Abstract
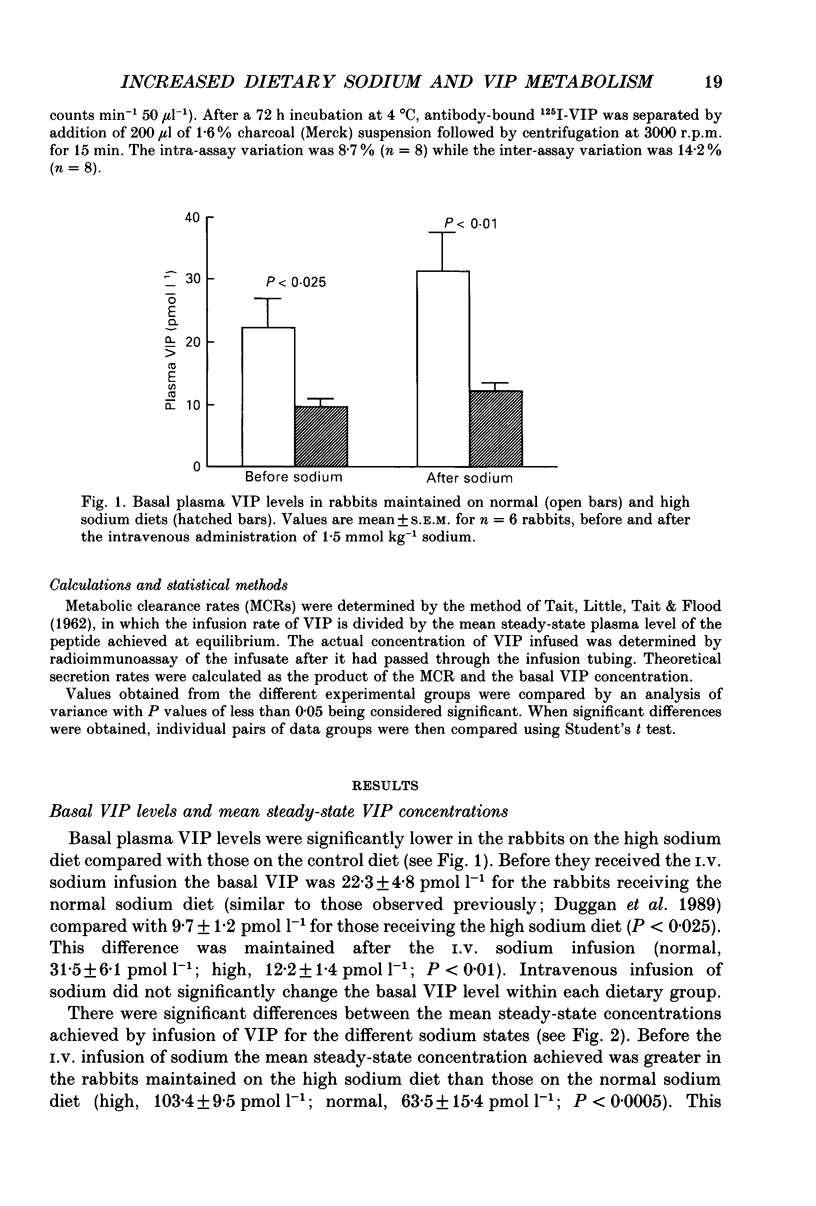
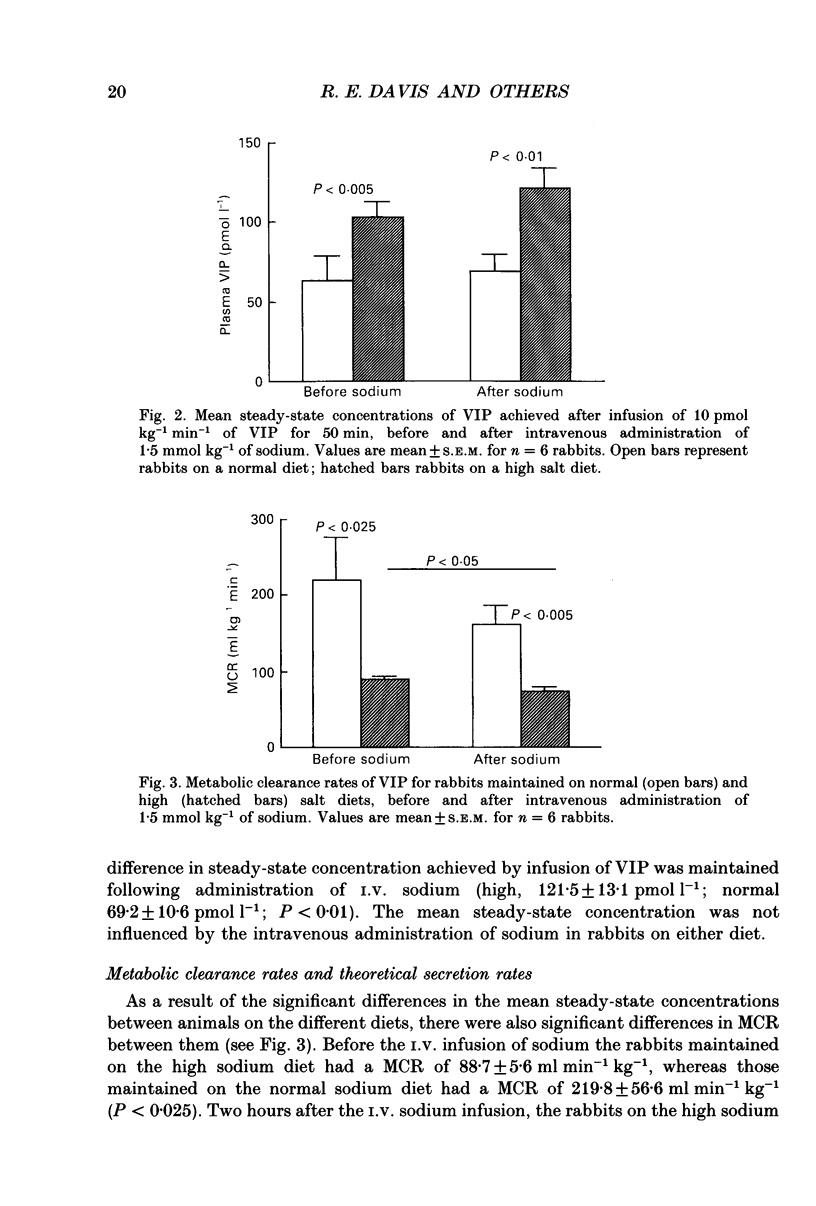
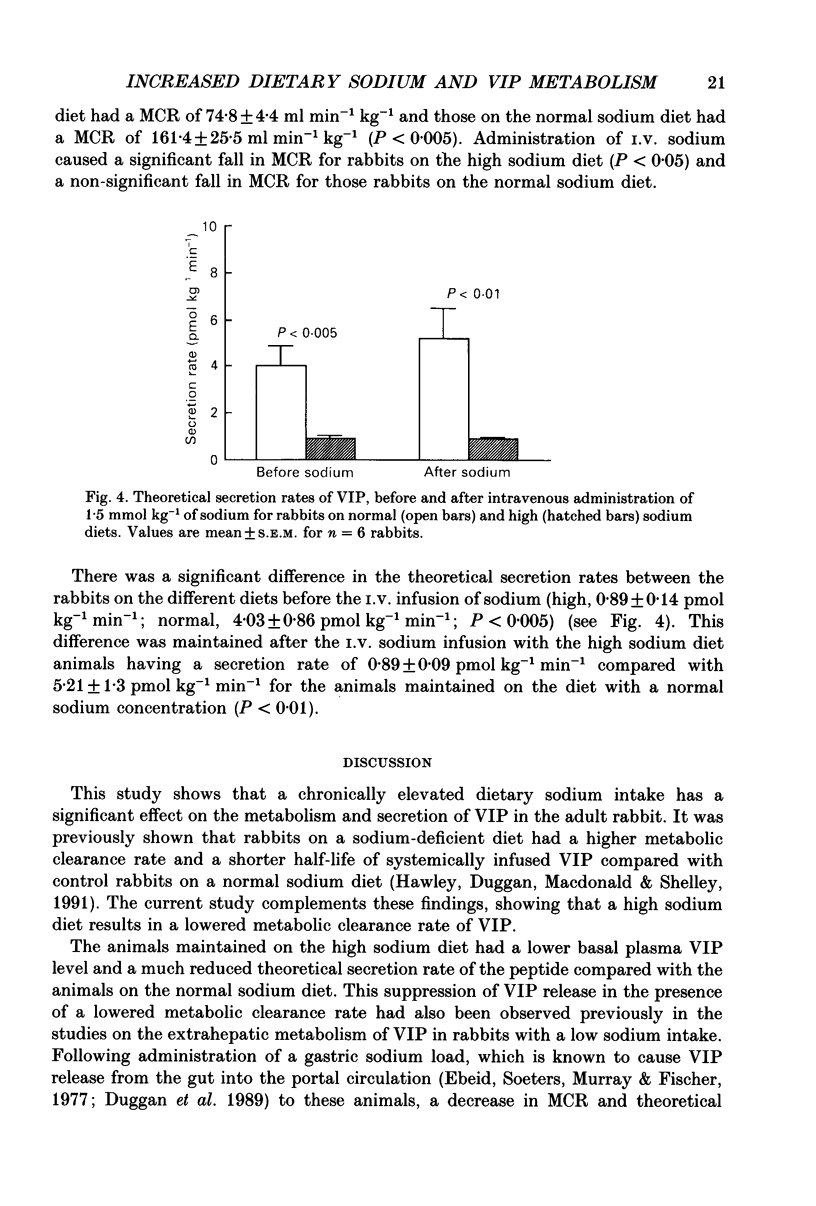
1. In view of previous observations that the metabolism of vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) is significantly increased in sodium-depleted rabbits, we wished to determine whether a high sodium intake also leads to alterations in VIP metabolism. We performed metabolic clearance studies in rabbits maintained on a high sodium diet and normal control diets. These studies were performed both before and after the administration of 1.5 mmol kg-1 of sodium intravenously to observe the effects of an acute increase in body sodium. 2. The rabbits maintained on the high sodium diet had a significantly lower basal plasma VIP level (P less than 0.025), a lower metabolic clearance rate (MCR) of the peptide (P less than 0.025) and a lower secretion rate (P less than 0.005), compared with the normal control animals. These differences were maintained following the intravenous sodium infusion. 3. The administration of the intravenous sodium infusion resulted in a further decrease in MCR in the rabbits on the high sodium diet (P less than 0.05). 4. These results confirm that VIP metabolism is affected by high dietary intake of sodium, as well as a low sodium intake, adding further support to the hypothesis that VIP may be involved in sodium homeostasis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Duggan K. A., Hawley C. M., Macdonald G. J., Shelley S. Sodium depletion decreases hepatic metabolism of vasoactive intestinal peptide in the rabbit. J Physiol. 1989 Nov;418:251–259. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duggan K. A., Macdonald G. J. Vasoactive intestinal peptide: a direct renal natriuretic substance. Clin Sci (Lond) 1987 Feb;72(2):195–200. doi: 10.1042/cs0720195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebeid A. M., Soeters P. B., Murray P., Fischer J. E. Release of vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) by intraluminal osmotic stimuli. J Surg Res. 1977 Jul;23(1):25–30. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(77)90185-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley C. M., Duggan K. A., Macdonald G. J., Shelley S. Oral sodium regulates extrahepatic metabolism of vasoactive intestinal peptide. Clin Sci (Lond) 1991 Jul;81(1):79–83. doi: 10.1042/cs0810079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leary W. P., Ledingham J. G. Inactivation of angiotensin II analogues by isolated perfused rat liver and kidney. Nature. 1970 Jul 11;227(5254):178–179. doi: 10.1038/227178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennane R. J., Carey R. M., Goodwin T. J., Peart W. S. A comparison of natriuresis after oral and intravenous sodium loading in sodium-depleted man: evidence for a gastrointestinal or portal monitor of sodium intake. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1975 Nov;49(5):437–440. doi: 10.1042/cs0490437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennane R. J., Peart W. S., Carey R. M., Shaw J. A comparison on natriuresis after oral and intravenous sodium loading in sodium-depleted rabbits: evidence for a gastrointestinal or portal monitor of sodium intake. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1975 Nov;49(5):433–436. doi: 10.1042/cs0490433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. L., Rose K., Hughes G. J., Magistretti P. J. [mono[125I]iodo-Tyr10,MetO17]-vasoactive intestinal polypeptide. Preparation, characterization, and use for radioimmunoassay and receptor binding. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 25;261(12):5320–5327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAIT J. F., LITTLE B., TAIT S. A., FLOOD C. The metabolic clearance rate of aldosterone in pregnant and nonpregnant subjects estimated by both single-injection and constant-infusion methods. J Clin Invest. 1962 Dec;41:2093–2100. doi: 10.1172/JCI104667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


