Abstract
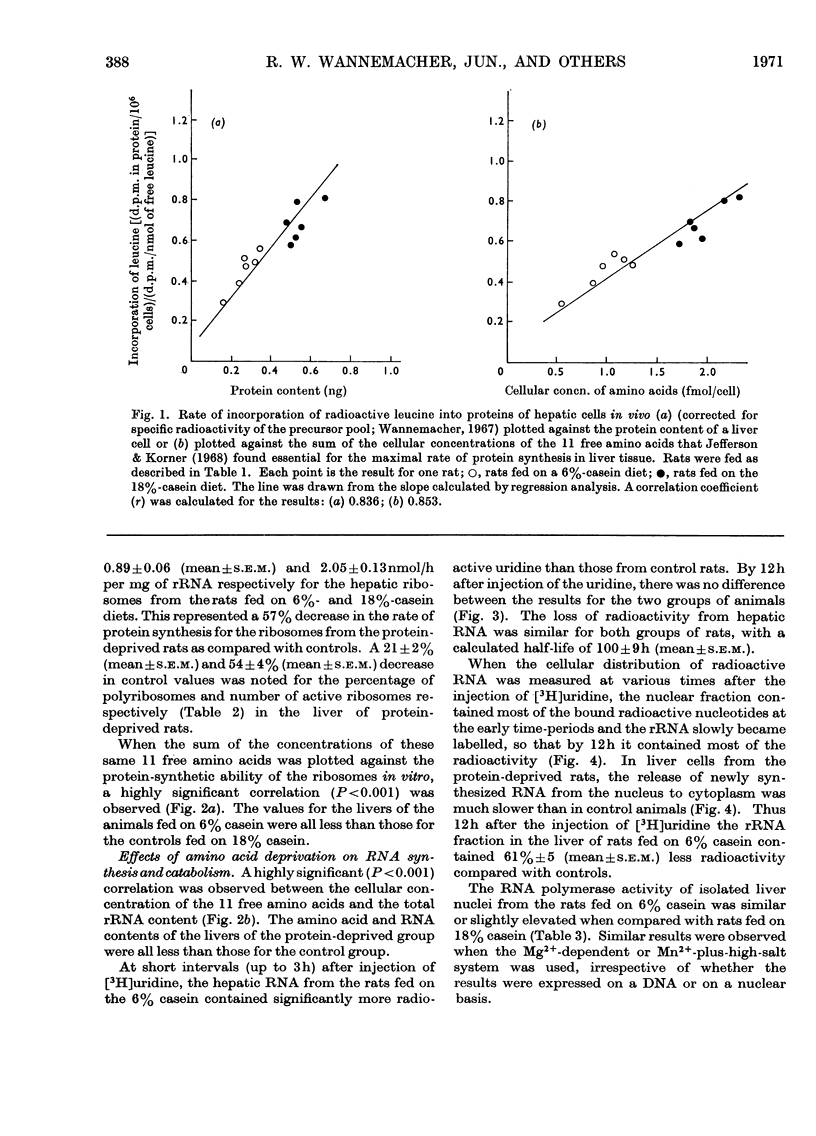
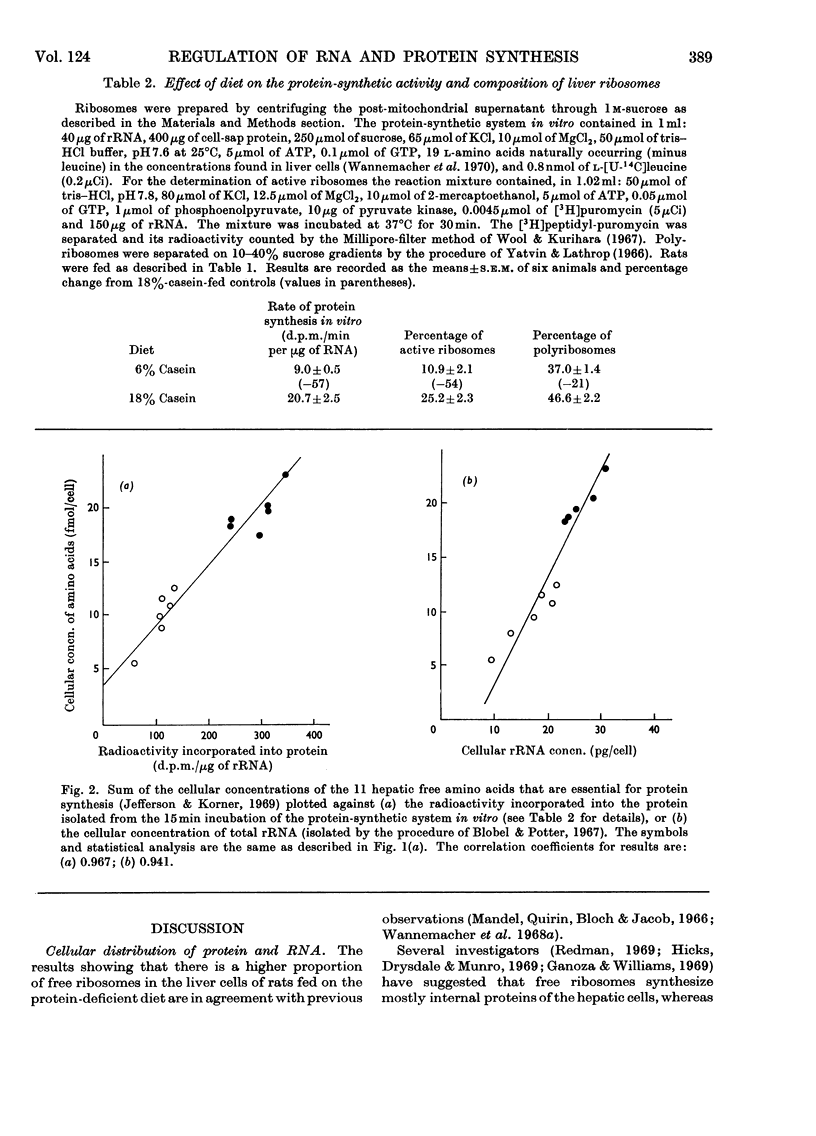
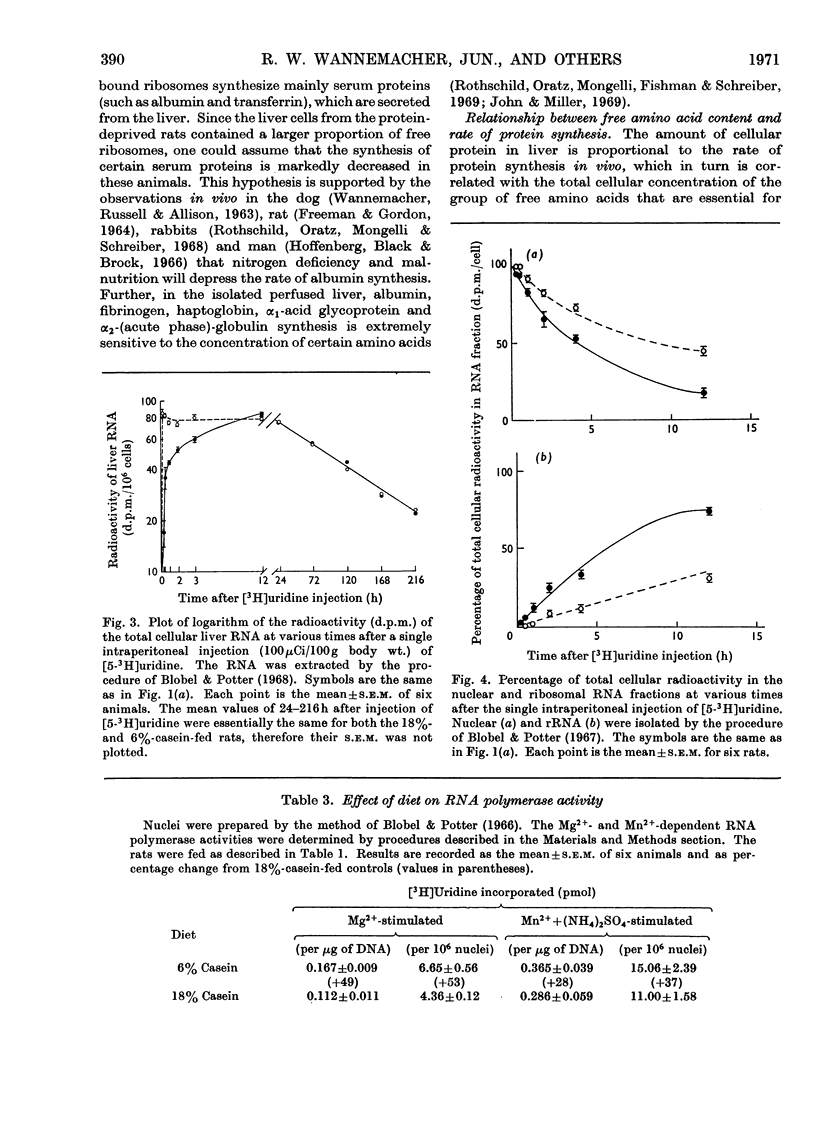
Weanling (23-day-old) rats were fed on either a low-protein diet (6% casein) or a diet containing an adequate amount of protein (18% casein) for 28 days. Hepatic cells from animals fed on the deficient diet were characterized by markedly lower concentrations of protein and RNA in all cellular fractions as compared with cells from control rats. The bound rRNA fraction was decreased to the greatest degree, whereas the free ribosomal concentrations were only slightly less than in control animals. A good correlation was observed between the rate of hepatic protein synthesis in vivo and the cellular protein content of the liver. Rates of protein synthesis both in vivo and in vitro were directly correlated with the hepatic concentration of individual free amino acids that are essential for protein synthesis. The decreased protein-synthetic ability of the ribosomes from the liver of protein-deprived rats was related to a decrease in the number of active ribosomes and heavy polyribosomes. The lower ribosomal content of the hepatocytes was correlated with the decreased concentration of essential free amino acids. In the protein-deprived rats, the rate of accumulation of newly synthesized cytoplasmic rRNA was markedly decreased compared with control animals. From these results it was concluded that amino acids regulate protein synthesis (1) by affecting the number of ribosomes that actively synthesize protein and (2) by inhibiting the rate of synthesis of new ribosomes. Both of these processes may involve the synthesis of proteins with a rapid rate of turnover.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLISON J. B., WANNEMACHER R. W., Jr, BANKS W. L., Jr, WUNNER W. H. THE MAGNITUDE AND SIGNIFICANCE OF THE PROTEIN RESERVES IN RATS FED AT VARIOUS LEVELS OF NITROGEN. J Nutr. 1964 Dec;84:383–388. doi: 10.1093/jn/84.4.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baliga B. S., Pronczuk A. W., Munro H. N. Regulation of polysome aggregation in a cell-free system through amino acid supply. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jul 14;34(2):199–218. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90247-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Potter V. R. Nuclei from rat liver: isolation method that combines purity with high yield. Science. 1966 Dec 30;154(3757):1662–1665. doi: 10.1126/science.154.3757.1662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Potter V. R. Studies on free and membrane-bound ribosomes in rat liver. I. Distribution as related to total cellular RNA. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):279–292. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90297-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper W. K., Muramatsu K., Wannemacher R. W., Jr An in vitro amino acid incorporating system for liver, brain and skeletal muscle ribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Nov 20;169(1):269–271. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90031-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdos T., Bessada R. The turnover of ribosomal RNA and soluble RNA in the rabbit uterus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Dec 21;129(3):628–631. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90080-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREEMAN T., GORDON A. H. METABOLISM OF ALBUMIN AND GAMMA-GLOBULIN IN PROTEIN DEFICIENT RATS. Clin Sci. 1964 Feb;26:17–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleck A., Shepherd J., Munro H. N. Protein synthesis in rat liver: influence of amino acids in diet on microsomes and polysomes. Science. 1965 Oct 29;150(3696):628–629. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3696.628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERBER G., ALTMAN K. I. The catabolism of tissue nucleic acid in the rat. II. Turnover time of ribonucleic acid and free nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1960 Sep;235:2682–2687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganoza M. C., Williams C. A. In vitro synthesis of different categories of specific protein by membrane-bound and free ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Aug;63(4):1370–1376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.4.1370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS H. FUNCTION OF THE SHORT-LIVED RIBONUCLEIC ACID IN THE CELL NUCLEUS. Nature. 1964 Feb 29;201:863–867. doi: 10.1038/201863a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hicks S. J., Drysdale J. W., Munro H. N. Preferential synthesis of ferritin and albumin by different populations of liver polysomes. Science. 1969 May 2;164(3879):584–585. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3879.584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffenberg R., Black E., Brock J. F. Albumin and gamma-globulin tracer studies in protein depletion states. J Clin Invest. 1966 Jan;45(1):143–152. doi: 10.1172/JCI105319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan B. L., Korner A. Ribosomal subunits of Landschütz ascites cells during changes in polysome distribution. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Nov 20;169(1):129–138. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90014-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson L. S., Korner A. Influence of amino acid supply on ribosomes and protein synthesis of perfused rat liver. Biochem J. 1969 Mar;111(5):703–712. doi: 10.1042/bj1110703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John D. W., Miller L. L. Regulation of net biosynthesis of serum albumin and acute phase plasma proteins. Induction of enhanced net synthesis of fibrinogen, alpha1-acid glycoprotein, alpha2 (acute phase)-globulin, and haptoglobin by amino acids and hormones during perfusion of the isolated normal rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 25;244(22):6134–6142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel P., Quirin C., Bloch M., Jacob M. The influence of protein intake on RNA and protein synthesis in rat liver. Life Sci. 1966 Feb;5(4):325–330. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(66)90017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariani A., Migliaccio P. A., Spadoni M. A., Ticca M. Amino acid activation in the liver of growing rats maintained with normal and with protein-deficient diets. J Nutr. 1966 Sep;90(1):25–30. doi: 10.1093/jn/90.1.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothschild M. A., Oratz M., Mongelli J., Fishman L., Schreiber S. S. Amino acid regulation of albumin synthesis. J Nutr. 1969 Aug;98(4):395–403. doi: 10.1093/jn/98.4.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothschild M. A., Oratz M., Mongelli J., Schreiber S. S. Effects of a short-term fast on albumin synthesis studied in vivo, in the perfused liver, and on amino acid incorporation by hepatic microsomes. J Clin Invest. 1968 Dec;47(12):2591–2599. doi: 10.1172/JCI105941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneir M., Moldave K. The isolation and biological activity of multiple forms of aminoacyl transferase I of rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Aug 23;166(1):58–67. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90490-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw C., Fillios L. C. RNA polymerase activities and other aspects of hepatic protein synthesis during early protein depletion in the rat. J Nutr. 1968 Nov;96(3):327–336. doi: 10.1093/jn/96.3.327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields R., Korner A. Regulation of mammalian ribosome synthesis by amino acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Apr 15;204(2):521–530. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90172-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidransky H., Sarma D. S., Bongiorno M., Verney E. Effect of dietary tryptophan on hepatic polyribosomes and protein synthesis in fasted mice. J Biol Chem. 1968 Mar 25;243(6):1123–1132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WANNEMACHER R. W., Jr, RUSSELL T. J., ALLISON J. B. Serum and liver protein metabolism in protein-depleted dogs. J Nutr. 1963 Jul;80:315–320. doi: 10.1093/jn/80.3.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wannemacher R. W., Cooper W. K., Yatvin M. B. The regulation of protein synthesis in the liver of rats. Mechanisms of dietary amino acid control in the immature animal. Biochem J. 1968 May;107(5):615–623. doi: 10.1042/bj1070615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wannemacher R. W., Jr, Banks W. L., Jr, Wunner W. H. Use of a single tissue extract to determine cellular protein and nucleic acid concentrations and rate of amino acid incorporation. Anal Biochem. 1965 May;11(2):320–326. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wannemacher R. W., Jr, Cooper W. K., Muramatsu K. Effect of amino acid levels on a cell-free system for protein synthesis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Oct;135(1):180–183. doi: 10.3181/00379727-135-35014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wannemacher R. W., Jr, McCoy J. R. Regulation of protein synthesis in the ventricular myocardium of hypertrophic hearts. Am J Physiol. 1969 Apr;216(4):781–787. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.4.781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wannemacher R. W., Jr, Muramatsu K., Cooper W. K. Size distribution and counting of liver nuclei by an electronic particle counter. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Dec;129(3):899–901. doi: 10.3181/00379727-129-33453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wool I. G., Kurihara K. Determination of the number of active muscle ribosomes: effect of diabetes and insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Dec;58(6):2401–2407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.6.2401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wunner W. H., Bell J., Munro H. N. The effect of feeding with a tryptophan-free amino acid mixture on rat-liver polysomes and ribosomal ribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1966 Nov;101(2):417–428. doi: 10.1042/bj1010417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


