Abstract
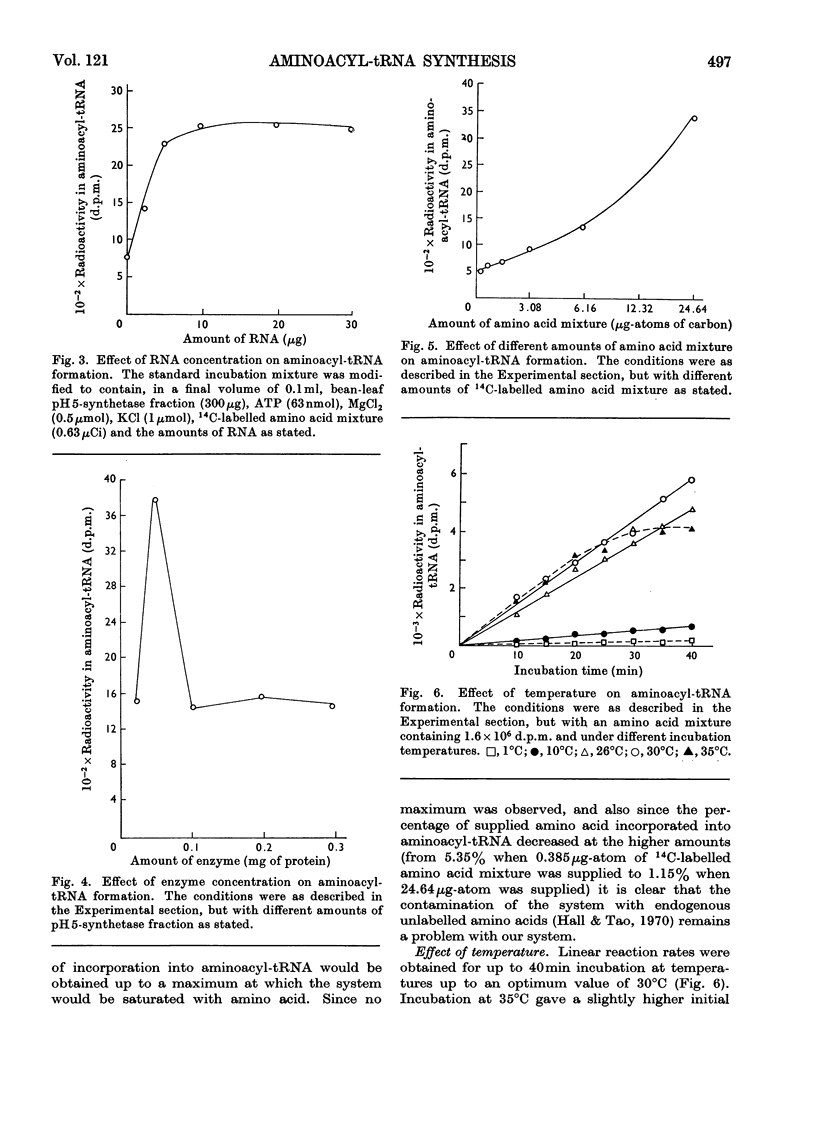
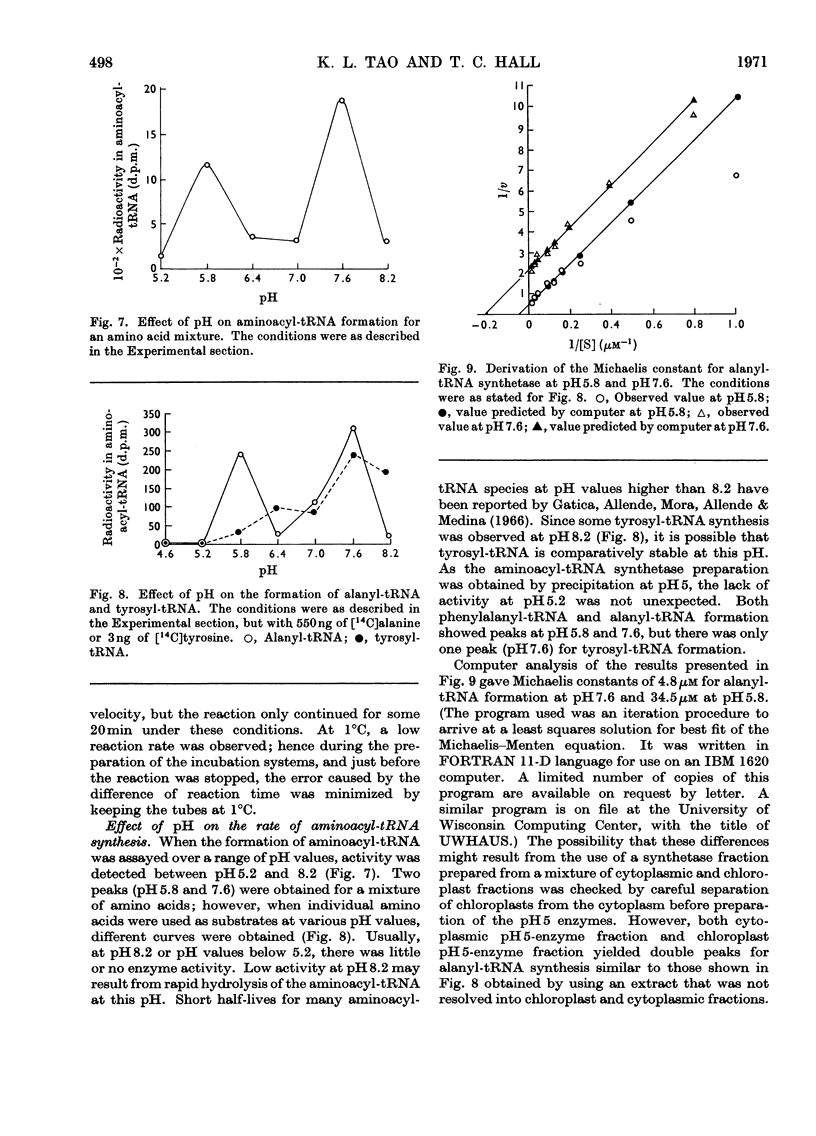
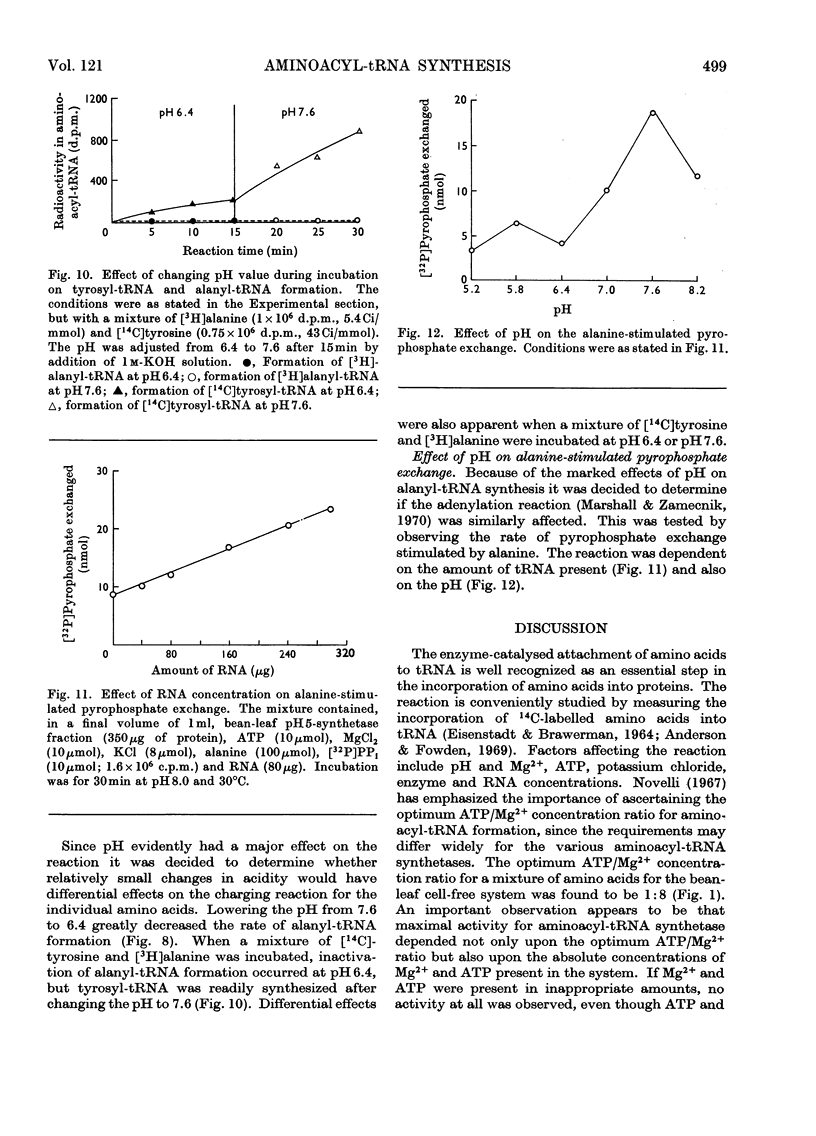
1. Factors affecting aminoacyl-tRNA synthesis in vitro by cell-free preparations from bean leaves were investigated. 2. Evidence was obtained that optimum concentrations as well as correct ratios of Mg2+ and ATP are required for aminoacyl-tRNA synthesis in the bean-leaf system. 3. The results indicated that pH is a controlling factor having differential effects on the formation of individual aminoacyl-tRNA species. The possible micro-regulatory function of pH in protein synthesis in vivo is discussed with special reference to alanyl-tRNA formation. 4. Very low rates of alanine-stimulated pyrophosphate exchange were observed in the absence of tRNA. This observation is discussed relative to proposals about the mechanism of aminoacyl-tRNA synthesis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. W., Rowan K. S. The extraction and assay of aminoacyl-transfer-ribonucleic acid synthetases of tobacco leaf. Biochem J. 1966 Oct;101(1):9–14. doi: 10.1042/bj1010009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson W. F. The effect of tRNA concentration on the rate of protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Feb;62(2):566–573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.2.566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attwood M. M., Cocking E. C. The purification and properties of the alanyl-transfer ribonucleic acid synthetase of tomato roots. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):616–625. doi: 10.1042/bj0960616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole F. X., Schimmel P. R. On the rate law and mechanism of the adenosine triphosphate--pyrophosphate isotope exchange reaction of amino acyl transfer ribonucleic acid synthetases. Biochemistry. 1970 Feb 3;9(3):480–489. doi: 10.1021/bi00805a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. W., Hall T. C. Liquid scintillation counting methods for accurate assay of beta radioactivity in biological experiments. Anal Biochem. 1969 Jan;27(1):77–90. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90221-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EISENSTADT J., BRAWERMAN G. CHARACTERISTICS OF A CELL-FREE SYSTEM FROM EUGLENA GRACILIS FOR THE INCORPORATION OF AMINO ACIDS INTO PROTEIN. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Mar 23;80:463–472. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(64)90149-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatica M., Allende C. C., Mora G., Allende J. E., Medina J. The effect of pH on the stability of several aminoacyl-sRNA's. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Oct 24;129(1):201–203. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90022-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall T. C., Tao K. L. Rates of aminoacyl-transfer-ribonucleic acid synthesis in vivo and in vitro by bean leaves. Biochem J. 1970 May;117(5):853–859. doi: 10.1042/bj1170853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosakowski M. H., Neidhardt F. C., Böck A. Complementation in vitro of phenylalanyl-tRNA synthetases of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Jan;12(1):74–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00822.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maclennan D. H., Beevers H., Harley J. L. 'Compartmentation' of acids in plant tissues. Biochem J. 1963 Nov;89(2):316–327. doi: 10.1042/bj0890316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall R. D., Zamecnik P. C. Aspects of the kinetic properties of lysyl-tRNA synthetase from Escherichia coli, strain B. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Feb 11;198(2):376–385. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(70)90070-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall R. D., Zamecnik P. C. Some physical properties of lysyl and arginyl-transfer RNA synthetases of Escherichia coli B. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jul 1;181(2):454–464. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(69)90279-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin I. B., Kelmers A. D., Goldstein G. The determination of transfer ribonucleic acid by aminoacylation. I. Leucine and phenylalanine transfer ribonucleic acid from E. coli B. Anal Biochem. 1967 Sep;20(3):533–544. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90298-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STENT G. S. THE OPERON: ON ITS THIRD ANNIVERSARY. MODULATION OF TRANSFER RNA SPECIES CAN PROVIDE A WORKABLE MODEL OF AN OPERATOR-LESS OPERON. Science. 1964 May 15;144(3620):816–820. doi: 10.1126/science.144.3620.816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shearn A., Horowitz N. H. A study of transfer ribonucleic acid in Neurospora. I. The attachment of amino acids and amino acid analogs. Biochemistry. 1969 Jan;8(1):295–303. doi: 10.1021/bi00829a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


