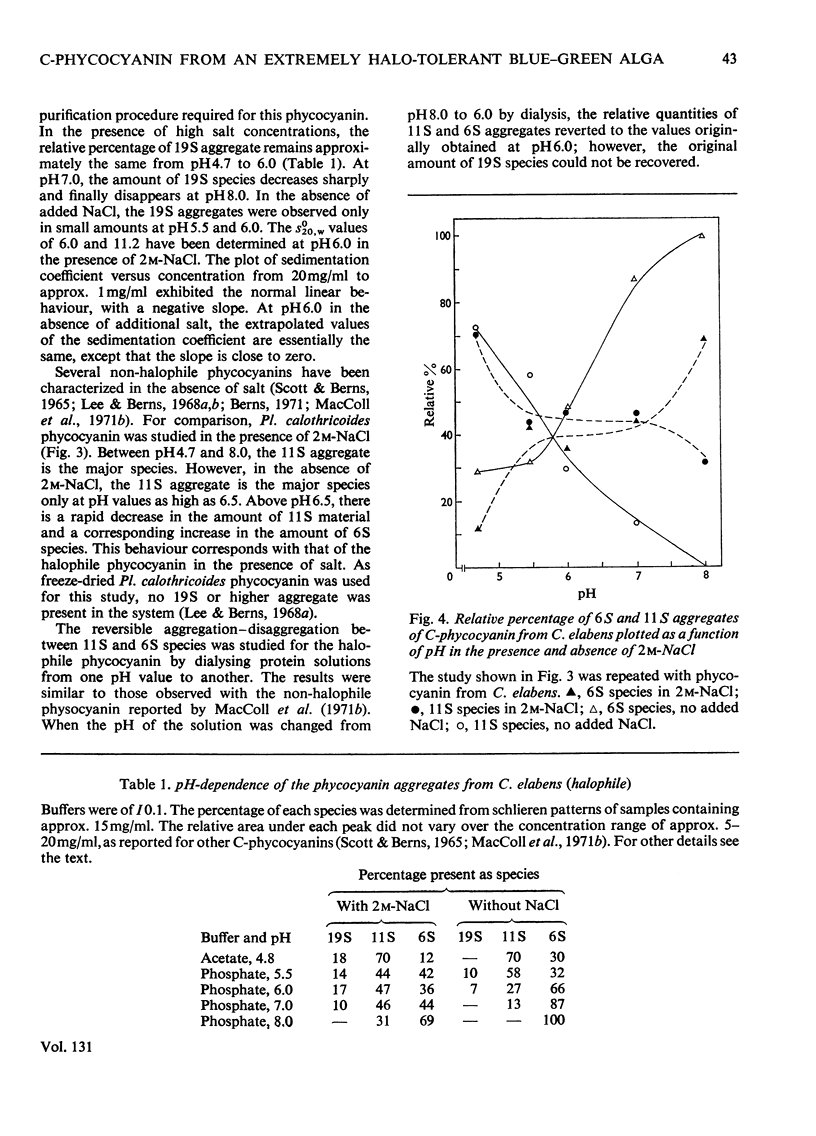
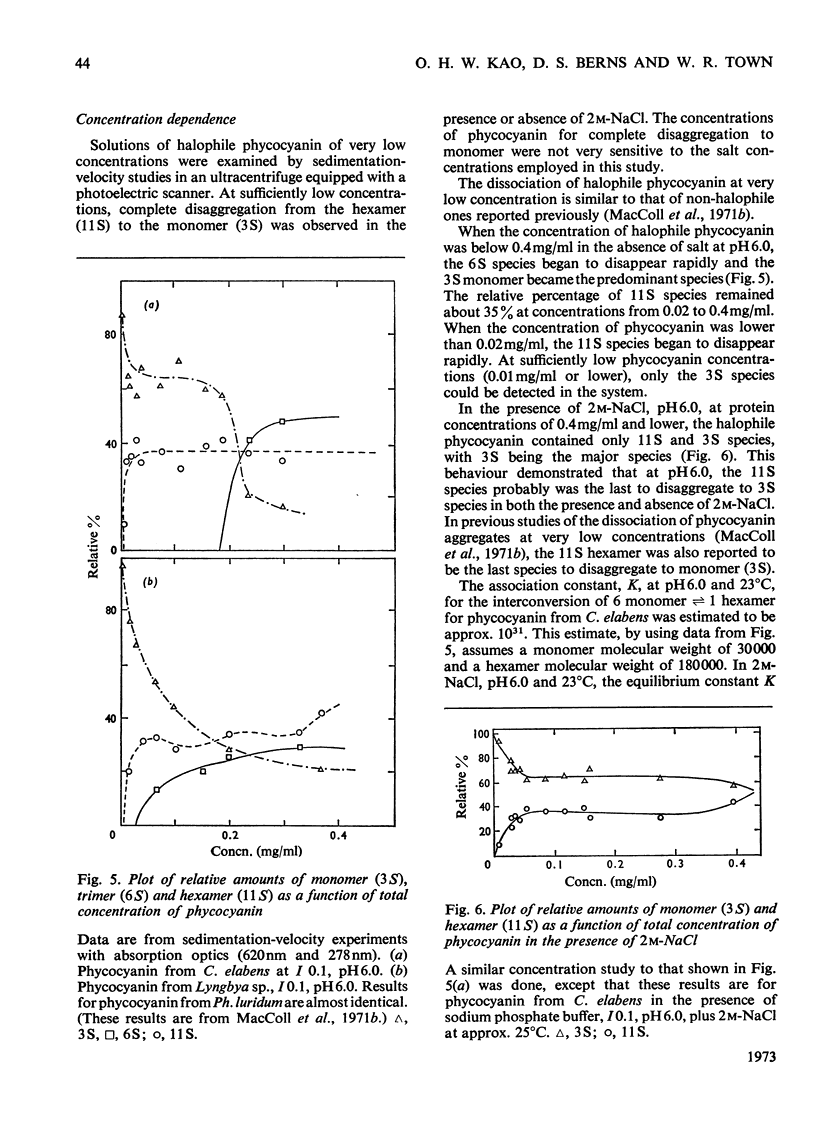
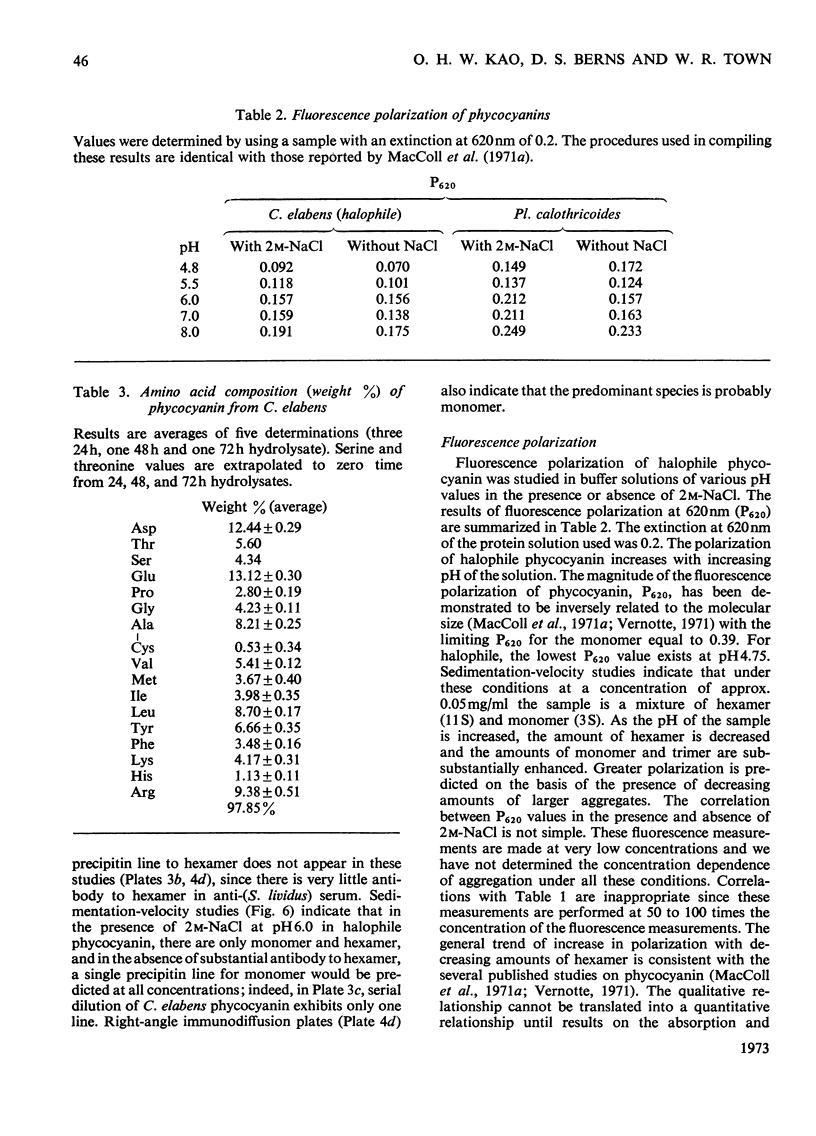
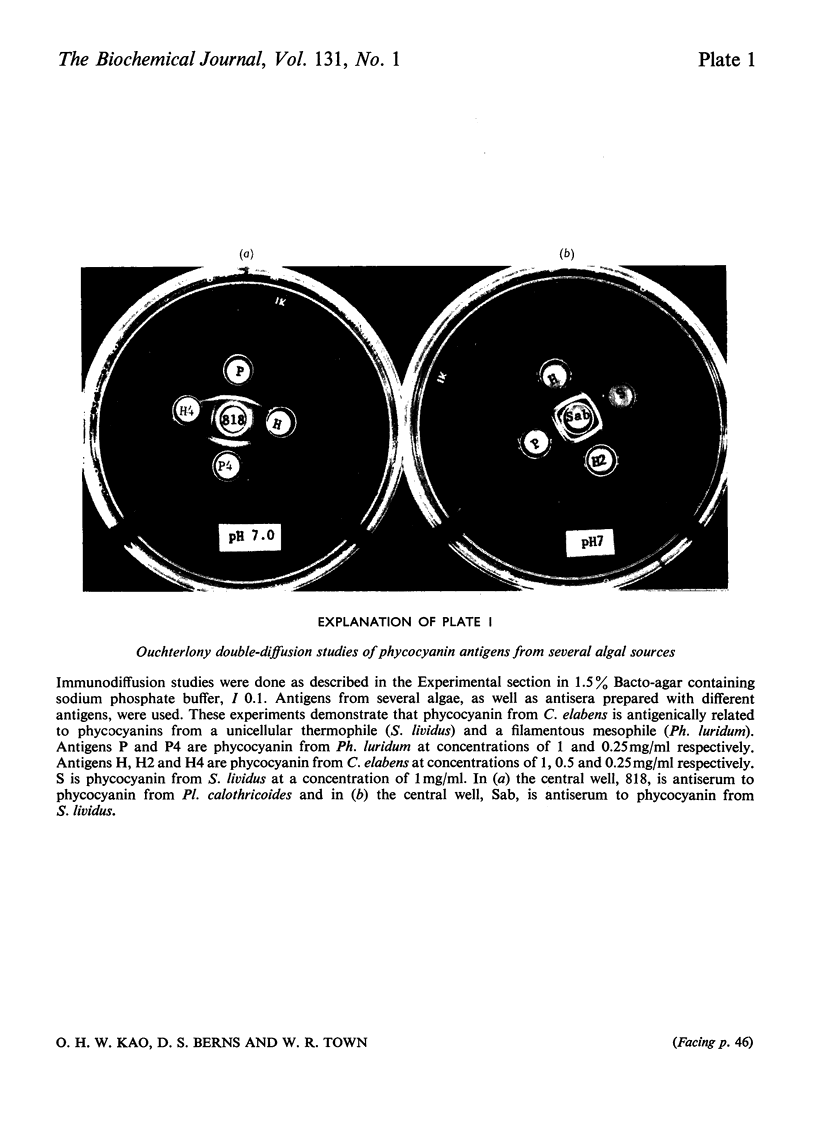
Abstract
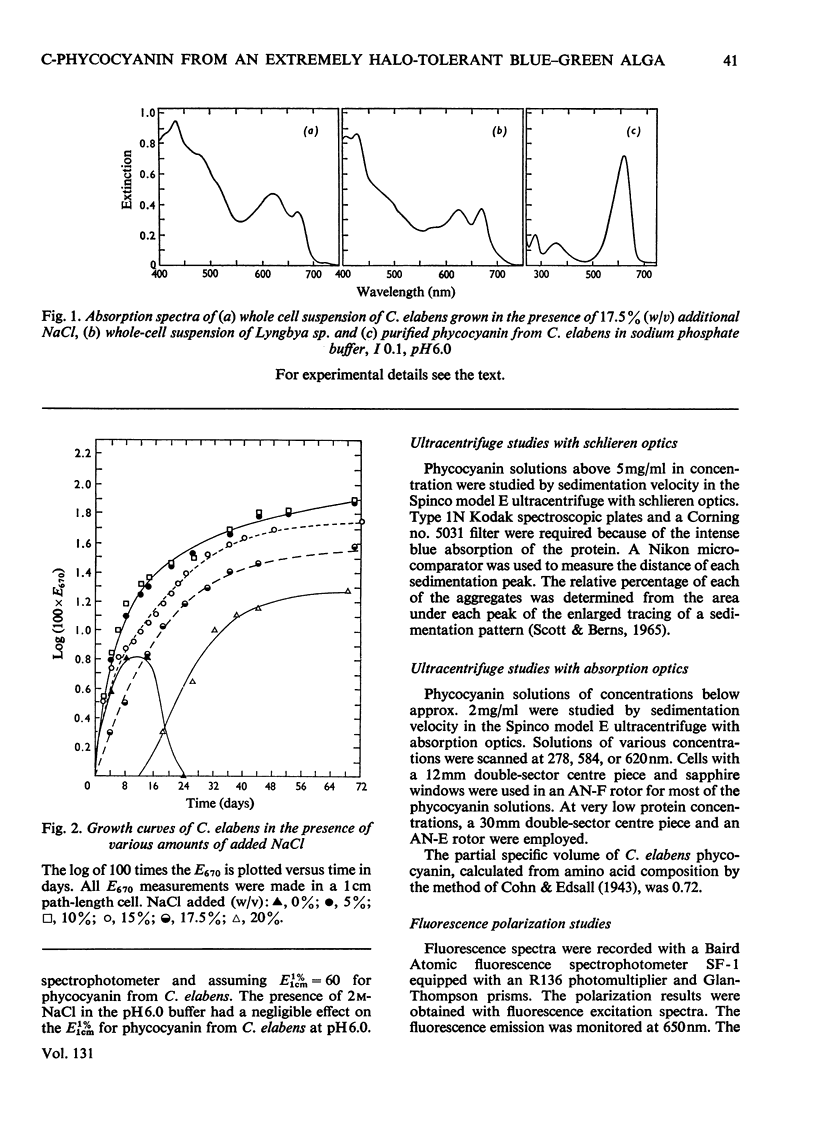
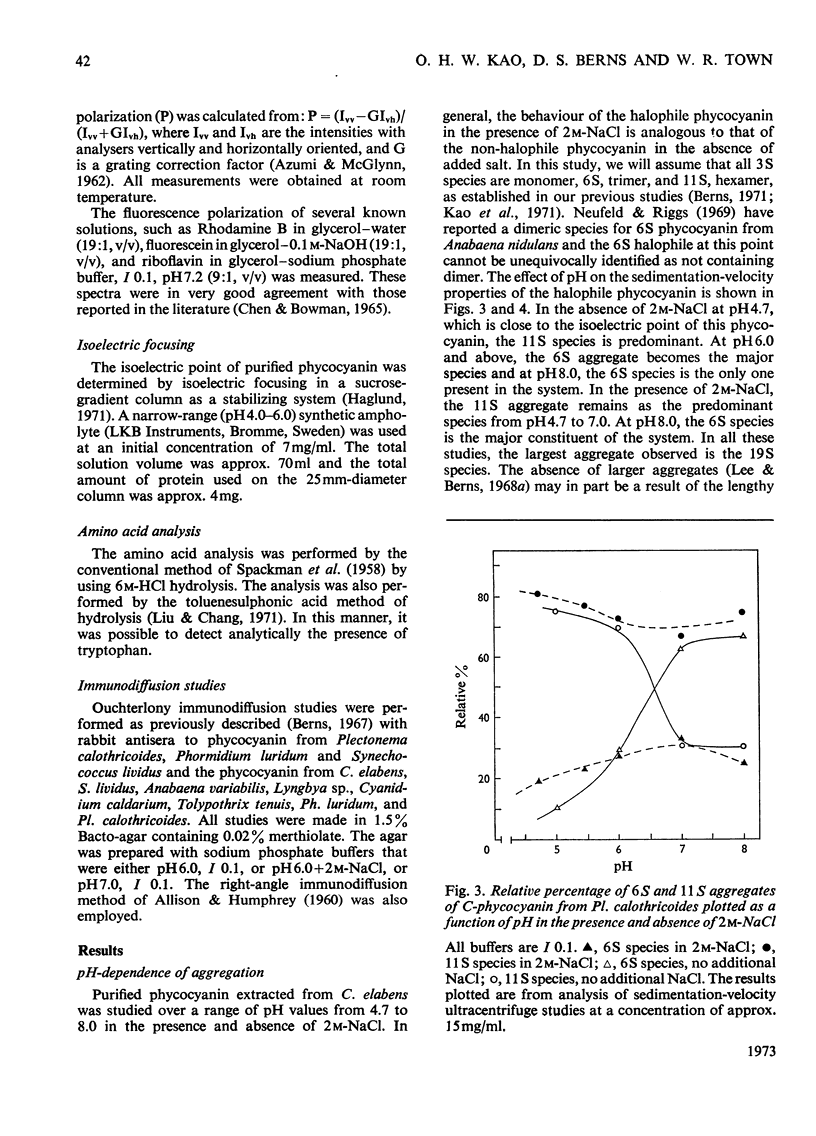
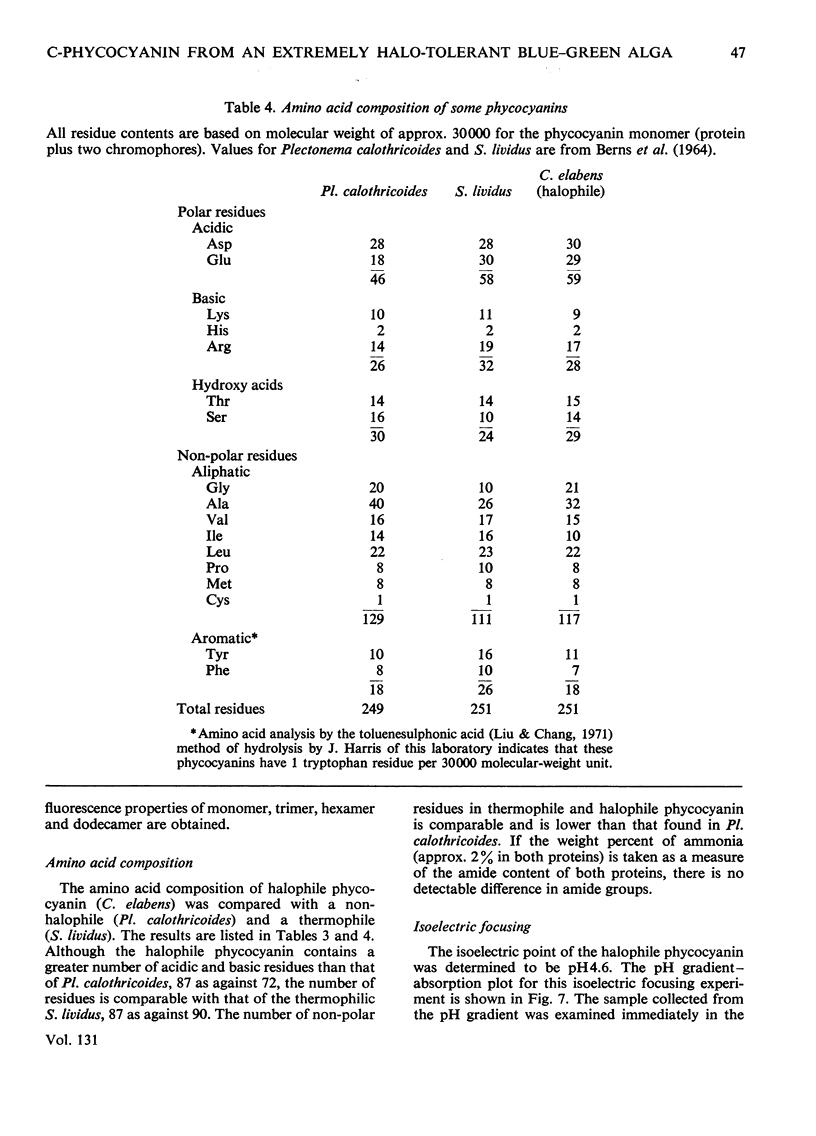
C-Phycocyanin was isolated and purified from a uni-algal culture of an extremely halo-tolerant blue–green alga, Coccochloris elabens. This alga can be grown under laboratory conditions in 25% (w/v) NaCl. Purified halophile phycocyanin was characterized by amino acid analysis and the measurement of sedimentation velocity, fluorescence polarization and immunodiffusion as a function of protein concentration, pH and ionic strength. The results were compared with those of studies of phycocyanin isolated from Plectonema calothricoides and from several other sources. The states of aggregation previously characterized as being present in other C-phycocyanins, monomer, trimer and hexamer, were present in halophile phycocyanin and were characterized as antigenically related to all C-phycocyanins tested. The equilibrium between 3S monomer and 11S hexamer at low concentrations in halophile phycocyanin was quantitatively similar to that for other phycocyanins. The effect of pH and ionic strength on the 6S (trimer) and 11S (hexamer) aggregation of halophile phycocyanin was markedly salt-dependent and the relative amount of each aggregate in the presence of 2m-NaCl was like that of C-phycocyanin from mesophiles, in the absence of additional salt. In antigenic relationship and aggregation properties, the phycocyanin from C. elabens appeared to be most closely related to that isolated from the thermophilic blue–green alga, Synechococcus lividus. Amino acid content of the halophile phycocyanin indicated the presence of a significantly larger number of acidic residues than that found in mesophiles. Explanations of the properties of the halophile protein require consideration of a strong contribution of hydrophobic forces and utilize both charge-shielding and salting-out effects.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLISON A. C., HUMPHREY J. H. A theoretical and experimental analysis of double diffusion precipitin reactions in gels, and its application to characterization of antigens. Immunology. 1960 Jan;3:95–106. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAXTER R. M. An interpretation of the effects of salts on the lactic dehydrogenase of Halobacterium salinarium. Can J Microbiol. 1959 Feb;5(1):47–57. doi: 10.1139/m59-006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERNS D. S., SCOTT E., O'REILLY K. T. C-PHYCOCYANIN: MINIMUM MOLECULAR WEIGHT. Science. 1964 Sep 4;145(3636):1054–1056. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3636.1054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batterton J. C., Jr, Van Baalen C. Growth responses of blue-green algae to sodium chloride concentration. Arch Mikrobiol. 1971;76(2):151–165. doi: 10.1007/BF00411789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berns D. S. Immunochemistry of biliproteins. Plant Physiol. 1967 Nov;42(11):1569–1586. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.11.1569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berns D. S., Morgenstern A. Two denaturant effects of guanidine salts on the protein C-phycocyanin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Mar 11;123(3):640–642. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90185-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berns D. S., Scott E. Protein aggregation in a thermophilic protein. Phycocyanin from Synechococcus lividus. Biochemistry. 1966 May;5(5):1528–1533. doi: 10.1021/bi00869a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHEN R. F., BOWMAN R. L. FLUORESCENCE POLARIZATION: MEASUREMENT WITH ULTRAVIOLET-POLARIZING FILTERS IN A SPECTROPHOTOFLUOROMETER. Science. 1965 Feb 12;147(3659):729–732. doi: 10.1126/science.147.3659.729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUILLARD R. R., RYTHER J. H. Studies of marine planktonic diatoms. I. Cyclotella nana Hustedt, and Detonula confervacea (cleve) Gran. Can J Microbiol. 1962 Apr;8:229–239. doi: 10.1139/m62-029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gantt E., Conti S. F. Phycobiliprotein localization in algae. Brookhaven Symp Biol. 1966;19:393–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLMES P. K., HALVORSON H. O. PROPERTIES OF A PURIFIED HALOPHILIC MALIC DEHYDROGENASE. J Bacteriol. 1965 Aug;90:316–326. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.2.316-326.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLMES P. K., HALVORSON H. O. PURIFICATION OF A SALT-REQUIRING ENZYME FROM AN OBLIGATELY HALOPHILIC BACTERIUM. J Bacteriol. 1965 Aug;90:312–315. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.2.312-315.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haglund H. Isoelectric focusing in pH gradients--a technique for fractionation and characterization of ampholytes. Methods Biochem Anal. 1971;19:1–104. doi: 10.1002/9780470110386.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilani A., Berns D. S. The effect of ferric ion on phycocyanin fluorescence. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Dec 17;45(6):1423–1430. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90179-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAUZMANN W. Some factors in the interpretation of protein denaturation. Adv Protein Chem. 1959;14:1–63. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60608-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao O., Berns D. S., MacColl R. C-phycocyanin monomer molecular weight. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Apr 30;19(4):595–599. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01353.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanyi J. K., Stevenson J. Studies of the electron transport chain of extremely halophilic bacteria. IV. Role of hydrophobic forces in the structure of menadione reductase. J Biol Chem. 1970 Aug 25;245(16):4074–4080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. J., Berns D. S. Protein aggregation. Studies of larger aggregates of C-phycocyanin. Biochem J. 1968 Dec;110(3):457–464. doi: 10.1042/bj1100457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. J., Berns D. S. Protein aggregation. The effect of deuterium oxide on large protein aggregates of C-phycocyanin. Biochem J. 1968 Dec;110(3):465–470. doi: 10.1042/bj1100465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman M. M., Lanyi J. K. Threonine deaminase from extremely halophilic bacteria. Cooperative substrate kinetics and salt dependence. Biochemistry. 1972 Jan 18;11(2):211–216. doi: 10.1021/bi00752a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu T. Y., Chang Y. H. Hydrolysis of proteins with p-toluenesulfonic acid. Determination of tryptophan. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 10;246(9):2842–2848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacColl R., Berns D. S., Koven N. L. Effect of salts on C-phycocyanin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Oct;146(2):477–482. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90151-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacColl R., Lee J. J., Berns D. S. Protein aggregation in C-phycocyanin. Studies at very low concentrations with the photoelectric scanner of the ultracentrifuge. Biochem J. 1971 May;122(4):421–426. doi: 10.1042/bj1220421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neufeld G. J., Riggs A. F. Aggregation properties of C-Phycocyanin from Anacystis nidulans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 May;181(1):234–243. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(69)90246-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reistad R. On the composition and nature of the bulk protein of extremely halophilic bacteria. Arch Mikrobiol. 1970;71(4):353–360. doi: 10.1007/BF00417131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHIBATA K., BENSON A. A., CALVIN M. The absorption spectra of suspensions of living micro-organisms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1954 Dec;15(4):461–470. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(54)90002-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott E., Berns D. S. Completely deuterated proteins. 3. Deuteration effects on protein-protein interaction in phycocyanin. Biochemistry. 1967 May;6(5):1327–1334. doi: 10.1021/bi00857a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott E., Berns D. S. Protein-protein interaction. The phycocyanin system. Biochemistry. 1965 Dec;4(12):2597–2606. doi: 10.1021/bi00888a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teale F. W., Dale R. E. Isolation and spectral characterization of phycobiliproteins. Biochem J. 1970 Jan;116(2):161–169. doi: 10.1042/bj1160161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]