Abstract
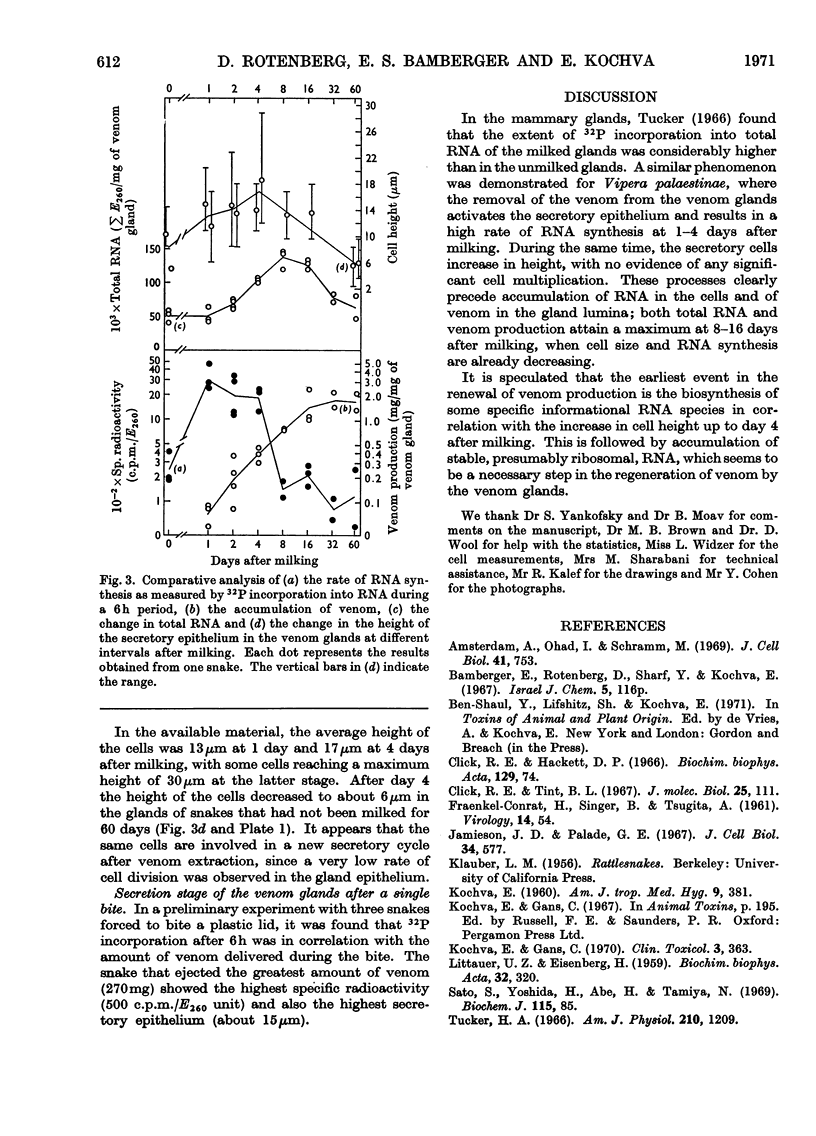
RNA metabolism in the venom glands of Vipera palaestinae was studied at different stages after manual extraction of the venom (milking). The rate of 32P incorporation into gland RNA was found to be maximal at 1–4 days after milking in correlation with the height of the secretory epithelium. Venom production attained a maximum only after 8–16 days, in parallel with the accumulation of stable species of cellular RNA.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amsterdam A., Ohad I., Schramm M. Dynamic changes in the ultrastructure of the acinar cell of the rat parotid gland during the secretory cycle. J Cell Biol. 1969 Jun;41(3):753–773. doi: 10.1083/jcb.41.3.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Click R. E., Tint B. L. Comparative sedimentation rates of plant, bacterial and animal ribosomal RNA. J Mol Biol. 1967 Apr 14;25(1):111–122. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90282-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRAENKEL-CONRAT H., SINGER B., TSUGITA A. Purification of viral RNA by means of bentonite. Virology. 1961 May;14:54–58. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90131-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson J. D., Palade G. E. Intracellular transport of secretory proteins in the pancreatic exocrine cell. I. Role of the peripheral elements of the Golgi complex. J Cell Biol. 1967 Aug;34(2):577–596. doi: 10.1083/jcb.34.2.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOCHVA E. A quantitative study of venom secretion by Vipera palaestinae. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1960 Jul;9:381–390. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1960.9.381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochva E., Gans C. Salivary glands of snakes. Clin Toxicol. 1970 Sep;3(3):363–387. doi: 10.3109/15563657008990115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTAUER U. Z., EISENBERG H. Ribonucleic acid from Escherichia coli; preparation, characterization and physical properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Apr;32:320–337. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90604-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato S., Yoshida H., Abe H., Tamiya N. Properties and biosynthesis of a neurotoxic protein of the venoms of s snakes Laticauda laticaudata and Laticauda colubrina. Biochem J. 1969 Oct;115(1):85–90. doi: 10.1042/bj1150085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker H. A. Regulation of mammary nucleic acid content by various suckling intensities. Am J Physiol. 1966 Jun;210(6):1209–1214. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.210.6.1209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]