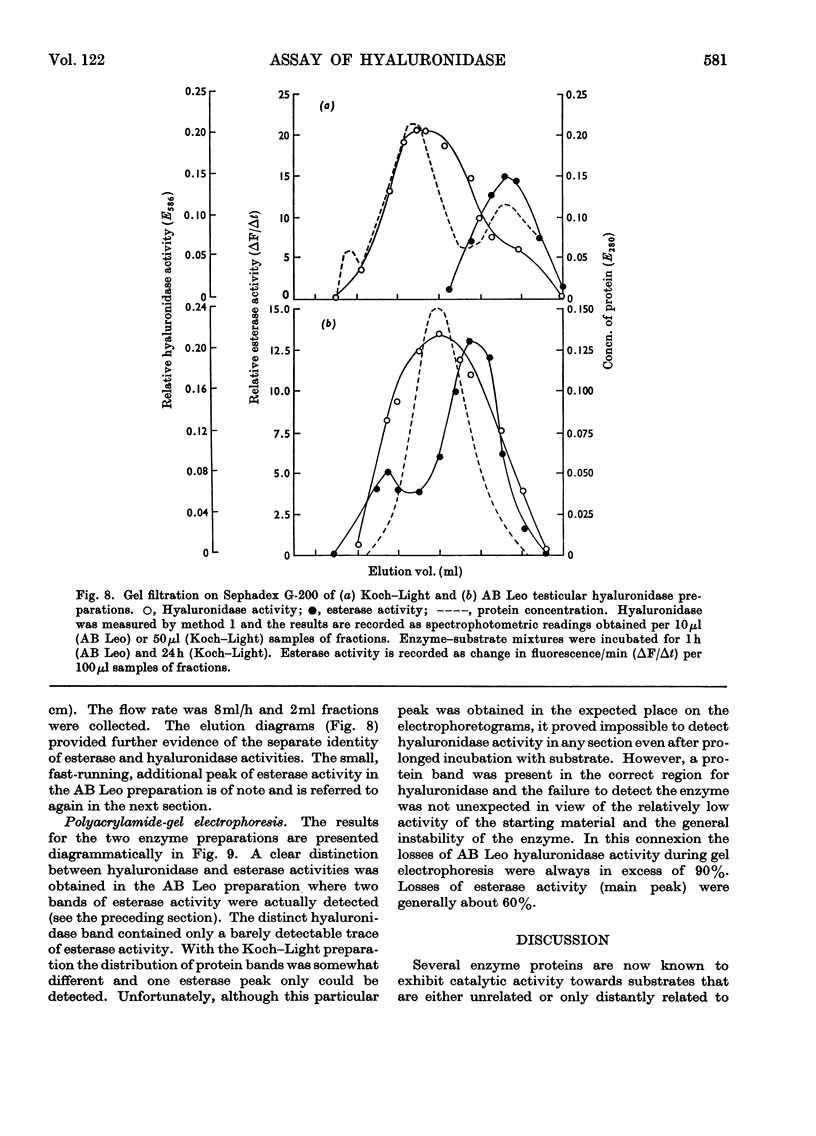
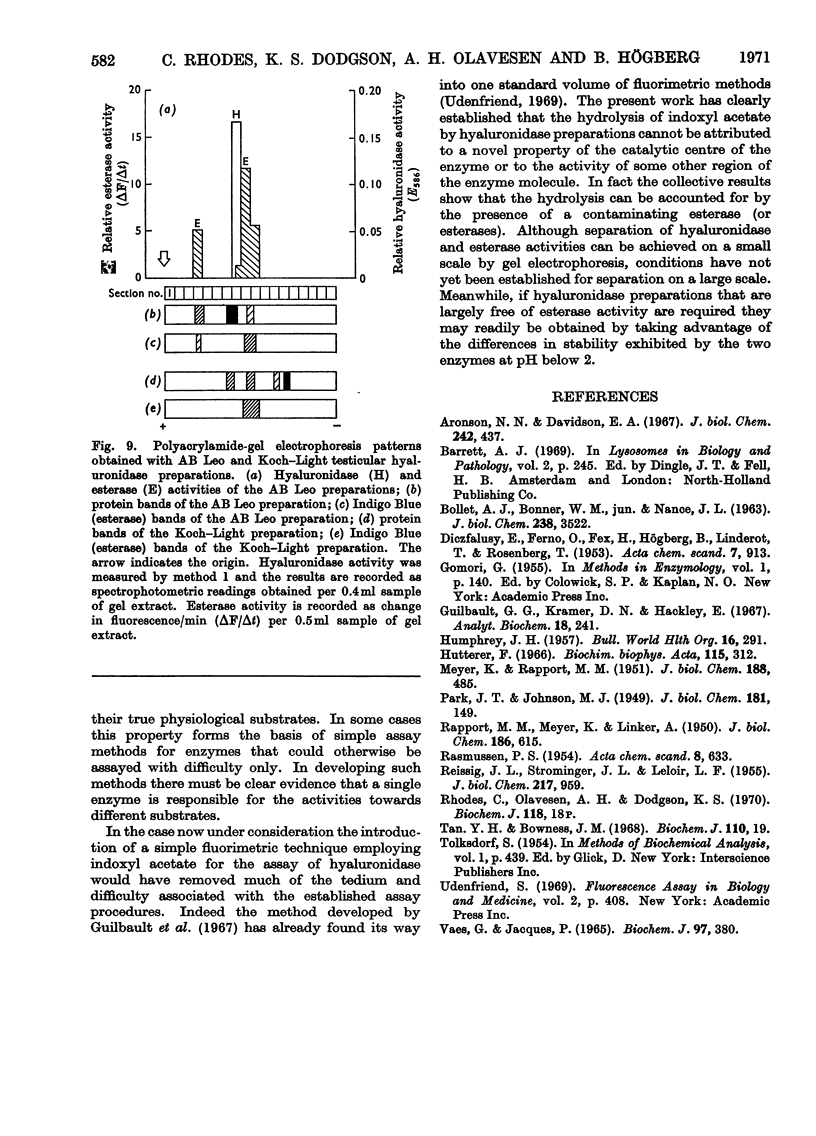
Abstract
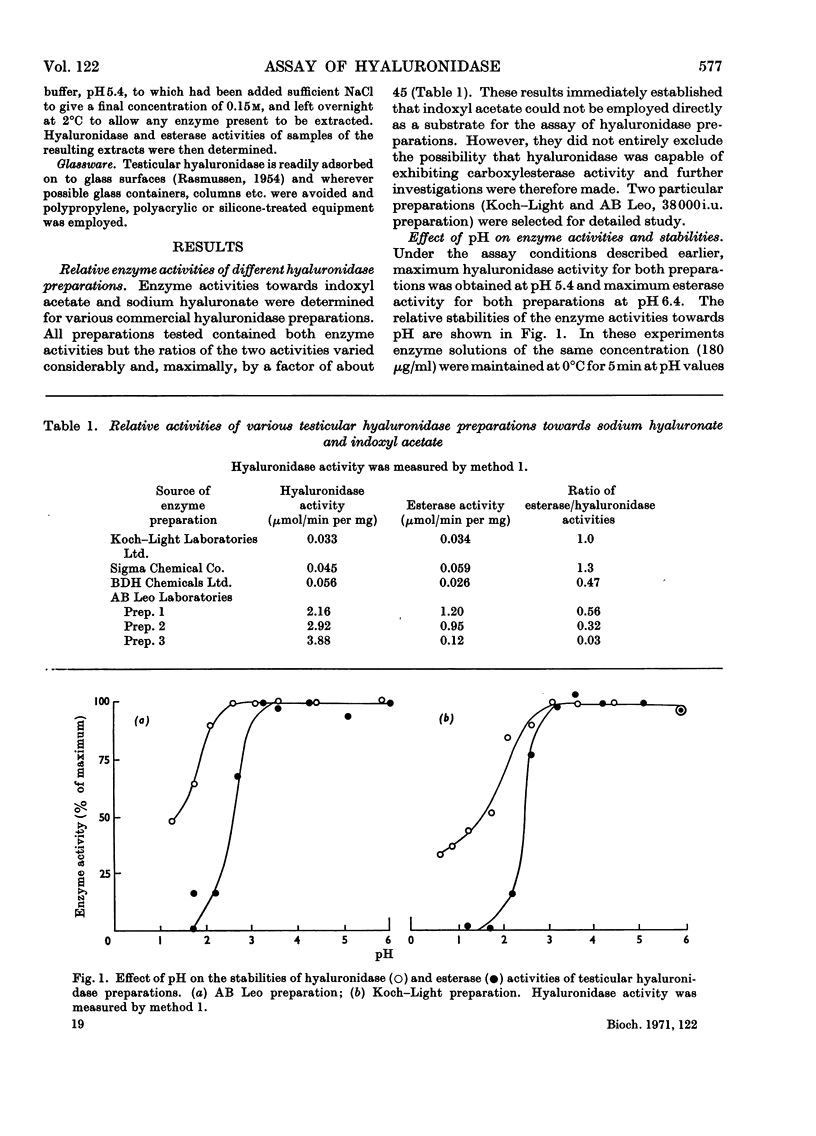
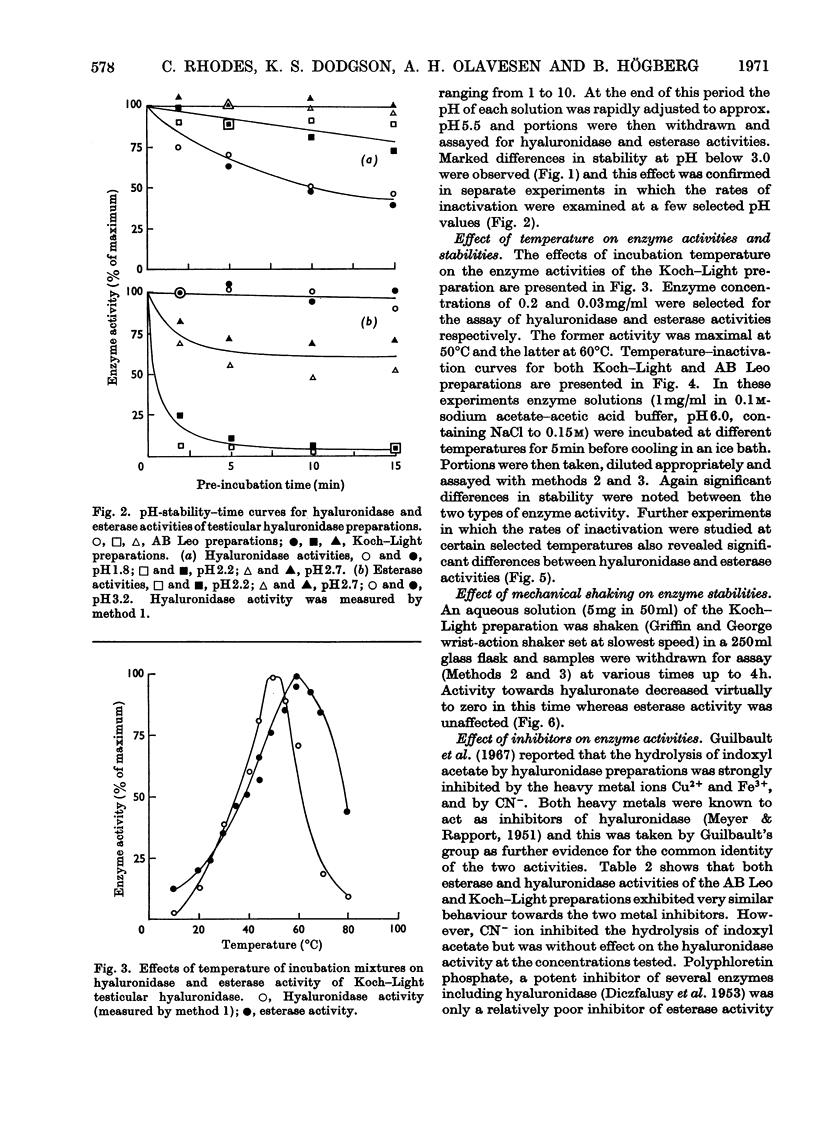
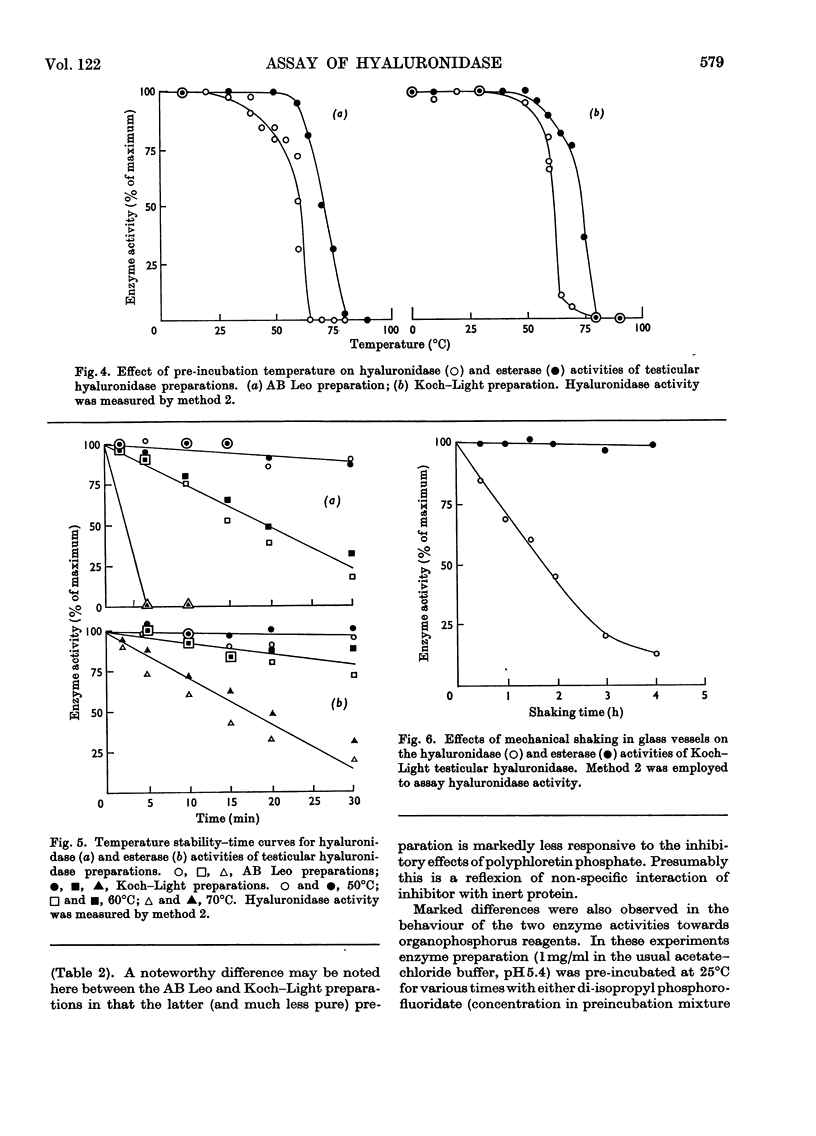
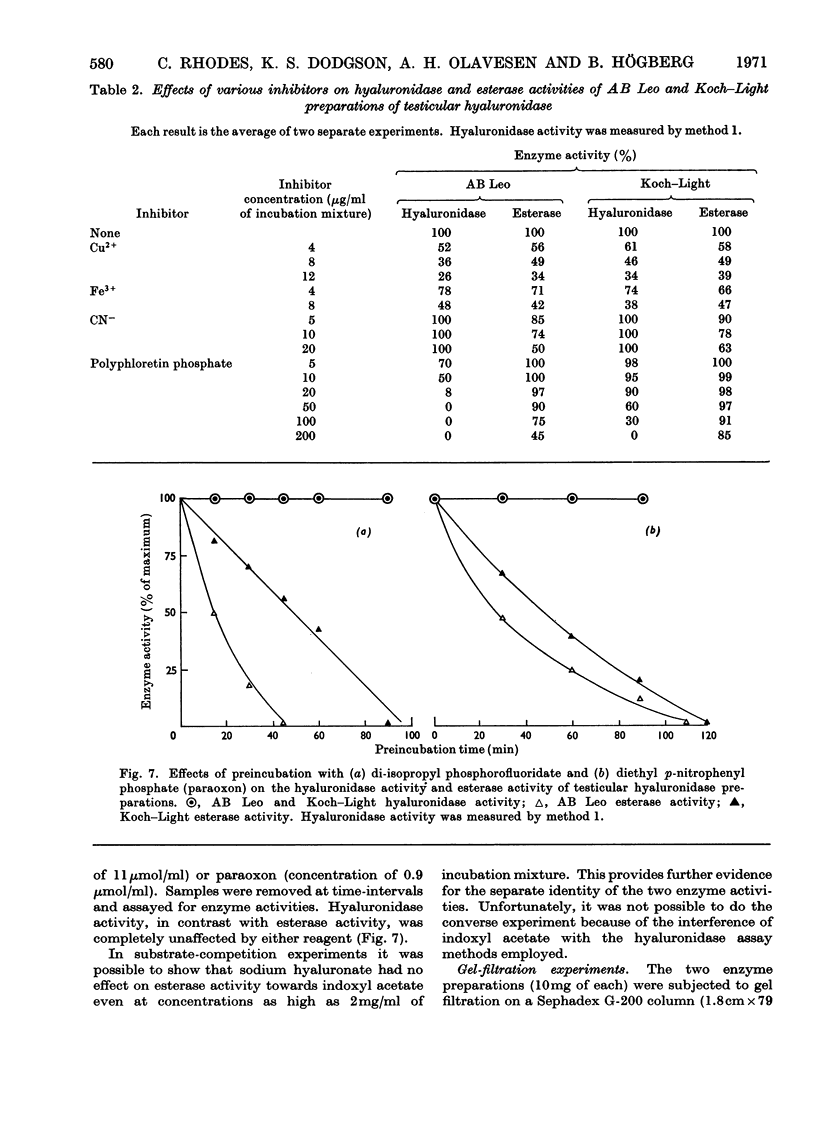
The most recently published method for the assay of testicular hyaluronidase preparations was based on the premise that the enzyme also exhibited carboxylesterase activity towards indoxyl acetate. Studies on the relative enzyme activities of various hyaluronidase preparations towards hyaluronate and indoxyl acetate, the relative stabilities towards pH, temperature and mechanical shaking and the behaviour towards a variety of inhibitors, showed that the activities towards the two substrates reflected the presence of at least two different enzyme systems in the preparations. Gel chromatography and polyacrylamide-gel-electrophoresis experiments confirmed these conclusions and the collective findings clearly establish that methods based on the use of indoxyl acetate cannot be employed to measure testicular hyaluronidase activity.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronson N. N., Jr, Davidson E. A. Lysosomal hyaluronidase from rat liver. I. Preparation. J Biol Chem. 1967 Feb 10;242(3):437–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOLLET A. J., BONNER W. M., Jr, NANCE J. L. THE PRESENCE OF HYALURONIDASE IN VARIOUS MAMMALIAN TISSUES. J Biol Chem. 1963 Nov;238:3522–3527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMPHREY J. H. International standard for hyaluronidase. Bull World Health Organ. 1957;16(2):291–294. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutterer F. Degradation of mucopolysaccharides by hepatic lysosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 28;115(2):312–319. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90430-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYER K., RAPPORT M. M. The inhibition of testicular hyaluronidase by heavy metals. J Biol Chem. 1951 Feb;188(2):485–490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARK J. T., JOHNSON M. J. A submicrodetermination of glucose. J Biol Chem. 1949 Nov;181(1):149–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPPORT M. M., MEYER K., LINKER A. Correlation of reductimetric and turbidimetric methods for hyaluronidase assay. J Biol Chem. 1950 Oct;186(2):615–623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REISSIG J. L., STORMINGER J. L., LELOIR L. F. A modified colorimetric method for the estimation of N-acetylamino sugars. J Biol Chem. 1955 Dec;217(2):959–966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaes G., Jacques P. Studies on bone enzymes. The assay of acid hydrolases and other enzymes in bone tissue. Biochem J. 1965 Nov;97(2):380–388. doi: 10.1042/bj0970380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


