Abstract
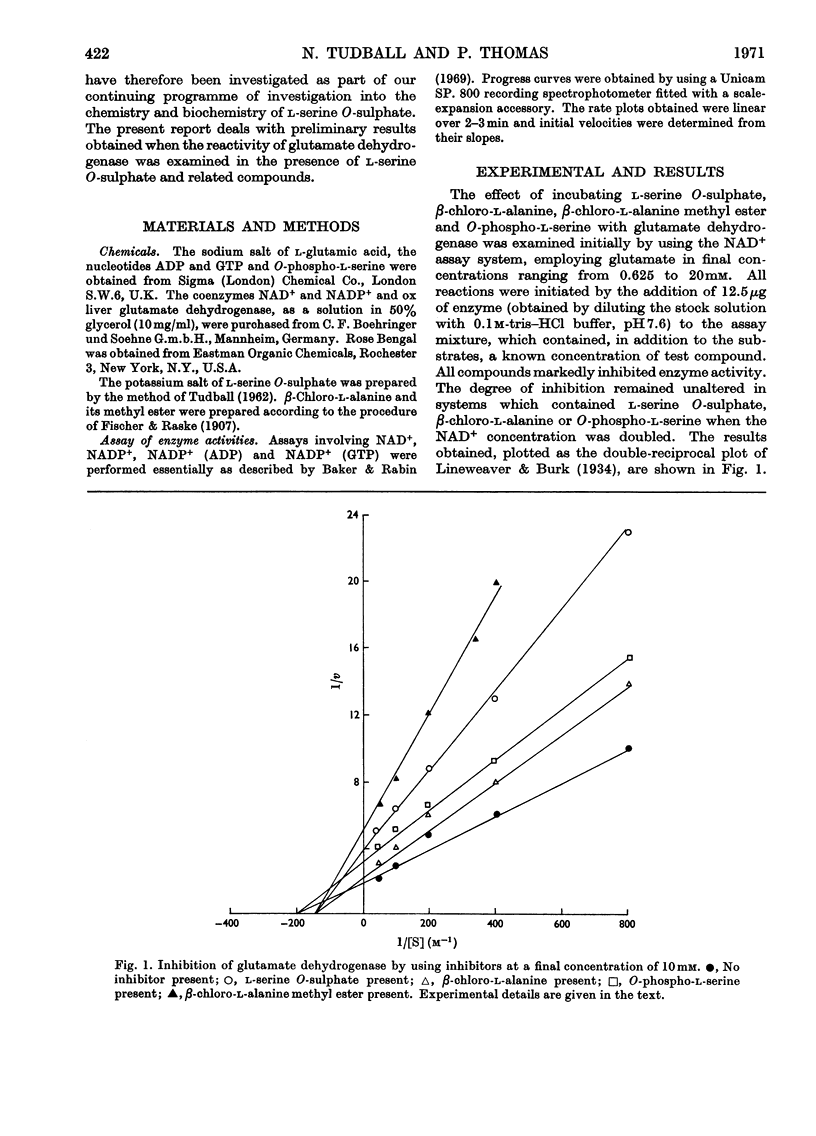
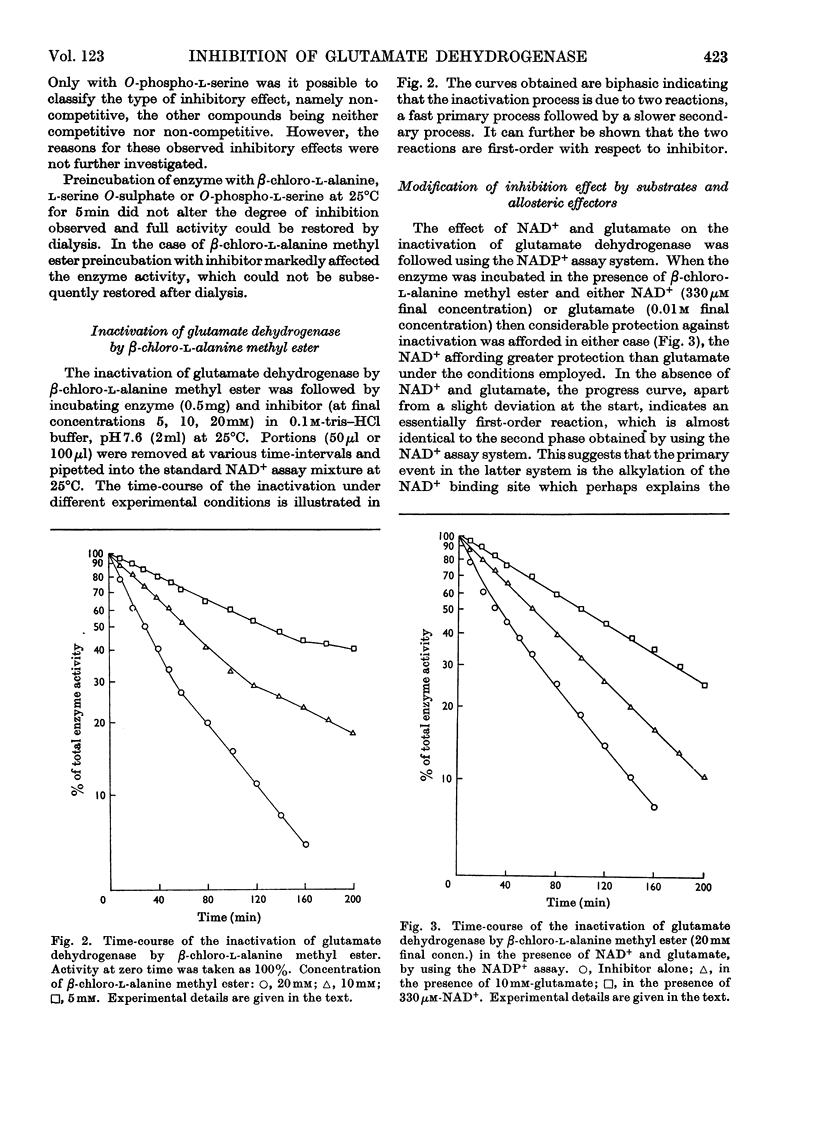
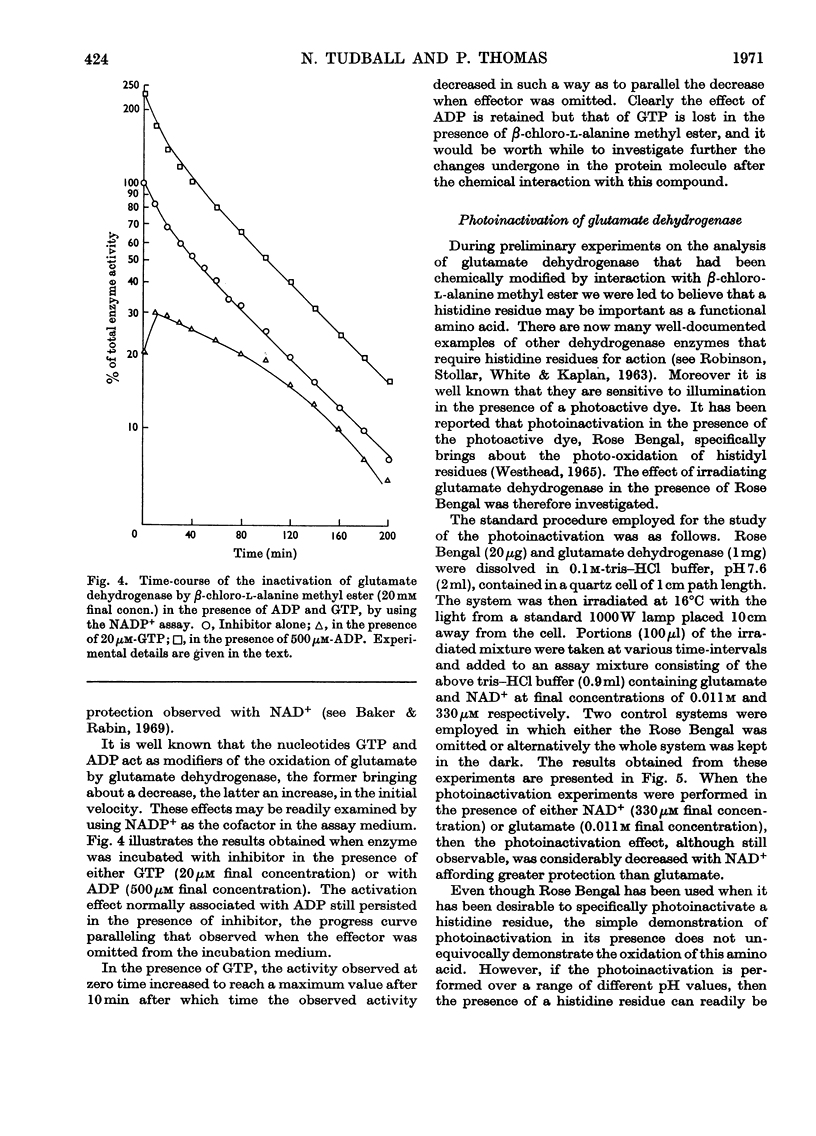
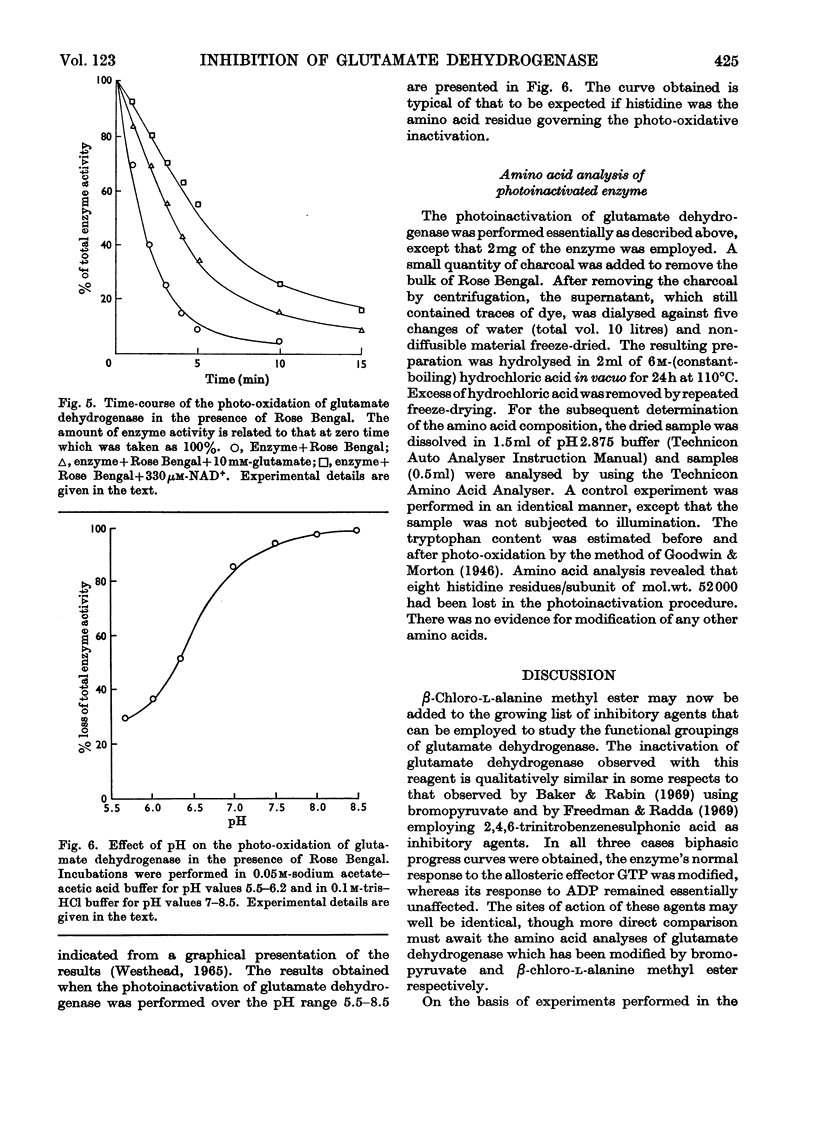
1. Glutamate dehydrogenase was inhibited by l-serine O-sulphate, β-chloro-l-alanine, O-phospho-l-serine and β-chloro-l-alanine methyl ester. With the exception of β-chloro-l-alanine methyl ester which was an irreversible inhibitor, it was possible to reverse the inhibitory effects by dialysis. 2. Both NAD+ and glutamate afford some protection against the inhibition due to the methyl ester. No change in the normal stimulatory effect exhibited by ADP was observed in the presence of β-chloro-l-alanine methyl ester but the effect due to GTP was modified. 3. Irradiation of glutamate dehydrogenase in the presence of Rose Bengal produced rapid inactivation. Amino acid analysis of the inactivated enzyme showed that eight histidine residues had been destroyed in the process.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker J. P., Rabin B. R. Effects of bromopyruvate on the control and catalytic properties of glutamate dehydrogenase. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Nov;11(1):154–159. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00753.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross D. G., Fisher H. F. The mechanism of glutamate dehydrogenase reaction. 3. The binding of ligands at multiple subsites and resulting kinetic effects. J Biol Chem. 1970 May 25;245(10):2612–2621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher H. F., Cross D. G. The involvement of a tryptophan residue of glutamate dehydrogenase in the binding of L-glutamate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Jul 12;20(2):120–123. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90333-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman R. B., Radda G. K. Chemical modification of glutamate dehydrogenase by 2,4,6-trinitrobenzenesulphonic acid. Biochem J. 1969 Sep;114(3):611–619. doi: 10.1042/bj1140611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin T. W., Morton R. A. The spectrophotometric determination of tyrosine and tryptophan in proteins. Biochem J. 1946;40(5-6):628–632. doi: 10.1042/bj0400628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook J. J., Jeckel R. A peptide containing a reactive lysyl group from ox liver glutamate dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1969 Mar;111(5):689–694. doi: 10.1042/bj1110689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John R. A., Fasella P. The reaction of L-serine O-sulfate with aspartate aminotransferase. Biochemistry. 1969 Nov;8(11):4477–4482. doi: 10.1021/bi00839a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malcolm A. D., Radda G. K. The reaction of glutamate dehydrogenase with 4-iodoacetamido salicylic acid. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Sep;15(3):555–561. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01040.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBINSON D., STOLLAR D., WHITE S., KAPLAN N. O. STRUCTURAL AND CATALYTIC ALTERATIONS OF DEHYDROGENASES AFTER PHOTOOXIDATION. Biochemistry. 1963 May-Jun;2:486–492. doi: 10.1021/bi00903a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tudball N. The metabolism of potassium l-serine O[S]-sulphate in the rat. Biochem J. 1962 Dec;85(3):456–460. doi: 10.1042/bj0850456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tudballn, Thmas J. H., Fowler J. A. A rat liver system that catalyses a pyridoxal phosphate-independent alpha beta-eliminto. Biochem J. 1969 Sep;114(2):299–305. doi: 10.1042/bj1140299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


