Abstract
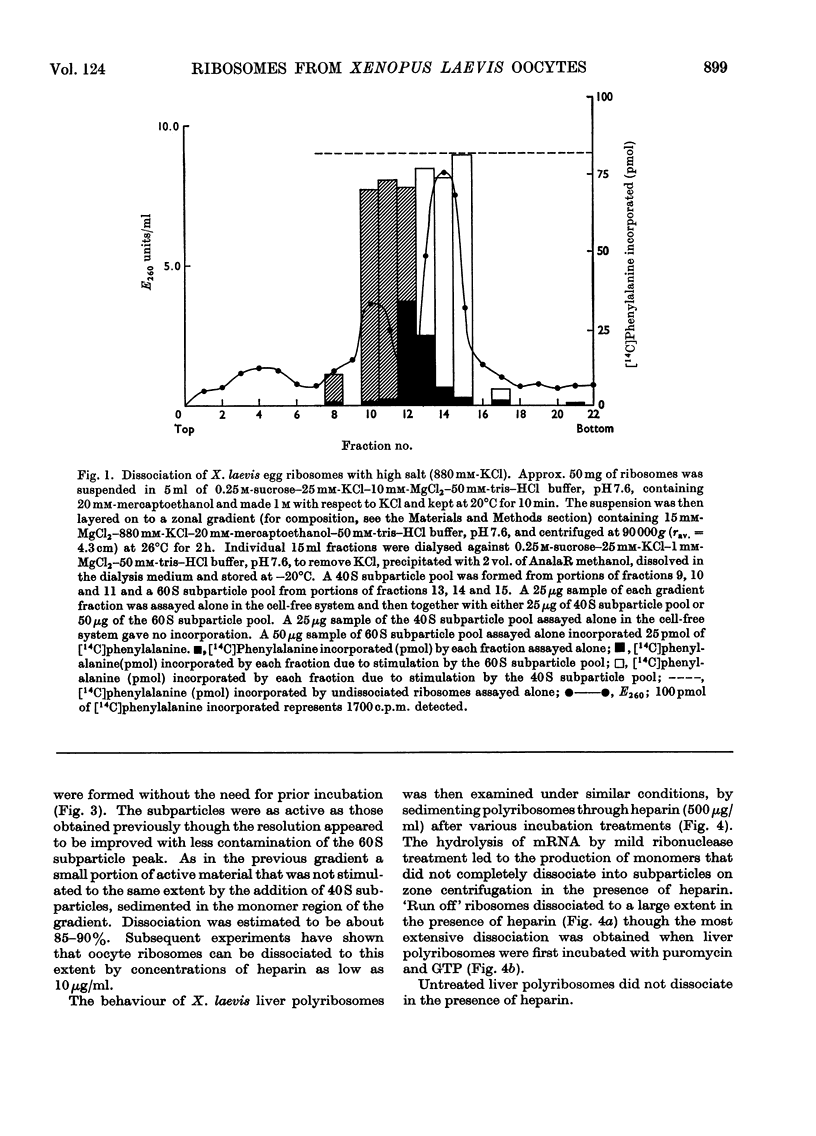
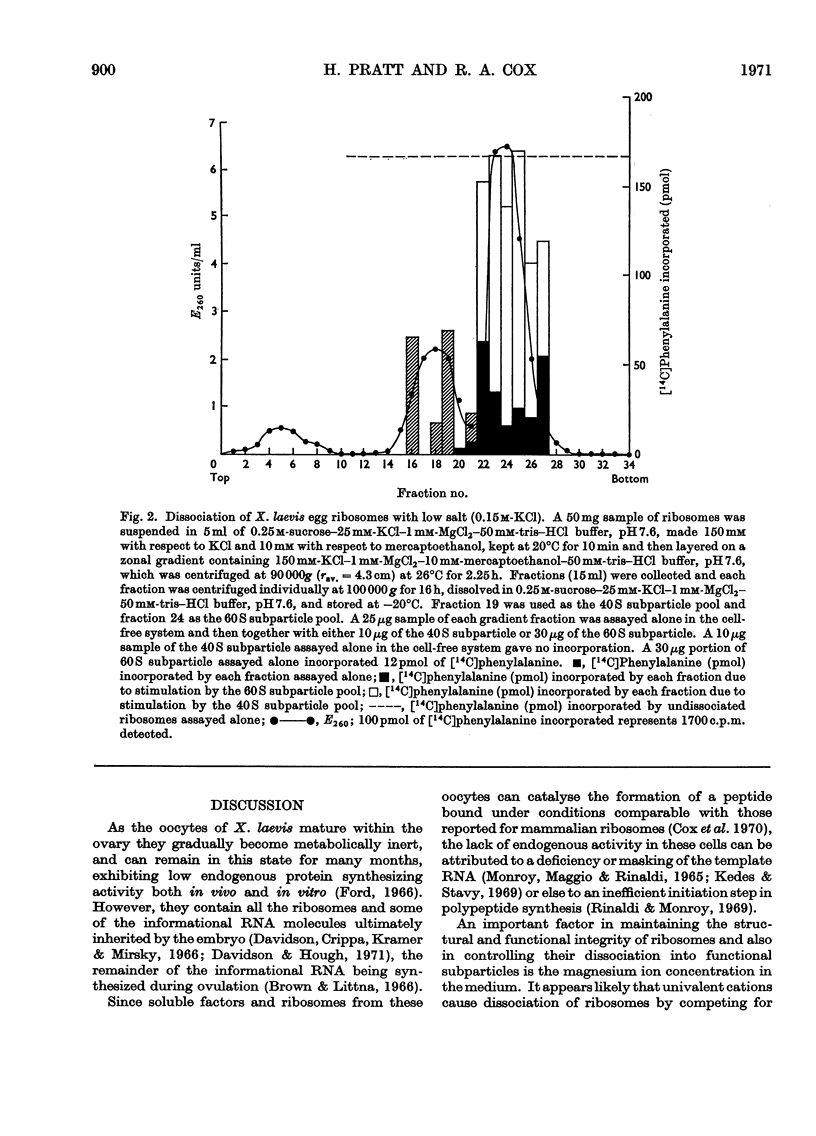
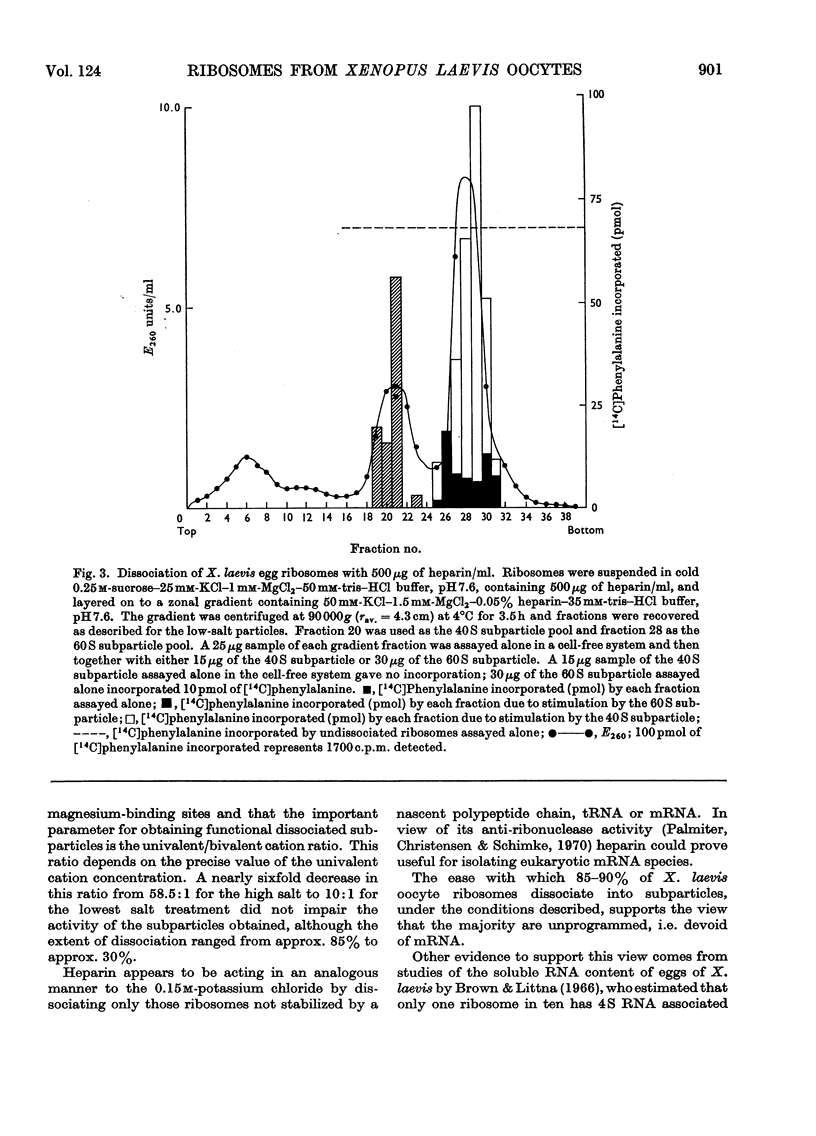
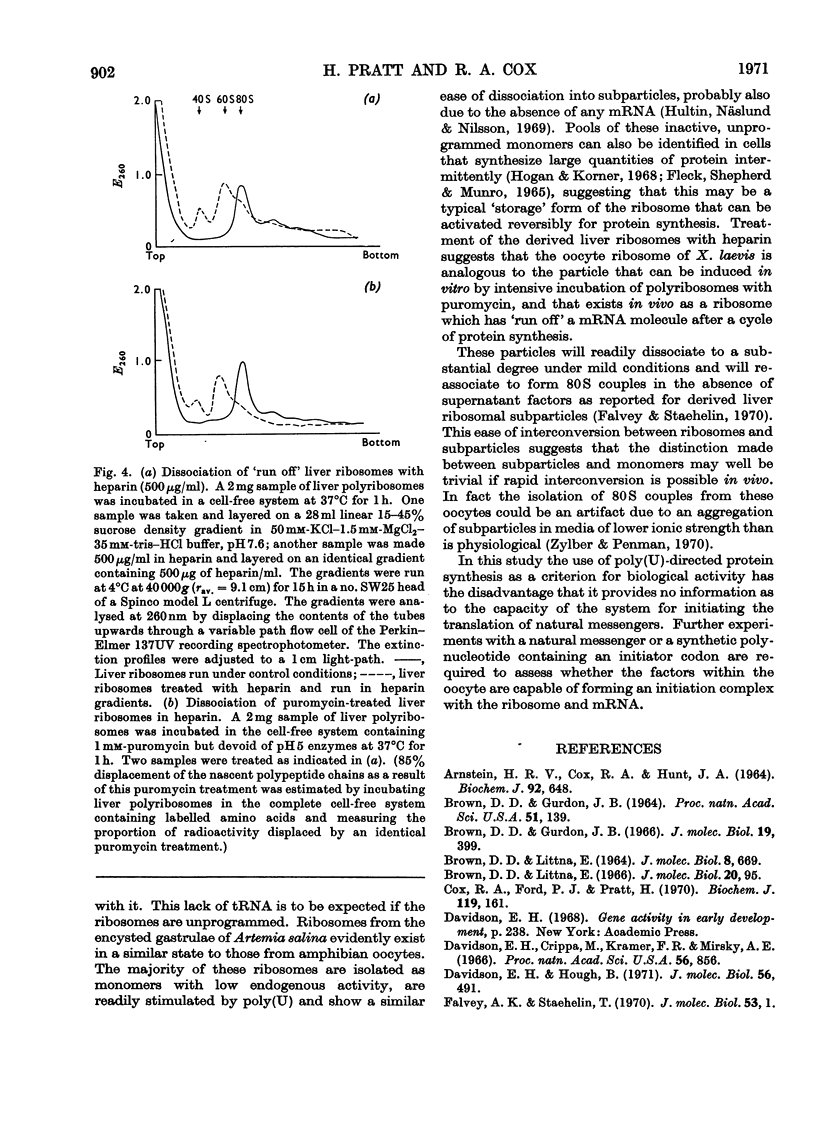
Ribosomes from oocytes of Xenopus laevis possess low endogenous activity in vivo and in vitro, yet are readily stimulated by poly(U). The ease with which these ribosomes dissociate into active subparticles under conditions where polyribosomes and active monoribosomes are stable supports the view that the majority are unprogrammed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnstein H. R., Cox R. A., Hunt J. A. The function of high-molecular-weight ribonucleic acid from rabbit reticulocytes in haemoglobin biosynthesis. Biochem J. 1964 Sep;92(3):648–661. doi: 10.1042/bj0920648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN D. D., GURDON J. B. ABSENCE OF RIBOSOMAL RNA SYNTHESIS IN THE ANUCLEOLATE MUTANT OF XENOPUS LAEVIS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jan;51:139–146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.1.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN D. D., LITTNA E. RNA SYNTHESIS DURING THE DEVELOPMENT OF XENOPUS LAEVIS, THE SOUTH AFRICAN CLAWED TOAD. J Mol Biol. 1964 May;8:669–687. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80116-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A., Ford P. J., Pratt H. Ribosomes from Xenopus laevis ovaries and the polyuridylic acid-directed biosynthesis of polyphenylalanine. Biochem J. 1970 Sep;119(2):161–164. doi: 10.1042/bj1190161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. H., Crippa M., Kramer F. R., Mirsky A. E. Genomic function during the lampbrush chromosome stage of amphibian oogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Sep;56(3):856–863. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.3.856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleck A., Shepherd J., Munro H. N. Protein synthesis in rat liver: influence of amino acids in diet on microsomes and polysomes. Science. 1965 Oct 29;150(3696):628–629. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3696.628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford P. J. A comparative study in vivo and in vitro of the ability of ribosomes from Xenopus liver and ovary to incorporate L-[U-14C]leucine. Biochem J. 1966 Nov;101(2):369–378. doi: 10.1042/bj1010369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould H. J., Arnstein H. R., Cox R. A. The dissociation of reticulocyte polysomes into subunits and the location of messenger RNA. J Mol Biol. 1966 Feb;15(2):600–618. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80130-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan B. L., Korner A. The role of ribosomal subunits and 80-S monomers in polysome formation in an ascites tumour cell. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Nov 20;169(1):139–149. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultin T., Näslund P. H., Nilsson M. O. Dissociation of ribosomes from dormant cysts of Artemia salina in potassium-free media. Exp Cell Res. 1969 May;55(2):269–274. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(69)90491-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedes L. H., Stavy L. Structural and functional identity of ribosomes from eggs and embryos of sea urchins. J Mol Biol. 1969 Jul 28;43(2):337–340. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90273-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawford G. R. The effect of incubation with puromycin on the dissociation of rat liver ribosomes into active subunits. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Sep 24;37(1):143–150. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90892-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loening U. E., Jones K. W., Birnstiel M. L. Properties of the ribosomal RNA precursor in Xenopus laevis; comparison to the precursor in mammals and in plants. J Mol Biol. 1969 Oct 28;45(2):353–366. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90110-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. E., Rolleston F. S., Low R. B., Wool I. G. Dissociation and reassociation of skeletal muscle ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1969 Jul 14;43(1):135–149. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90084-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monroy A., Maggio R., Rinaldi A. M. Experimentally induced activation of the ribosomes of the unfertilized sea urchin egg. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jul;54(1):107–111. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.1.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Christensen A. K., Schimke R. T. Organization of polysomes from pre-existing ribosomes in chick oviduct by a secondary administration of either estradiol or progesterone. J Biol Chem. 1970 Feb 25;245(4):833–845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldi A. M., Monroy A. Polyribosome formation and RNA synthesis in the early post-fertilization stages of the sea urchin egg. Dev Biol. 1969 Jan;19(1):73–86. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(69)90071-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zylber E. A., Penman S. The effect of high ionic strength on monomers, polyribosomes, and puromycin-treated polyribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Mar 19;204(1):221–229. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90505-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der Decke A., Ashby P., McIlreavy D., Campbell P. N. The reverible dissociation and activity ofribosoma subunits of liver and skeletal muscle from rats. Biochem J. 1970 Dec;120(4):815–819. doi: 10.1042/bj1200815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


