Abstract
Membranes of chromaffin granules were isolated from the adrenal glands of four different species. The solubilized membrane proteins could be resolved into several bands by polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis (alkaline and acid gel systems). Two major protein components appeared to be common to the chromaffin granule membranes of ox, horse, pig and man. The various membrane proteins of bovine chromaffin granules were separated by filtration on Sephadex G-200 in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulphate. Two major membrane proteins (A and B) were obtained in purified form. Treatment of protein A with 2-mercaptoethanol before electrophoresis resulted in two more rapidly migrating subunits, whereas protein B was unaffected by mercaptoethanol treatment. The amino acid compositions of the two purified proteins were determined. They are very similar to that of the total membrane proteins but significantly different from that of the chromogranins, the soluble proteins of chromaffin granules.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BANKS P. THE ADENOSINE-TRIPHOSPHATASE ACTIVITY OF ADRENAL CHROMAFFIN GRANULES. Biochem J. 1965 May;95:490–496. doi: 10.1042/bj0950490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belpaire F., Laduron P. Tissue fractionation and catecholamines. I. Latency and activation properties of dopamine-beta-hydroxylase in adrenal medulla. Biochem Pharmacol. 1968 Mar;17(3):411–421. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(68)90251-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaschko H., Comline R. S., Schneider F. H., Silver M., Smith A. D. Secretion of a chromaffin granule protein, chromogranin, from the adrenal gland after splanchnic stimulation. Nature. 1967 Jul 1;215(5096):58–59. doi: 10.1038/215058a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaschko H., Firemark H., Smith A. D., Winkler H. Lipids of the adrenal medulla. Lysolecithin, a characteristic constituent of chromaffin granules. Biochem J. 1967 Aug;104(2):545–549. doi: 10.1042/bj1040545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRESTFIELD A. M., MOORE S., STEIN W. H. The preparation and enzymatic hydrolysis of reduced and S-carboxymethylated proteins. J Biol Chem. 1963 Feb;238:622–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. J., Bandemer S. L., Davidson J. A., Heinlein K., Vaghefi S. S. Binding of lipid to protein in the low-density lipoprotein from the hen's egg. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Dec 18;164(3):566–574. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(68)90186-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helle K. B. Some chemical and physical properties of the soluble protein fraction of bovine adrenal chromaffin granules. Mol Pharmacol. 1966 Jul;2(4):298–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood D. An immunohistochemical study of the adrenal medulla of the ox. A comparison of antibodies against whole ox chromaffin granules and ox chromogranin A. Histochemie. 1968;13(4):323–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell J. I., Lucy J. A. Cell fusion induced by lysolecithin. FEBS Lett. 1969 Aug;4(3):147–150. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80218-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörtnagl H., Winkler H. Bovine splenic nerve: characterization of noradrenaline-containing vesicles and other cell organelles by density gradient centrifugation. J Physiol. 1969 Nov;205(1):103–114. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa Y., Yamano T. Cytochrome 559 in the microsomes of the adrenal medulla. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Jul 26;20(3):263–268. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90357-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAUFMAN S., FRIEDMAN S. DOPAMINE-BETA-HYDROXYLASE. Pharmacol Rev. 1965 Jun;17:71–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirshner N., Kirshner A. G., Kamin D. L. Adenosine triphosphatase activity of adrenal medulla catecholamine granules. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 14;113(2):332–335. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(66)80072-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poisner A. M., Trifaró J. M., Douglas W. W. The fate of the chromaffin granule during catecholamine release from the adrenal medulla. II. Loss of protein and retention of lipid in subcellular fractions. Biochem Pharmacol. 1967 Nov;16(11):2101–2108. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(67)90007-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage H. J., Smith W. J., Kirshner N. Mechanism of secretion from the adrenal medulla. I. A microquantitative immunologic assay for bovine adrenal catecholamine storage vesicle protein and its application to studies of the secretory process. Mol Pharmacol. 1967 Jan;3(1):81–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider F. H., Smith A. D., Winkler H. Secretion from the adrenal medulla: biochemical evidence for exocytosis. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1967 Sep;31(1):94–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1967.tb01980.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. D., Winkler H. A simple method for the isolation of adrenal chromaffin granules on a large scale. Biochem J. 1967 May;103(2):480–482. doi: 10.1042/bj1030480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. D., Winkler H. Purification and properties of an acidic protein from chromaffin granules of bovine adrenal medulla. Biochem J. 1967 May;103(2):483–492. doi: 10.1042/bj1030483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. J., Kirshner N. A specific soluble protein from the catecholamine storage vesicles of bovine adrenal medulla. I. Purification and chemical characterization. Mol Pharmacol. 1967 Jan;3(1):52–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strieder N., Ziegler E., Winkler H., Smith A. D. Some properties of soluble proteins from chromaffin granules of different species. Biochem Pharmacol. 1968 Aug;17(8):1553–1556. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(68)90214-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
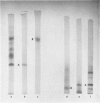
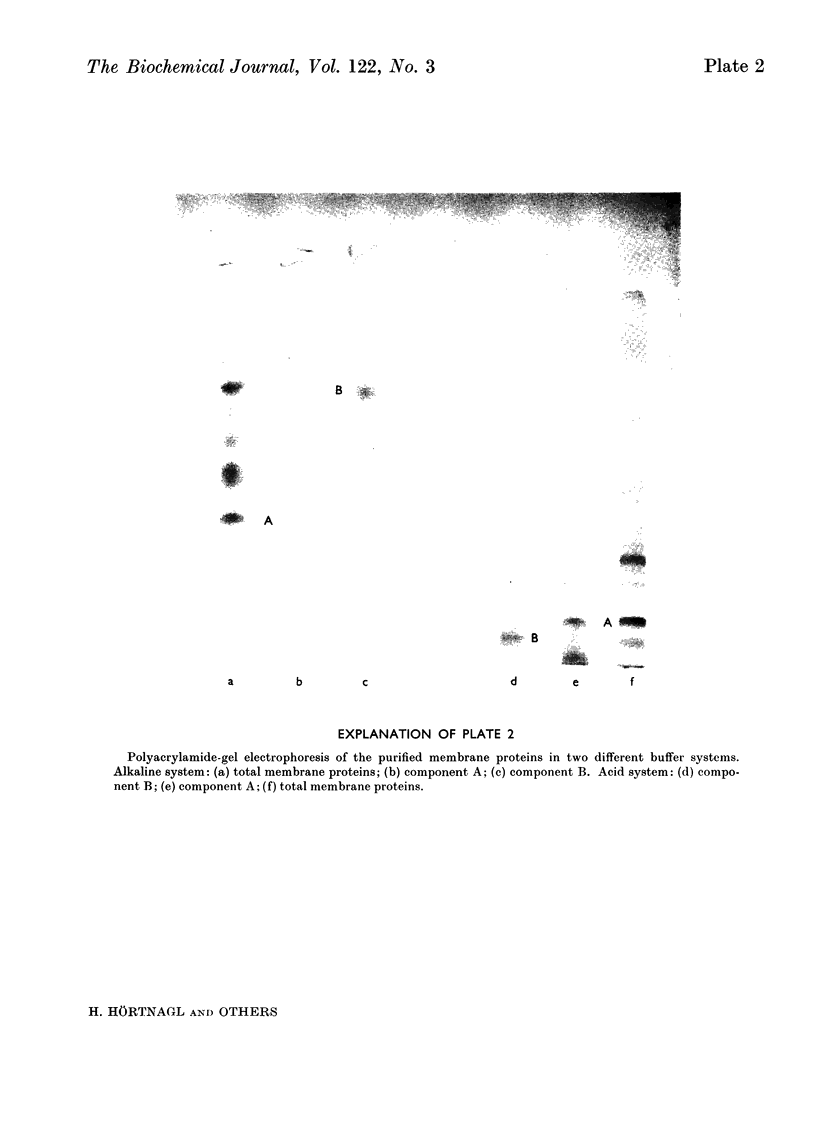
- Winkler H., Hörtnagl H., Smith A. D. Membranes of the adrenal medulla. Behaviour of insoluble proteins of chromaffin granules on gel electrophoresis. Biochem J. 1970 Jun;118(2):303–310. doi: 10.1042/bj1180303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. Isolierung und Charakterisierung von chromaffinen Noradrenalin-Granula aus Schweine-Nebennierenmark. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1969;263(2):340–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H., Smith A. D. Lipids of adrenal chromaffin granules: fatty acids composition of phospholipids, in particular lysolecithin. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1968;261(4):379–388. doi: 10.1007/BF00537182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H., Strieder N., Ziegler E. Uber Lipide, insbesondere Lysolecithin, in den chromaffinen Granula verschiedener Species. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1967;256(4):407–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H., Ziegler E., Strieder N. Gewinnung und Eigenschaften der Katecholamin-speichernden Granulaeines Phäochromocytoms. Klin Wochenschr. 1967 Dec 15;45(24):1238–1241. doi: 10.1007/BF01746270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H., Ziegler E., Strieder N. Studies on the proteins from chromaffin granules of ox, horse and pig. Nature. 1966 Aug 27;211(5052):982–983. doi: 10.1038/211982a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]