Abstract
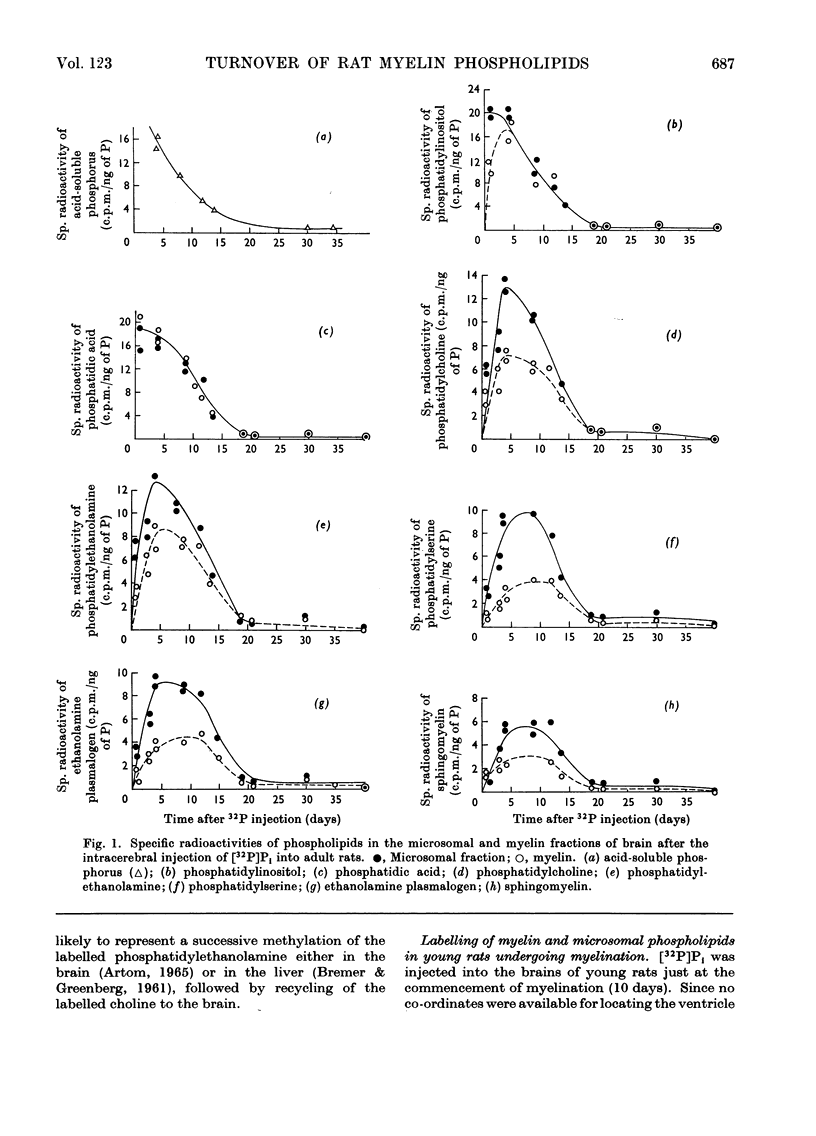
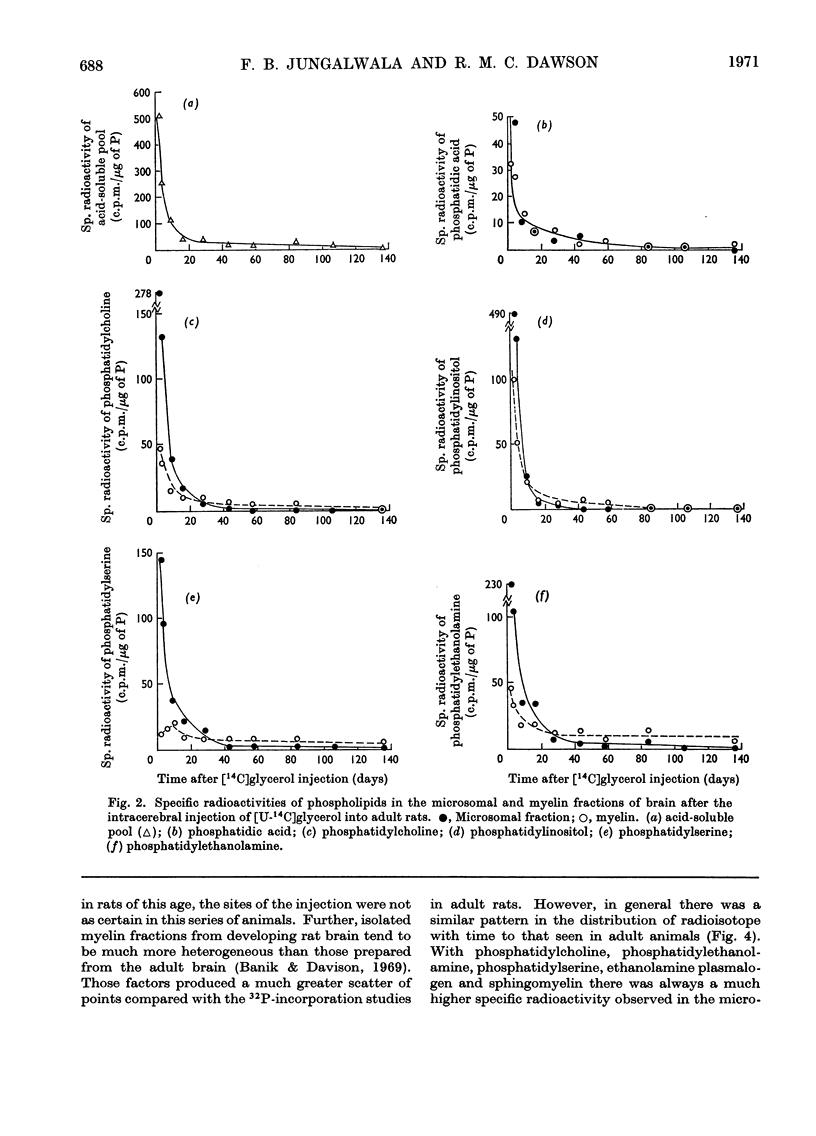
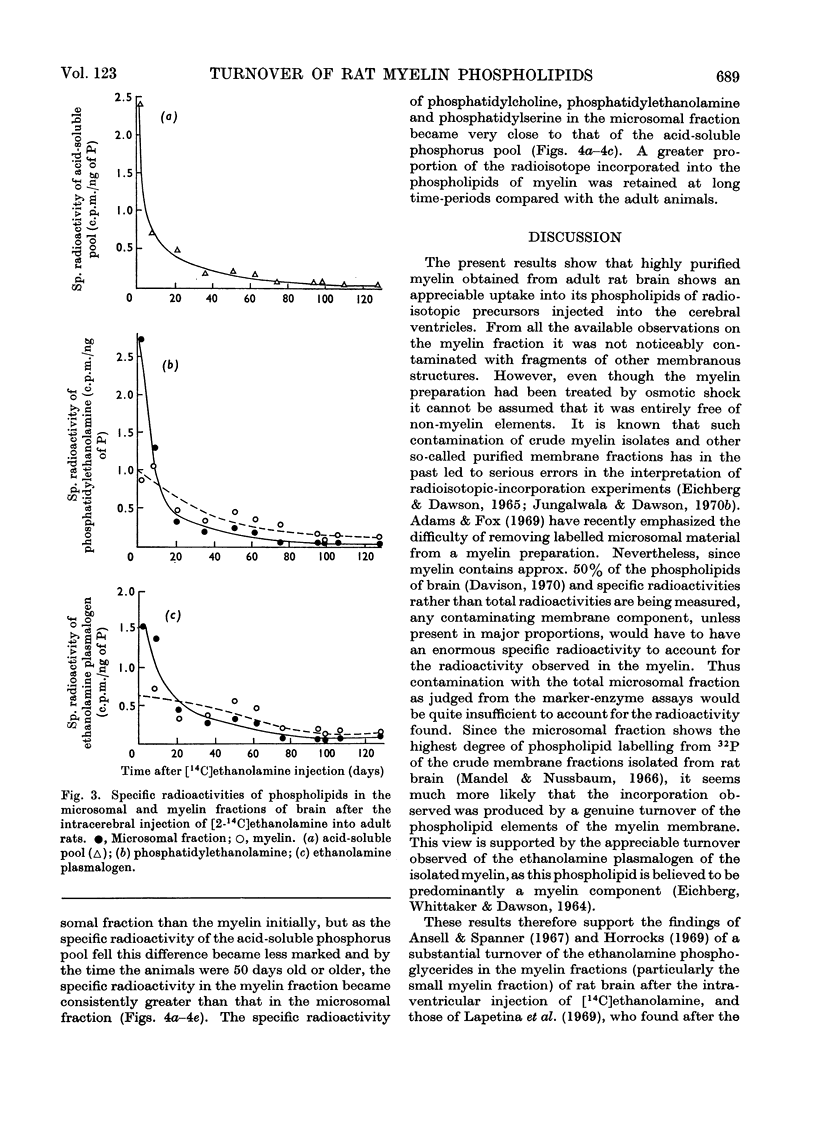
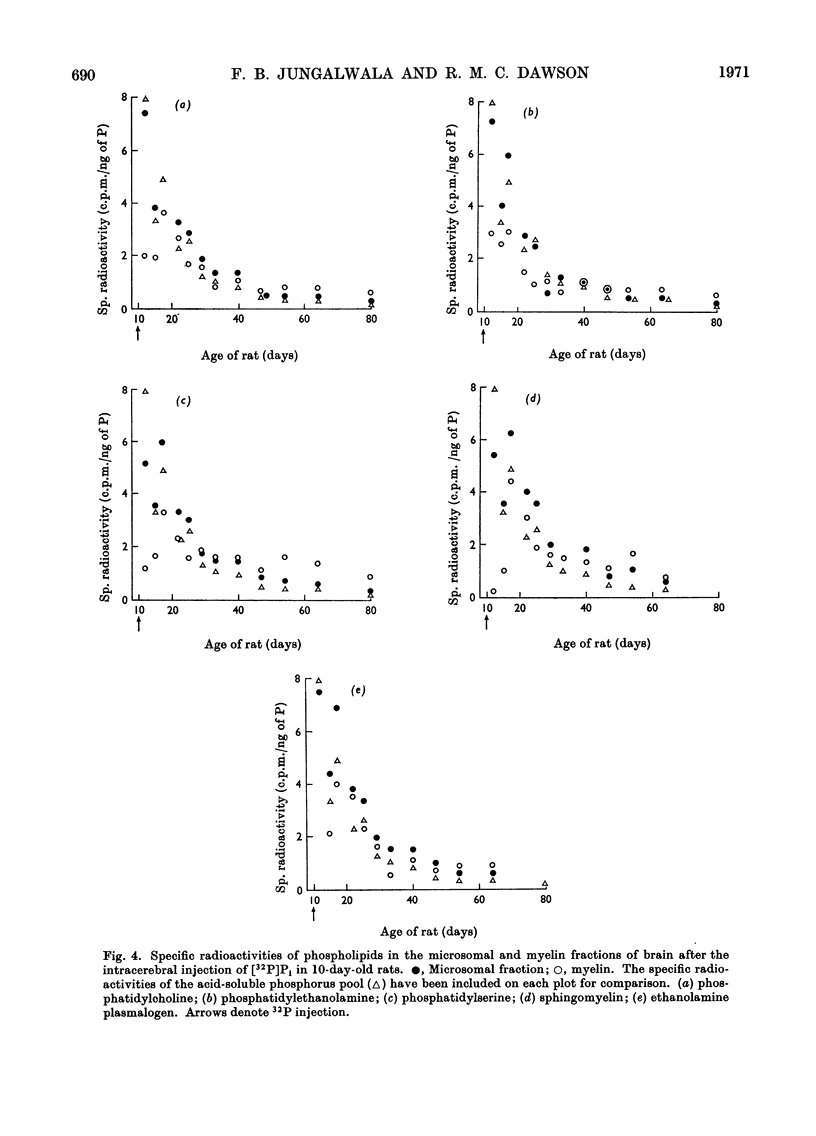
1. Inorganic [32P]phosphate, [U-14C]glycerol and [2-14C]ethanolamine were injected into the lateral ventricles in the brains of adult rats, and the labelling of individual phospholipids was followed over 2–4 months in both a microsomal and a highly purified myelin fraction. 2. All the phospholipids in myelin became appreciably labelled, although initially the specific radioactivities of the microsomal phospholipids were somewhat higher. Eventually the specific radioactivities in microsomal and myelin phospholipids fell rapidly at a rate corresponding to the decline of radioactivity in the acid-soluble pools. 3. Equivalent experiments carried out in developing rats with [32P]phosphate administered at the start of myelination showed some persistence of phospholipid labelling in the myelin, but this could partly be attributed to the greater retention of 32P in the acid-soluble phosphorus pool and recycling. 4. It is concluded that a substantial part of the phospholipid molecules in adult myelin membranes is readily exchangeable, although a small pool of slowly exchangeable material also exists. 5. A slow incorporation into or loss of labelled precursor from myelin phospholipids does not necessarily give a good indication of the rate of renewal of the molecules in the membrane. As presumably such labelled molecules originate by exchange with those in another membrane site (not necessarily where synthesis occurs) it is only possible to calculate the turnover rate in the myelin membrane if the behaviour of the specific radioactivity with time of the phospholipid molecules in the immediate precursor pool is known.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABDEL-LATIF A. A., ABOOD L. G. INCORPORATION OF ORTHO (32P)PHOSPHATE INTO THE SUBCELLULAR FRACTIONS OF DEVELOPING RAT BRAIN. J Neurochem. 1965 Mar;12:157–166. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1965.tb06752.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ADAMS C. W., DAVISON A. N., GREGSON N. A. Enzyme inactivity of myelin: histochemical and biochemical evidence. J Neurochem. 1963 Jun;10:383–395. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1963.tb13666.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALDRIDGE W. N., EMERY R. C., STREET B. W. A tissue homogenizer. Biochem J. 1960 Nov;77:326–327. doi: 10.1042/bj0770326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AUGUST C., DAVISON A. N., MAURICE-WILLIAMS F. Phospholipid metabolism in nervous tissue. 4. Incorporation of P32 into the lipids of subcellular fractions of the brain. Biochem J. 1961 Oct;81:8–12. doi: 10.1042/bj0810008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AUTILIO L. A., NORTON W. T., TERRY R. D. THE PREPARATION AND SOME PROPERTIES OF PURIFIED MYELIN FROM THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. J Neurochem. 1964 Jan;11:17–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1964.tb06719.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams D. H., Fox M. E. The homogeneity and protein composition of rat brain myelin. Brain Res. 1969 Aug;14(3):647–661. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(69)90205-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aeberhard E., Menkes J. H. Biosynthesis of long chain fatty acids by subcellular particles of mature brain. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jul 25;243(14):3834–3840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansell G. B., Spanner S. The long-term metabolism of the ethanolamine moiety of rat brain myelin phospholipids. J Neurochem. 1968 Nov;15(11):1371–1373. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1968.tb05916.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansell G. B., Spanner S. The metabolism of labelled ethanolamine in the brain of the rat in vivo. J Neurochem. 1967 Sep;14(9):873–885. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1967.tb09576.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BANGHAM A. D., DAWSON R. M. Electrokinetic requirements for the reaction between Cl. perfringens alpha-toxin (phospholipase C) and phospholipid substrates. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 May 7;59:103–115. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90701-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banik N. L., Davison A. N. Enzyme activity and composition of myelin and subcellular fractions in the developing rat brain. Biochem J. 1969 Dec;115(5):1051–1062. doi: 10.1042/bj1151051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borell U., Orström A. The turnover of phosphate in the pineal body compared with that in other parts of the brain. Biochem J. 1947;41(3):398–403. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CUZNER M. L., DAVISON A. N., GREGSON N. A. CHEMICAL AND METABOLIC STUDIES OF RAT MYELIN OF THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Mar 31;122:86–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb20194.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chevallier F., Gautheron C. A method for the study of cholesterol biosynthesis in the central nervous system. Incorporation of [2-14C]mevalonic lactone after intraperitoneal, intracisternal and intraventricular administration in the rat. J Neurochem. 1969 Mar;16(3):323–331. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb10371.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuzner M. L., Davison A. N., Gregson N. A. Turnover of brain mitochondrial membrane lipids. Biochem J. 1966 Dec;101(3):618–626. doi: 10.1042/bj1010618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON R. M., HEMINGTON N., DAVENPORT J. B. Improvements in the method of determining individual phospholipids in a complex mixture by successive chemical hydrolyses. Biochem J. 1962 Sep;84:497–501. doi: 10.1042/bj0840497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. N., Gregson N. A. Metabolism of cellular membrane sulpholipids in the rat brain. Biochem J. 1966 Mar;98(3):915–922. doi: 10.1042/bj0980915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobiasová M., Radin N. S. Uptake of cerebroside, cholesterol and lecithin by brain myelin and mitochondria. Lipids. 1968 Sep;3(5):439–448. doi: 10.1007/BF02531284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichberg J., Dawson R. M. Polyphosphoinositides in myelin. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):644–650. doi: 10.1042/bj0960644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendelman W. J., Bunge R. P. Radioautographic studies of choline incorporation into peripheral nerve myelin. J Cell Biol. 1969 Jan;40(1):190–208. doi: 10.1083/jcb.40.1.190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horrocks L. A. Metabolism of the ethanolamine phosphoglycerides of mouse brain myelin and microsomes. J Neurochem. 1969 Jan;16(1):13–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb10338.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungalwala F. B., Dawson R. M. Phospholipid synthesis and exchange in isolated liver cells. Biochem J. 1970 Apr;117(3):481–490. doi: 10.1042/bj1170481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungalwala F. B., Dawson R. M. The origin of mitochondrial phosphatidylcholine within the liver cell. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Feb;12(2):399–402. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00865.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurihara T., Nussbaum J. L., Mandel P. 2',3'-cyclic nucleotide 3'-phosphohydrolase in brains of mutant mice with deficient myelination. J Neurochem. 1970 Jul;17(7):993–997. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1970.tb02252.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurihara T., Tsukada Y. The regional and subcellular distribution of 2',3'-cyclic nucleotide 3'-phosphohydrolase in the central nervous system. J Neurochem. 1967 Dec;14(12):1167–1174. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1967.tb06164.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Rodríguez De Lores A., De Robertis E. 32P incorporation into different membranous structures separated from rat cerebral cortex. J Neurochem. 1969 Jan;16(1):101–106. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb10347.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg O., Ernster L. The turnover of radioactive phosphate injected into the subarachnoid space of the brain of the rat. Biochem J. 1950 Jan;46(1):43–47. doi: 10.1042/bj0460043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel P., Nussbaum J. L. Incorporation of 32P into the phosphatides of myelin sheaths and of intracellular membranes. J Neurochem. 1966 Aug;13(8):629–642. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb09871.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMurray W. C., Dawson R. M. Phospholipid exchange reactions within the liver cell. Biochem J. 1969 Mar;112(1):91–108. doi: 10.1042/bj1120091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olafson R. W., Drummond G. I., Lee J. F. Studies on 2',3'-cyclic nucleotide-3'-phosphohydrolase from brain. Can J Biochem. 1969 Oct;47(10):961–966. doi: 10.1139/o69-151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROREM E. S. Ultra-violet fluorescence of quinine sulphate for detection of phosphate ester spots on paper. Nature. 1959 Jun 20;183(4677):1739–1740. doi: 10.1038/1831739b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rathbone L. The effect of diet on the fatty acid compositions of serum, brain, brain mitochondria and myelin in the rat. Biochem J. 1965 Dec;97(3):620–628. doi: 10.1042/bj0970620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riekkinen P. J., Clausen J. Proteinase activity of myelin. Brain Res. 1969 Oct;15(2):413–430. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(69)90164-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheltawy A., Dawson R. M. The deposition and metabolism of polyphosphoinositides in rat and guinea-pig brain during development. Biochem J. 1969 Jan;111(2):147–154. doi: 10.1042/bj1110147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. E. An in vitro system for the study of myelin synthesis. J Neurochem. 1969 Jan;16(1):83–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb10345.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. E., Eng L. F. The turnover of the lipid components of myelin. J Am Oil Chem Soc. 1965 Dec;42(12):1013–1018. doi: 10.1007/BF02636894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. E. The turnover of myelin in the adult rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Oct 22;164(2):285–293. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(68)90154-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirtz K. W., Zilversmit D. B. Exchange of phospholipids between liver mitochondria and microsomes in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jul 10;243(13):3596–3602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. G., King N. Turnover of basic protein of rat brain. Nature. 1971 Jan 1;229(5279):56–58. doi: 10.1038/229056a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


