Abstract
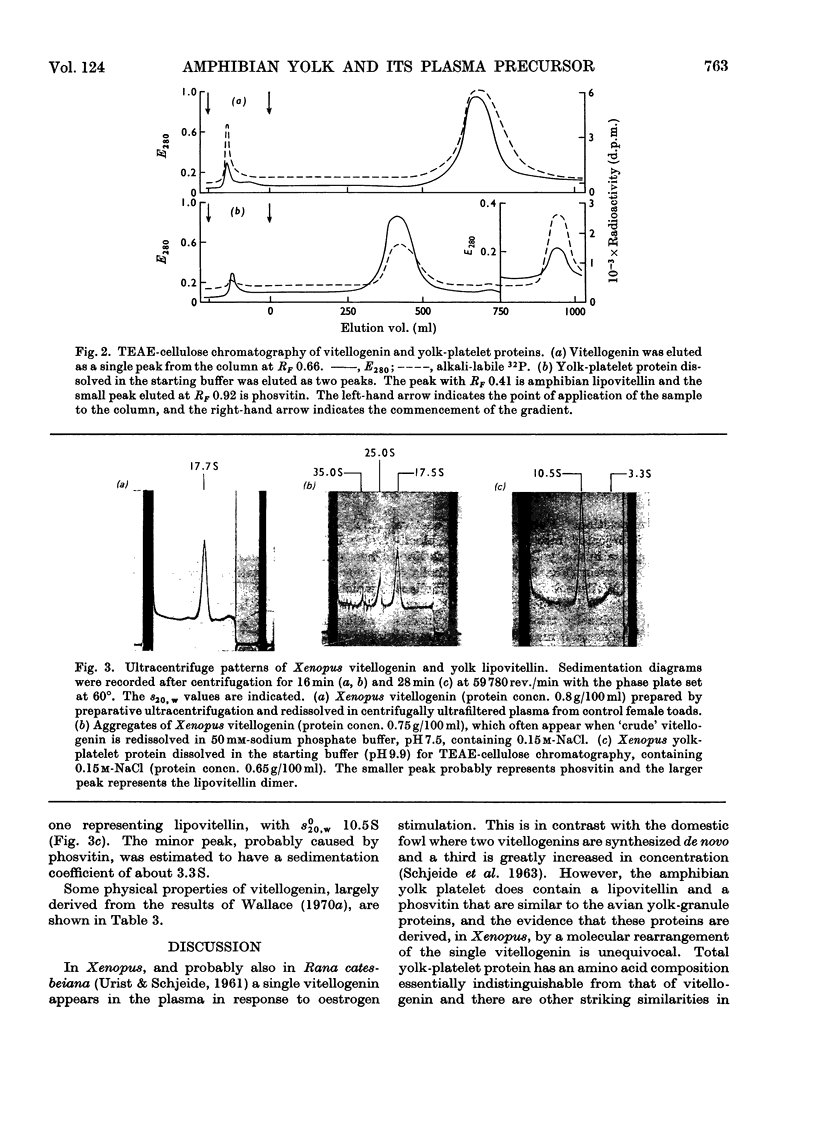
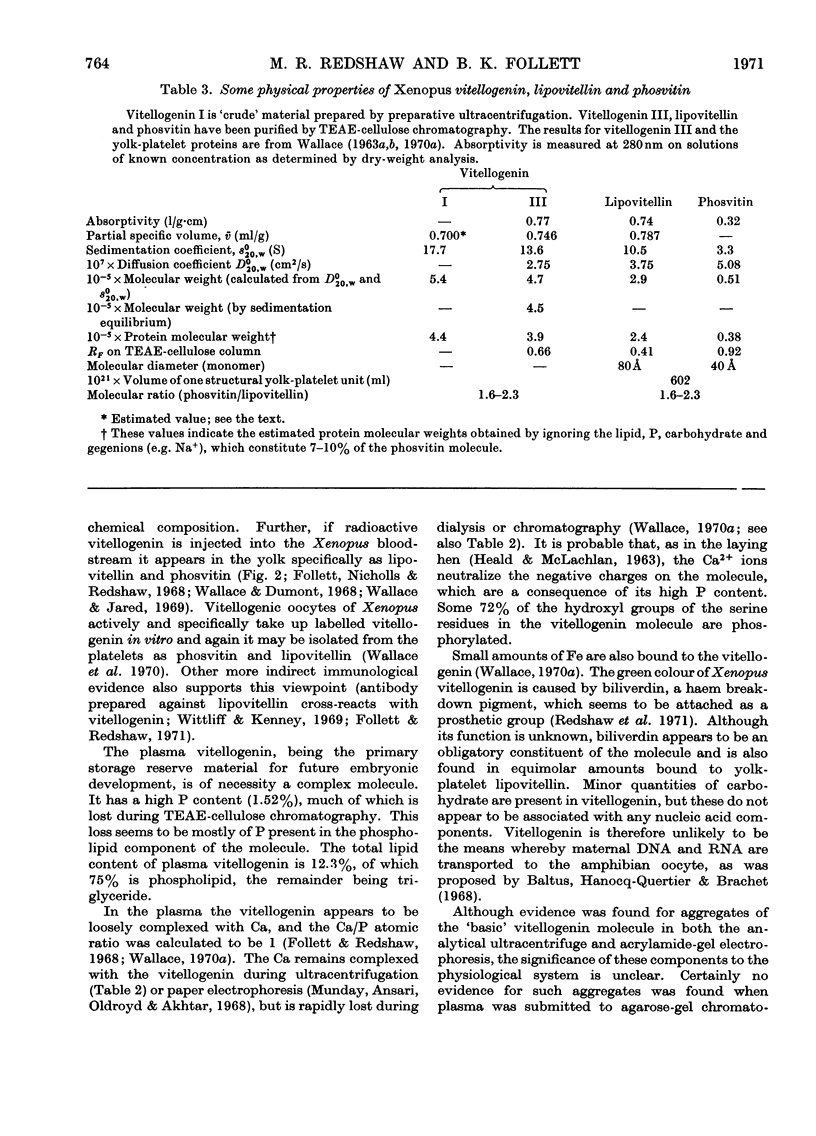
A single lipophosphoprotein complex, vitellogenin, was isolated and purified from the plasma of oestrogen-stimulated female toads by preparative ultracentrifugation and chromatography on TEAE-cellulose (triethylaminoethylcellulose). The protein contains 12% lipid, 1.5% phosphorus, 1.6% calcium and smaller amounts of carbohydrates and biliverdin. In amino acid composition it is identical with total yolk-platelet protein. The platelet protein, however, is fractionated on TEAE-cellulose into two components, a high-molecular-weight lipovitellin and a smaller phosvitin. Analyses of the soluble plasma vitellogenin suggest that it is a complex of two phosvitin molecules covalently bound to one lipovitellin dimer, and that it is the immediate precursor of the yolk proteins, into which it is converted by a molecular rearrangement. Uptake of vitellogenin from the plasma into the growing oocyte, and its subsequent crystallization as a yolk platelet, appear to be enhanced by gonadotrophic hormones.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. The gel-filtration behaviour of proteins related to their molecular weights over a wide range. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):595–606. doi: 10.1042/bj0960595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltus E., Hanocq-Quertier J., Brachet J. Isolation of deoxyribonucleic acid from the yolk platelets of Xenopus laevis oöcyte. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Oct;61(2):469–476. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.2.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook W. H., Wallace R. A. Dissociation and subunit size of beta-lipovitellin. Can J Biochem. 1965 Jun;43(6):661–670. doi: 10.1139/o65-077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Follett B. K., Redshaw M. R. The effects of oestrogen and gonadotrophins on lipid and protein metabolism in Xenopus laevis Daudin. J Endocrinol. 1968 Apr;40(4):439–456. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0400439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEALD P. J., McLACHLAN P. M. Isolation of phosvitin from the plasma of the laying hen. Biochem J. 1963 Jun;87:571–576. doi: 10.1042/bj0870571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McINDOE W. M. A lipophosphoprotein complex in hen plasma associated with yolk production. Biochem J. 1959 May;72(1):153–159. doi: 10.1042/bj0720153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munday K. A., Ansari A. Q., Oldroyd D., Akhtar M. Oestrogen-induced calcium-binding protein in Xenopus laevis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Oct 29;166(3):748–751. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90393-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORNSTEIN L. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. I. BACKGROUND AND THEORY. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:321–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PIEZ K. A., MORRIS L. A modified procedure for the automatic analysis of amino acids. Anal Biochem. 1960 Nov;1:187–201. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(60)90045-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan M. L., Bell W. J., Telfer W. H. Vitellogenic blood protein synthesis by insect fat body. Science. 1969 Jul 25;165(3891):393–394. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3891.393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHJEIDE O. A., LEVI E., FLICKINGER R. A. A study of the yolk proteins of frog eggs by physical and chemical means. Growth. 1955 Dec;19(4):297–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHJEIDE O. A., URIST M. R. Proteins induced in plasma by oestrogens. Nature. 1960 Oct 22;188:291–294. doi: 10.1038/188291a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TORIBARA T. Y., TEREPKA A. R., DEWEY P. A. The ultrafiltrable calcium of human serum. I. Ultrafiltration methods and normal values. J Clin Invest. 1957 May;36(5):738–748. doi: 10.1172/JCI103477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- URIST M. R., SCHJEIDE A. O. The partition of calcium and protein in the blood of oviparous vertebrates during estrus. J Gen Physiol. 1961 Mar;44:743–756. doi: 10.1085/jgp.44.4.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALLACE R. A. STUDIES ON AMPHIBIAN YOLK. IV. AN ANALYSIS OF THE MAIN-BODY COMPONENT OF YOLK PLATELETS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Aug 13;74:505–518. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91393-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS J., SANGER F. The grouping of serine phosphate residues in phosvitin and casein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 May;33(1):294–296. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90545-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINZLER R. J. Determination of serum glycoproteins. Methods Biochem Anal. 1955;2:279–311. doi: 10.1002/9780470110188.ch10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. A., Jared D. W., Nelson B. L. Protein incorporation by isolated amphibian oocytes. I. Preliminary studies. J Exp Zool. 1970 Nov;175(3):259–269. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401750302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. A., Jared D. W. Studies on amphibian yolk. 8. The estrogen-induced hepatic synthesis of a serum lipophosphoprotein and its selective uptake by the ovary and trasformation into yolk platelet proteins in Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1969 May;19(5):498–526. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(69)90085-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. A. Resolution and isolation of avian and amphibian yolk-granule proteins using TEAE-cellulose. Anal Biochem. 1965 May;11(2):297–311. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. A. Resolution and isolation of avian and amphibian yolk-granule proteins using TEAE-cellulose. Anal Biochem. 1965 May;11(2):297–311. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. A. Studies on amphibian yolk. IX. Xenopus vitellogenin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jul 21;215(1):176–183. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90400-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]