Abstract
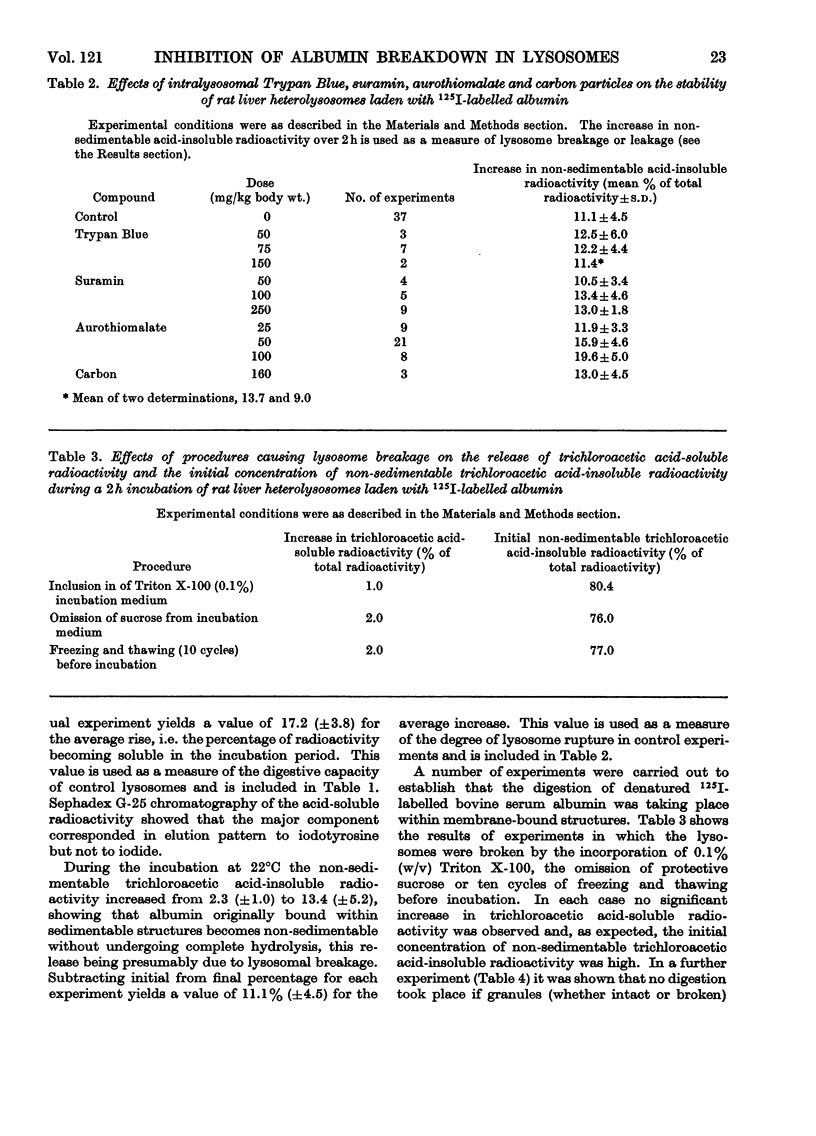
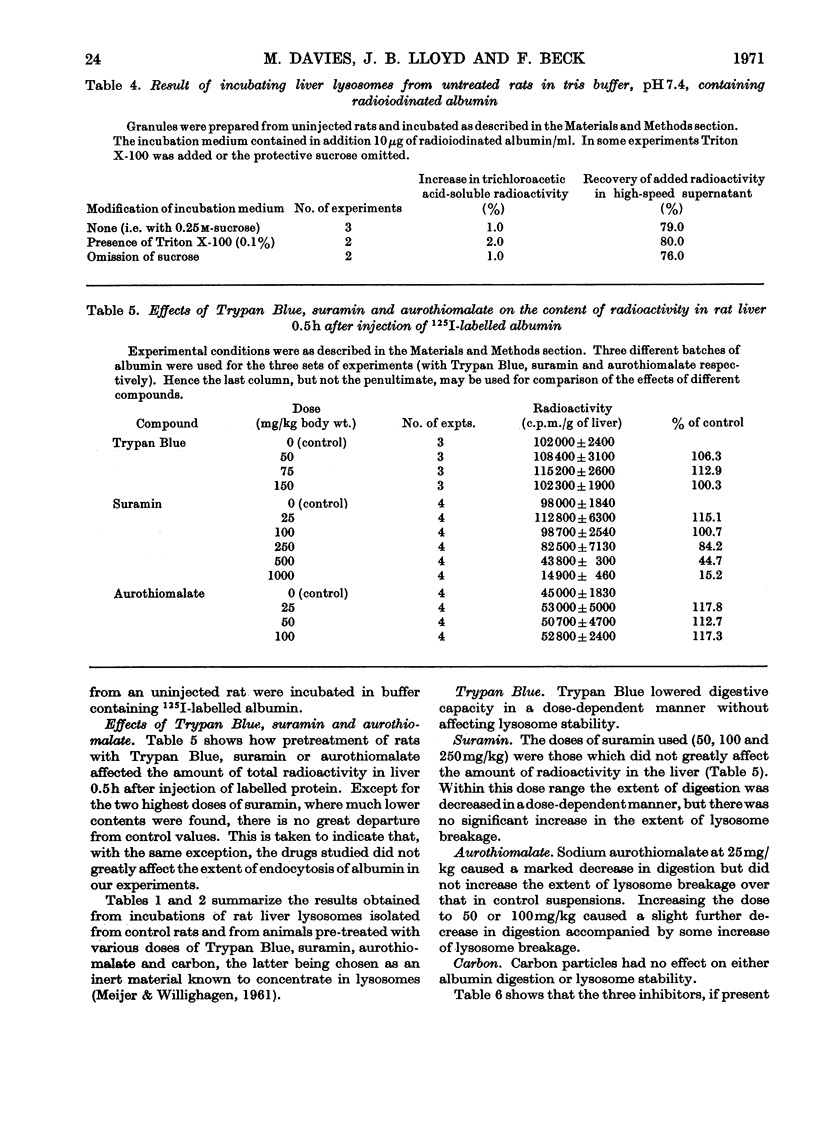
1. A fraction enriched in lysosomes was prepared by centrifugation from the livers of rats that had been injected 0.5h before death with 125I-labelled albumin. When suspended in sucrose-protected buffer, pH7.4, and incubated at 22°C for 2h, the particles progressively released iodotyrosine into the medium. Albumin digestion did not occur if the particles were subjected to treatments known to break lysosomes or if particles from uninjected rats were incubated in medium containing 125I-labelled albumin. It is concluded that the observed production of iodotyrosine results from protein hydrolysis within intact heterolysosomes. 2. Particles from rats pre-treated with Trypan Blue, suramin or aurothiomalate released iodotyrosine more slowly than controls. Since these compounds are enzyme inhibitors that concentrate in liver lysosomes after administration in vivo, their effect is ascribed to intralysosomal inhibition of proteolysis. The doses used did not decrease endocytosis of albumin into liver or cause increased lysosome breakage during incubation, thus allowing some alternative explanations of the decreased proteolysis to be eliminated. Particulate carbon, a non-inhibitor that also concentrates in lysosomes, did not affect albumin hydrolysis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison A. The role of lysosomes in the action of drugs and hormones. Adv Chemother. 1968;3:253–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck F., Lloyd J. B., Griffiths A. Lysosomal enzyme inhibition by trypan blue: a theory of teratogenesis. Science. 1967 Sep 8;157(3793):1180–1182. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3793.1180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies M., Lloyd J. B., Beck F. Protein digestion in isolated lysosomes inhibited by intralysosomal trypan blue. Science. 1969 Mar 28;163(3874):1454–1456. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3874.1454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies M., Lloyd J. B. The effects of trypan blue on rat liver heterolysosomes. Biochem J. 1968 Sep;109(3):26P–26P. doi: 10.1042/bj1090026pa. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenreich B. A., Cohn Z. A. The uptake and digestion of iodinated human serum albumin by macrophages in vitro. J Exp Med. 1967 Nov 1;126(5):941–958. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.5.941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ennis R. S., Granda J. L., Posner A. S. Effect of gold salts and other drugs on the release and activity of lysosomal hydrolases. Arthritis Rheum. 1968 Dec;11(6):756–764. doi: 10.1002/art.1780110605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd J. B., Beck F. The relationship of chemical structure to teratogenic activity among bisazo dyes: a re-evaluation. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1966 Aug;16(1):29–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEIJER A. E., WILLIGHAGEN R. G. Increased activity of acid phosphatase and beta-glucuronidase in the liver and spleen of mice after intraperitoneal administration of various macromolecular substances. Biochem Pharmacol. 1961 Dec;8:389–397. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(61)90056-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOUGEY E. H., MASON J. W. SEPARATION OF SOME IODOAMINO ACIDS AND IODIDE BY GEL FILTRATION. Anal Biochem. 1963 Sep;6:223–233. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(63)90129-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mego J. L., Bertini F., McQueen J. D. The use of formaldehyde-treated 131-I-albumin in the study of digestive vacuoles and some properties of these particles from mouse liver. J Cell Biol. 1967 Mar;32(3):699–707. doi: 10.1083/jcb.32.3.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mego J. L., McQueen J. D. Heterolysosome formation in mouse liver. J Cell Physiol. 1967 Aug;70(1):115–120. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040700115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton W. L., Lewis D. C., Ziff M. Electron-dense deposits following injection of gold sodium thiomalate and thiomalic acid. Arthritis Rheum. 1968 Jun;11(3):436–443. doi: 10.1002/art.1780110309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persellin R. H., Ziff M. The effect of gold salt on lysosomal enzymes of the peritoneal macrophage. Arthritis Rheum. 1966 Feb;9(1):57–65. doi: 10.1002/art.1780090107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Askonas B. A. Persistence of immunogenicity of antigen after uptake by macrophages. J Exp Med. 1968 May 1;127(5):915–926. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.5.915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLS E. D. Enzyme inhibition by suramin and the measurement of the isoelectric points of some enzymes. Biochem J. 1952 Jan;50(3):421–425. doi: 10.1042/bj0500421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


