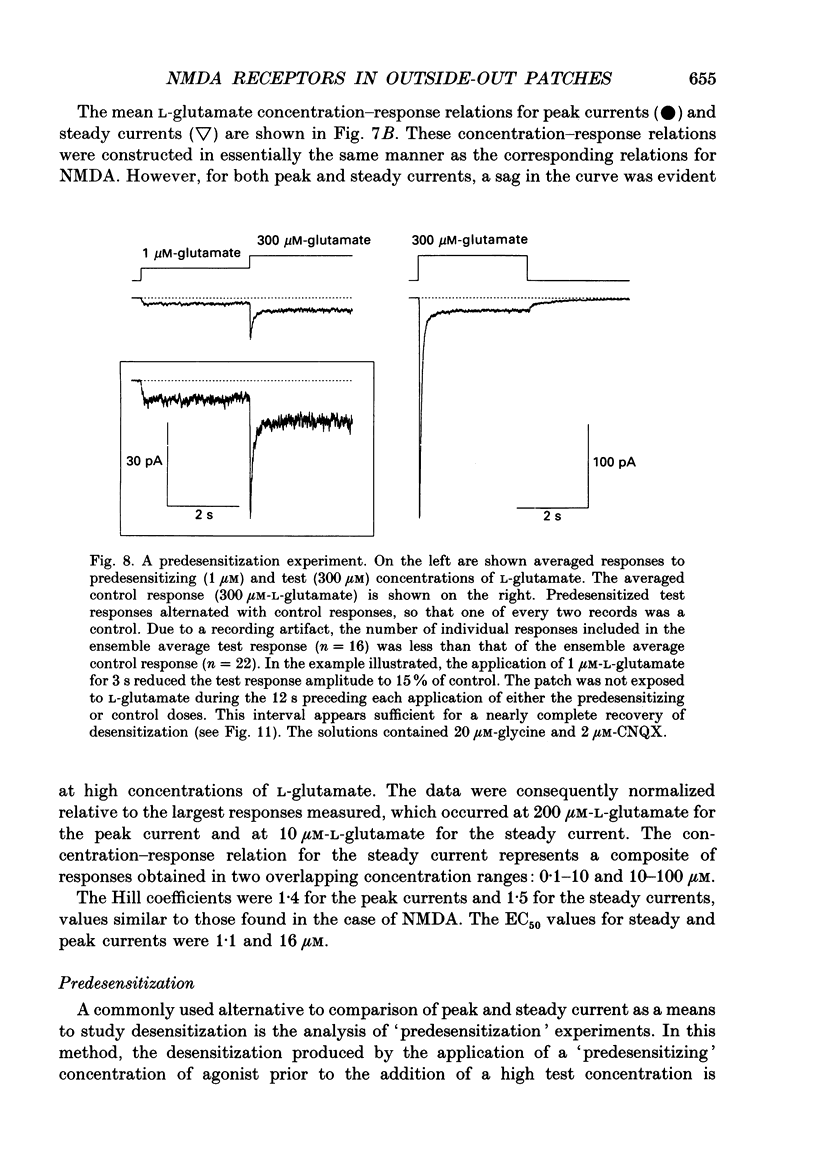
1. Activation and desensitization of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors were studied in large outside-out patches excised from cultured embryonic neurones dissociated from mouse forebrain. The patches were exposed to rapid changes of NMDA or L-glutamate concentrations in the presence of glycine at concentrations (10-20 microM) saturating the modulatory site of the NMDA receptor. 2. Immediately after formation of the patch the responses to NMDA and L-glutamate showed a slow and small desensitization, even with high concentrations of agonist. During the following hour, the peak response either decreased or remained relatively stable, but in all cases the desensitization increased and accelerated until it stabilized. In this 'stabilized' state, the desensitization produced by high concentrations of NMDA (1 mM) or L-glutamate (300 microM) had an exponential time course, with a time constant of about 30 ms. The ratio of the peak over the steady-state current was in the order of 40 for NMDA and about 30 for L-glutamate. 3. Concentration-response curves were built for the peak and the plateau responses, for NMDA and for L-glutamate. The comparison of these curves indicated that (i) the EC50 of the peak (K(app) was always higher than the EC50 of the plateau (Kss); (ii) the two EC50 values for NMDA (K(app) and Kss) were higher than those for L-glutamate; (iii) the Hill coefficient was close to 1.4 for each of the four curves. 4. The application of NMDA or L-glutamate at a low concentration for 3 s periods reduced the response to a subsequent application of the same agonist at a saturating concentration. The IC50 of this 'predesensitization', termed Kpre, was lower than the EC50 of the steady-state response, Kss. 5. The onset rates of desensitization increased with the concentration of agonist. The EC50 of this relation was close to the value of K(app). 6. The decay of the currents at the end of a 3 s application of agonist was usually well described by the sum of two exponentials both of which were faster for NMDA than for L-glutamate. 7. The recovery from desensitization after a long (3 s) pulse of agonist was approximately exponential, with a time constant of about 0.5 s for NMDA and about 3.5 s for L-glutamate.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




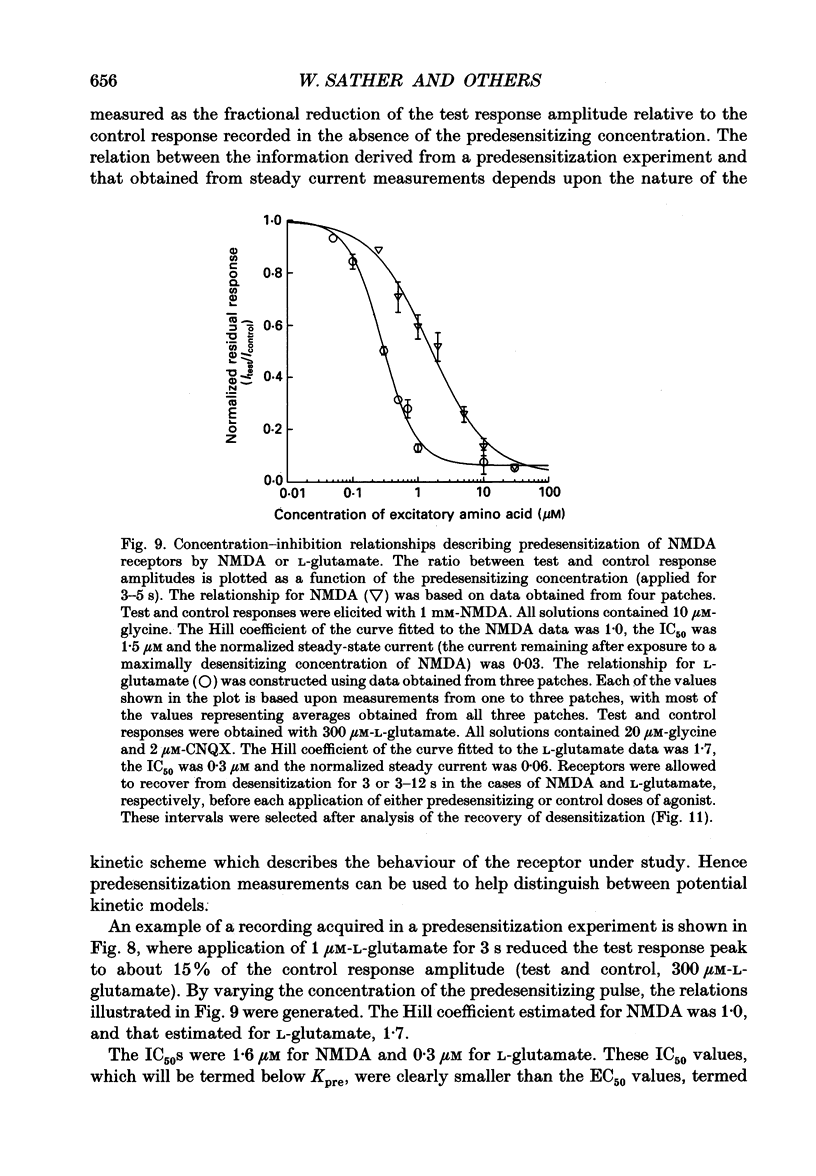
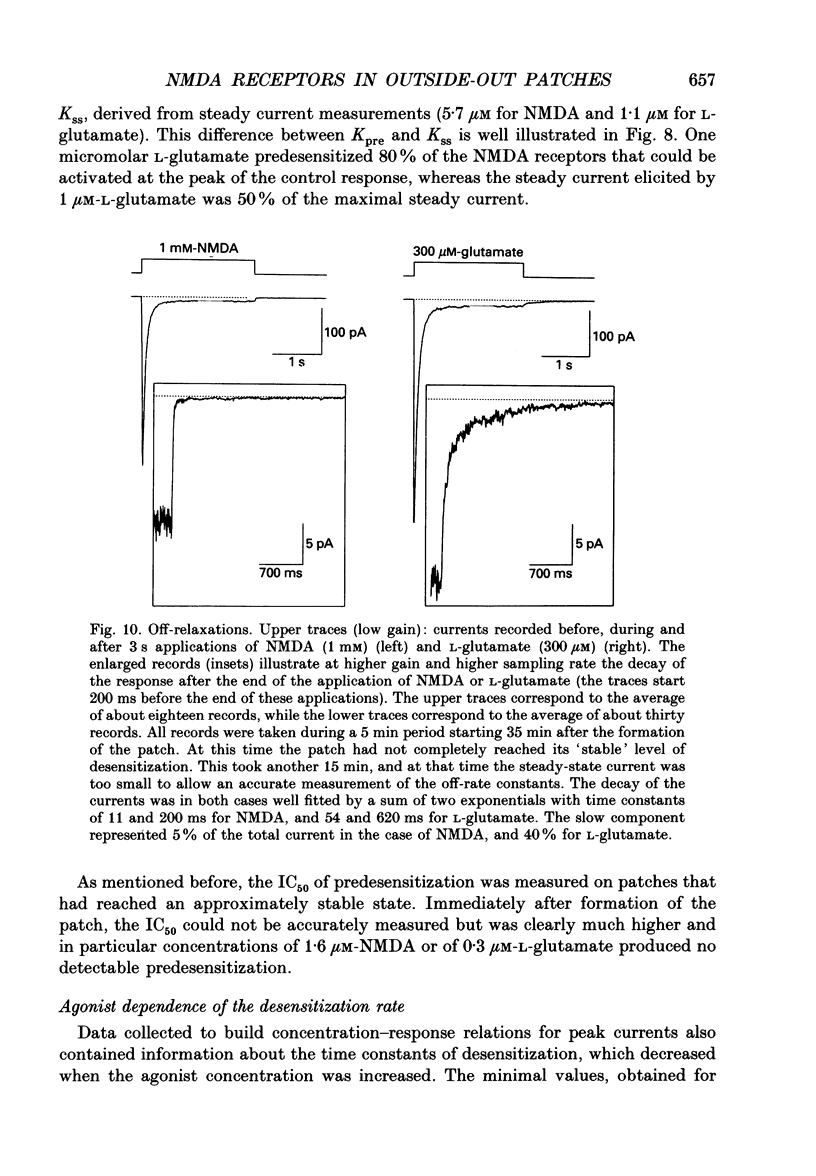

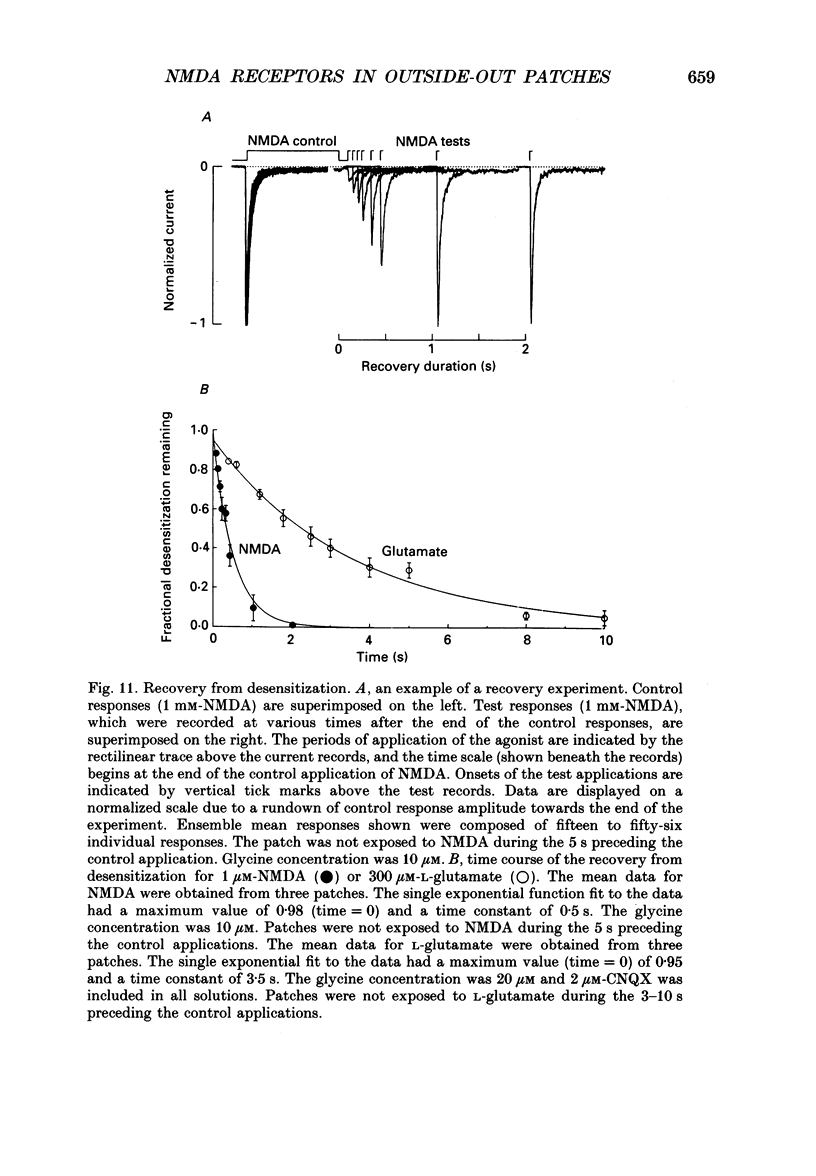




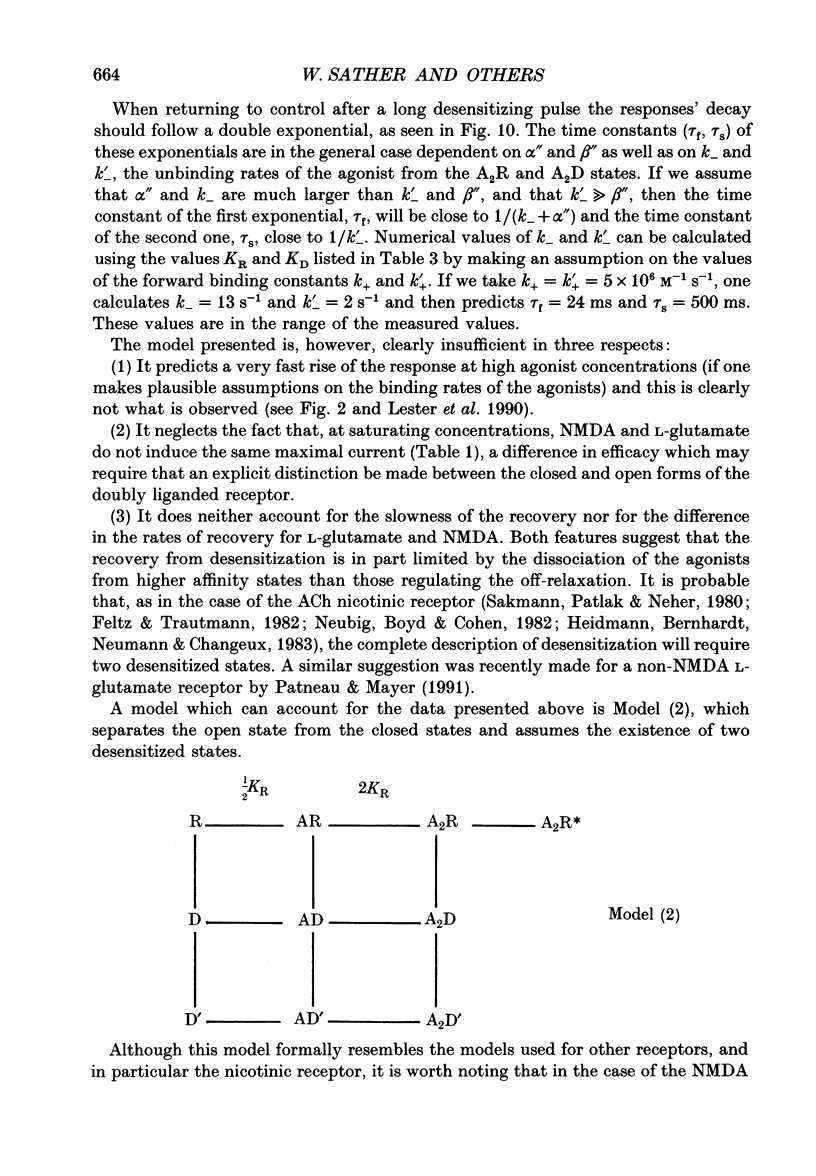








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ascher P., Bregestovski P., Nowak L. N-methyl-D-aspartate-activated channels of mouse central neurones in magnesium-free solutions. J Physiol. 1988 May;399:207–226. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste M., Clements J., Vyklický L., Jr, Mayer M. L. A kinetic analysis of the modulation of N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptors by glycine in mouse cultured hippocampal neurones. J Physiol. 1990 Sep;428:333–357. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste M., Mayer M. L. Kinetic analysis of antagonist action at N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptors. Two binding sites each for glutamate and glycine. Biophys J. 1991 Mar;59(3):560–573. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82272-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birch P. J., Grossman C. J., Hayes A. G. 6,7-Dinitro-quinoxaline-2,3-dion and 6-nitro,7-cyano-quinoxaline-2,3-dion antagonise responses to NMDA in the rat spinal cord via an action at the strychnine-insensitive glycine receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Oct 26;156(1):177–180. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90163-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cachelin A. B., Colquhoun D. Desensitization of the acetylcholine receptor of frog end-plates measured in a Vaseline-gap voltage clamp. J Physiol. 1989 Aug;415:159–188. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chizhmakov I. V., Kiskin N. I., Tsyndrenko AYa, Krishtal O. A. Desensitization of NMDA receptors does not proceed in the presence of kynurenate. Neurosci Lett. 1990 Jan 1;108(1-2):88–92. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90711-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark G. D., Clifford D. B., Zorumski C. F. The effect of agonist concentration, membrane voltage and calcium on N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor desensitization. Neuroscience. 1990;39(3):787–797. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90261-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Westbrook G. L. Activation kinetics reveal the number of glutamate and glycine binding sites on the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor. Neuron. 1991 Oct;7(4):605–613. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90373-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covarrubias M., Steinbach J. H. Excision of membrane patches reduces the mean open time of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Jun;416(4):385–392. doi: 10.1007/BF00370744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dilger J. P., Brett R. S. Direct measurement of the concentration- and time-dependent open probability of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor channel. Biophys J. 1990 Apr;57(4):723–731. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82593-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudel J., Franke C., Hatt H. Rapid activation, desensitization, and resensitization of synaptic channels of crayfish muscle after glutamate pulses. Biophys J. 1990 Mar;57(3):533–545. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82569-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feltz A., Trautmann A. Desensitization at the frog neuromuscular junction: a biphasic process. J Physiol. 1982 Jan;322:257–272. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke C., Hatt H., Dudel J. Steep concentration dependence and fast desensitization of nicotinic channel currents elicited by acetylcholine pulses, studied in adult vertebrate muscle. Pflugers Arch. 1991 Jan;417(5):509–516. doi: 10.1007/BF00370947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibb A. J., Colquhoun D. Glutamate activation of a single NMDA receptor-channel produces a cluster of channel openings. Proc Biol Sci. 1991 Jan 22;243(1306):39–45. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1991.0007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimwood S., Foster A. C., Kemp J. A. The pharmacological specificity of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in rat cerebral cortex: correspondence between radioligand binding and electrophysiological measurements. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Jun;103(2):1385–1392. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb09799.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidmann T., Bernhardt J., Neumann E., Changeux J. P. Rapid kinetics of agonist binding and permeability response analyzed in parallel on acetylcholine receptor rich membranes from Torpedo marmorata. Biochemistry. 1983 Nov 8;22(23):5452–5459. doi: 10.1021/bi00292a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson G., Johnson J. W., Ascher P. Competitive antagonists and partial agonists at the glycine modulatory site of the mouse N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor. J Physiol. 1990 Nov;430:189–212. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hestrin S., Sah P., Nicoll R. A. Mechanisms generating the time course of dual component excitatory synaptic currents recorded in hippocampal slices. Neuron. 1990 Sep;5(3):247–253. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90162-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue M., Kuriyama H. Properties of the nicotinic-receptor-activated current in adrenal chromaffin cells of the guinea-pig. Pflugers Arch. 1991 Aug;419(1):13–20. doi: 10.1007/BF00373741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. W., Ascher P. Glycine potentiates the NMDA response in cultured mouse brain neurons. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):529–531. doi: 10.1038/325529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., THESLEFF S. A study of the desensitization produced by acetylcholine at the motor end-plate. J Physiol. 1957 Aug 29;138(1):63–80. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N. W., Dingledine R. Requirement for glycine in activation of NMDA-receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Science. 1988 Aug 12;241(4867):835–837. doi: 10.1126/science.2841759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerma J., Kushner L., Spray D. C., Bennett M. V., Zukin R. S. mRNA from NCB-20 cells encodes the N-methyl-D-aspartate/phencyclidine receptor: a Xenopus oocyte expression study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1708–1711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerma J., Zukin R. S., Bennett M. V. Glycine decreases desensitization of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes and is required for NMDA responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2354–2358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester R. A., Clements J. D., Westbrook G. L., Jahr C. E. Channel kinetics determine the time course of NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic currents. Nature. 1990 Aug 9;346(6284):565–567. doi: 10.1038/346565a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald J. F., Mody I., Salter M. W. Regulation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors revealed by intracellular dialysis of murine neurones in culture. J Physiol. 1989 Jul;414:17–34. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maconochie D. J., Knight D. E. A method for making solution changes in the sub-millisecond range at the tip of a patch pipette. Pflugers Arch. 1989 Sep;414(5):589–596. doi: 10.1007/BF00580996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., MacDermott A. B., Westbrook G. L., Smith S. J., Barker J. L. Agonist- and voltage-gated calcium entry in cultured mouse spinal cord neurons under voltage clamp measured using arsenazo III. J Neurosci. 1987 Oct;7(10):3230–3244. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-10-03230.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Vyklicky L., Jr, Clements J. Regulation of NMDA receptor desensitization in mouse hippocampal neurons by glycine. Nature. 1989 Mar 30;338(6214):425–427. doi: 10.1038/338425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L. The action of N-methyl-D-aspartic acid on mouse spinal neurones in culture. J Physiol. 1985 Apr;361:65–90. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neubig R. R., Boyd N. D., Cohen J. B. Conformations of Torpedo acetylcholine receptor associated with ion transport and desensitization. Biochemistry. 1982 Jul 6;21(14):3460–3467. doi: 10.1021/bi00257a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patneau D. K., Mayer M. L. Kinetic analysis of interactions between kainate and AMPA: evidence for activation of a single receptor in mouse hippocampal neurons. Neuron. 1991 May;6(5):785–798. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90175-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patneau D. K., Mayer M. L. Structure-activity relationships for amino acid transmitter candidates acting at N-methyl-D-aspartate and quisqualate receptors. J Neurosci. 1990 Jul;10(7):2385–2399. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-07-02385.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rang H. P., Ritter J. M. On the mechanism of desensitization at cholinergic receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1970 Jul;6(4):357–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakmann B., Patlak J., Neher E. Single acetylcholine-activated channels show burst-kinetics in presence of desensitizing concentrations of agonist. Nature. 1980 Jul 3;286(5768):71–73. doi: 10.1038/286071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sather W., Johnson J. W., Henderson G., Ascher P. Glycine-insensitive desensitization of NMDA responses in cultured mouse embryonic neurons. Neuron. 1990 May;4(5):725–731. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90198-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirasaki T., Nakagawa T., Wakamori M., Tateishi N., Fukuda A., Murase K., Akaike N. Glycine-insensitive desensitization of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in acutely isolated mammalian central neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1990 Jan 1;108(1-2):93–98. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90712-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siara J., Ruppersberg J. P., Rüdel R. Human nicotinic acetylcholine receptor: the influence of second messengers on activation and desensitization. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Mar;415(6):701–706. doi: 10.1007/BF02584008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang C. M., Dichter M., Morad M. Quisqualate activates a rapidly inactivating high conductance ionic channel in hippocampal neurons. Science. 1989 Mar 17;243(4897):1474–1477. doi: 10.1126/science.2467378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson A. M. Glycine is a coagonist at the NMDA receptor/channel complex. Prog Neurobiol. 1990;35(1):53–74. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(90)90040-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traynelis S. F., Cull-Candy S. G. Pharmacological properties and H+ sensitivity of excitatory amino acid receptor channels in rat cerebellar granule neurones. J Physiol. 1991 Feb;433:727–763. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trussell L. O., Fischbach G. D. Glutamate receptor desensitization and its role in synaptic transmission. Neuron. 1989 Aug;3(2):209–218. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90034-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdoorn T. A., Dingledine R. Excitatory amino acid receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes: agonist pharmacology. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Sep;34(3):298–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyklický L., Jr, Benveniste M., Mayer M. L. Modulation of N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor desensitization by glycine in mouse cultured hippocampal neurones. J Physiol. 1990 Sep;428:313–331. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


