Abstract
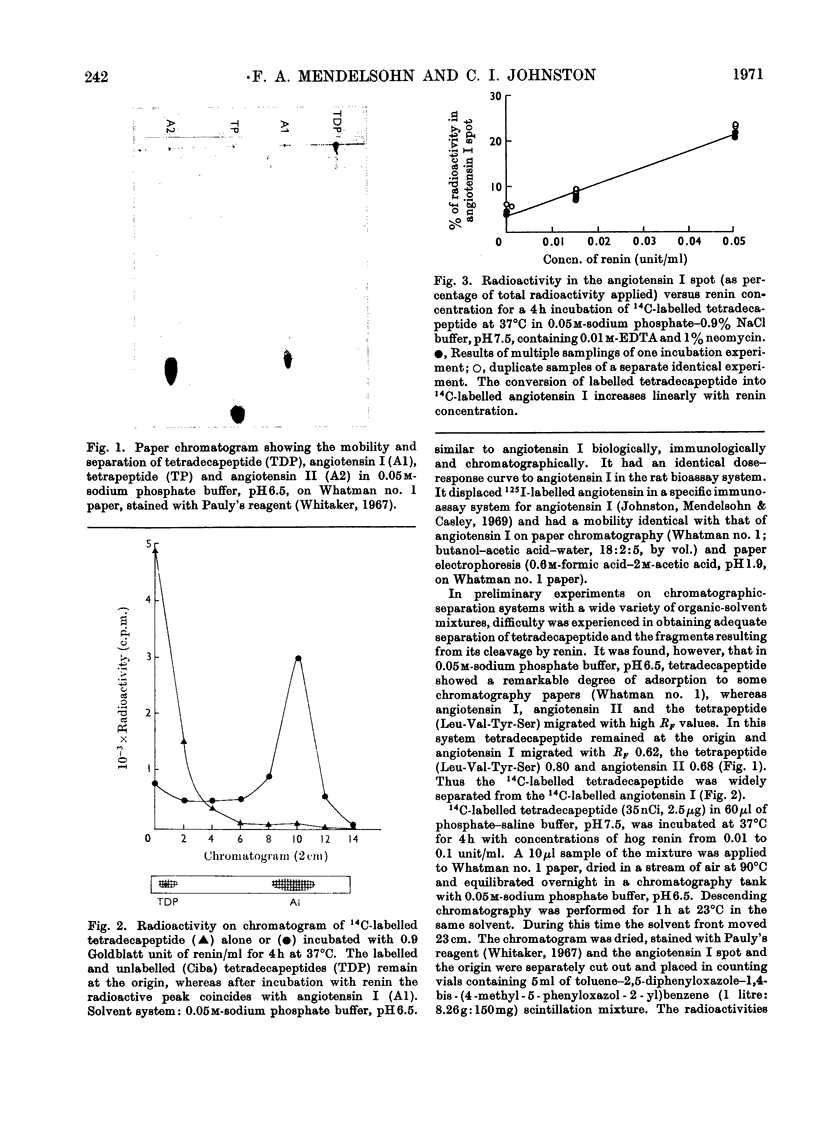
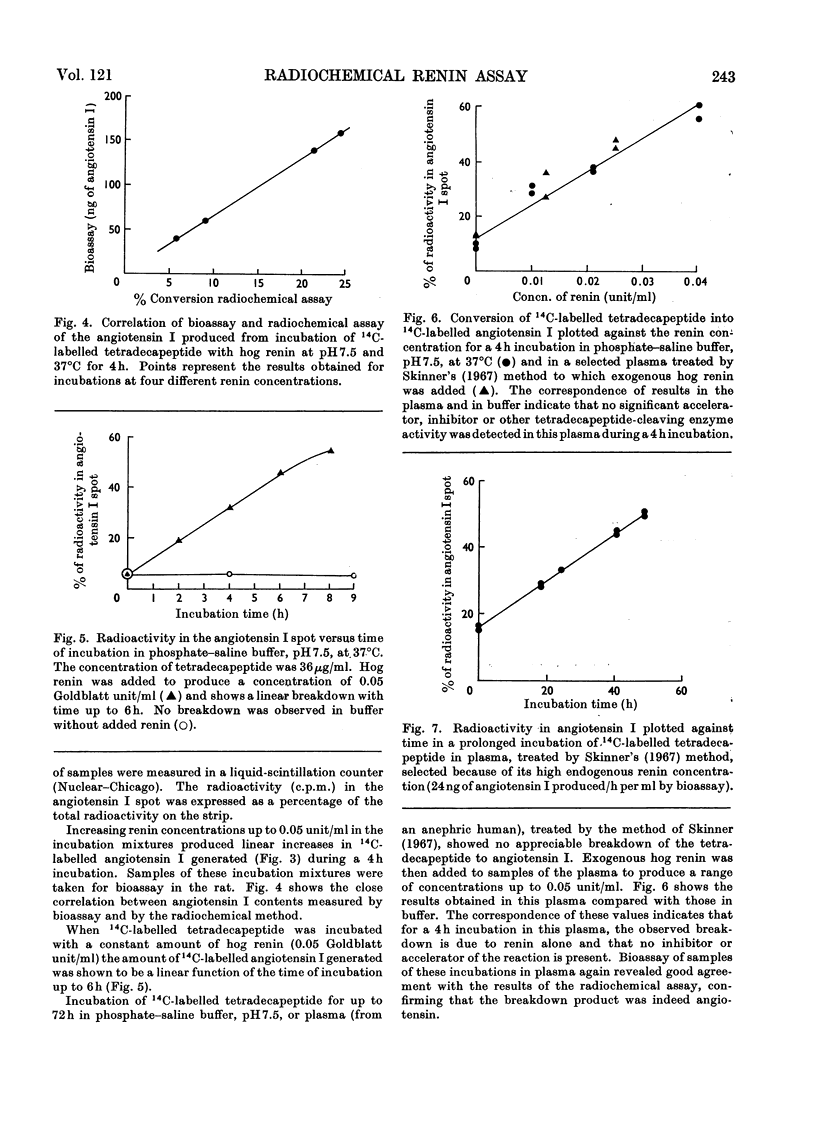
1. A synthetic 3-([14C]valine)-labelled tetradecapeptide renin substrate was used to measure renin concentration. Renin liberated 14C-labelled angiotensin I, which was separated from the labelled substrate by paper chromatography. The conversion of substrate into angiotensin I was quantitated by liquid-scintillation counting of radioactivity. 2. The rate of conversion of the substrate into angiotensin I was shown to be linearly related to renin concentration and time under suitable conditions. Angiotensin generation measured in this system agrees well with that measured by bioassay. 3. It is suggested that the use of a pure substrate offers advantages that include the standardization of current units of renin measurement.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Haas E., Gould A. B., Goldblatt H. Estimation of endogenous renin in human blood. Lancet. 1968 Mar 30;1(7544):657–661. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92097-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montague D., Riniker B., Brunner H., Gross F. Synthesis and biological activities of a tetradecapeptide renin substrate. Am J Physiol. 1966 Mar;210(3):591–594. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.210.3.591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montague D., Riniker B., Gross F. Kinetics of the renin-substrate reaction employing a synthetic substrate. Am J Physiol. 1966 Mar;210(3):595–598. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.210.3.595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEART W. S. A new method of large-scale preparation of hypertensin, with a note on its assay. Biochem J. 1955 Feb;59(2):300–302. doi: 10.1042/bj0590300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKEGGS L. T., Jr, KAHN J. R., LENTZ K., SHUMWAY N. P. The preparation, purification, and amino acid sequence of a polypeptide renin substrate. J Exp Med. 1957 Sep 1;106(3):439–453. doi: 10.1084/jem.106.3.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKEGGS L. T., Jr, LENTZ K. E., KAHN J. R., SHUMWAY N. P. The synthesis of a tetradecapeptide renin substrate. J Exp Med. 1958 Sep 1;108(3):283–297. doi: 10.1084/jem.108.3.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLUYTERMAN L. A. The effect of oxygen upon the micro determination of histidine with the aid of the Pauly reaction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Feb 26;38:218–221. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91234-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skeggs L. T., Lentz K. E., Kahn J. R., Dorer F. E., Levine M. Pseudorenin. A new angiotensin-forming enzyme. Circ Res. 1969 Oct;25(4):451–462. doi: 10.1161/01.res.25.4.451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skeggs L. T., Lentz K. E., Kahn J. R., Hochstrasser H. Kinetics of the reaction of renin with nine synthetic peptide substrates. J Exp Med. 1968 Jul 1;128(1):13–34. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner S. L. Improved assay methods for renin "concentration" and "activity" in human plasma. Methods using selective denaturation of renin substrate. Circ Res. 1967 Apr;20(4):391–402. doi: 10.1161/01.res.20.4.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



