Abstract
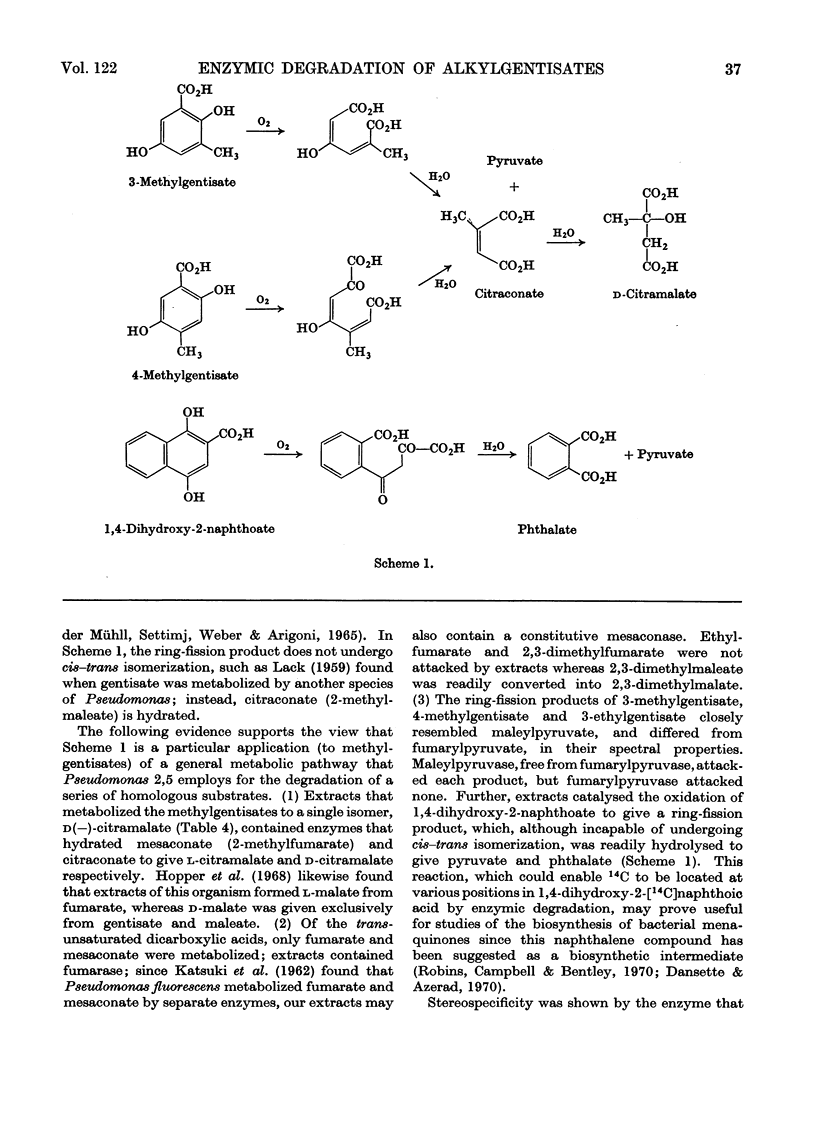
1. Cell-free extracts, prepared from a non-fluorescent Pseudomonas grown on m-cresol, oxidized gentisate and certain alkyl-substituted gentisates with the consumption of 1 mol of oxygen and the formation of 1 mol of pyruvate from 1 mol of substrate. 2. In addition to pyruvate, malate was formed from gentisate; citramalate was formed from 3-methylgentisate and 4-methylgentisate; 2,3-dimethylmalate was formed from 3,4-dimethylgentisate. 3. One enantiomer, d-(−)-citramalate, was formed enzymically from 3-methylgentisate, 4-methylgentisate and citraconate. l-(+)-Citramalate was formed from mesaconate by the same extracts. When examined as its dimethyl ester by gas–liquid chromatography, enzymically formed 2,3-dimethylmalate showed the same behaviour as one of the two racemates prepared from the synthetic compound. 4. Maleate, citraconate and 2,3-dimethylmaleate were rapidly hydrated by cell extracts, but ethylfumarate and 2,3-dimethylfumarate were not attacked. 5. Cell extracts oxidized 1,4-dihydroxy-2-naphthoate to give pyruvate and phthalate. 6. Alkylgentisates were oxidized by a gentisate oxygenase (EC 1.13.1.4) present in Pseudomonas 2,5. The ring-fission products were attacked by maleylpyruvase, but not by fumarylpyruvase, and their u.v.-absorption spectra were those expected for alkyl-substituted maleylpyruvates. 7. When supplemented with ATP, CoA, succinate and Mg2+ ions, an enzyme system from cells grown with 2,5-xylenol formed pyruvate from d- but not from l-citramalate. Extracts from cells grown with dl-citramalate or with itaconate attacked both d- and l-citramalate; other alkylmalates were cleaved in similar fashion to give pyruvate or 2-oxobutyrate. 8. These results accord with a general sequence of reactions in which the benzene nucleus of an alkylgentisate is cleaved to give an alkyl-substituted maleylpyruvate. The ring-fission products are hydrolysed to give pyruvate, plus alkylmalic acids which then undergo aldol fissions, probably as their CoA esters. In Pseudomonas 2,5 several homologous sequences of this general type appear to be catalysed by a single battery of enzymes with broad substrate specificities, whereas the metabolic capabilities of the fluorescent Pseudomonas 3,5 are more restricted. 9. Intact cells of both organisms metabolize d-malic acid by reactions that have not been elucidated, but are different from those which degrade alkylmalates.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayly R. C., Dagley S., Gibson D. T. The metabolism of cresols by species of Pseudomonas. Biochem J. 1966 Nov;101(2):293–301. doi: 10.1042/bj1010293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayly R. C., Dagley S. Oxoenoic acids as metabolites in the bacterial degradation of catechols. Biochem J. 1969 Feb;111(3):303–307. doi: 10.1042/bj1110303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne G. A. The separation of 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazones by thin-layer chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1965 Dec;20(3):528–540. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)97455-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CALVO J. M., KALYANPUR M. G., STEVENS C. M. 2-Isopropylmalate and 3-isopropylmalate as intermediates in leucine biosynthesis. Biochemistry. 1962 Nov;1:1157–1161. doi: 10.1021/bi00912a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHEFTEL R. I., MUNIER R., MACHEBOEUF M. Microchromatographie de partage sur papier des acides aliphatiques hydrosolubles et non volatils. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1951;33(7):840–845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman P. J., Hopper D. J. The bacterial metabolism of 2,4-xylenol. Biochem J. 1968 Dec;110(3):491–498. doi: 10.1042/bj1100491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper R. A., Kornberg H. L. The utilization of itaconate by Pseudomonas sp. Biochem J. 1964 Apr;91(1):82–91. doi: 10.1042/bj0910082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagley S., Chapman P. J., Gibson D. T. The metabolism of beta-phenylpropionic acid by an Achromobacter. Biochem J. 1965 Dec;97(3):643–650. doi: 10.1042/bj0970643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagley S., Geary P. J., Wood J. M. The metabolism of protocatechuate by Pseudomonas testosteroni. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(4):559–568. doi: 10.1042/bj1090559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dansette P., Azerad R. A new intermediate in naphthoquinone and menaquinone biosynthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Sep 10;40(5):1090–1095. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90906-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper D. J., Chapman P. J., Dagley S. Enzymic formation of D-malate. Biochem J. 1968 Dec;110(4):798–800. doi: 10.1042/bj1100798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper D. J., Chapman P. J., Dagley S. Metabolism of l-Malate and d-Malate by a Species of Pseudomonas. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1197–1202. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1197-1202.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper D. J., Chapman P. J. Gentisic acid and its 3- and 4-methyl-substituted homologoues as intermediates in the bacterial degradation of m-cresol, 3,5-xylenol and 2,5-xylenol. Biochem J. 1971 Mar;122(1):19–28. doi: 10.1042/bj1220019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INOUYE H. Uber die Bestandteile von Pirola japonica Sieb. V. Die Konstitution des Pirolatins. (3). Pharm Bull. 1954 Dec;2(4):359–367. doi: 10.1248/cpb1953.2.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISHERWOOD F. A., HANES C. S. Separation and estimation of organic acids on paper chromatograms. Biochem J. 1953 Dec;55(5):824–830. doi: 10.1042/bj0550824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KALBE H. Papierchromatographie aliphatischer Dicarbonsäuren. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1954;297(1):19–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATSUKI H., ARIGA N., KATSUKI F., NAGAI J., EGASHIRA S., TANAKA S. Enzymic hydration of mesaconate by Pseudomonas fluorescens. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jan 29;56:545–551. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90606-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOEGEL R. J., McCALLUM R. A., GREENSTEIN J. P., WINITZ M., BIRNBAUM S. M. The solid-state infrared absorption of the optically active and racemic straight-chain alpha-amino acids. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1957 Sep 7;69(1):94–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1957.tb49652.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs H. A., Eggleston L. V. The effect of citrate on the rotation of the molybdate complexes of malate, citramalate and isocitrate. Biochem J. 1943 Sep;37(3):334–338. doi: 10.1042/bj0370334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LACK L. The enzymic oxidation of gentisic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Jul;34:117–123. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90239-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornston L. N. The conversion of catechol and protocatechuate to beta-ketoadipate by Pseudomonas putida. 3. Enzymes of the catechol pathway. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 25;241(16):3795–3799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornston L. N. The conversion of catechol and protocatechuate to beta-ketoadipate by Pseudomonas putida. II. Enzymes of the protocatechuate pathway. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 25;241(16):3787–3794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabin R., Salamon I. I., Bleiweis A. S., Carlin J., Ajl S. J. Metabolism of ethylmalic acids by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochemistry. 1968 Jan;7(1):377–388. doi: 10.1021/bi00841a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins D. J., Campbell I. M., Bentley R. Glutamate--a precusor for the naphthalene nucleus of bacterial menaquinones. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970;39(6):1081–1086. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90669-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRASSMAN M., CECI L. N. Enzymatic formation of alpha-isopropylmalic acid, an intermediate in leucine biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jul;238:2445–2452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw D. A., Borkenhagen L. F., Talalay P. Enzymatic oxidation of steroids by cell-free extracts of Pseudomonas testosteroni: isolation of cleavage products of ring A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Sep;54(3):837–844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.3.837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


