Abstract
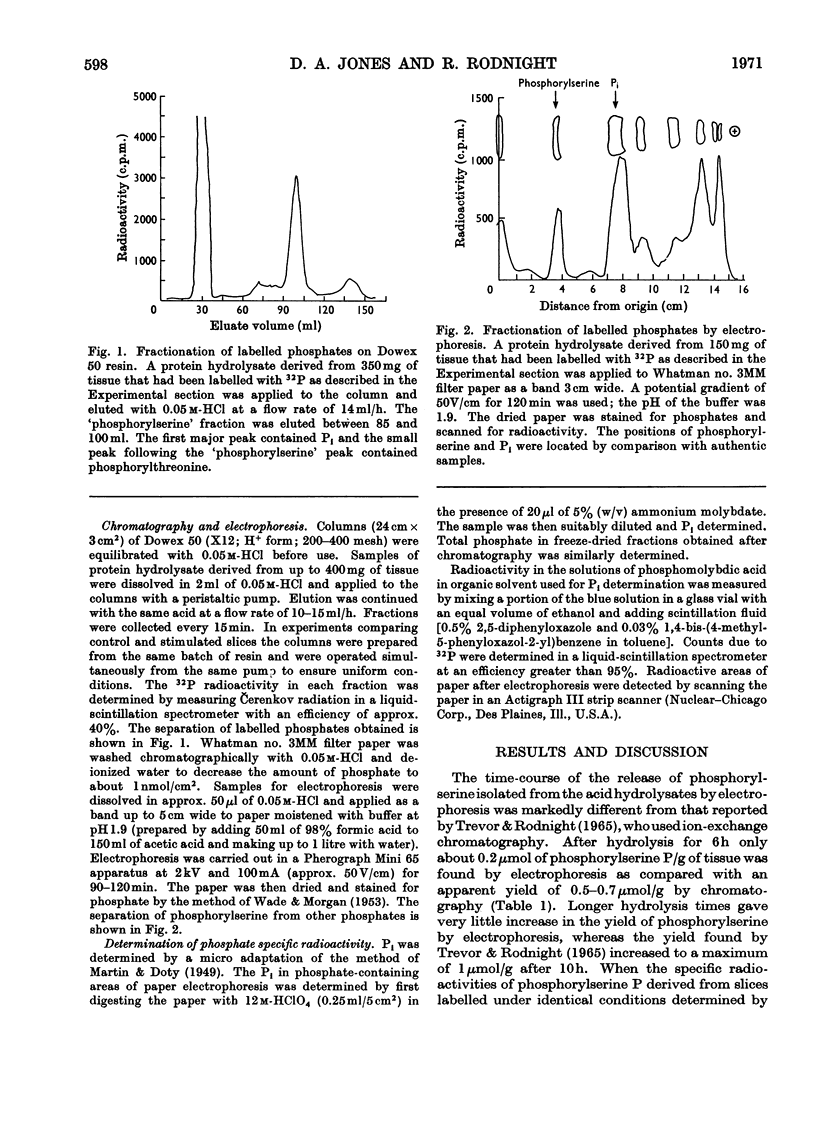
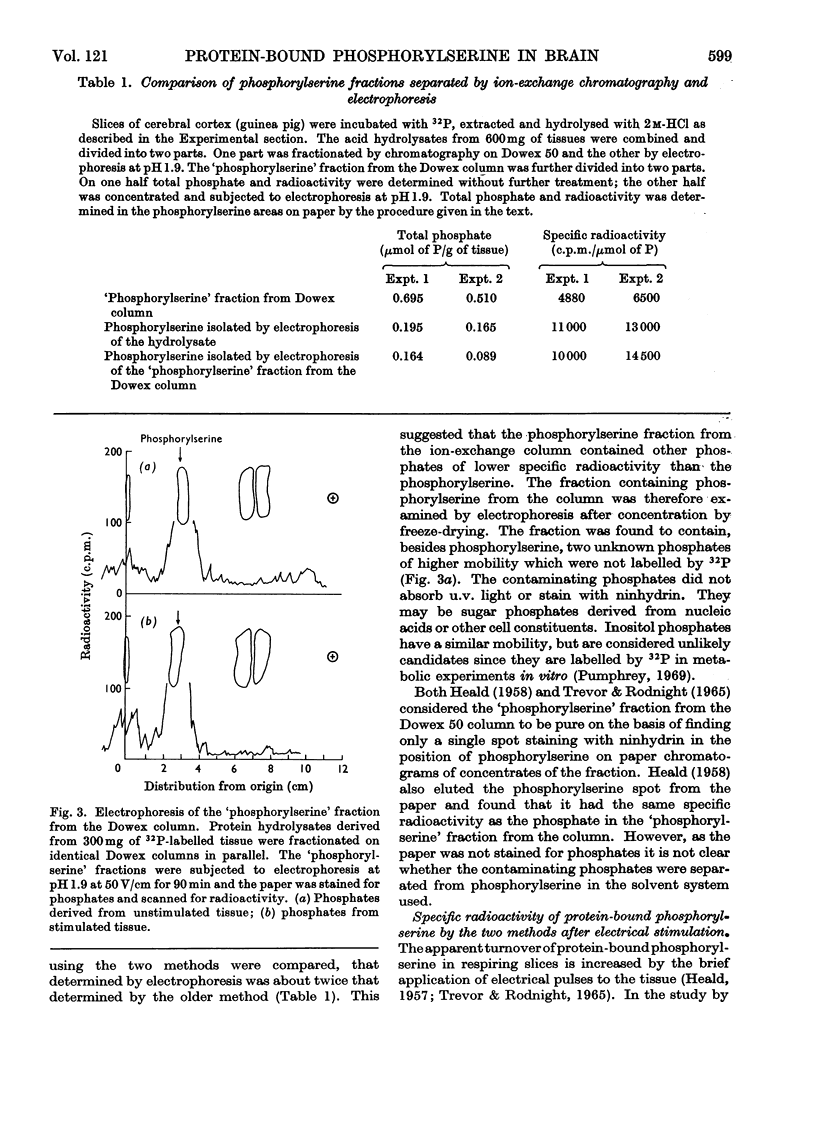
1. Partial acid hydrolysates of proteins derived from cortical slices of guinea-pig brain were divided into two parts and fractionated by ion-exchange chromatography and high-voltage electrophoresis. 2. The apparent yield of protein-bound phosphorylserine by the ion-exchange method was about three times that obtained by electrophoresis. 3. The specific radioactivity of phosphorylserine isolated from 32P-labelled slices by electrophoresis was twice that isolated by chromatography. 4. The discrepancies were found to be due to the presence of unlabelled phosphates of unknown composition in the `phosphorylserine' fraction obtained by the ion-exchange method. 5. Electrical stimulation of slices respiring in the presence of [32P]phosphate increased the specific radioactivity of the total phosphate in the chromatographic `phosphorylserine' fraction by 53±11%, as compared with only 19±5% for the phosphorylserine isolated by electrophoresis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AHMED K., JUDAH J. D. Role of phosphoproteins in ion transport in liver slices. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Feb 26;57:245–252. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)91117-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AHMED K., JUDAH J. D., WALLGREN H. Phosphoproteins and ion transport of cerebral cortex slices. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Feb 5;69:428–430. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91285-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEALD P. J. Phosphorylserine and cerebral phosphoprotein. Biochem J. 1958 Apr;68(4):580–584. doi: 10.1042/bj0680580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEALD P. J. The incorporation of phosphate into cerebral phosphoportein promoted by electrical impulses. Biochem J. 1957 Aug;66(4):659–663. doi: 10.1042/bj0660659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pumphrey A. M. Incorporation of [32P]orthophosphate into brain-slice phospholipids and their precursors. Effects of electrical stimulation. Biochem J. 1969 Mar;112(1):61–70. doi: 10.1042/bj1120061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAFFER N. K., MAY S. C., Jr, SUMMERSON W. H. Serine phosphoric acid from diisopropylphosphoryl chymotrypsin. J Biol Chem. 1953 May;202(1):67–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TREVOR A. J., RODNIGHT R. THE SUBCELLULAR LOCALIZATION OF CEREBRAL PHOSPHOPROTEINS SENSITIVE TO ELECTRICAL STIMULATION. Biochem J. 1965 Jun;95:889–896. doi: 10.1042/bj0950889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WADE H. E., MORGAN D. M. Detection of phosphate esters on paper chromatograms. Nature. 1953 Mar 21;171(4351):529–530. doi: 10.1038/171529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


