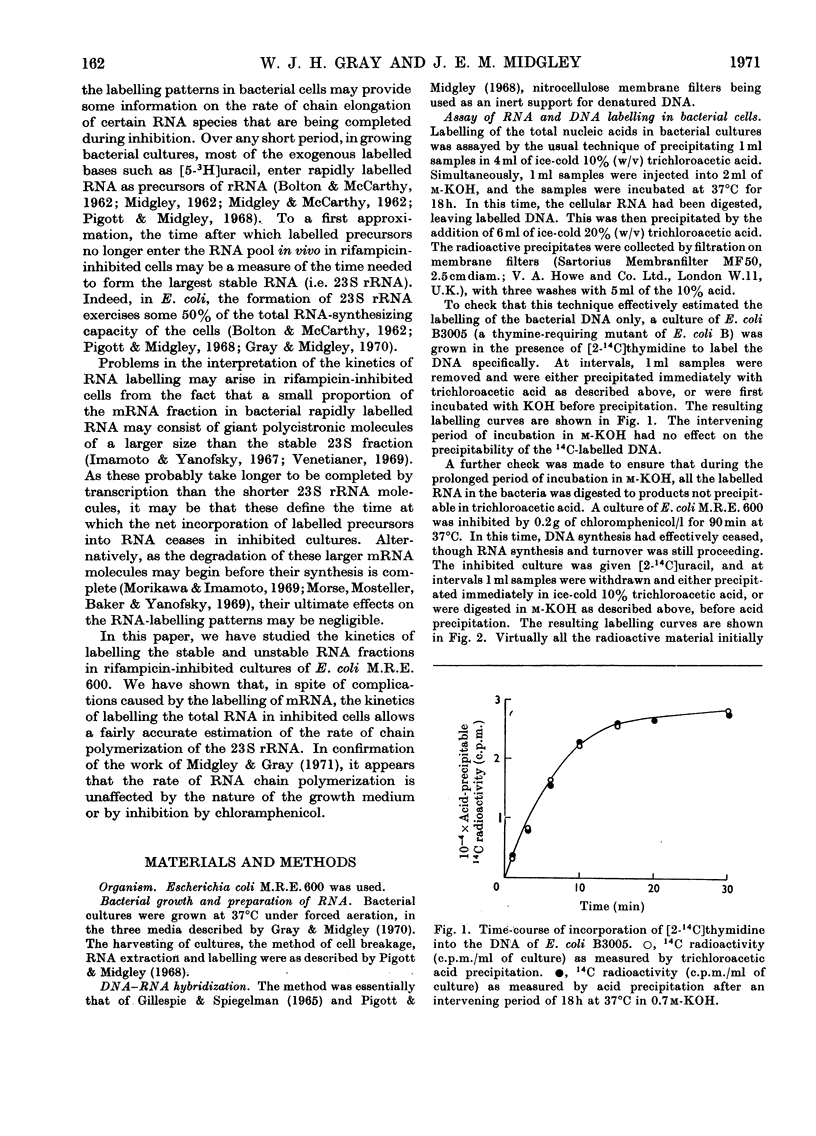
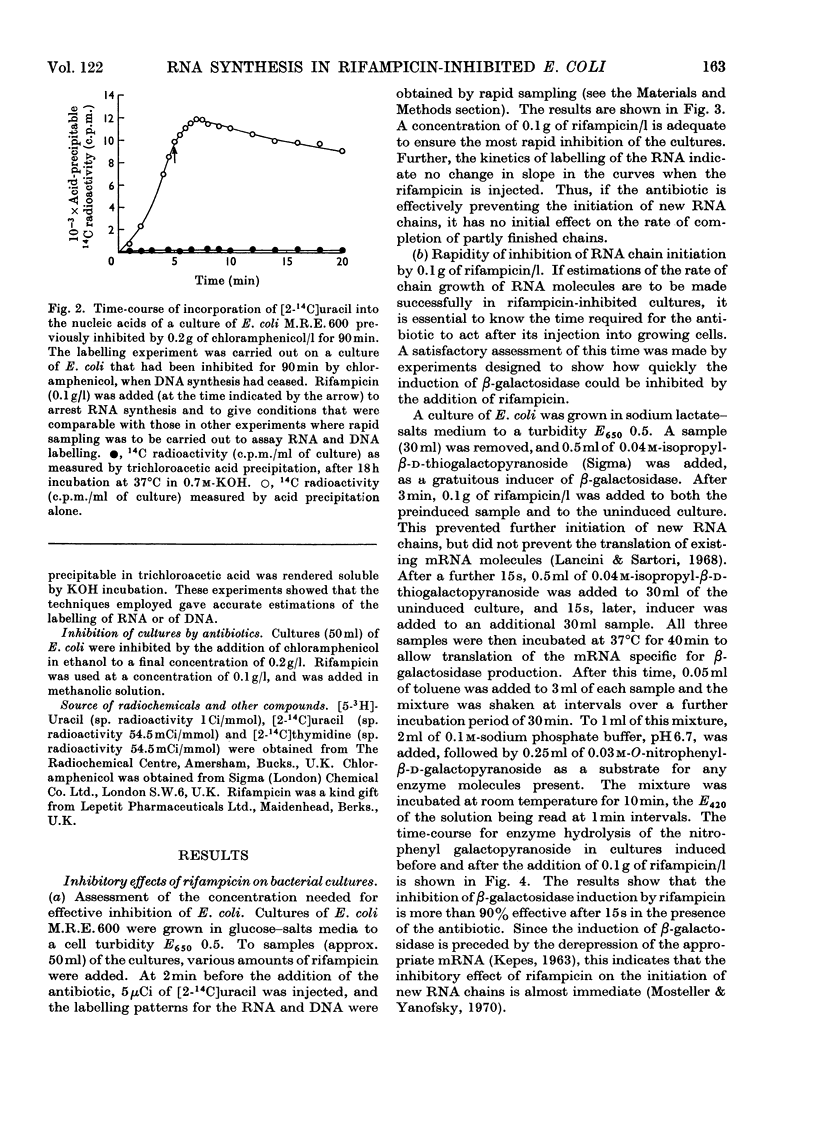
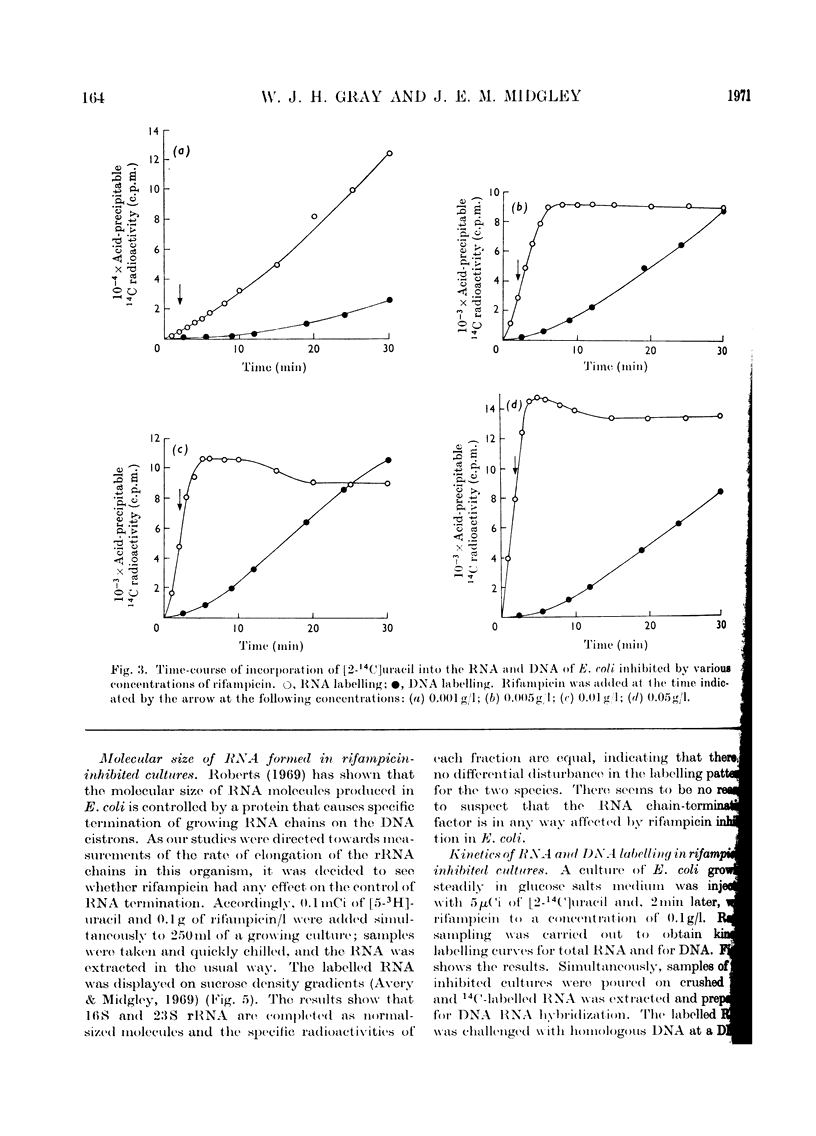
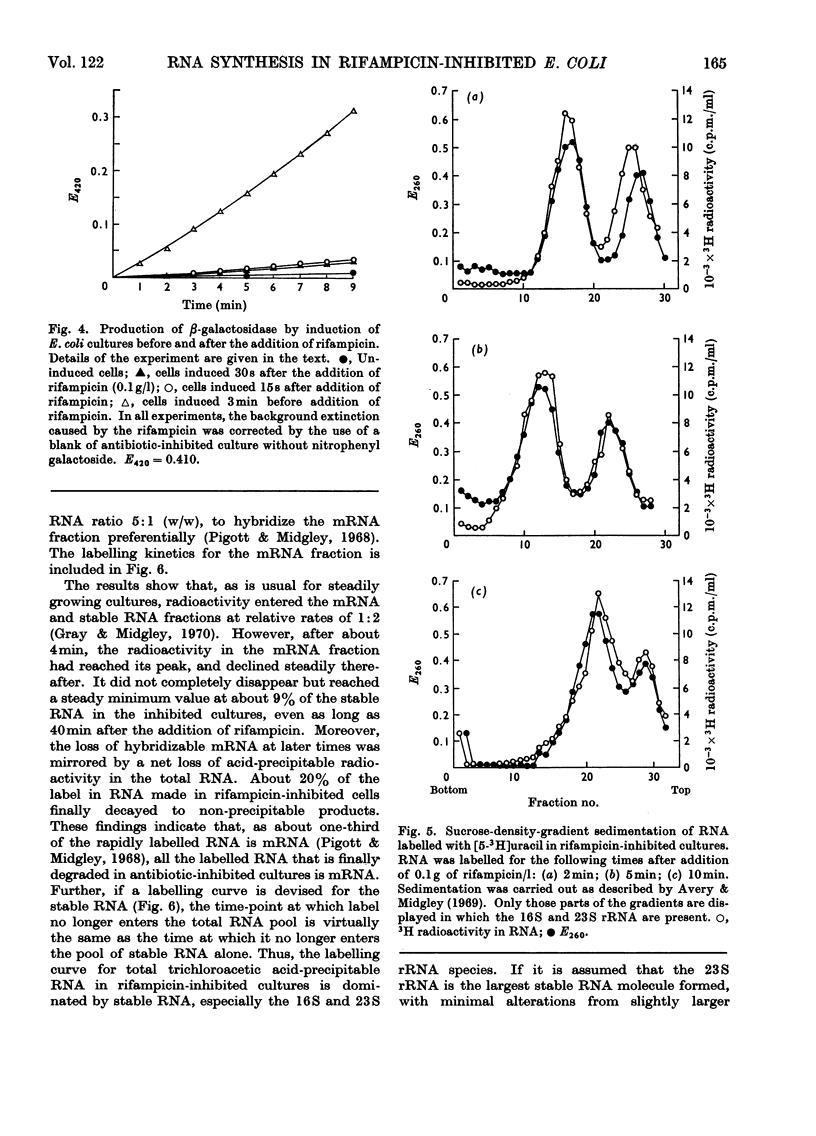
Abstract
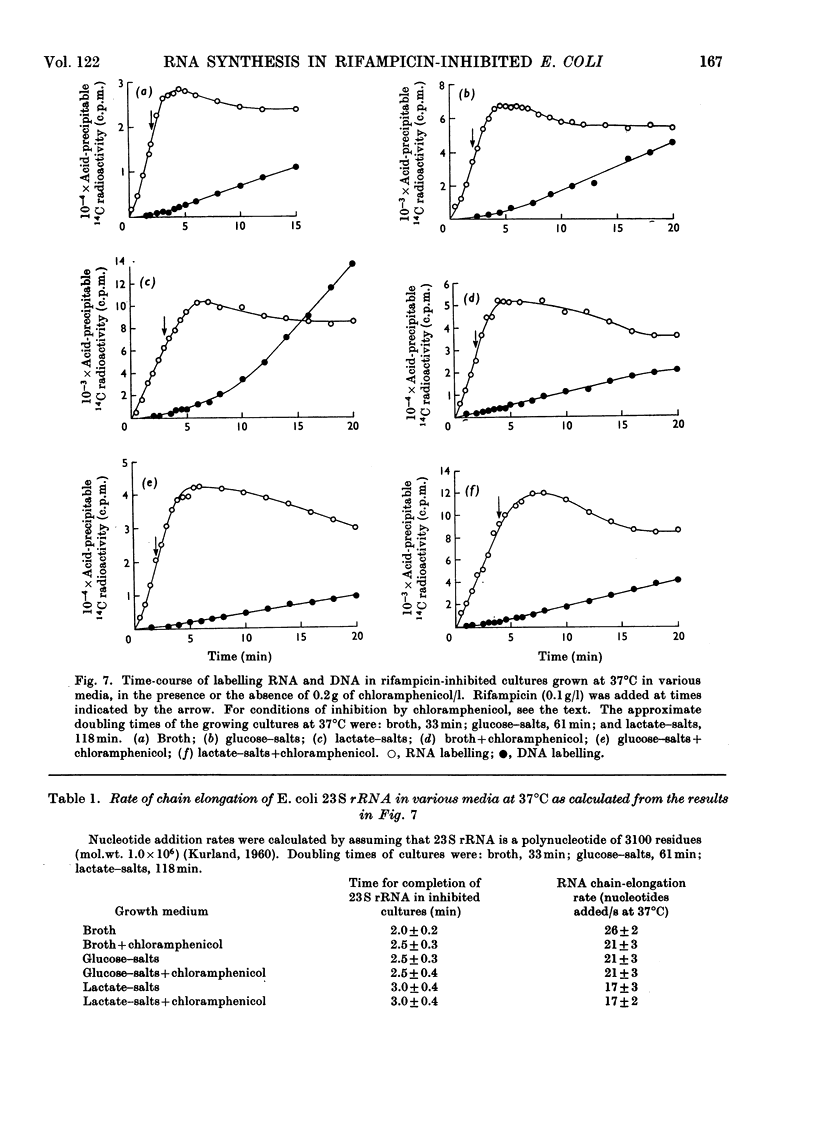
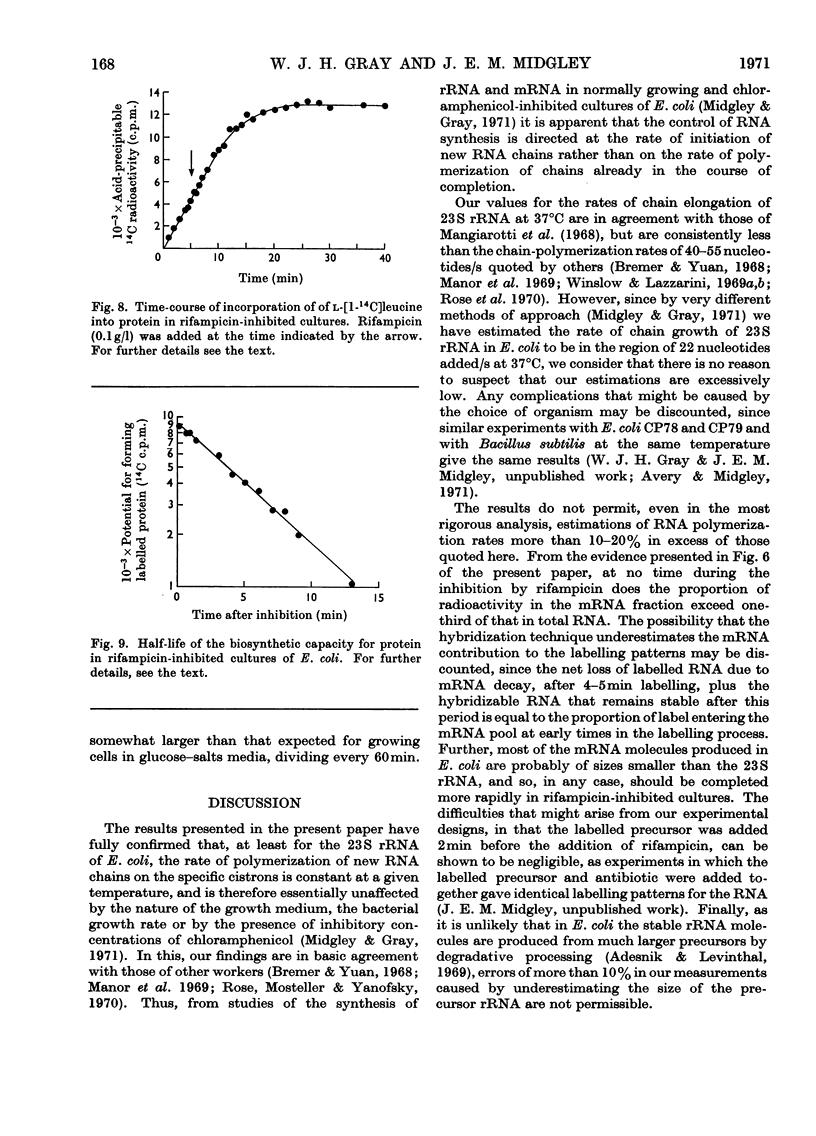
A study was made of the kinetics of labelling of the stable ribonucleic acids (rRNA+tRNA) and the unstable mRNA fraction in cultures of Escherichia coli M.R.E.600, inhibited by the addition of 0.1g of rifampicin/l. Labelling was carried out by adding either [2-14C]- or [5-3H]-uracil as an exogenous precursor of the cellular nucleic acids. From studies using DNA RNA hybridization, the kinetics of the synthesis and degradation of mRNA was followed in the inhibited cultures. Although a considerable proportion of the mRNA labelled in the presence of rifampicin decayed to non-hybridizable products, about 25% was stabilized beyond the point where protein synthesis had finally ceased. It therefore seems unwise to extrapolate the results of studies on mRNA stability in rifampicin-inhibited cultures to the situation existing in the rate of steady growth, where there appears to be little, if any, stable messenger. The kinetics of labelling of RNA in inhibited cultures indicated that the clapsed time from the addition of rifampicin to the point at which radioactivity no longer enters the total cellular ribonucleic acids is a measure of the time required to polymerize a molecule of rRNA. At 37°C, in culture grown in broth, glucose–salts or lactate salts media, exogenous [2-14C]uracil entered rifampicin-inhibited cells and was incorporated into RNA for 2 3min after the antibiotic was added. Taking this time as that required to polymerize a complete chain of 23S rRNA, the polymerization rate of this fraction in the three media was 25, 22 and 19 nucleotides added/s to the growing chains. Similar experiments in cultures previously inhibited by 0.2g of chloramphenicol/l showed virtually identical behaviour. This confirmed the work of Midgley & Gray (1971), who, by a different approach, showed that the polymerization rate of rRNA in steadily growing and chloramphenicol-inhibited cultures of E. coli at 37°C was essentially constant at about 22 nucleotides added/s. It was thus confirmed that the rate of polymerization of at least the rRNA fraction in E. coli is virtually unaffected by the nature of the growth medium and therefore by bacterial growth rate.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adesnik M., Levinthal C. Synthesis and maturation of ribosomal RNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 Dec 14;46(2):281–303. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90422-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avery R. J., Midgley J. E. A new approach to the analysis of hybridization of bacterial nucleic acids. Analysis of the ribosomal ribonucleic acids of Bacillus subtilis. Biochem J. 1969 Nov;115(3):383–394. doi: 10.1042/bj1150383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avery R. J., Midgley J. E. Ribosomal ribonucleic acid synthesis in Bacillus subtilis. Biochem J. 1971 Apr;122(2):139–148. doi: 10.1042/bj1220139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOLTON E. T., McCARTHY B. J. A general method for the isolation of RNA complementary to DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Aug;48:1390–1397. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.8.1390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremer H., Yuan D. RNA chain growth-rate in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1968 Dec 14;38(2):163–180. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90404-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie D., Spiegelman S. A quantitative assay for DNA-RNA hybrids with DNA immobilized on a membrane. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jul;12(3):829–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80331-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray W. J., Midgley J. E. The control of ribonucleic acid synthesis in bacteria. Steady-state content of messenger ribonucleic acid in Escherichia coli M.R.E. 600. Biochem J. 1970 Nov;120(2):279–288. doi: 10.1042/bj1200279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEPES A. KINETICS OF INDUCED ENZYME SYNTHESIS. DETERMINATION OF THE MEAN LIFE OF GALACTOSIDASE-SPECIFIC MESSENGER RNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Oct 15;76:293–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacroute F., Stent G. S. Peptide chain growth of -galactosidase in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jul 14;35(1):165–173. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(68)80044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancini G. C., Sartori G. Rifamycins LXI: in vivo inhibition of RNA synthesis of rifamycins. Experientia. 1968 Nov 15;24(11):1105–1106. doi: 10.1007/BF02147783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIDGLEY J. E., McCARTHY B. J. The synthesis and kinetic behavior of deoxyribonucleic acid-like ribonucleic acid in bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Nov 26;61:696–717. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(62)90053-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangiarotti G., Apirion D., Schlessinger D., Silengo L. Biosynthetic precursors of 30S and 50S ribosomal particles in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1968 Jan;7(1):456–472. doi: 10.1021/bi00841a058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midgley J. E., Gray W. J. The control of ribonucleic acid synthesis in bacteria. The synthesis and stability of ribonucleic acid in chloramphenicol-inhibited cultures of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1971 Apr;122(2):149–159. doi: 10.1042/bj1220149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno S., Yamazaki H., Nitta K., Umezawa H. Inhibition of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase reaction of Escherichia coli by an antimicrobial antibiotic, streptovaricin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Apr 22;157(2):322–332. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90086-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morikawa N., Imamoto F. Degradation of tryptophan messenger. On the degradation of messenger RNA for the tryptophan operon in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1969 Jul 5;223(5201):37–40. doi: 10.1038/223037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse D. E., Mosteller R., Baker R. F., Yanofsky C. Direction of in vivo degradation of tryptophan messenger RNA--a correction. Nature. 1969 Jul 5;223(5201):40–43. doi: 10.1038/223040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosteller R. D., Yanofsky C. Transcription of the tryptophan operon in Escherichia coli: rifampicin as an inhibitor of initiation. J Mol Biol. 1970 Mar;48(3):525–531. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90064-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pigott G. H., Midgley J. E. Characterization of rapidly labelled ribonucleic acid in Escherichia coli by deoxyribonucleic acid-ribonucleic acid hybridization. Biochem J. 1968 Nov;110(2):251–263. doi: 10.1042/bj1100251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. W. Termination factor for RNA synthesis. Nature. 1969 Dec 20;224(5225):1168–1174. doi: 10.1038/2241168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Mosteller R. D., Yanofsky C. Tryptophan messenger ribonucleic acid elongation rates and steady-state levels of tryptophan operon enzymes under various growth conditions. J Mol Biol. 1970 Aug;51(3):541–550. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sippel A., Hartmann G. Mode of action of rafamycin on the RNA polymerase reaction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Mar 18;157(1):218–219. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90286-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tocchini-Valentini G. P., Marino P., Colvill A. J. Mutant of E. coli containing an altered DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Nature. 1968 Oct 19;220(5164):275–276. doi: 10.1038/220275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venetianer P. Level of messenger RNA transcribed from the histidine operon in repressed, derepressed and histidine-starved Salmonella typhimurium. J Mol Biol. 1969 Oct 28;45(2):375–384. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90112-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wehrli W., Nüesch J., Knüsel F., Staehelin M. Action of rifamycins on RNA polymerase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Mar 18;157(1):215–217. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90285-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winslow R. M., Lazzarini R. A. Amino acid regulation of the rates of synthesis and chain elongation of ribonucleic acid in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 25;244(12):3387–3392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winslow R. M., Lazzarini R. A. The rates of synthesis and chain elongation of ribonucleic acid in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1969 Mar 10;244(5):1128–1136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


