Abstract
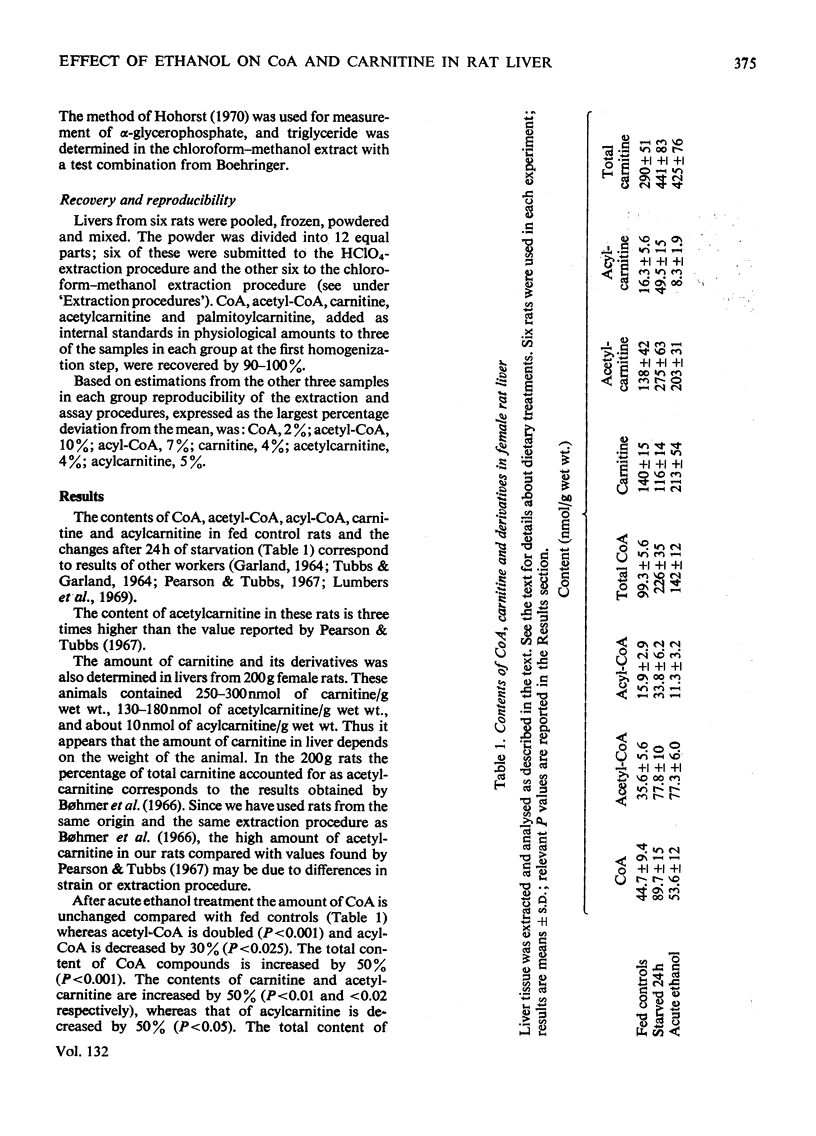
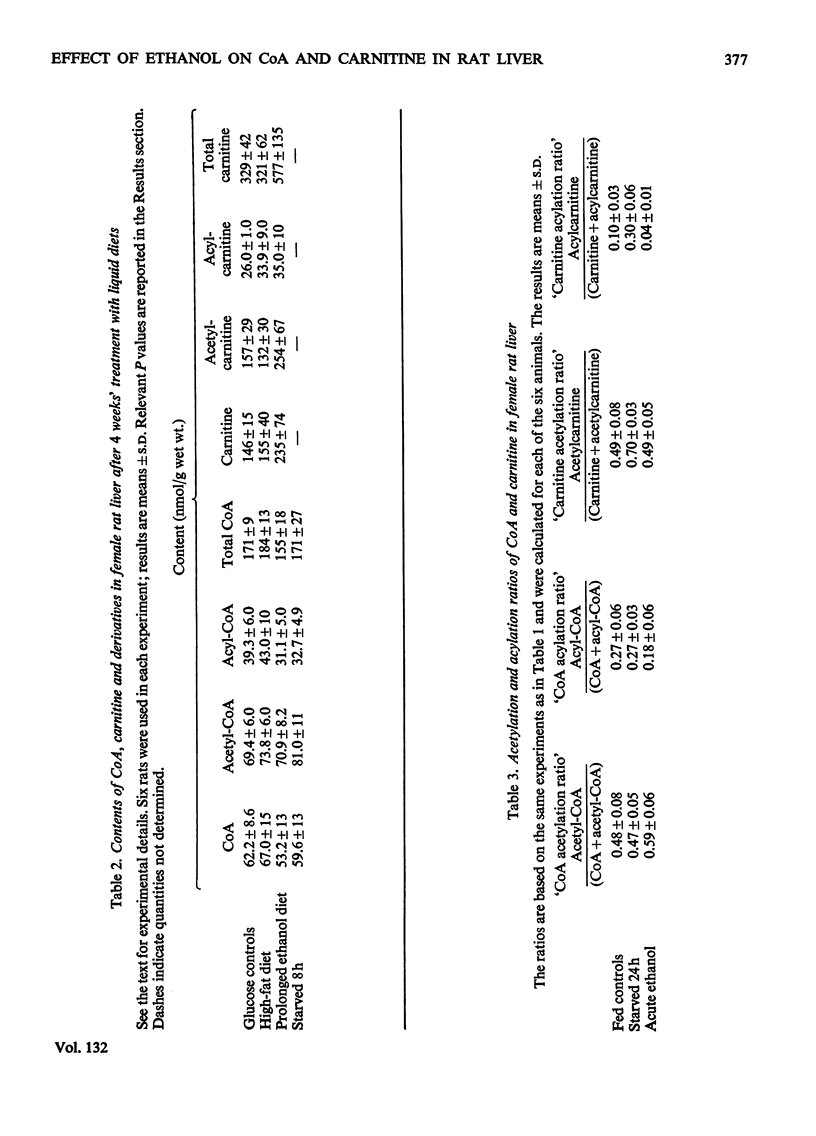
1. CoA, acetyl-CoA, long-chain acyl-CoA, carnitine, acetylcarnitine and long-chain acylcarnitine were measured in rat liver under various conditions. 2. Starvation caused an increase in the contents of these intermediates, except that of carnitine. 3. A single dose of ethanol had no effect on CoA content, whereas those of acetyl-CoA, acetylcarnitine and carnitine were increased and those of long-chain acyl-CoA and acylcarnitine were decreased. 4. Four weeks' adaptation to ethanol consumption did not change the effect of ethanol administration on these metabolites. 5. It is suggested that ethanol directly increases hepatic fatty acid synthesis and esterification. It is also suggested that this change is reversible and limited to the period of ethanol oxidation. 6. It is demonstrated that ethanol-induced triglyceride accumulation is not related to carnitine deficiency.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bode C., Stähler E., Kono H., Goebell H. Effects of ethanol on free coenzyme A, free carnitine and their fatty acid esters in rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Sep 8;210(3):448–455. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(70)90041-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohmer T. Tissue levels of activated fatty acids (acylcarnitines) and the regulation of fatty acid metabo.ism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Oct 2;144(2):259–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breen K. J., Shaw J., Levinson J. D., Schenker S. The acute effect of alcohol on hepatic coenzyme A and acetyl CoA concentrations. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Dec;138(3):1096–1100. doi: 10.3181/00379727-138-36058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bressler R., Wittels B. The effect of diphtheria toxin on carnitine metabolism in the heart. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jun 15;104(1):39–45. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90217-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckel W., Eggerer H. Zur optischen Bestimmung von Citrat-Synthase und von Acetyl-Coenzym A. Biochem Z. 1965 Nov 5;343(1):29–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corredor C., Mansbach C., Bressler R. Carnitine depletion in the choline-deficient state. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Oct 2;144(2):366–374. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(67)90165-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsander O. A., Lindros K. O. Influence of ethanol on the acetyl-coenzyme A level of intact rat liver. Acta Chem Scand. 1967;21(9):2568–2568. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.21-2568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho R. J., Meng H. C. A simple and ultrasensitive method for determination of free fatty acid by radiochemical assay. Anal Biochem. 1969 Oct 1;31(1):426–436. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90284-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieber C. S., DeCarli L. M. Quantitative relationship between amount of dietary fat and severity of alcoholic fatty liver. Am J Clin Nutr. 1970 Apr;23(4):474–478. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/23.4.474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieber C. S., Lefèvre A., Spritz N., Feinman L., DeCarli L. M. Difference in hepatic metabolism of long- and medium-chain fatty acids: the role of fatty acid chain length in the production of the alcoholic fatty liver. J Clin Invest. 1967 Sep;46(9):1451–1460. doi: 10.1172/JCI105637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieber C. S., Spritz N., DeCarli L. M. Role of dietary, adipose, and endogenously synthesized fatty acids in the pathogenesis of the alcoholic fatty liver. J Clin Invest. 1966 Jan;45(1):51–62. doi: 10.1172/JCI105323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumbers J., Threlfall C. J., Stoner H. B. Measurement of acetyl coenzyme A in rat liver. Anal Biochem. 1969 Oct 1;31(1):21–32. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90237-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORUM K. R. PALMITYL-COA:CARNITINE PALMITYLTRANSFERASE. PURIFICATION FROM CALF-LIVER MITOCHONDRIA AND SOME PROPERTIES OF THE ENZYME. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jul 8;89:95–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson D. J., Tubbs P. K. Carnitine and derivatives in rat tissues. Biochem J. 1967 Dec;105(3):953–963. doi: 10.1042/bj1050953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tubbs P. K., Garland P. B. Variations in tissue contents of coenzyme A thio esters and possible metabolic implications. Biochem J. 1964 Dec;93(3):550–557. doi: 10.1042/bj0930550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIELAND O., WEISS L. Increase in liver acetyl-coenzyme A during ketosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 Feb 18;10:333–339. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90534-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson J. R., Scholz R., Browning E. T., Thurman R. G., Fukami M. H. Metabolic effects of ethanol in perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1969 Sep 25;244(18):5044–5054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittels B., Spann J. F., Jr Defective lipid metabolism in the failing heart. J Clin Invest. 1968 Aug;47(8):1787–1794. doi: 10.1172/JCI105868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakim D. Effect of ethanol on hepatic acyl-coenzyme A metabolism. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1965 Aug;111(2):253–256. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(65)90185-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


