Abstract
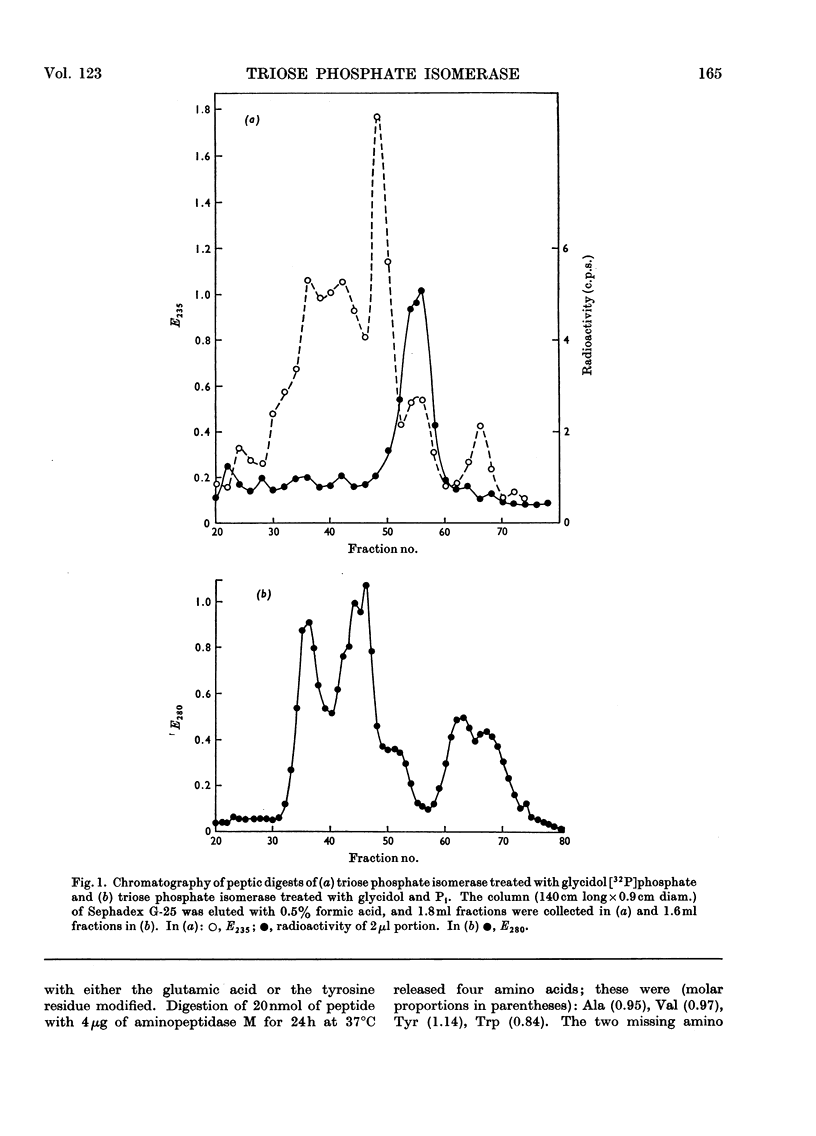
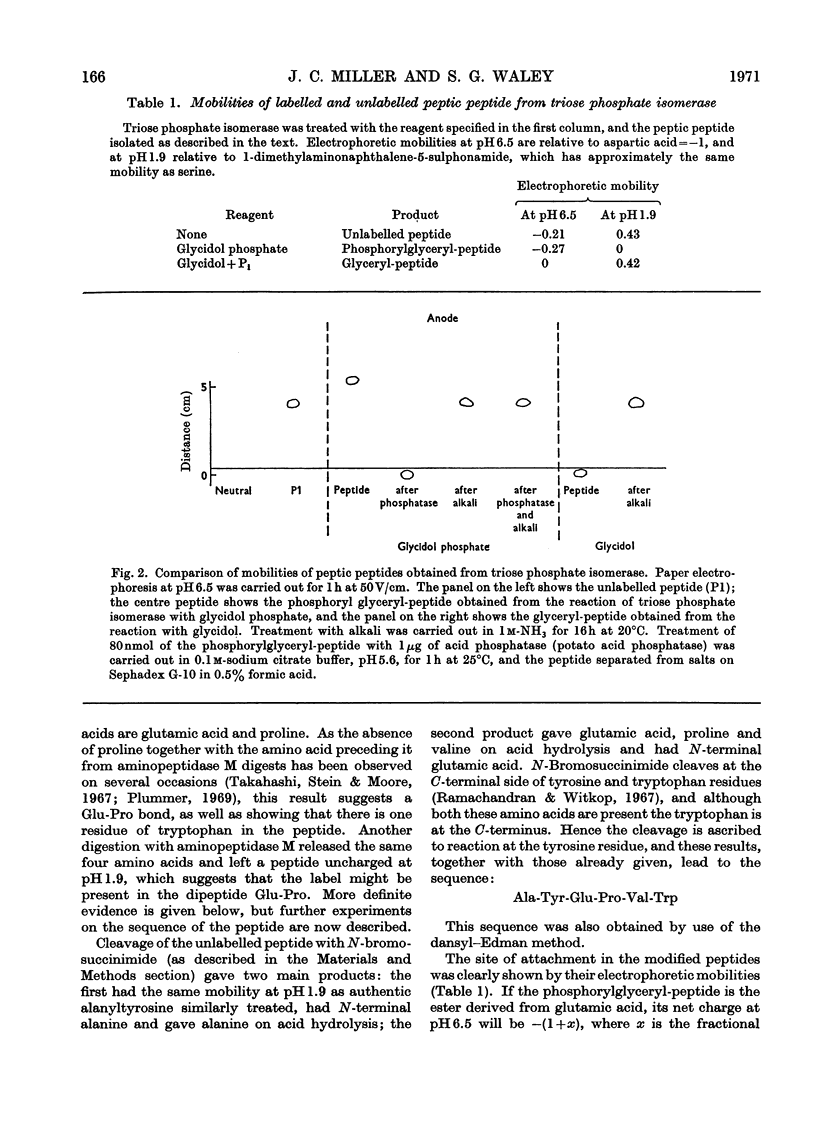
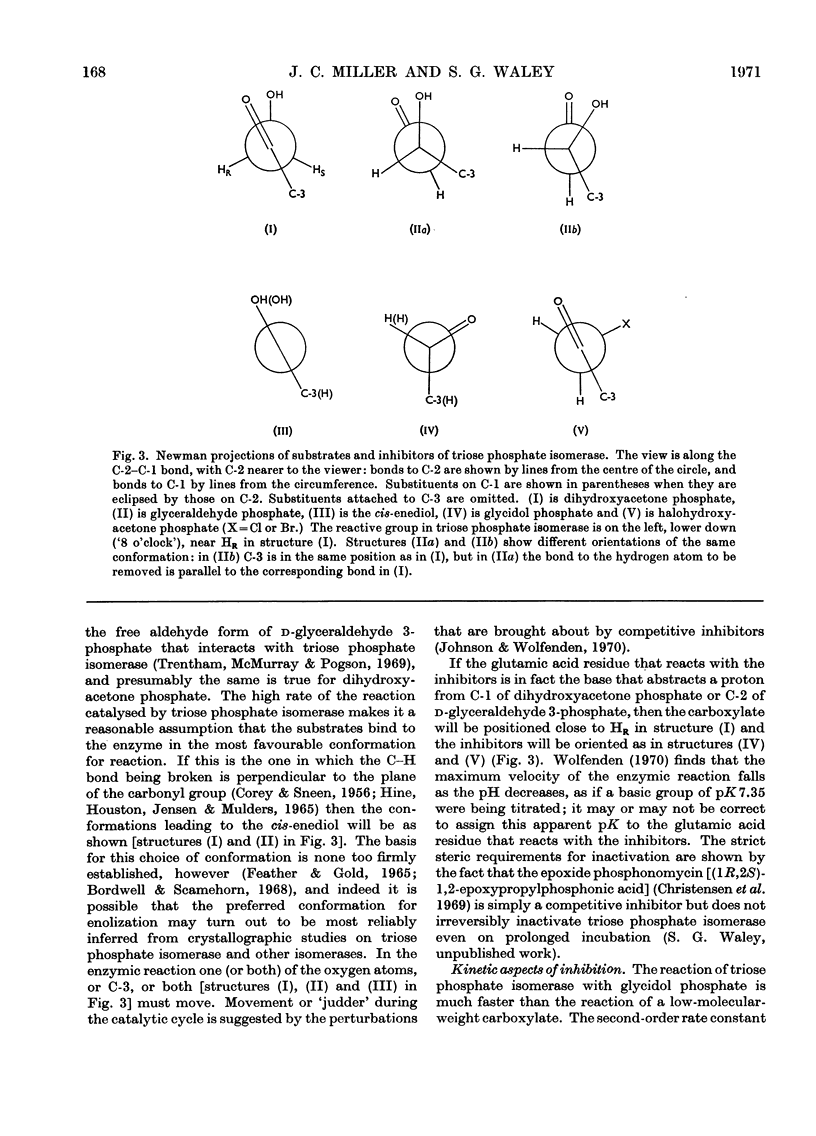
1. Glycidol (2,3-epoxypropanol) phosphate is a specific irreversible inhibitor of rabbit muscle triose phosphate isomerase (EC 5.3.1.1); the site of attachment has now been studied. 2. The labelled enzyme was digested with pepsin and a modified peptide isolated. The sequence of the peptide is: Ala-Tyr-Glu-Pro-Val-Trp. 3. It is the glutamic acid residue in this peptide that is labelled: the peptide is thus a γ-glutamyl ester derived from glycerol phosphoric acid. The same site is labelled by a mixture of glycidol and inorganic phosphate. 4. Kinetic and stereochemical features of these reactions are discussed.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMBLER R. P. THE AMINO ACID SEQUENCE OF PSEUDOMONAS CYTOCHROME C-551. Biochem J. 1963 Nov;89:349–378. doi: 10.1042/bj0890349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton P. M., Waley S. G. Kinetics of triose phosphate isomerase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Mar 25;151(3):714–715. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(68)90028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton P. M., Waley S. G. The active centre of triose phosphate isomerase. Biochem J. 1966 Sep;100(3):702–710. doi: 10.1042/bj1000702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardenas J. M., Wold F. Studies on rabbit muscle enolase. Evicence for two identical polypeptide chains and two substrate binding sites in the active enzyme. Biochemistry. 1968 Aug;7(8):2736–2741. doi: 10.1021/bi00848a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen B. G., Leanza W. J., Beattie T. R., Patchett A. A., Arison B. H., Ormond R. E., Kuehl F. A., Jr, Albers-Schonberg G., Jardetzky O. Phosphonomycin: structure and synthesis. Science. 1969 Oct 3;166(3901):123–125. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3901.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulson A. F., Knowles J. R., Priddle J. D., Offord R. E. Uniquely labelled active site sequence in chicken muscle triose phosphate isomerase. Nature. 1970 Jul 11;227(5254):180–181. doi: 10.1038/227180a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DATTA S. P., GRZYBOWSKI A. K. Thermodynamic quantities for the dissociation equilibria of biologically important compounds. 7. The second acid dissociation of glycerol 1-phosphates. Biochem J. 1958 Jun;69(2):218–223. doi: 10.1042/bj0690218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEILMANN J., BARROLLIER J., WATZKE E. Beitrag zur Aminosäurebestimmung auf Papierchromatogrammen. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1957;309(4-6):219–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman F. C. Isolation and characterization of an active-site peptide from triose phosphate isomerase. J Am Chem Soc. 1970 Apr 8;92(7):2170–2172. doi: 10.1021/ja00710a082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman F. C. Partial sequence of an active-site peptide from triose phosphate isomerase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 May 11;39(3):384–388. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90588-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inagami T., Hatano H. Effect of alkylguanidines on the inactivation of trypsin by alkylation and phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1969 Mar 10;244(5):1176–1182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krietsch W. K., Pentchev P. G., Klingenbürg H., Hofstätter T., Bücher T. The isolation and crystallization of yeast and rabbit liver triose phosphate isomerase and a comparative characterization with the rabbit muscle enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Jun;14(2):289–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00289.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. C., Waley S. G. Amino acid sequences around the cysteine residues of rabbit muscle triose phosphate isomerase. Biochem J. 1971 Apr;122(2):209–218. doi: 10.1042/bj1220209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offord R. E. Electrophoretic mobilities of peptides on paper and their use in the determination of amide groups. Nature. 1966 Aug 6;211(5049):591–593. doi: 10.1038/211591a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plummer T. H., Jr Isolation and sequence of peptides at the active center of bovine carboxypeptidase B. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 10;244(19):5246–5253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSE I. A. Mechanism of C-H bond cleavage in aldolase and isomerase reactions. Brookhaven Symp Biol. 1962 Dec;15:293–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose I. A., O'Connell E. L. Inactivation and labeling of triose phosphate isomerase and enolase by glycidol phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1969 Dec 10;244(23):6548–6550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH I. Colour reactions on paper chromatograms by a dipping technique. Nature. 1953 Jan 3;171(4340):43–44. doi: 10.1038/171043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J. Covalent labeling of active sites. Adv Protein Chem. 1967;22:1–54. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60040-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Stein W. H., Moore S. The identification of a glutamic acid residue as part of the active site of ribonuclease T-1. J Biol Chem. 1967 Oct 25;242(20):4682–4690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trentham D. R., McMurray C. H., Pogson C. I. The active chemical state of D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate in its reactions with D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase, aldolase and triose phosphate isomerase. Biochem J. 1969 Aug;114(1):19–24. doi: 10.1042/bj1140019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waley S. G., Miller J. C., Rose I. A., O'Connell E. L. Identification of site in triose phosphate isomerase labelled by glycidol phosphate. Nature. 1970 Jul 11;227(5254):181–181. doi: 10.1038/227181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilchek M., Spande T., Witkop B. A convenient spectrophotometric procedure for the determination of amino-terminal tyrosine residues. Biochemistry. 1968 May;7(5):1787–1791. doi: 10.1021/bi00845a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfenden R. Binding of substrate and transition state analog to trisephosphate isomerase. Biochemistry. 1970 Aug 18;9(17):3404–3407. doi: 10.1021/bi00819a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


