Abstract
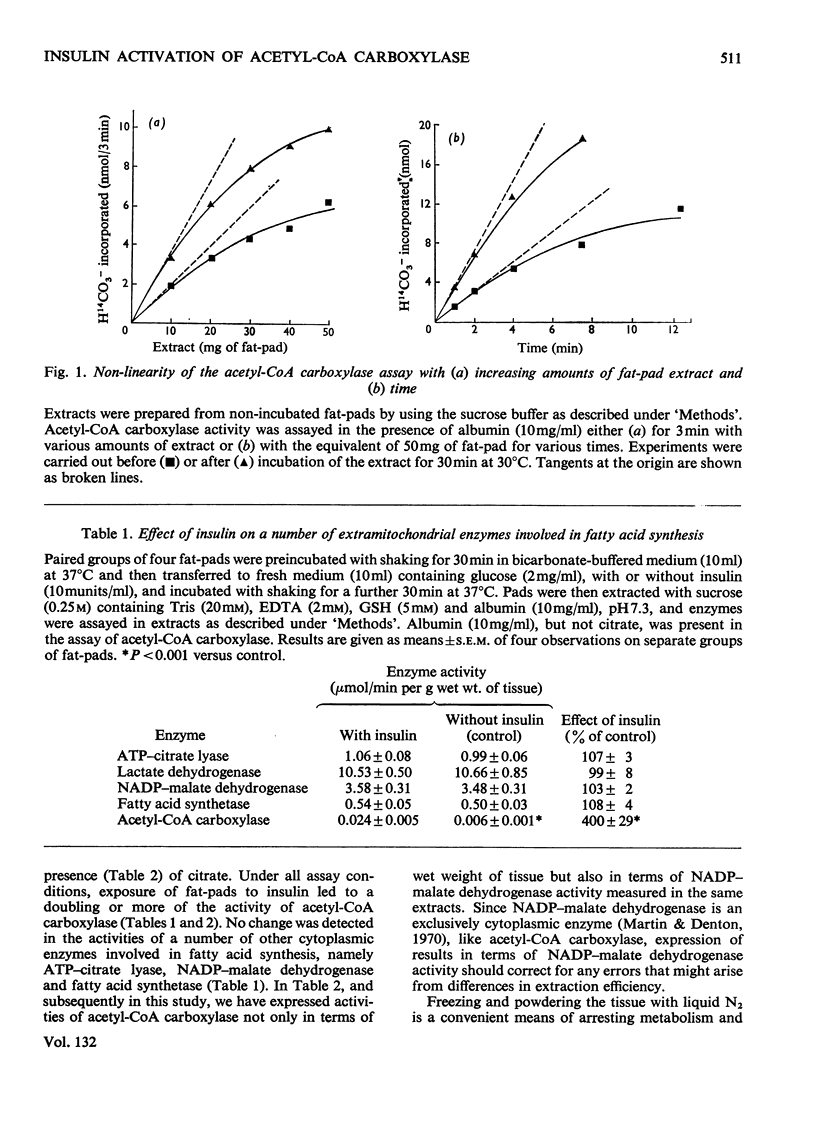
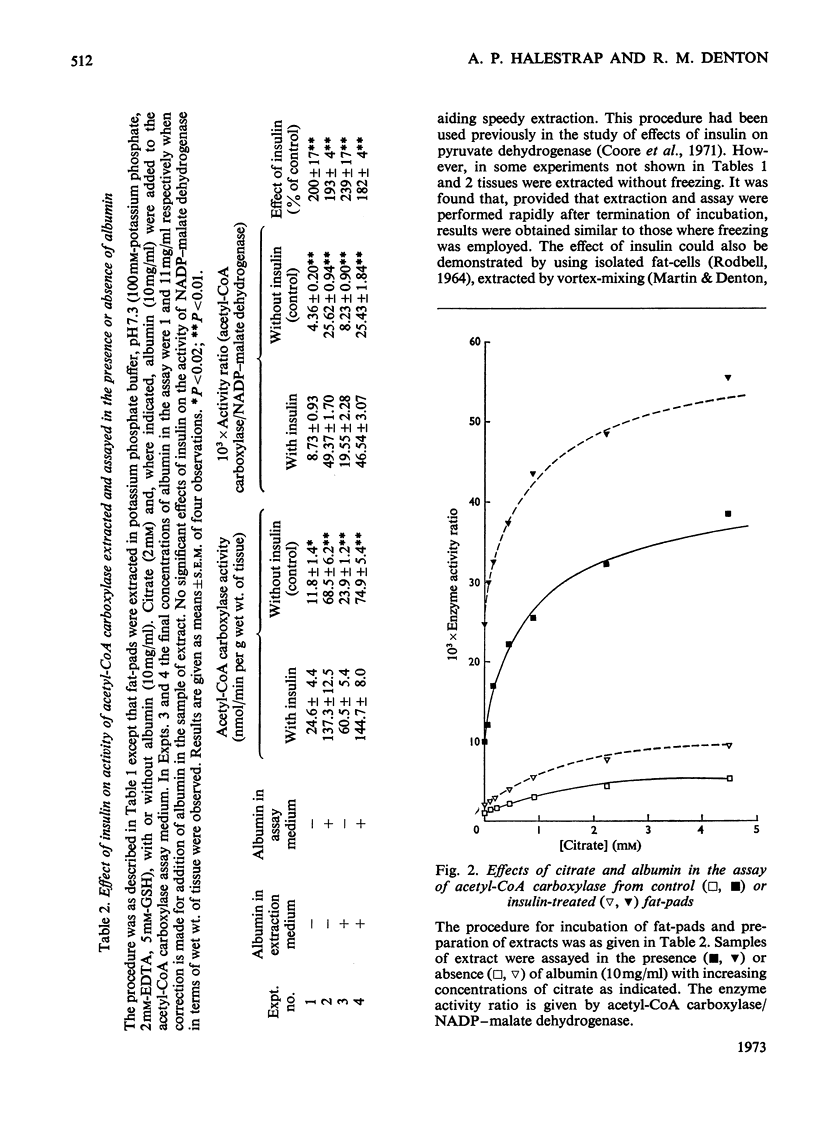
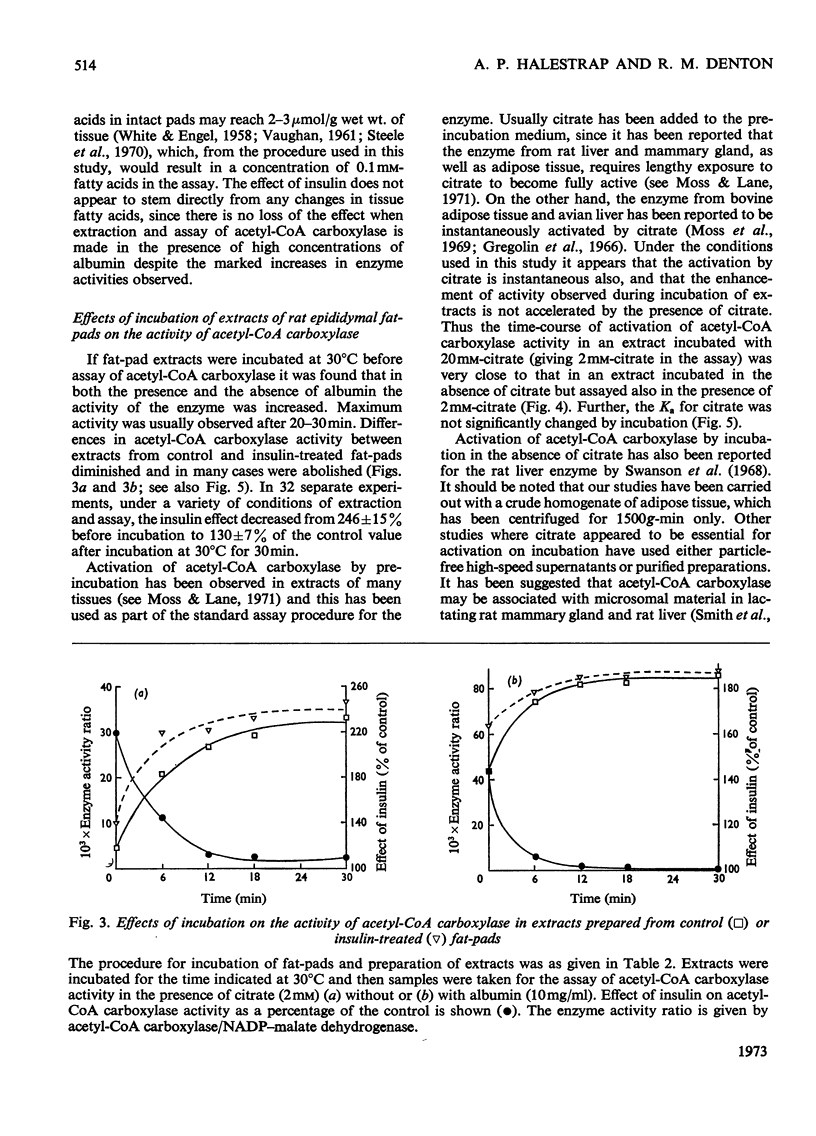
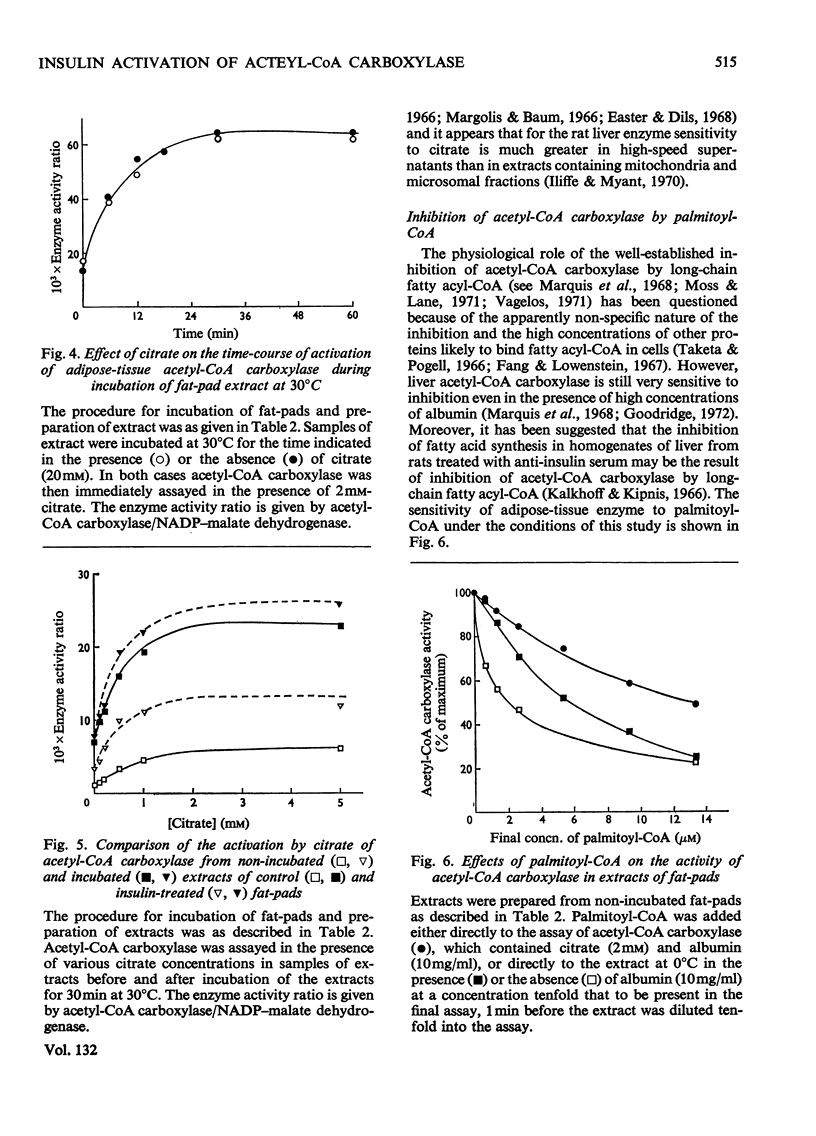
Rat epididymal fat-pads were incubated for 30min with glucose (2mg/ml) in the presence or absence of insulin. A twofold or greater increase in acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity was observed in extracts from insulin-treated tissue provided that assays were performed rapidly after extraction. This effect of insulin was evident whether or not extracts were prepared with albumin, and was not noticeably diminished by the presence of citrate or albumin or both in the assay. Incubation of extracts before assay led to activation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase and a marked diminution in the insulin effect. The enzyme in extracts was very sensitive to reversible inhibition by palmitoyl-CoA even in the presence of albumin (10mg/ml); inhibition persisted on dilution of enzyme and inhibitor. It is suggested that the observed activation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase by insulin may reflect changes in enzyme activity in the fat-cell resulting from the reduction of long-chain fatty-acyl-CoA that occurs in the presence of insulin. Activation of the enzyme with loss of the insulin effect on incubation of the extracts may be due to the slow dissociation of long-chain fatty acyl-CoA from the enzyme.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CROFFORD O. B., RENOLD A. E. GLUCOSE UPTAKE BY INCUBATED RAT EPIDIDYMAL ADIPOSE TISSUE. RATE-LIMITING STEPS AND SITE OF INSULIN ACTION. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jan;240:14–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coore H. G., Denton R. M., Martin B. R., Randle P. J. Regulation of adipose tissue pyruvate dehydrogenase by insulin and other hormones. Biochem J. 1971 Nov;125(1):115–127. doi: 10.1042/bj1250115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dakshinamurti K., Desjardins P. R. Acetyl-CoA carboxylase from rat adipose tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Mar 4;176(2):221–229. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(69)90181-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton R. M., Halperin M. L. The control of fatty acid and triglyceride synthesis in rat epididymal adipose tissue. Roles of coenzyme A derivatives, citrate and L-glycerol 3-phosphate. Biochem J. 1968 Nov;110(1):27–38. doi: 10.1042/bj1100027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easter D. J., Dils R. Fatty acid biosynthesis. IV. Properties of acetyl-CoA carboxylase in lactating-rabbit mammary gland. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jul 1;152(4):653–668. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(68)90112-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLATT J. P., BALL E. G. STUDIES ON THE METABOLISM OF ADIPOSE TISSUE. XV. AN EVALUATION OF THE MAJOR PATHWAYS OF GLUCOSE CATABOLISM AS INFLUENCED BY INSULIN AND EPINEPHRINE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Mar;239:675–685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang M., Lowenstein J. M. Citrate and the conversion of carbohydrate into fat. The regulation of fatty acid synthesis by rat liver extracts. Biochem J. 1967 Nov;105(2):803–811. doi: 10.1042/bj1050803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz I. B., Hsu M. P. Studies on the control of fatty acid synthesis. I. Stimulation by (+)-palmitylcarnitine of fatty acid synthesis in liver preparations from fed and fasted rats. J Biol Chem. 1967 Mar 10;242(5):865–872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregolin C., Ryder E., Kleinschmidt A. K., Warner R. C., Lane M. D. Molecular characteristics of liver acetyl CoA carboxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jul;56(1):148–155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.1.148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iliffe J., Myant N. B. The sensitivity of acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase to citrate stimulation in a homogenate of rat liver containing subcellular particles. Biochem J. 1970 Apr;117(2):385–395. doi: 10.1042/bj1170385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungas R. L. Effect of insulin on fatty acid ynthesis from pyruvate, lactage, or endogenous sources in adipose tissue: evidence for the hormonal regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase. Endocrinology. 1970 Jun;86(6):1368–1375. doi: 10.1210/endo-86-6-1368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalkhoff R. K., Kipnis D. M. Studies of the metabolic effects of acute insulin deficiency. I. Mechanism of impairment of hepatic fatty acid and protein synthesis. Diabetes. 1966 Jul;15(7):443–450. doi: 10.2337/diab.15.7.443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN D. B., VAGELOS P. R. The mechanism of tricarboxylic acid cycle regulation of fatty acid synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jun;237:1787–1792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majerus P. W., Kilburn E. Acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase. The roles of synthesis and degradation in regulation of enzyme levels in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 25;244(22):6254–6262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis S. A., Baum H. The association of acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase with the microsomal fraction of pigeon liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Jun;114(3):445–451. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90366-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquis N. R., Francesconi R. P., Villee C. A. A role for carnitine and long chain acylcarnitine in the regulation of lipogenesis. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1968;6:31–55. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(68)90006-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin B. R., Denton R. M. The intracellular localization of enzymes in white-adipose-tissue fat-cells and permeability properties of fat-cell mitochondria. Transfer of acetyl units and reducing power between mitochondria and cytoplasm. Biochem J. 1970 May;117(5):861–877. doi: 10.1042/bj1170861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Lane M. D. The biotin-dependent enzymes. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1971;35:321–442. doi: 10.1002/9780470122808.ch7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi S., Numa S. Purification of rat liver acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase and immunochemical studies on its synthesis and degradation. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Sep;16(1):161–173. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01068.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M. METABOLISM OF ISOLATED FAT CELLS. I. EFFECTS OF HORMONES ON GLUCOSE METABOLISM AND LIPOLYSIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saggerson E. D., Greenbaum A. L. The regulation of triglyceride synthesis and fatty acid synthesis in rat epididymal adipose tissue. Biochem J. 1970 Sep;119(2):193–219. doi: 10.1042/bj1190193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S., Easter D. J., Dils R. Fatty acid biosynthesis. 3. Intracellular site of enzymes in lactating-rabbit mammary gland. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Dec 7;125(3):445–455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele A. A., Brown J. D., Stone D. B. Antilipolytic effect of porcine proinsulin. Diabetes. 1970 Feb;19(2):91–97. doi: 10.2337/diab.19.2.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson R. F., Curry W. M., Anker H. S. The activation of rat liver acetyl-CoA carboxylase by incubation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jun 4;159(2):390–397. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(68)90087-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taketa K., Pogell B. M. The effect of palmityl coenzyme A on glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase and other enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1966 Feb 10;241(3):720–726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE J. E., ENGEL F. L. Lipolytic action of corticotropin on rat adipose tissue in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1958 Nov;37(11):1556–1563. doi: 10.1172/JCI103748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L., Löffler G., Schirmann A., Wieland O. Control of pyruvate dehydrogenase interconversion in adipose tissue by insulin. FEBS Lett. 1971 Jun 24;15(3):229–231. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80318-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


