Abstract
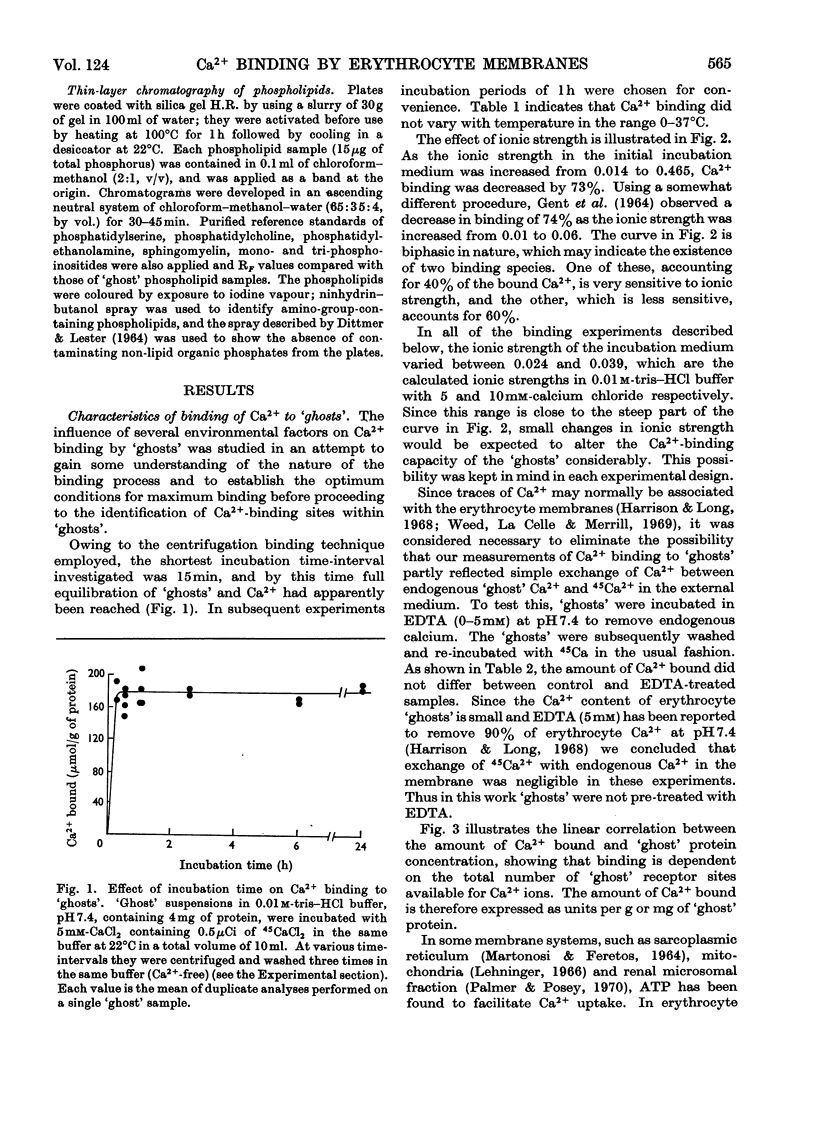
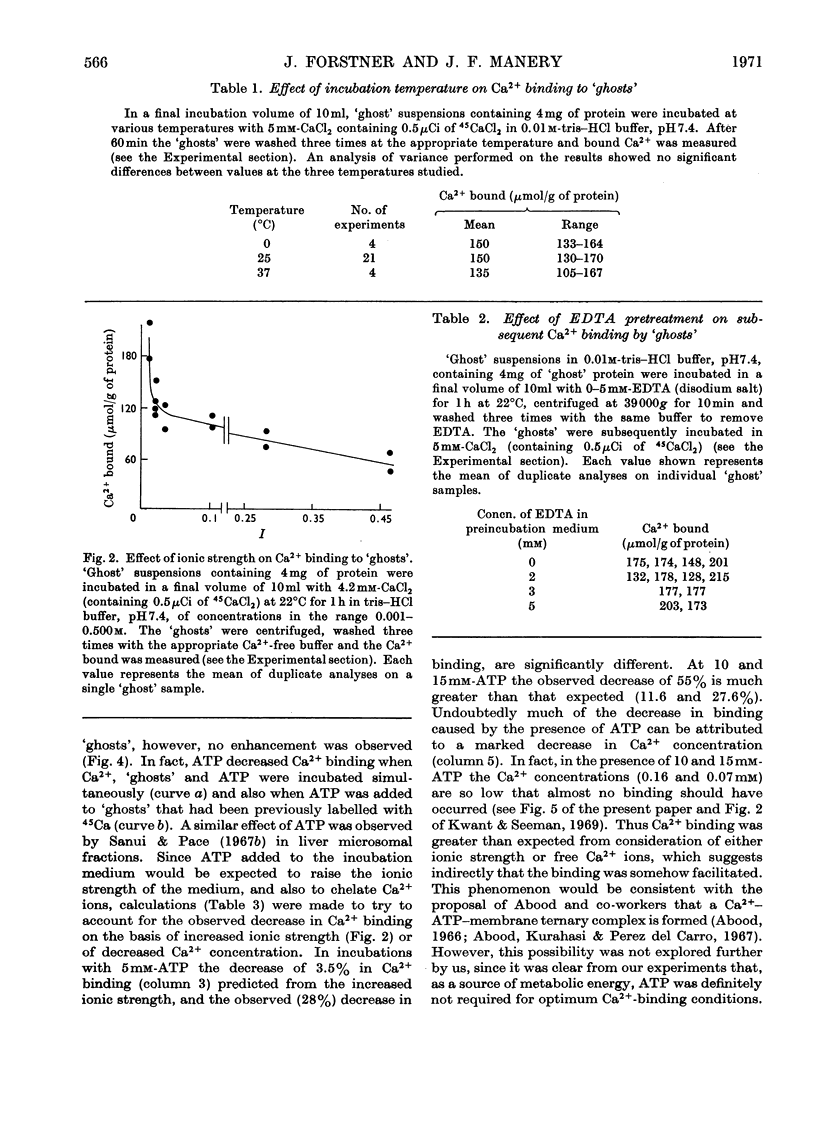
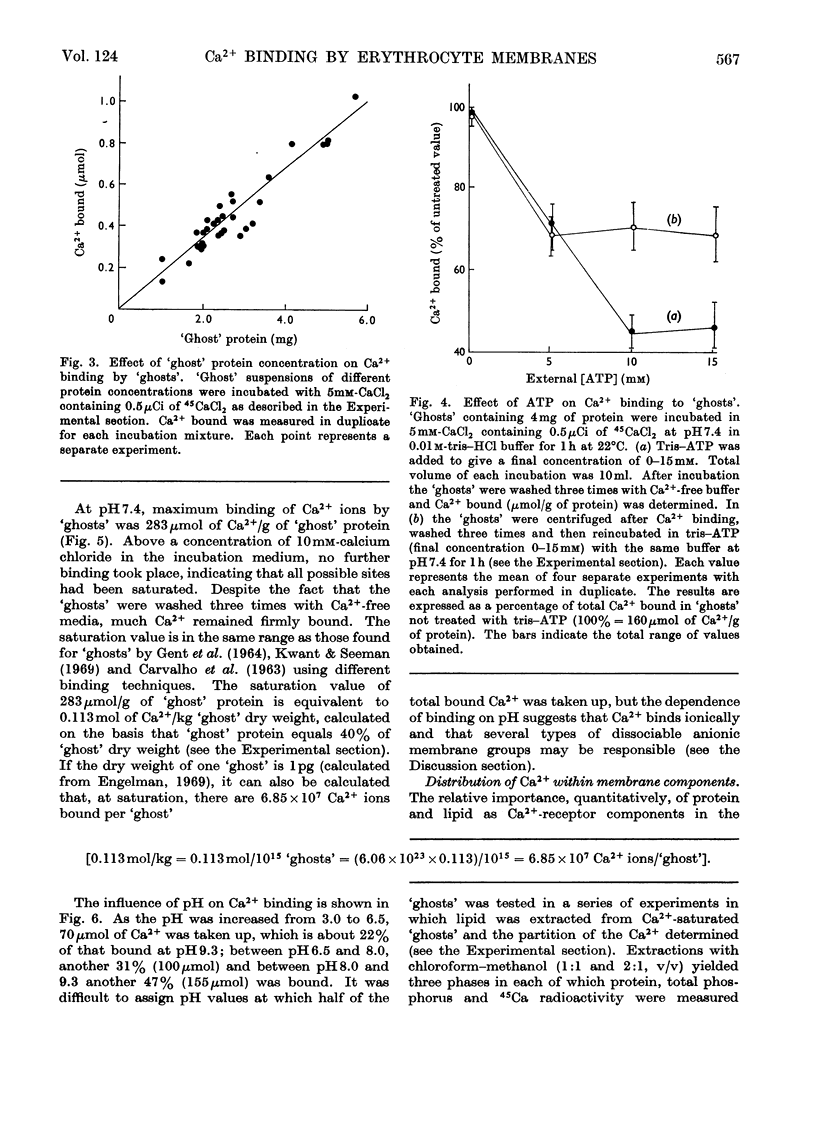
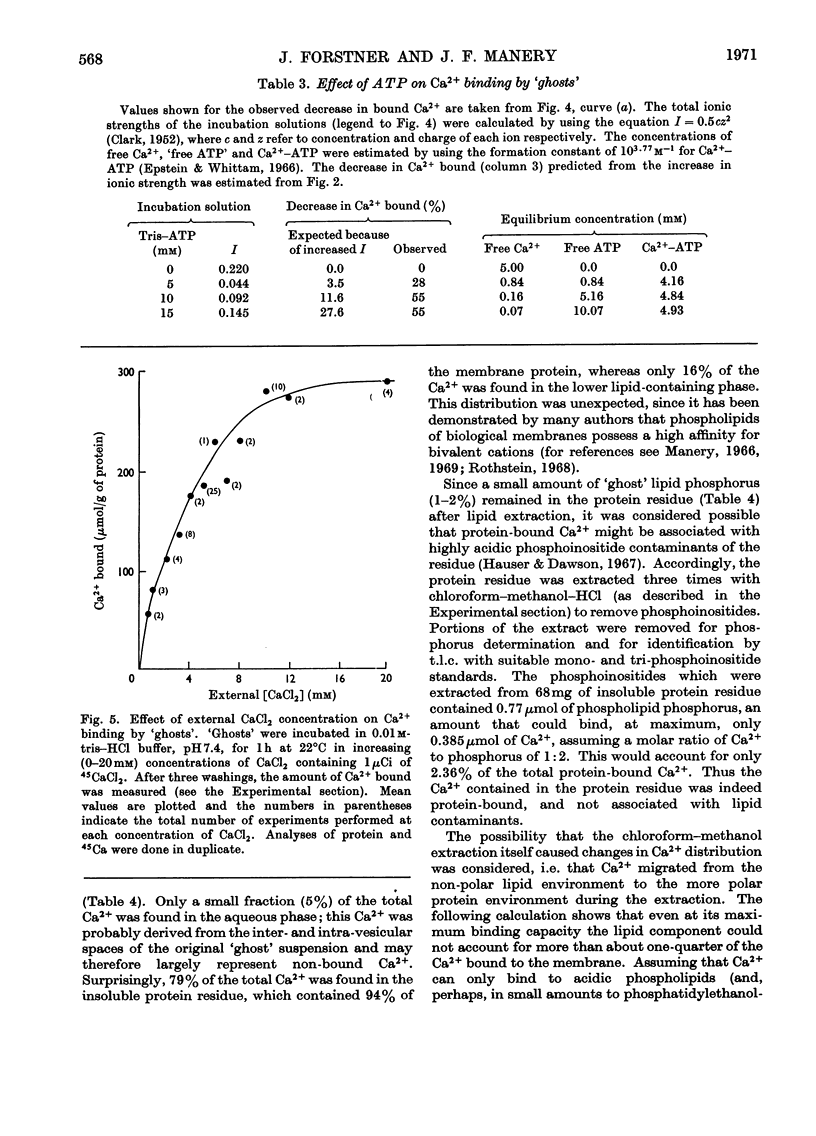
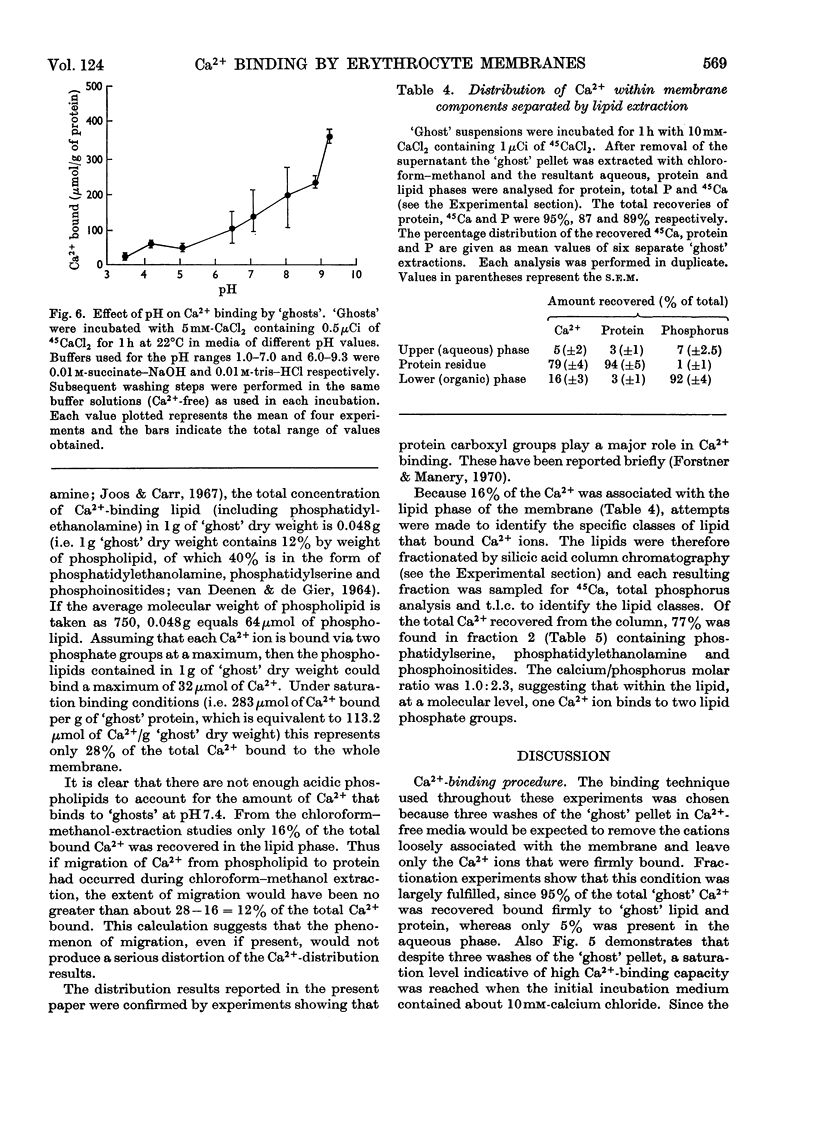
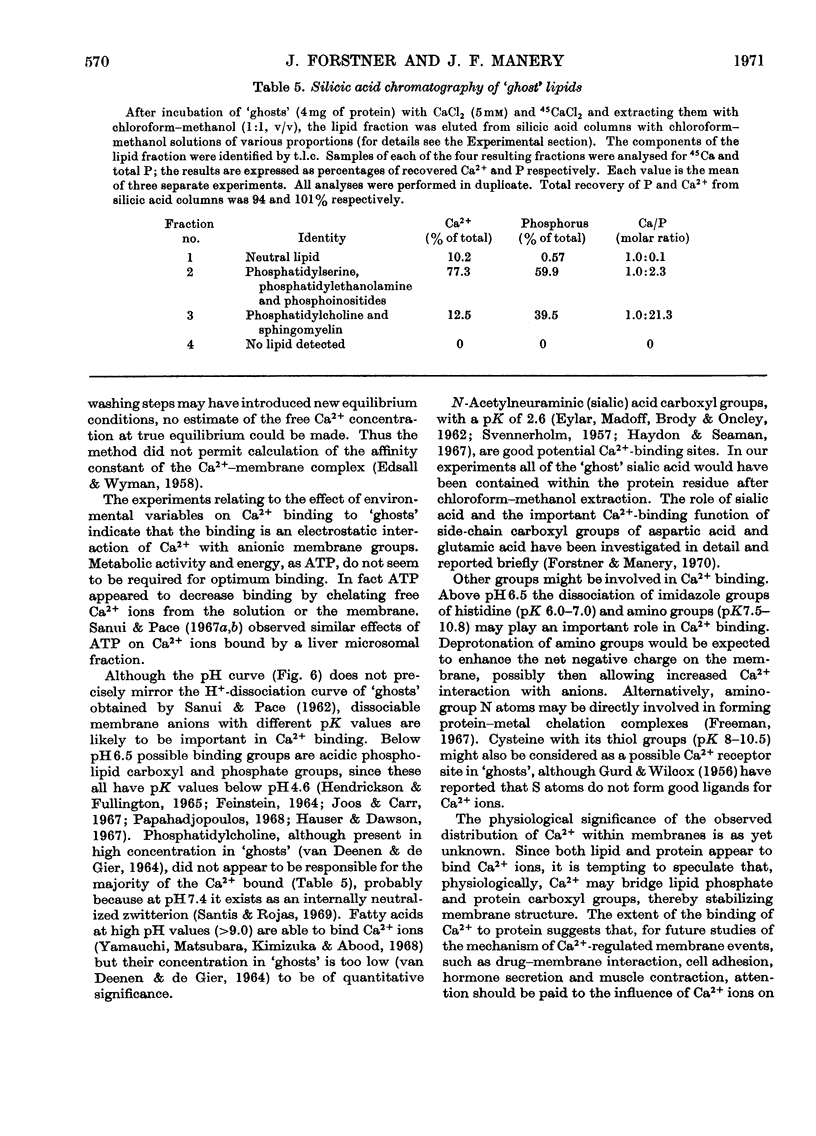
1. The characteristics of Ca2+ binding to haemoglobin-free human erythrocyte membranes were investigated by using 45Ca and centrifugation partition of `ghosts' from their external incubation medium. Equilibrium of `ghosts' with external Ca2+ required less than 15min. 2. The binding did not vary with temperature in the range 0–37°C. 3. At pH7.4 `ghosts' bound a maximum of 283μmol of Ca2+/g of `ghost' protein, equivalent to 6.85×107 Ca2+ ions per cell. 4. Increasing the ionic strength from 0.01 to 0.46 diminished Ca2+ binding, as did ATP in concentrations ranging from 0 to 15mm in the incubation medium. 5. An increase of the pH from 3.0 to 9.3 caused a marked increase in the amount of Ca2+ bound. 6. Extraction of 45Ca-labelled `ghosts' with chloroform–methanol showed that the distribution of Ca2+ was: 79% protein-bound, 16% lipid-bound, 5% in the aqueous phase, presumably non-bound. Most of the lipid-bound Ca2+ (about 80%) was associated with a phospholipid fraction containing phosphatidylserine, phosphoinositides and phosphatidylethanolamine, giving a molar Ca2+: phosphorus ratio of about 1:2.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abood L. G. Interrelationships between phosphates and calcium in bioelectric phenomena. Int Rev Neurobiol. 1966;9:223–261. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7742(08)60139-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abood L. G., Kurahasi K., Perez del Cerro M. Biochemical studies on isolated nerve endings and other particulates of bullfrog brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Apr 25;136(3):521–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLUMENSTEIN J. STUDIES IN PHOSPHOLIPID METABOLISM. I. EFFECT OF GUANIDOACETIC ACID AND CHOLINE ON LIVER PHOSPHOLIPIDS. Can J Biochem. 1964 Aug;42:1183–1194. doi: 10.1139/o64-128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger S. P., Fujii T., Hanahan D. J. Stability of the bovine erythrocyte membrane. Release of enzymes and lipid components. Biochemistry. 1968 Oct;7(10):3682–3700. doi: 10.1021/bi00850a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARVALHO A. P., SANUI H., PACE N. CALCIUM AND MAGNESIUM BINDING PROPERTIES OF CELL MEMBRANE MATERIALS. J Cell Physiol. 1963 Dec;62:311–317. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030620311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DITTMER J. C., LESTER R. L. A SIMPLE, SPECIFIC SPRAY FOR THE DETECTION OF PHOSPHOLIPIDS ON THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAMS. J Lipid Res. 1964 Jan;5:126–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODGE J. T., MITCHELL C., HANAHAN D. J. The preparation and chemical characteristics of hemoglobin-free ghosts of human erythrocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Jan;100:119–130. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dryden E. E., Manery J. F. Preparation of tissue and fluid samples for determination of tissue spaces using sorbitol and-or inulin labeled with carbon-14 or tritium. Anal Biochem. 1970 Jun;35(2):384–392. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90199-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EYLAR E. H., MADOFF M. A., BRODY O. V., ONCLEY J. L. The contribution of sialic acid to the surface charge of the erythrocyte. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jun;237:1992–2000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichberg J., Hauser G. Concentrations and disappearance post mortem of polyphosphoinositides in developing rat brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Oct 2;144(2):415–422. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(67)90171-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman D. M. Surface area per lipid molecule in the intact membrane of the human red cell. Nature. 1969 Sep 20;223(5212):1279–1280. doi: 10.1038/2231279a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein F. H., Whittam R. The mode of inhibition by calcium of cell-membrane adenosine-triphosphatase activity. Biochem J. 1966 Apr;99(1):232–238. doi: 10.1042/bj0990232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEINSTEIN M. B. REACTION OF LOCAL ANESTHETICS WITH PHOSPHOLIPIDS. A POSSIBLE CHEMICAL BASIS FOR ANESTHESIA. J Gen Physiol. 1964 Nov;48:357–374. doi: 10.1085/jgp.48.2.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman H. C. Crystal structures of metal-peptide complexes. Adv Protein Chem. 1967;22:257–424. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60043-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GENT W. L., TROUNCE J. R., WALSER M. THE BINDING OF CALCIUM ION BY THE HUMAN ERYTHROCYTE MEMBRANE. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Jun;105:582–589. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(64)90054-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Sastre F., Folch-Pi J. Thin-layer chromatography of the phosphoinositides. J Lipid Res. 1968 Jul;9(4):532–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANAHAN D. J., DITTMER J. C., WARASHINA E. A column chromatographic separation of classes of phospholipides. J Biol Chem. 1957 Oct;228(2):685–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison D. G., Long C. The calcium content of human erythrocytes. J Physiol. 1968 Dec;199(2):367–381. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser H., Chapman D., Dawson R. M. Physical studies of phospholipids. XI. Ca2+ binding to monolayers of phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylinositol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jul 15;183(2):320–333. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90088-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser H., Dawson R. M. The binding of calcium at lipid-water interfaces. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Mar;1(1):61–69. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-25813-2_11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haydon D. A., Seaman G. V. Electrokinetic studies on the ultrastructure of the human erythrocyte. I. Electrophoresis at high ionic strengths--the cell as a polyanion. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 Oct;122(1):126–136. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90131-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickson H. S., Fullington J. G. Stabilities of metal complexes of phospholipids: Ca(II), Mg(II), and Ni(II) complexes of phosphatidylserine and triphosphoinositide. Biochemistry. 1965 Aug;4(8):1599–1605. doi: 10.1021/bi00884a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joos R. W., Carr C. W. The binding of calcium in mixtures of phospholipids. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Apr;124(4):1268–1272. doi: 10.3181/00379727-124-31984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joos R. W., Carr C. W. The binding of calcium to phospholipid-protein complexes. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Dec;132(3):865–870. doi: 10.3181/00379727-132-34325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwant W. O., Seeman P. The displacement of membrane calcium by a local anesthetic (chlorpromazine). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969;193(2):338–349. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90194-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTONOSI A., FERETOS R. SARCOPLASMIC RETICULUM. I. THE UPTAKE OF CA++ BY SARCOPLASMIC RETICULUM FRAGMENTS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:648–658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manery J. F. Effects of Ca ions on membranes. Fed Proc. 1966 Nov-Dec;25(6):1804–1810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohki S., Goldup A. Influence of pH, sodium and calcium ions on the d.c. resistance of black egg lecithin-cholesterol films. Nature. 1968 Feb 3;217(5127):458–459. doi: 10.1038/217458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. F., Posey V. A. Calcium and adenosine triphosphate binding to renal membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Jan;55(1):89–103. doi: 10.1085/jgp.55.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papahadjopoulos D. Surface properties of acidic phospholipids: interaction of monolayers and hydrated liquid crystals with uni- and bi-valent metal ions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Sep 17;163(2):240–254. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90103-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROELOFSEN B., DE GIER J., VAN DEENENL BINDING OF LIPIDS IN THE RED CELL MEMBRANE. J Cell Physiol. 1964 Apr;63:233–243. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030630214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SVENNERHOLM L. Quantitative estimation of sialic acids. II. A colorimetric resorcinol-hydrochloric acid method. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Jun;24(3):604–611. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90254-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santis M., Rojas E. On the chemistry of ion exchange in monomolecular layers of lipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969;193(2):319–332. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90192-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Breemen C. Permselectivity of a porous phospholipid-cholesterol artificial membrane. Calcium and lanthanum effects. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Sep 30;32(6):977–983. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90124-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weed R. I., LaCelle P. L., Merrill E. W. Metabolic dependence of red cell deformability. J Clin Invest. 1969 May;48(5):795–809. doi: 10.1172/JCI106038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamauchi A., Matsubara A., Kimizuka H., Abood L. G. Differential effect of sodium and potassium on calcium adsorption to stearic acid monolayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Mar 1;150(2):181–185. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90161-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


