Abstract
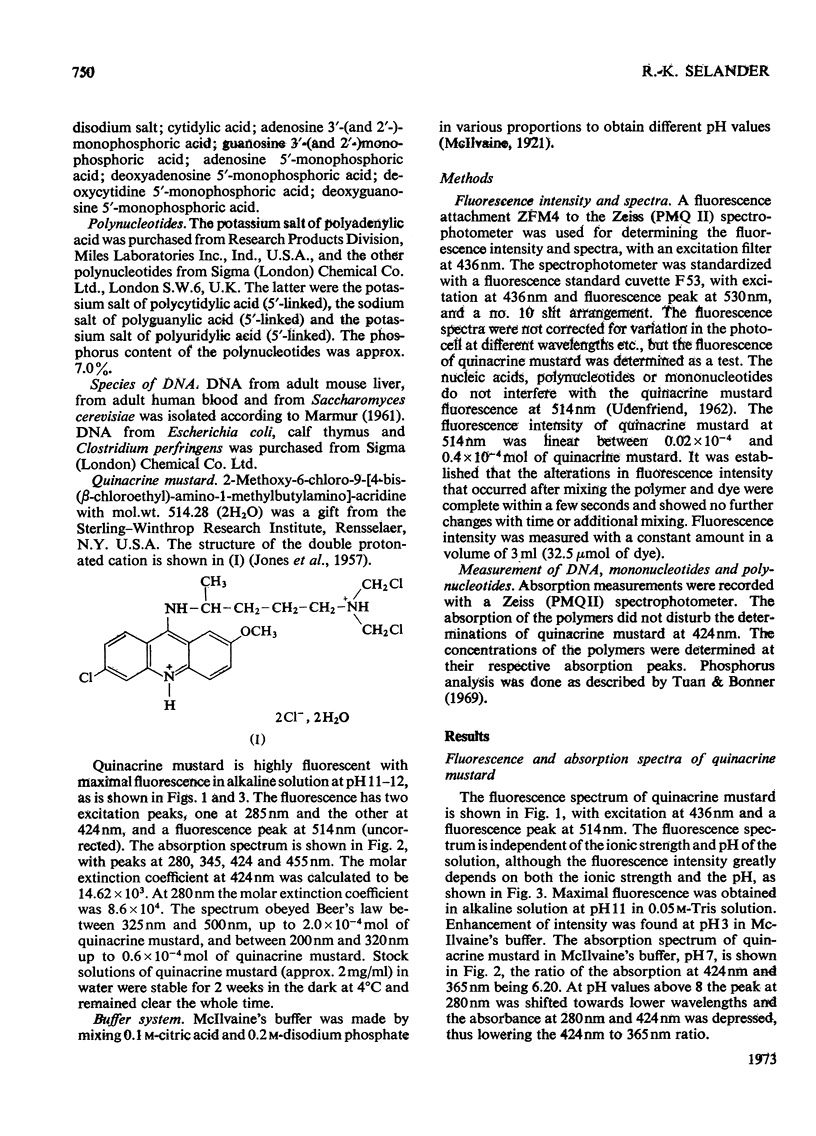
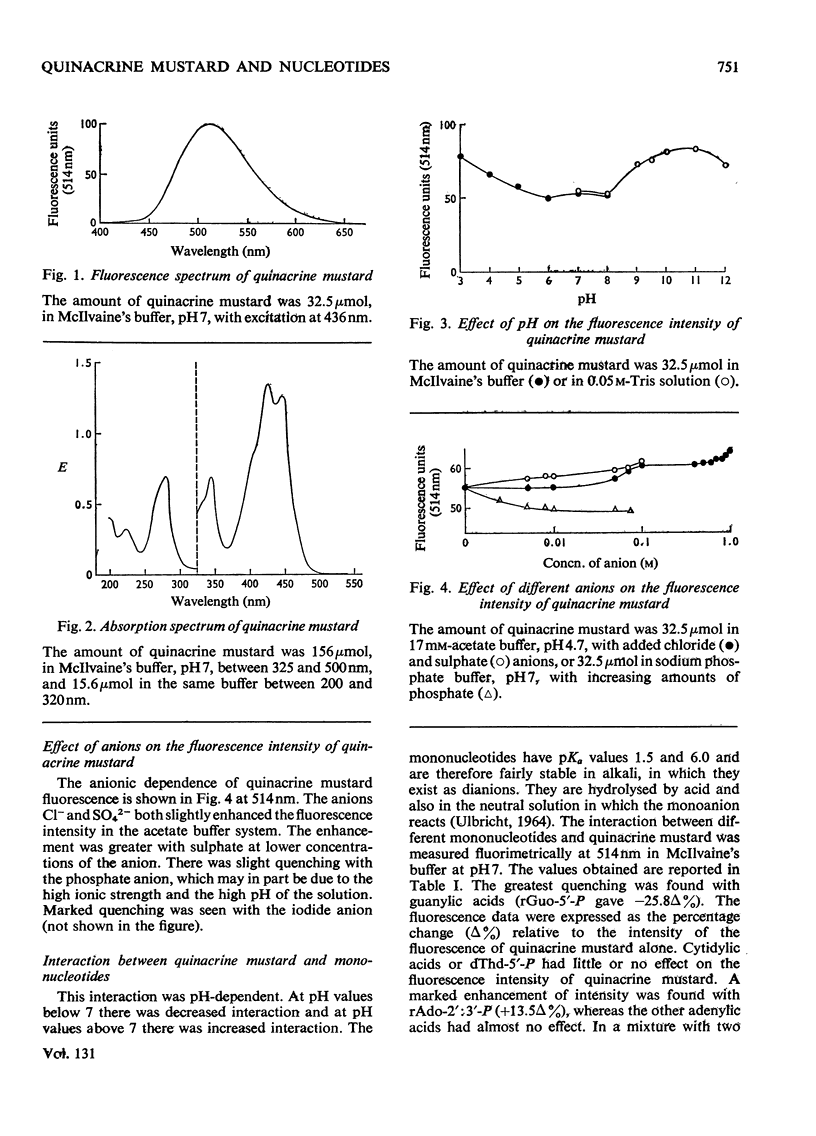
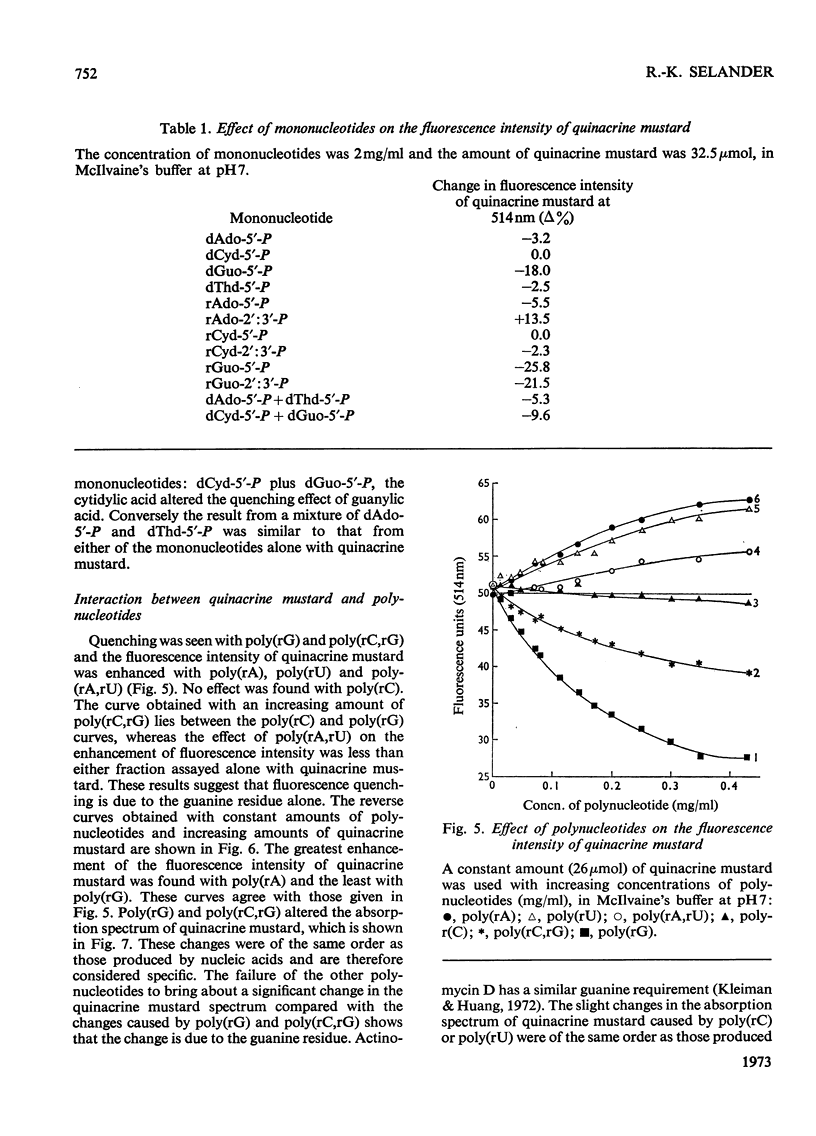
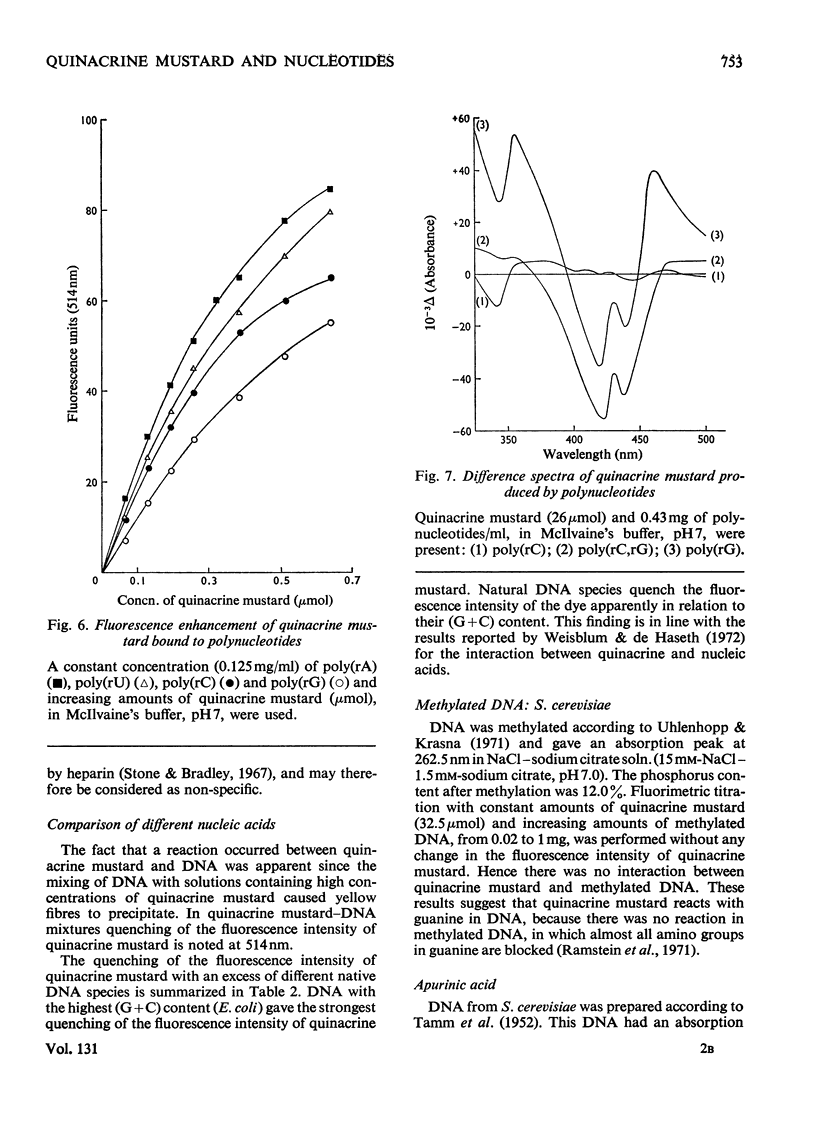
1. The interaction between quinacrine mustard and mononucleotides and polynucleotides was investigated by fluorimetry and absorbance spectrophotometry. 2. The fluorescence spectrum of quinacrine mustard is independent of the ionic strength and pH. The dependence of the quinacrine mustard fluorescence intensity on ionic strength, pH and anions is described. 3. The fluorescence intensity of quinacrine mustard was enhanced with the mononucleotide adenylic acid and polynucleotides such as poly(rA), poly(rU) and poly(rA,rU). 4. Quenching of the fluorescence intensity of quinacrine mustard occurred with the mononucleotide guanylic acid and with poly(rG) and poly(rC,rG). 5. The mononucleotide cytidylic acid or poly(rC) showed no effect on the fluorescence intensity of quinacrine mustard. 6. The interaction between the dye and native DNA species was also dependent on the presence of base-specific binding sites in the DNA. The higher the (G+C) content was in the native DNA tested the higher was the quenching effect on the fluorescence intensity of quinacrine mustard. 7. No interaction was found between the dye and methylated DNA. The binding between quinacrine mustard and apurinic DNA was confirmed to be in the phosphate groups of the purines.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azzi A., Fabbro A., Santato M., Gherardini P. L. Energy transduction in mitochondrial fragments. Interaction of the membrane with acridine dyes. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Aug 16;21(3):404–410. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01484.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake A., Peacocke A. R. The interaction of aminocridines with nucleic acids. Biopolymers. 1968;6(9):1225–1253. doi: 10.1002/bip.1968.360060902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brookes P., Lawley P. D. The reaction of mono- and di-functional alkylating agents with nucleic acids. Biochem J. 1961 Sep;80(3):496–503. doi: 10.1042/bj0800496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN S. N., YIELDING K. L. SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC STUDIES OF THE INTERACTION OF CHLOROQUINE WITH DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jul;240:3123–3131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspersson T., Zech L., Modest E. J., Foley G. E., Wagh U., Simonsson E. Chemical differentiation with fluorescent alkylating agents in Vicia faba metaphase chromosomes. Exp Cell Res. 1969 Nov;58(1):128–140. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(69)90123-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspersson T., Zech L., Modest E. J., Foley G. E., Wagh U., Simonsson E. DNA-binding fluorochromes for the study of the organization of the metaphase nucleus. Exp Cell Res. 1969 Nov;58(1):141–152. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(69)90124-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison J. R., Barr H. J. Chromosome variation within Drosophila simulans detected by quinacrine staining. Genetics. 1971 Sep;69(1):119–122. doi: 10.1093/genetics/69.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleiman L., Huang R. C. Reconstitution of chromatin. The sequential binding of histones to DNA in the presence of salt and urea. J Mol Biol. 1972 Feb 28;64(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90317-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LePecq J. B., Paoletti C. A fluorescent complex between ethidium bromide and nucleic acids. Physical-chemical characterization. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jul 14;27(1):87–106. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90353-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löber G., Achtert G. On the complex formation of acridine dyes with DNA. VII. Dependence of the binding on the dye structure. Biopolymers. 1969;8(5):595–608. doi: 10.1002/bip.1969.360080504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien R. L., Olenick J. G., Hahn F. E. Reactions of quinine, chloroquine, and quinacrine with DNA and their effects on the DNA and RNA polymerase reactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jun;55(6):1511–1517. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.6.1511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramstein J., Héléne C., Leng M. A study of chemically methylated deoxyribonucleic acid. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Jul 15;21(1):125–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01448.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone A. L., Bradley D. F. Aggregation of cationic dyes on acid polysaccharides. I. Spectrophotometric titration with acridine orange and other metachromatic dyes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Oct 9;148(1):172–192. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(67)90293-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAMM C., HODES M. E., CHARGAFF E. The formation apurinic acid from the desoxyribonucleic acid of calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1952 Mar;195(1):49–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomes J. C., Weill G., Daune M. Fluorescence of proflavine--DNA complexes: heterogeneity of binding sites. Biopolymers. 1969;8(5):647–669. doi: 10.1002/bip.1969.360080507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuan D. Y., Bonner J. Optical absorbance and optical rotatory dispersion studies on calf thymus nucleohistone. J Mol Biol. 1969 Oct 14;45(1):59–76. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90209-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlenhopp E. L., Krasna A. I. Alterations in the structure of deoxyribonucleic acid on chemical methylation. Biochemistry. 1971 Aug 17;10(17):3290–3295. doi: 10.1021/bi00793a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward D. C., Reich E., Goldberg I. H. Base specificity in the interaction of polynucleotides with antibiotic drugs. Science. 1965 Sep 10;149(3689):1259–1263. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3689.1259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisblum B., De Haseth P. L. Quinacrine, a chromosome stain specific for deoxyadenylate-deoxythymidylaterich regions in DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):629–632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


