Abstract
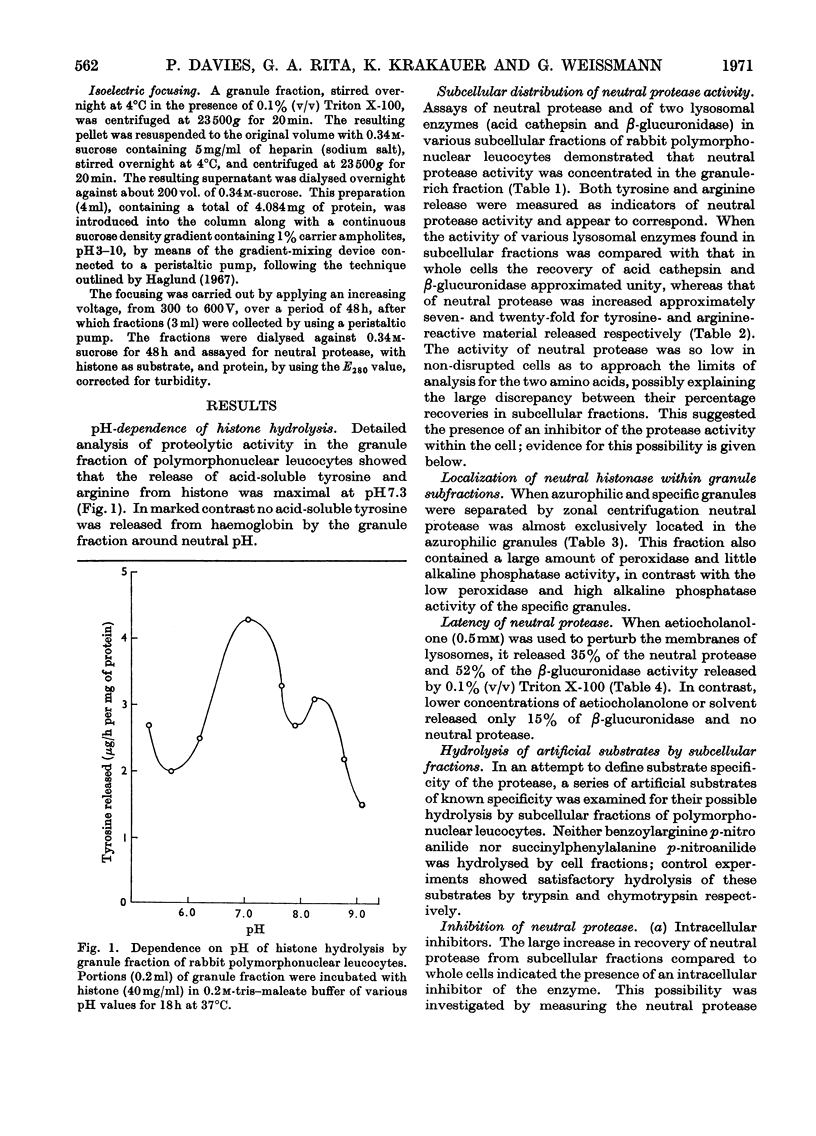
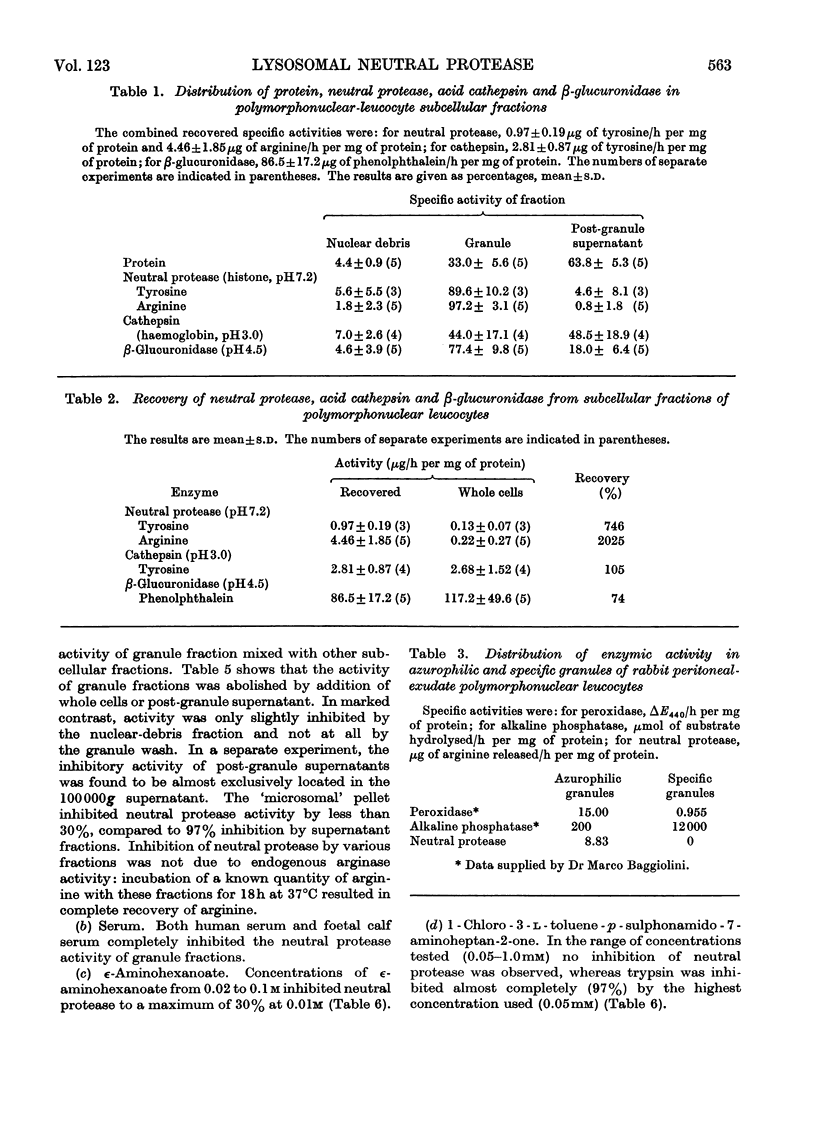
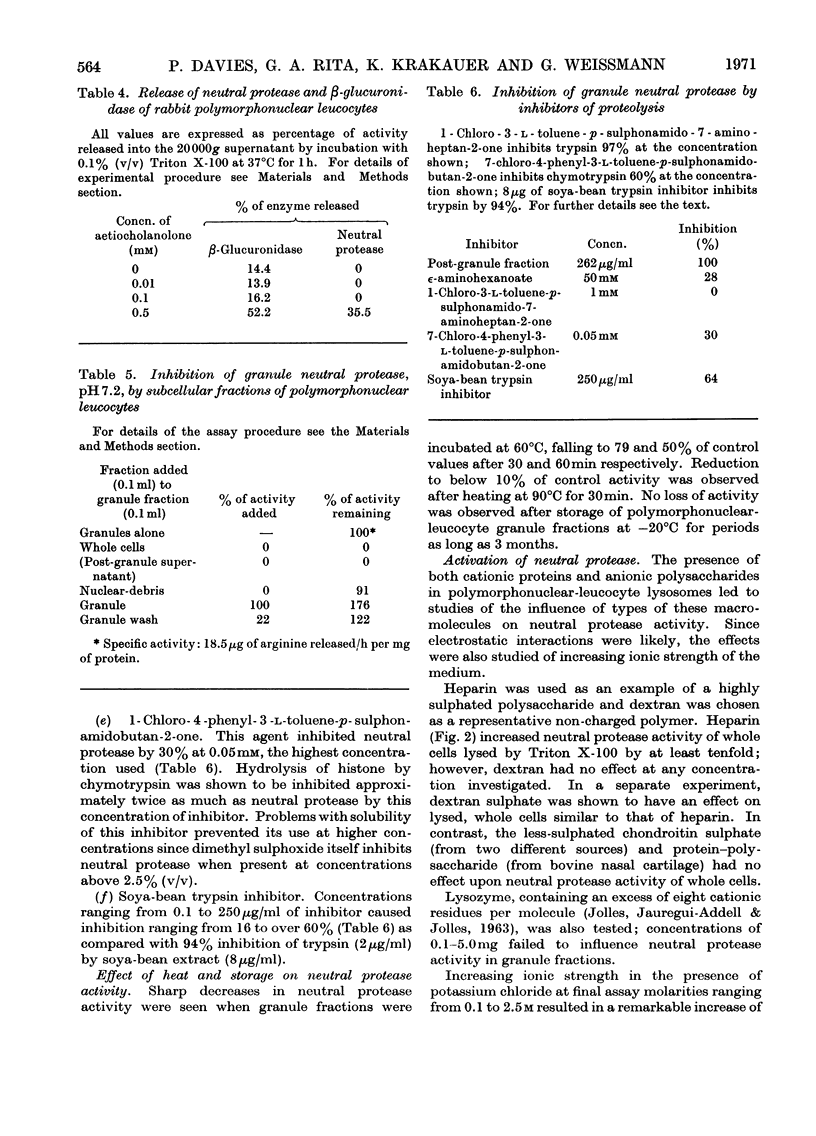
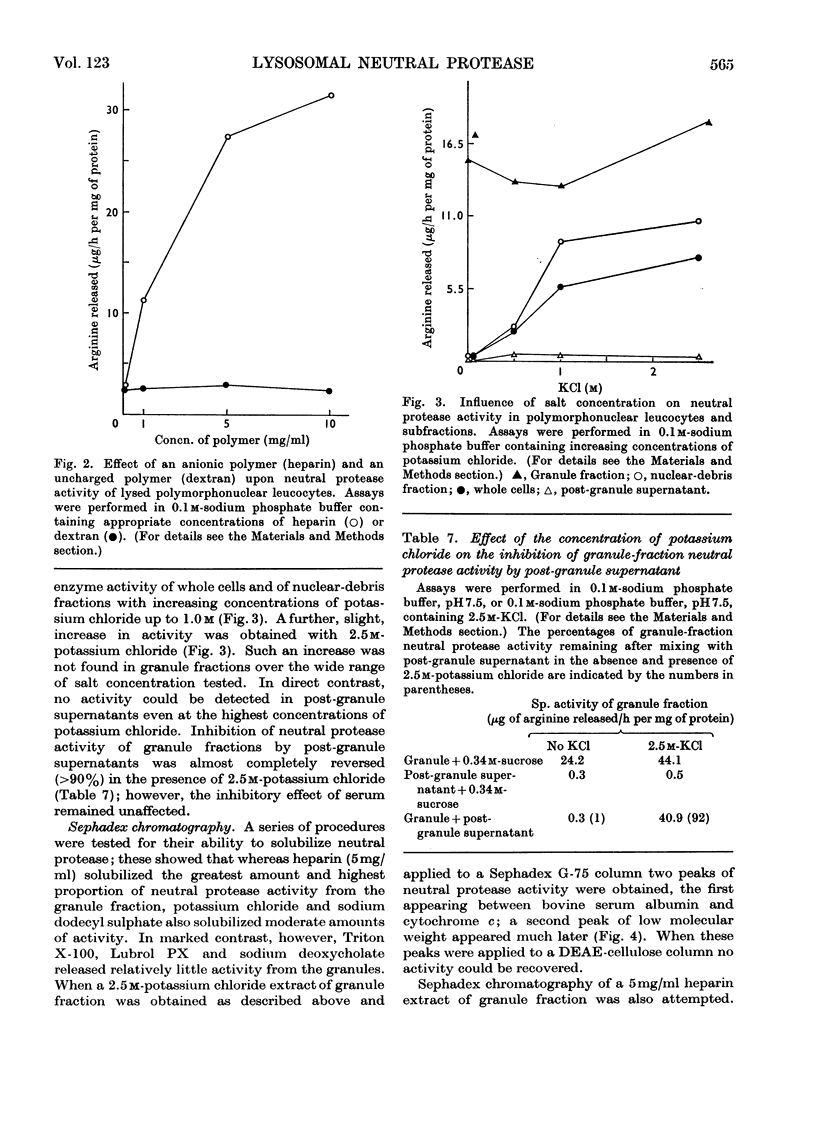
1. The subcellular distribution has been investigated of a protease from rabbit polymorphonuclear leucocytes, obtained from peritoneal exudates. The enzyme, optimally active between pH7.0 and 7.5, hydrolyses histone but not haemoglobin, sediments almost exclusively with a granule fraction rich in other lysosomal enzymes, and is latent until the granules are disrupted by various means. 2. Enzymic analysis of specific and azurophilic granules separated by zonal centrifugation showed that neutral protease activity was confined to fractions rich in enzymes characteristic of azurophile granules. 3. Recovery of neutral protease activity from subcellular fractions was several times greater than that found in whole cells. This finding was explained by the presence of a potent inhibitor of the enzyme activity in the cytoplasm. 4. The effect of the inhibitor was reversed by increasing ionic strength (up to 2.5m-potassium chloride) and by polyanions such as heparin and dextran sulphate, but not by an uncharged polymer, dextran. 5. The enzyme was also inhibited, to a lesser extent, by 1-chloro-4-phenyl-3-l-toluene-p-sulphonamidobutan-2-one, soya-bean trypsin inhibitor and ∈-aminohexanoate (∈-aminocaproate). 6. The granule fractions failed to hydrolyse artificial substrates for trypsin and chymotrypsin. 7. Partial separation of the enzyme was achieved by Sephadex gel filtration at high ionic strength and by isoelectric focusing. The partially separated, activated enzyme showed an approximately 300-fold increase in specific activity over that in whole cells.
Full text
PDF


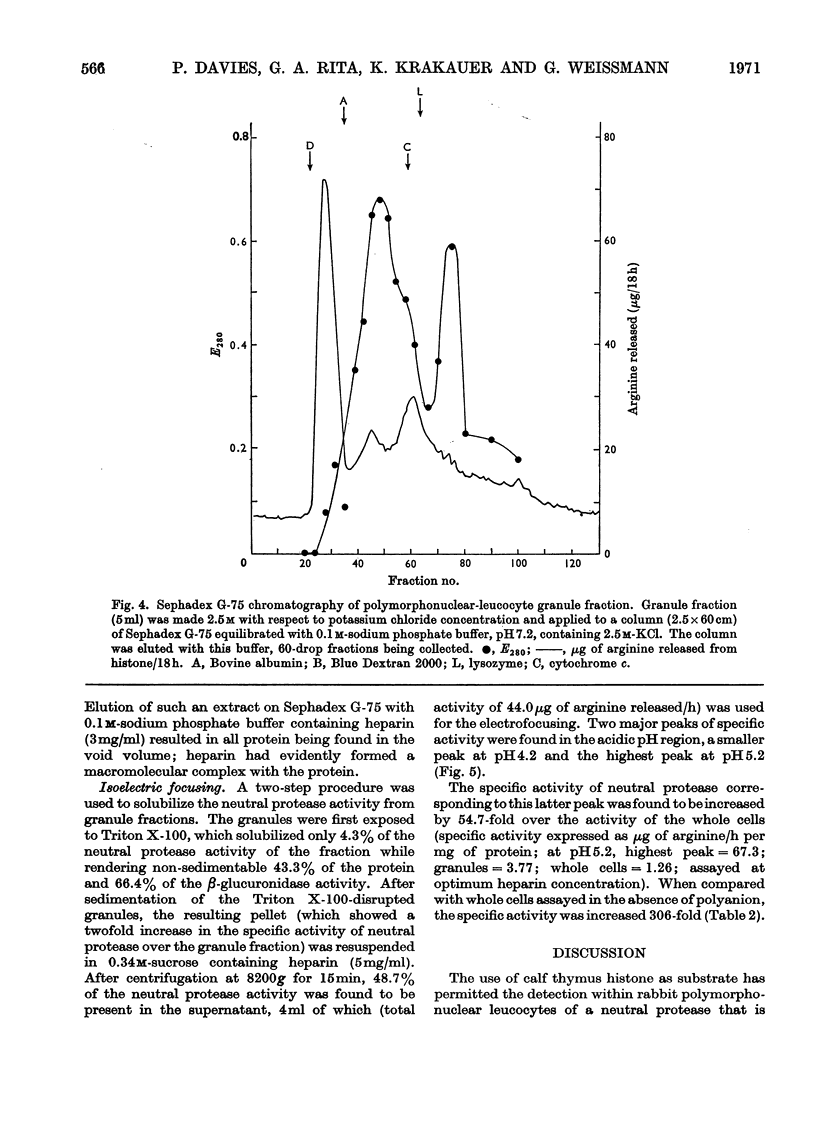
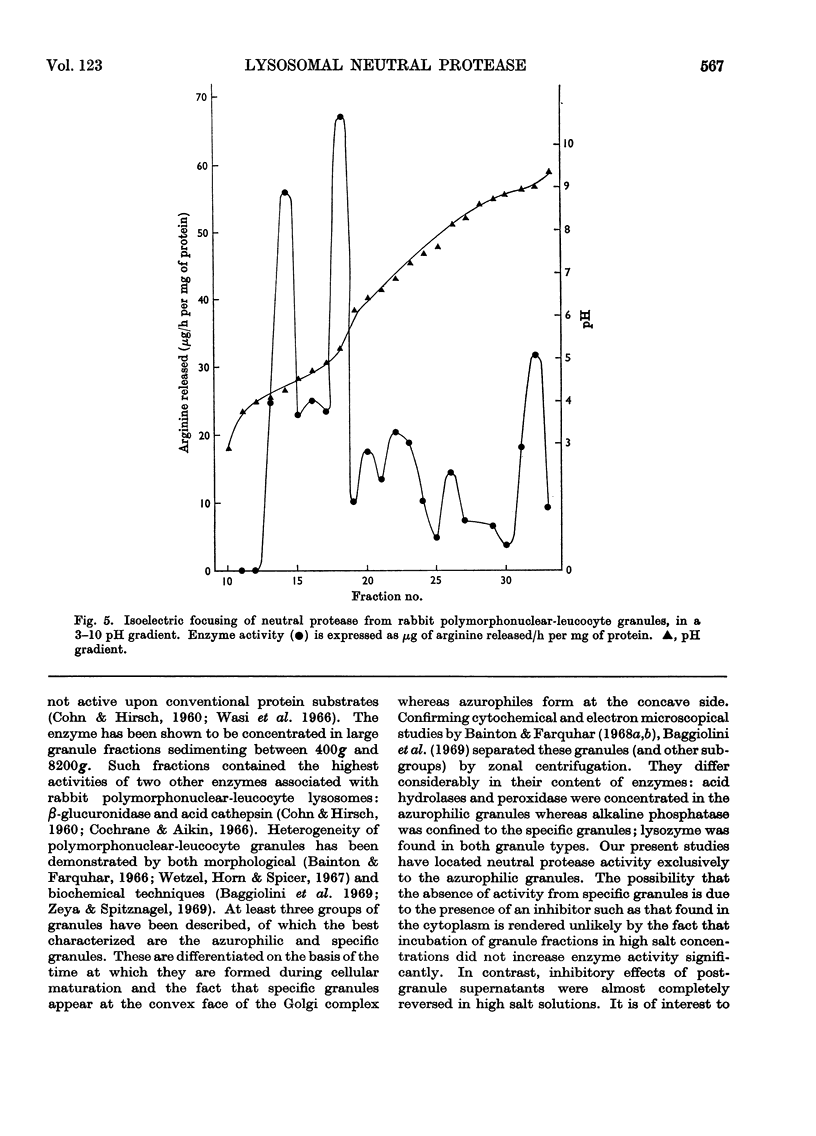


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baggiolini M., Hirsch J. G., De Duve C. Resolution of granules from rabbit heterophil leukocytes into distinct populations by zonal sedimentation. J Cell Biol. 1969 Feb;40(2):529–541. doi: 10.1083/jcb.40.2.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bainton D. F., Farquhar M. G. Differences in enzyme content of azurophil and specific granules of polymorphonuclear leukocytes. I. Histochemical staining of bone marrow smears. J Cell Biol. 1968 Nov;39(2):286–298. doi: 10.1083/jcb.39.2.286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bainton D. F., Farquhar M. G. Differences in enzyme content of azurophil and specific granules of polymorphonuclear leukocytes. II. Cytochemistry and electron microscopy of bone marrow cells. J Cell Biol. 1968 Nov;39(2):299–317. doi: 10.1083/jcb.39.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bainton D. F., Farquhar M. G. Origin of granules in polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Two types derived from opposite faces of the Golgi complex in developing granulocytes. J Cell Biol. 1966 Feb;28(2):277–301. doi: 10.1083/jcb.28.2.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN Z. A., HIRSCH J. G. The isolation and properties of the specific cytoplasmic granules of rabbit polymorphonuclear leucocytes. J Exp Med. 1960 Dec 1;112:983–1004. doi: 10.1084/jem.112.6.983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane C. G., Aikin B. S. Polymorphonuclear leukocytes in immunologic reactions. The destruction of vascular basement membrane in vivo and in vitro. J Exp Med. 1966 Oct 1;124(4):733–752. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.4.733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE DUVE C., PRESSMAN B. C., GIANETTO R., WATTIAUX R., APPELMANS F. Tissue fractionation studies. 6. Intracellular distribution patterns of enzymes in rat-liver tissue. Biochem J. 1955 Aug;60(4):604–617. doi: 10.1042/bj0600604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P., Krakauer K., Weissmann G. Subcellular distribution of neutral protease and peptidases in rabbit polymorphonuclear leucocytes. Nature. 1970 Nov 21;228(5273):761–762. doi: 10.1038/228761a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn W. B., Spicer S. S. Histochemical demonstration of sulfated mucosubstances and cationic proteins in human granulocytes and platelets. J Histochem Cytochem. 1969 Oct;17(10):668–674. doi: 10.1177/17.10.668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEDORKO M. E., MORSE S. I. ISOLATION, CHARACTERIZATION, AND DISTRIBUTION OF ACID MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDES IN RABBIT LEUCOCYTES. J Exp Med. 1965 Jan 1;121:39–48. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.1.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz H., Trautschold I., Haendle H., Werle E. Chemistry and biochemistry of proteinase inhibitors from mammalian tissues. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1968 Jun 28;146(2):400–413. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1968.tb20301.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlan M., Jericijo M., Suhar A. Purification and properties of a neutral protease from alf thymus nuclei. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Aug 27;167(1):154–160. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(68)90285-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOLLES J., JAUREGUI-AOLLES P. Preliminary contribution to the study of the disulfide bonds in hen's egg-white lysozyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 May 14;71:488–490. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91115-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janoff A. Alanine p-nitrophenyl esterase activity of human leucocyte granules. Biochem J. 1969 Aug;114(1):157–159. doi: 10.1042/bj1140157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janoff A., Scherer J. Mediators of inflammation in leukocyte lysosomes. IX. Elastinolytic activity in granules of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1968 Nov 1;128(5):1137–1155. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.5.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janoff A., Zeligs J. D. Vascular injury and lysis of basement membrane in vitro by neutral protease of human leukocytes. Science. 1968 Aug 16;161(3842):702–704. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3842.702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye C., Dabich D. An inhibitor of trypsin-like activity in rat liver. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Sep;131(4):1366–1368. doi: 10.3181/00379727-131-34108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kihara H., De la Flor S. D. Arginase in fetal calf serum. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Oct;129(1):303–304. doi: 10.3181/00379727-129-33308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAPRESLE C., WEBB T. Study of a proteolytic enzyme from rabbit spleen. Biochem J. 1960 Sep;76:538–543. doi: 10.1042/bj0760538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarus G. S., Daniels J. R., Brown R. S., Bladen H. A., Fullmer H. M. Degradation of collagen by a human granulocyte collagenolytic system. J Clin Invest. 1968 Dec;47(12):2622–2629. doi: 10.1172/JCI105945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOUNTER L. A., ATIYEH W. Proteases of human leukocytes. Blood. 1960 Jan;15:52–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson I. Intracellular distribution and sites of synthesis of glycosaminoglycans (mucopolysaccharides) in human leukocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1969 Mar;54(3):314–317. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(69)90208-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHOELLMANN G., SHAW E. Direct evidence for the presence of histidine in the active center of chymotrypsin. Biochemistry. 1963 Mar-Apr;2:252–255. doi: 10.1021/bi00902a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seegers W., Janoff A. Mediators of inflammation in leukocyte lysosomes. VI. Partial purification and characterization of a mast cell-rupturing component. J Exp Med. 1966 Nov 1;124(5):833–849. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.5.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles M. A., Fraenkel-Conrat J. Subcellular distribution of human leukocytic cathepsins. Blood. 1968 Jul;32(1):119–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umaña R. Reevaluation of the method of Kunitz for the assay of proteolytic activities in liver and brain homogenates. Anal Biochem. 1968 Dec;26(3):430–438. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90204-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISSMANN G. STUDIES OF LYSOSOMES. VI. THE EFFECT OF NEUTRAL STEROIDS AND BILE ACIDS ON LYSOSOMES IN VITRO. Biochem Pharmacol. 1965 Apr;14:525–535. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(65)90225-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasi S., Murray R. K., Macmorine D. R., Movat H. Z. The role of PMN-leucocyte lysosomes in tissue injury, inflammation and hypersensitivity. II. Studies on the proteolytic activity of PMN-leucocyte lysosomes of the rabbit. Br J Exp Pathol. 1966 Aug;47(4):411–423. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann G., Spilberg I. Breakdown of cartilage proteinpolysaccharide by lysosomes. Arthritis Rheum. 1968 Apr;11(2):162–169. doi: 10.1002/art.1780110206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann G., Spilberg I., Krakauer K. Arthritis induced in rabbits by lysates of granulocyte lysosomes. Arthritis Rheum. 1969 Apr;12(2):103–116. doi: 10.1002/art.1780120207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weston P. D., Barrett A. J., Dingle J. T. Specific inhibition of cartilage breakdown. Nature. 1969 Apr 19;222(5190):285–286. doi: 10.1038/222285b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetzel B. K., Horn R. G., Spicer S. S. Fine structural studies on the development of heterophil, eosinophil, and basophil granulocytes in rabbits. Lab Invest. 1967 Mar;16(3):349–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeya H. I., Spitznagel J. K. Cationic protein-bearing granules of polymorphonuclear leukocytes: separation from enzyme-rich granules. Science. 1969 Mar 7;163(3871):1069–1071. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3871.1069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeya H. I., Spitznagel J. K. Cationic proteins of polymorphonuclear leukocyte lysosomes. II. Composition, properties, and mechanism of antibacterial action. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):755–762. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.755-762.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


