Abstract
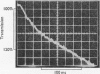
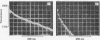
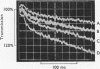
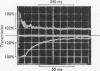
Transient kinetic methods have been used to study the influence of NAD+ on the rate of elementary processes of the reversible oxidative phosphorylation of d-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate catalysed by d-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. In the pH range 5–8 NAD+ is bound to the enzyme during the following elementary processes of the mechanism: phosphorolysis of the acyl-enzyme, its formation from 1,3-diphosphoglycerate and the enzyme and the formation and breakdown of the glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate–enzyme complex. The rates of these four elementary processes only equal or exceed the turnover rate of the enzyme when NAD+ is bound and are as much as 104 times the rates in the absence of NAD+. Autocatalysis of the reductive dephosphorylation of 1,3-diphosphoglycerate occurs when glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate release is rate determining because NAD+ is a reaction product. An important feature of the enzyme mechanism is that the negative-free-energy change of a chemical reaction, acyl-enzyme formation, is linked in a simple way to the positive-free-energy change of a dissociation reaction, NAD+ release.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLISON W. S., KAPLAN N. O. THE COMPARATIVE ENZYMOLOGY OF TRIOSEPHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jul;239:2140–2152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson B. E., Sajgò M., Noller H. F., Harris J. I. Amino-acid sequence of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase from lobster muscle. Nature. 1967 Dec 23;216(5121):1181–1185. doi: 10.1038/2161181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FURFINE C. S., VELICK S. F. THE ACYL-ENZYME INTERMEDIATE AND THE KINETIC MECHANISM OF THE GLYCERALDEHYDE 3-PHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE REACTION. J Biol Chem. 1965 Feb;240:844–855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher H. F., Adija D. L., Cross D. G. Dehydrogenae-reduced coenzyme difference spectra, their resolution and relationship to the stereospecificity of hydrogen transfer. Biochemistry. 1969 Nov;8(11):4424–4431. doi: 10.1021/bi00839a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARTING J., VELICK S. F. Transfer reactions of acetyl phosphate catalyzed by glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1954 Apr;207(2):867–878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENCKS W. P., CORDES S., CARRIUOLO J. The free energy of thiol ester hydrolysis. J Biol Chem. 1960 Dec;235:3608–3614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malhotra O. P., Bernhard S. A. Spectrophotometric identification of an active site-specific acyl glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. The regulation of its kinetic and equilibrium properties by coenzyme. J Biol Chem. 1968 Mar 25;243(6):1243–1252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARK J. H., MERIWETHER B. P., CLODFELDER P., CUNNINGHAM L. W. The hydrolysis of p-nitrophenyl acetate catalyzed by 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1961 Jan;236:136–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RACKER E., KRIMSKY I. The mechanism of oxidation of aldehydes by glyceralde-hyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1952 Oct;198(2):731–743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SZEWCZUK A., WOLNY E., WOLNY M., BARANOWSKI T. [A new method for obtaining d-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate]. Acta Biochim Pol. 1961;8:201–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trentham D. R. Aspects of the chemistry of D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(4):603–612. doi: 10.1042/bj1090603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trentham D. R., McMurray C. H., Pogson C. I. The active chemical state of D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate in its reactions with D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase, aldolase and triose phosphate isomerase. Biochem J. 1969 Aug;114(1):19–24. doi: 10.1042/bj1140019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trentham D. R. Rate-determining processes and the number of simultaneously active sties of D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1971 Mar;122(1):71–77. doi: 10.1042/bj1220071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vijlder J. J., Hilvers A. G., Van Lis J. M., Slater E. C. Function and role of NAD+ in mechanism of action of rabbit-muscle glyceraldehydephosphate dehydrogenase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Nov 4;191(2):221–228. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(69)90241-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]