Abstract
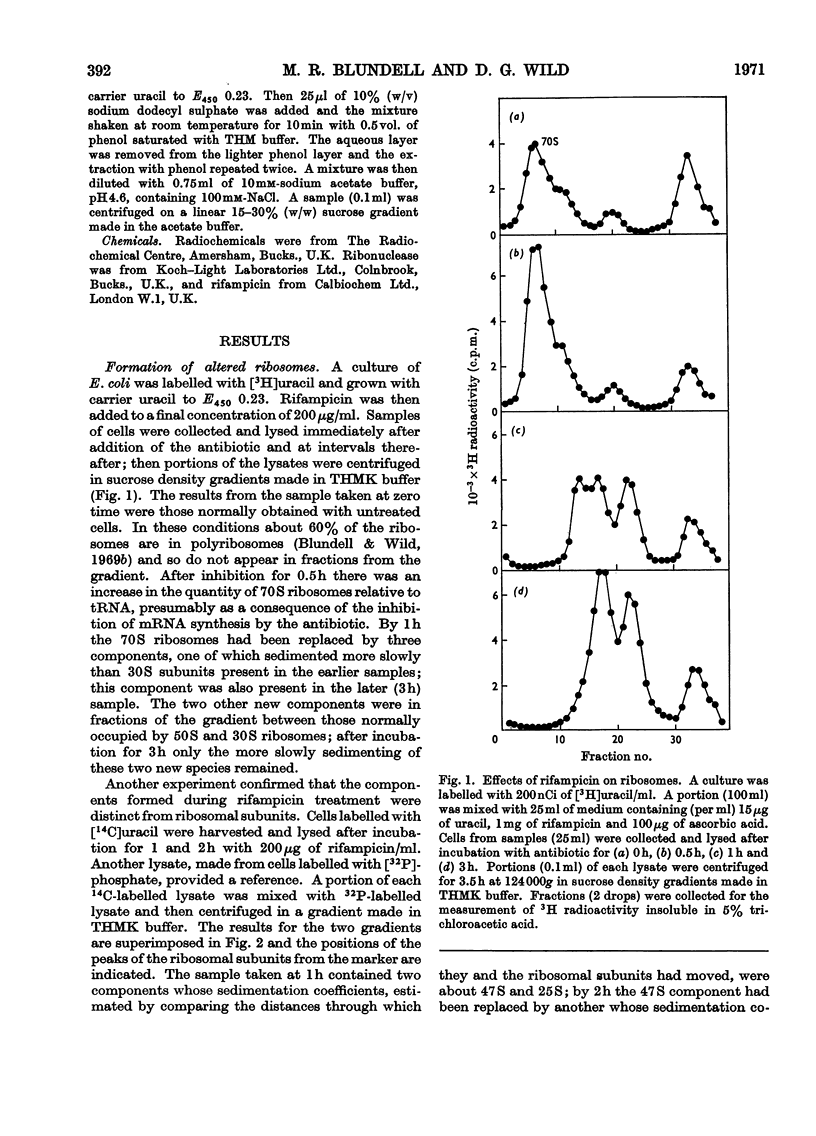
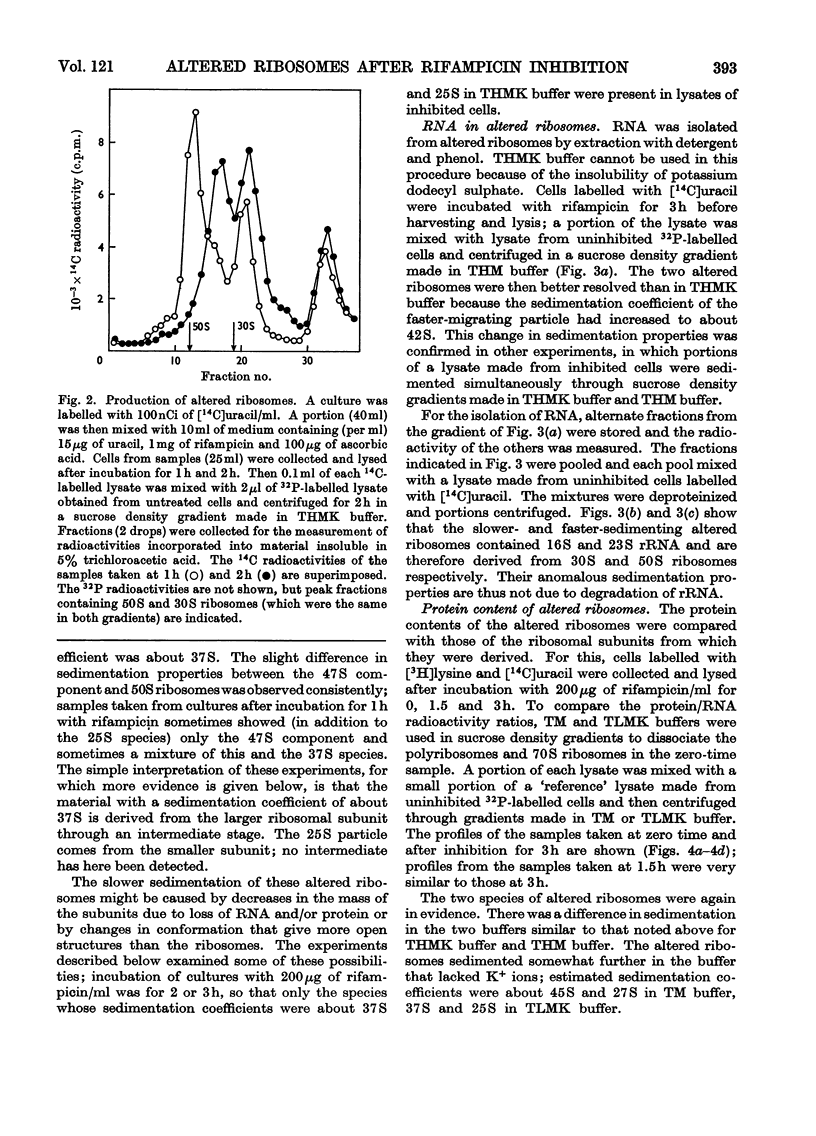
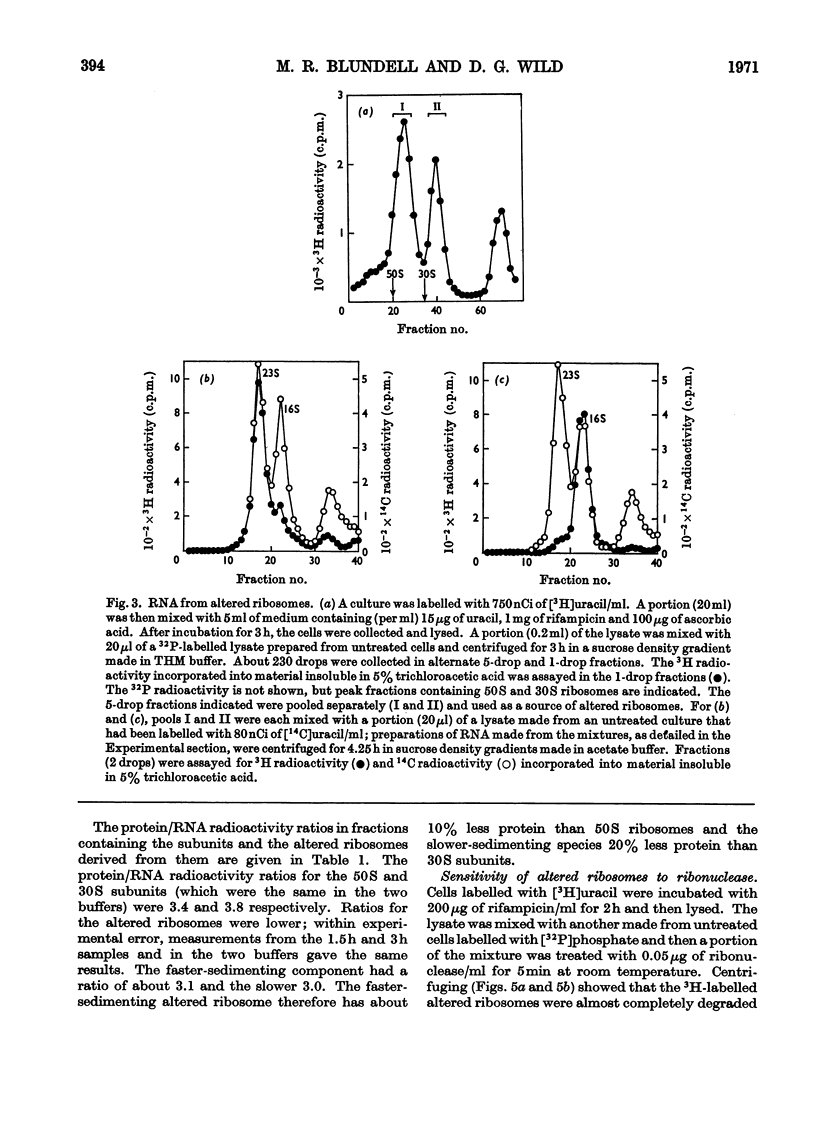
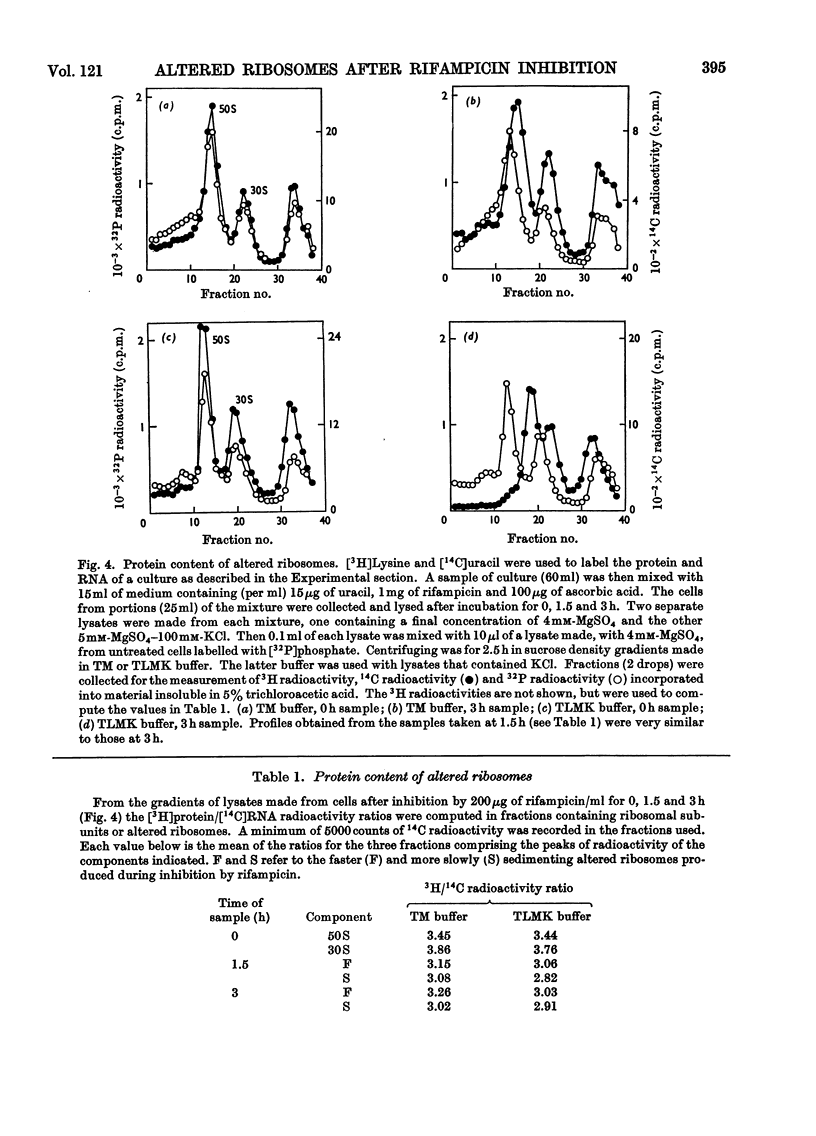
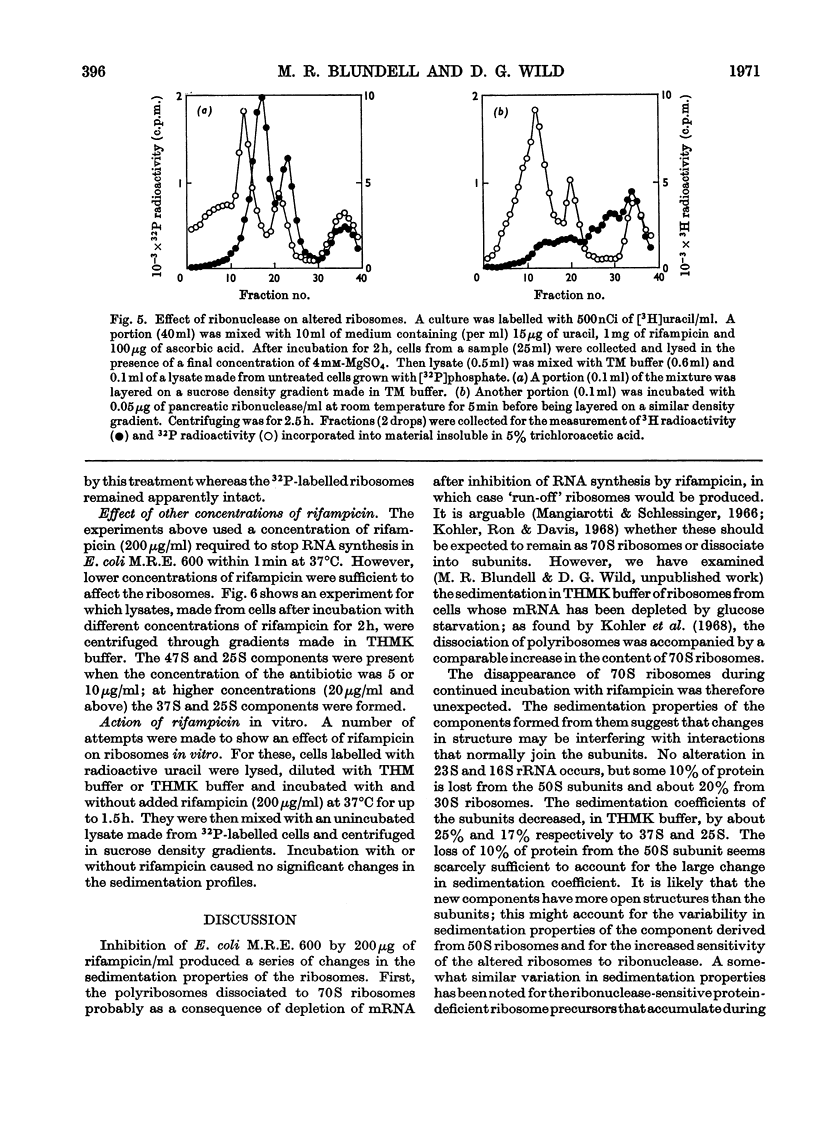
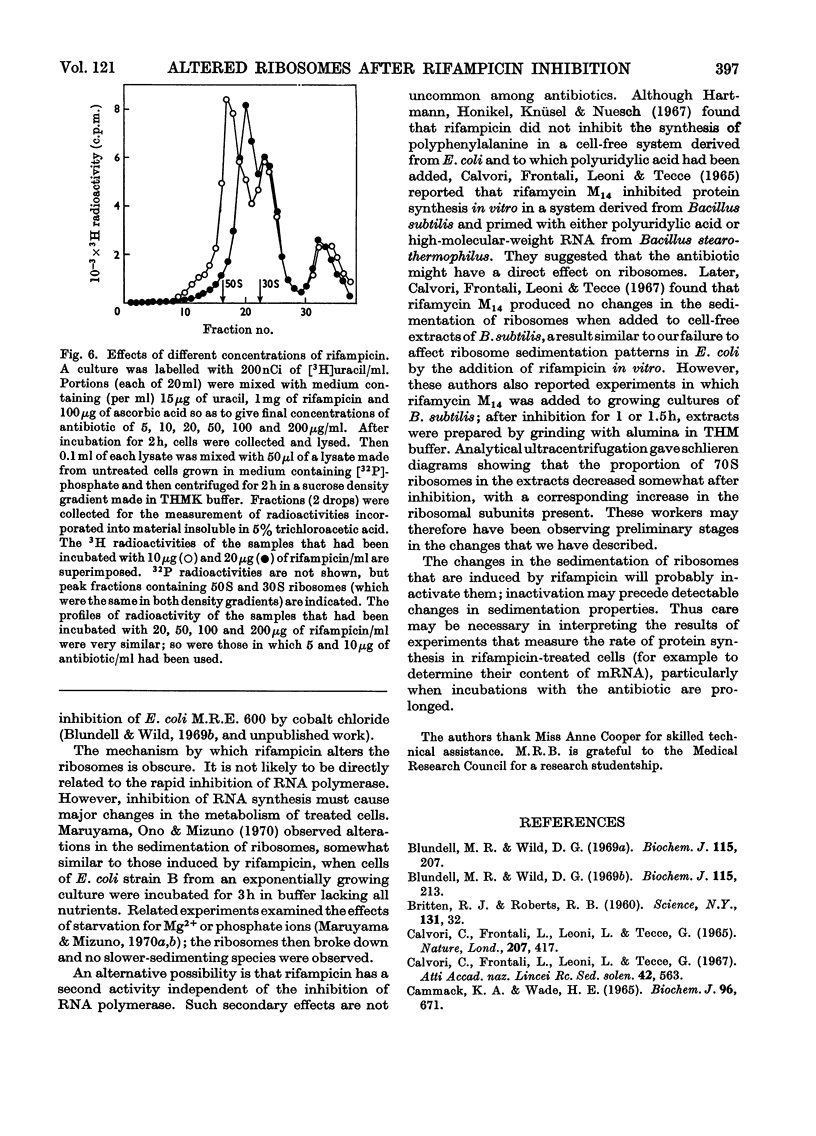
Addition of rifampicin to growing cells of Escherichia coli affected the ribosomes. The polyribosomes first decayed to 70S ribosomes. These later dissociated to particles distinct from ribosomal subunits. The altered ribosomes sedimented more slowly than the corresponding subunits and had lost some protein; their ribosomal RNA was intact, but they were more susceptible to degradation by ribonuclease than normal ribosomes. The addition of rifampicin to preparations of lysed cells caused no detectable changes in the ribosome fraction.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blundell M. R., Wild D. G. Inhibition of bacterial growth by metal salts. A survey of effects on the synthesis of ribonucleic acid and protein. Biochem J. 1969 Nov;115(2):207–212. doi: 10.1042/bj1150207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blundell M. R., Wild D. G. Inhibition of bacterial growth by metal salts. The accumulation of ribonucleic acid during inhibition of Escherichia coli by cobalt chloride. Biochem J. 1969 Nov;115(2):213–223. doi: 10.1042/bj1150213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvori C., Frontali L., Leoni L., Tecce G. Effect of rifamycin on protein synthesis. Nature. 1965 Jul 24;207(995):417–418. doi: 10.1038/207417a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cammack K. A., Wade H. E. The sedimentation behaviour of ribonuclease-active and -inactive ribosomes from bacteria. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):671–680. doi: 10.1042/bj0960671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann G., Honikel K. O., Knüsel F., Nüesch J. The specific inhibition of the DNA-directed RNA synthesis by rifamycin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967;145(3):843–844. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90147-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangiarotti G., Schlessinger D. Polyribosome metabolism in Escherichia coli. I. Extraction of polyribosomes and ribosomal subunits from fragile, growing Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1966 Sep;20(1):123–143. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90122-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama H., Mizuno D. Ribosome degradation and the degradation products in starved Escherichia coli. I. Comparison of the degradation rate and of the nucleotide pool between Escherichia coli B and Q-13 strains in phosphate deficiency. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jan 21;199(1):159–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama H., Mizuno D. Ribosome degradation and the degradation products in starved Escherichia coli. II. Changes in base sequence of ribosomal RNA during degradation induced by phosphate and magnesium starvation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jan 21;199(1):166–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama H., Ono M., Mizuno D. Ribosome degradation and the degradation products in starved Escherichia coli. 3. Ribosomal RNA degradation during the complete deprivation of nutrients. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jan 21;199(1):176–183. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90706-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuhoff V., Schill W. B., Sternbach H. Micro-analysis of pure deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase from Escherichia coli. Action of heparin and rifampicin on structure and function. Biochem J. 1970 Apr;117(3):623–631. doi: 10.1042/bj1170623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sippel A., Hartmann G. Mode of action of rafamycin on the RNA polymerase reaction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Mar 18;157(1):218–219. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90286-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wehrli W., Knüsel F., Staehelin M. Action of rifamycin on RNA-polymerase from sensitive and resistant bacteria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Jul 26;32(2):284–288. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90382-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


