Abstract
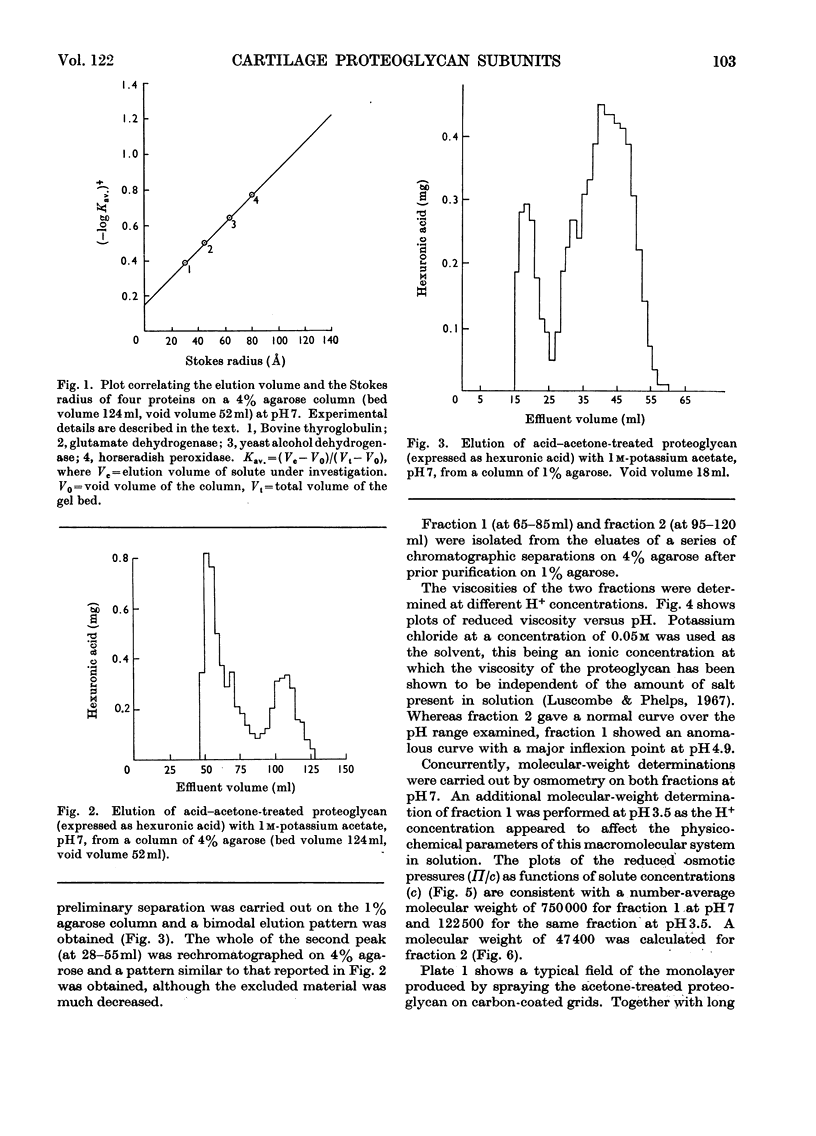
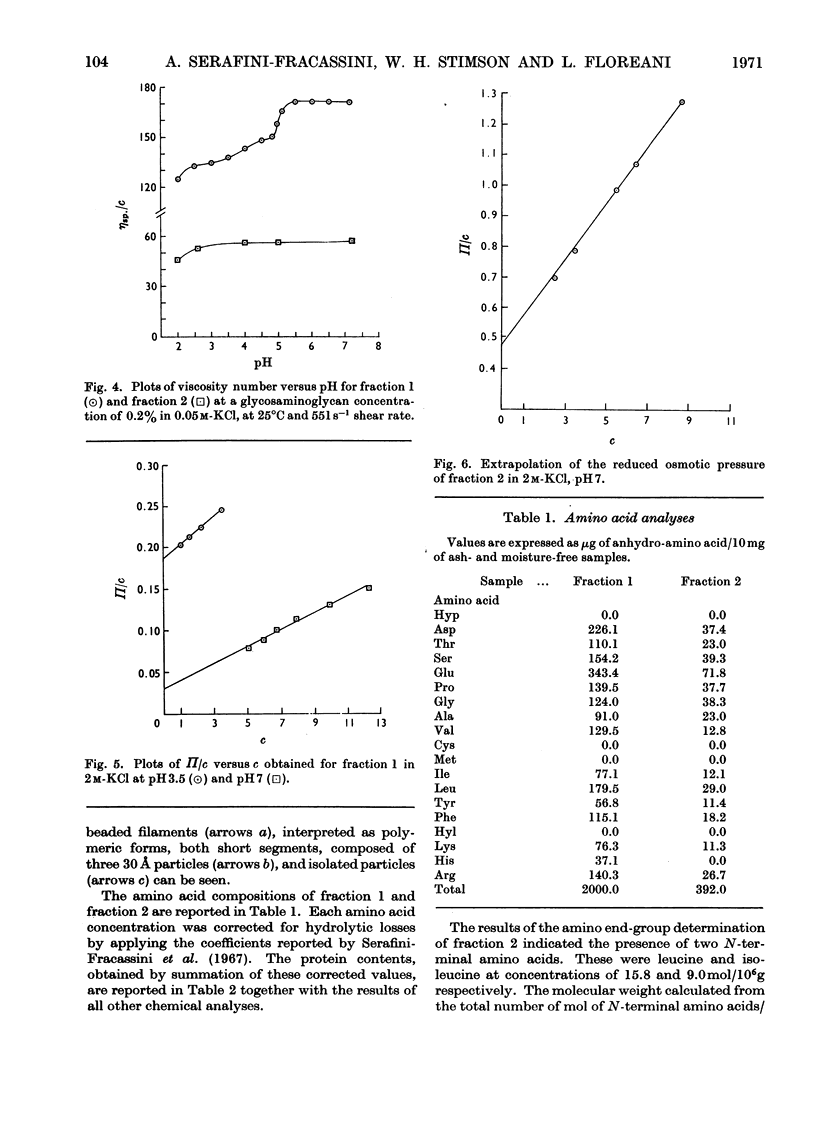
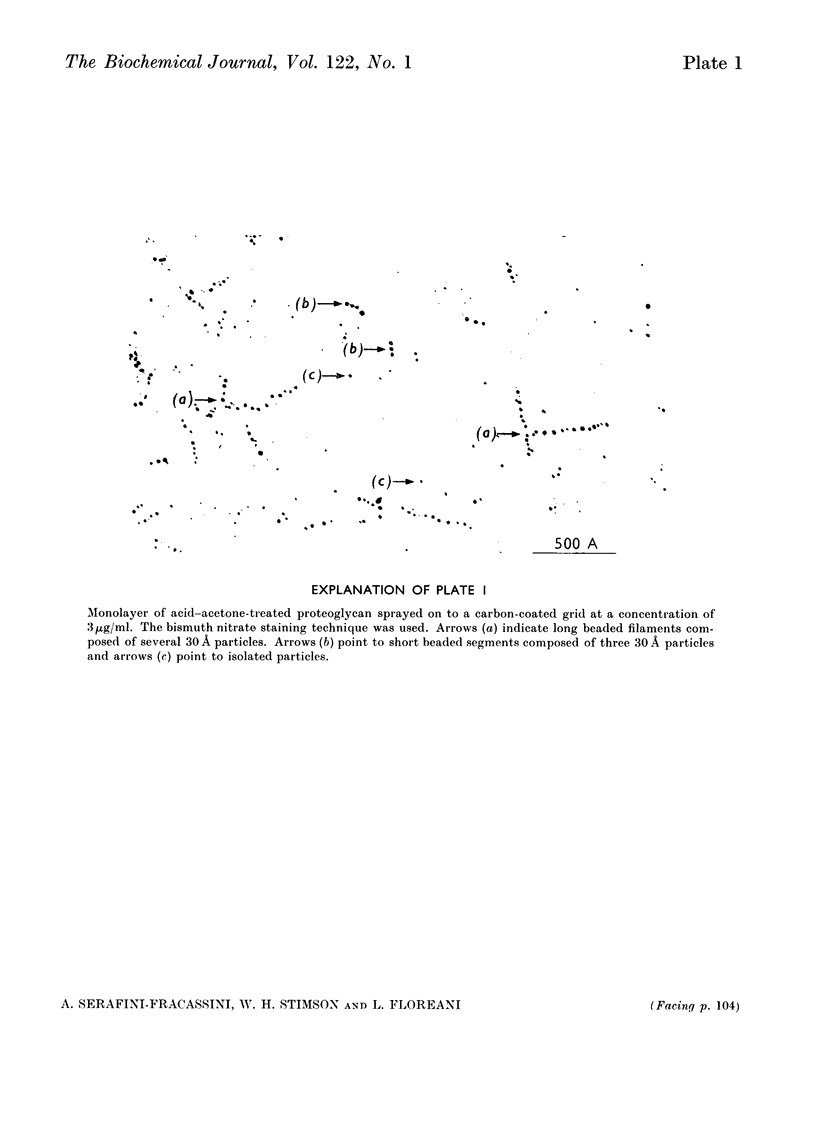
1. The light fraction of the proteoglycan of bovine nasal cartilage was split by treatment with 0.1m-hydrochloric acid in acetone. The products were separated by gel filtration on 4% agarose and two retarded fractions were detected and isolated. These two fractions were found to have a Stokes radius of 134 and 47 Å respectively, as determined by calibration of the column against proteins of known hydrodynamic volumes. 2. The 47 Å fraction had a protein content of 4% and a glucosamine/galactosamine ratio 1:23. The 134 Å fraction had a protein content of 20% and a glucosamine/galactosamine ratio 1:4.8. 3. The results of the viscometric studies on both fractions suggested that the 134 Å fraction alone exhibited the property of undergoing reversible pH-dependent aggregation with a transition point at pH4.9. 4. It was concluded that these fractions could represent subunits of the native cartilage proteoglycan.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BITTER T., MUIR H. M. A modified uronic acid carbazole reaction. Anal Biochem. 1962 Oct;4:330–334. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(62)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boothroyd B., Napier E. J., Somerfield G. A. The demethylation of griseofulvin by fungi. Biochem J. 1961 Jul;80(1):34–37. doi: 10.1042/bj0800034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CECIL R., OGSTON A. G. Determination of sedimentation and diffusion constants of horse-radish peroxidase. Biochem J. 1951 Jun;49(1):105–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CESSI C., PILIEGO F. The determination of amino sugars in the presence of amino acids and glucose. Biochem J. 1960 Dec;77:508–510. doi: 10.1042/bj0770508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDELHOCH H. The properties of thyroglobulin. I. The effects of alkali. J Biol Chem. 1960 May;235:1326–1334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson L. A., Morgan W. T. A colorimetric method for the determination of glucosamine and chondrosamine. Biochem J. 1933;27(6):1824–1828. doi: 10.1042/bj0271824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERBER B. R., FRANKLIN E. C., SCHUBERT M. Ultracentrifugal fractionation of bovine nasal chondromucoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1960 Oct;235:2870–2875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYES J. E., Jr, VELICK S. F. Yeast alcohol dehydrogenase: molecular weight, coenzyme binding, and reaction equilibria. J Biol Chem. 1954 Mar;207(1):225–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hascall V. C., Sajdera S. W. Proteinpolysaccharide complex from bovine nasal cartilage. The function of glycoprotein in the formation of aggregates. J Biol Chem. 1969 May 10;244(9):2384–2396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P., Mashburn T. A., Jr, Meyer K., Bray B. A. Proteinpolysaccharide of bovine cartilage. I. Extraction and electrophoretic studies. J Biol Chem. 1967 Sep 10;242(17):3799–3804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P., Mashburn T. A., Jr, Meyer K. Proteinpolysaccharide of bovine cartilage. II. The relation of keratan sulfate and chondroitin sulfate. J Biol Chem. 1967 Sep 10;242(17):3805–3809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ITZHAKI R. F., GILL D. M. A MICRO-BIURET METHOD FOR ESTIMATING PROTEINS. Anal Biochem. 1964 Dec;9:401–410. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(64)90200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luscombe M., Phelps C. F. The composition and physicochemical properties of bovine nasal-septa protein-polysaccharide complex. Biochem J. 1967 Jan;102(1):110–119. doi: 10.1042/bj1020110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALAWISTA I., SCHUBERT M. Chondromucoprotein: new extraction method and alkaline degradation. J Biol Chem. 1958 Jan;230(1):535–544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATHEWS M. B., LOZAITYTE I. Sodium chondroitin sulfate-protein complexes of cartilage. I. Molecular weight and shape. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1958 Mar;74(1):158–174. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(58)90210-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. B., Cifonelli J. A. Comparative biochemistry of keratosulfates. J Biol Chem. 1965 Nov;240(11):4140–4145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROGERS K. S., HELLERMAN L., THOMPSON T. E. L-GLUTAMATE DEHYDROGENASE. 3. MOLECULAR SIZE OF BOVINE GLUTAMATE DEHYDROGENASE AND THE METHYLMERCURIC BROMIDE-ACTIVATED ENZYME IN THE CONCENTRATION RANGE OF ENZYMATIC ASSAY. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jan;240:198–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serafini-Fracassini A., Durward J. J., Crawford J. The morphology of the heparin-protein macromolecule and its organization in the mast cell granule. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Jul;28(1):131–140. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serafini-Fracassini A., Peters T. J., Floreani L. The protein-polysaccharide complex of bovine nasal cartilage. Studies on the protein core. Biochem J. 1967 Nov;105(2):569–575. doi: 10.1042/bj1050569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serafini-Fracassini A., Smith J. W. Observations on the morphology of the proteinpolysaccharide complex of bovine nasal cartilage and its relationship to collagen. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1966 Oct 11;165(1001):440–449. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1966.0076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serafini-Fracassini A. The protein-polysaccharide complex of bovine nasal cartilage. Studies on the molecular organisation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Dec 23;170(2):289–300. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(68)90009-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. W., Peters T. J., Serafini-Fracassini A. Observations on the distribution of the proteinpolysaccharide complex and collagen in bovine articular cartilage. J Cell Sci. 1967 Mar;2(1):129–136. doi: 10.1242/jcs.2.1.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



