Abstract
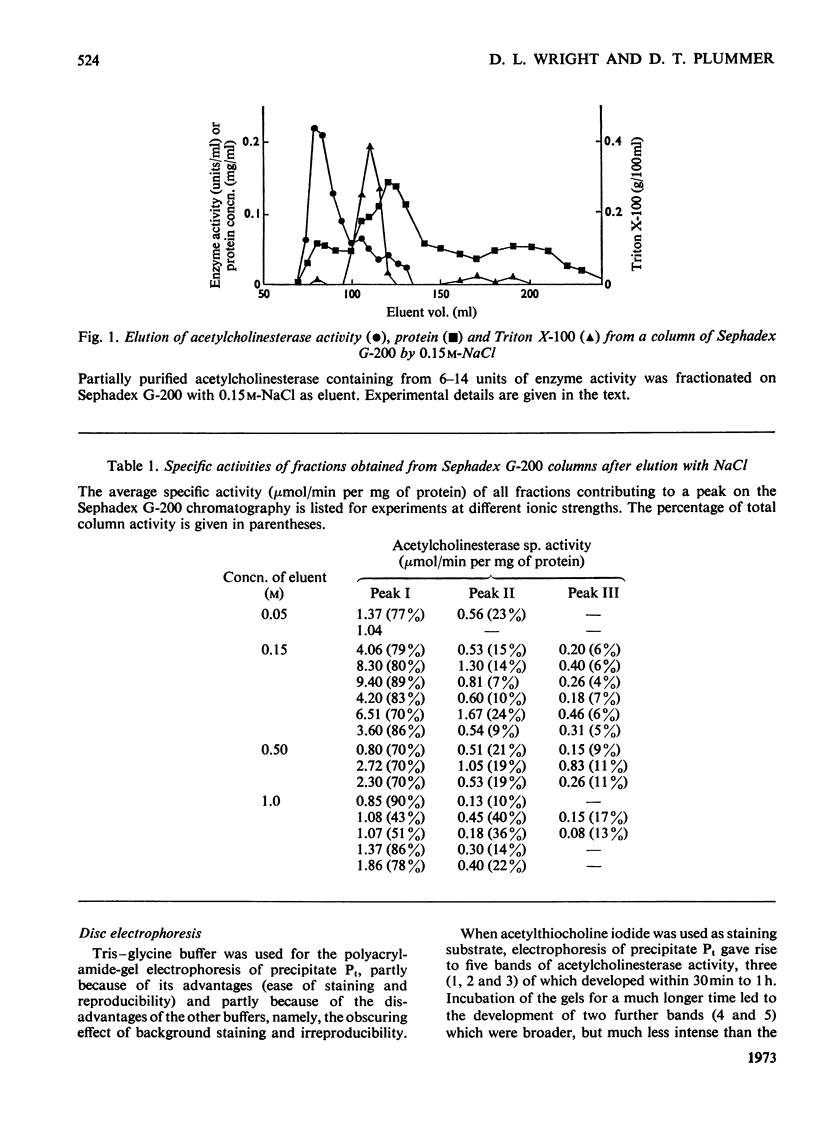
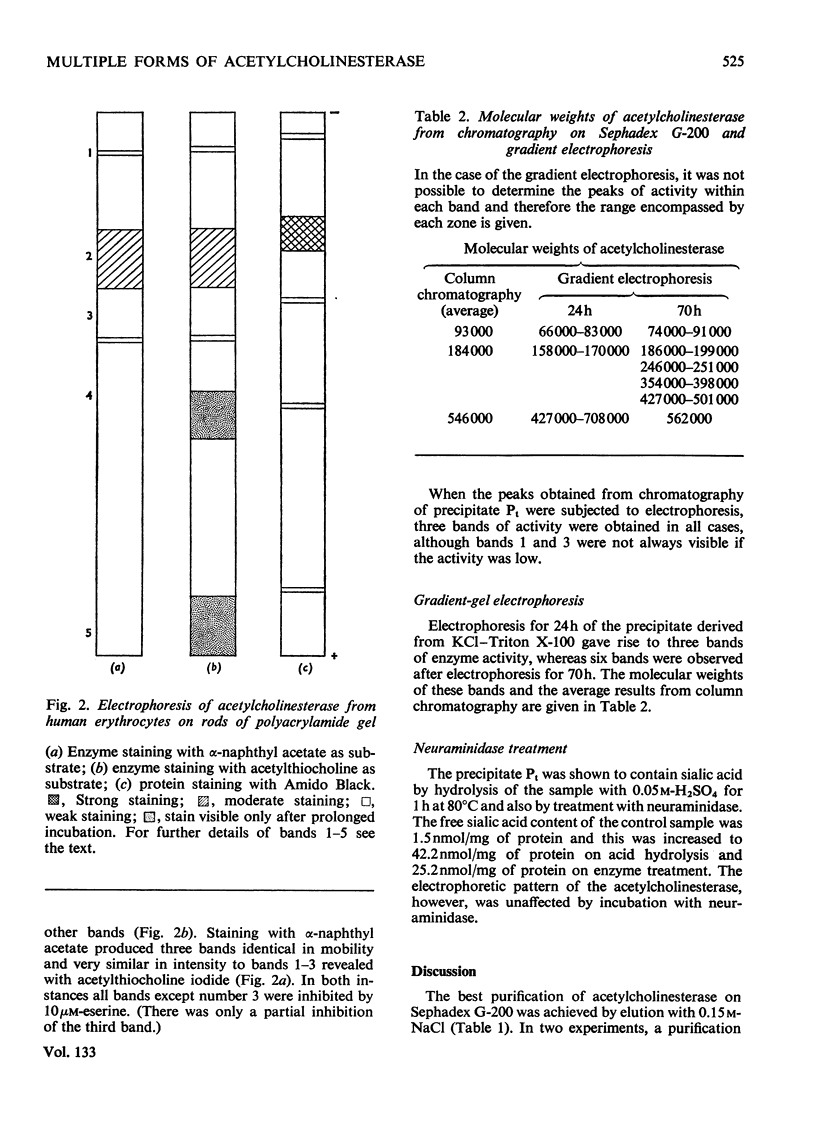
1. Acetylcholinesterase from human erythrocytes was solubilized with Triton X-100 in strong salt solution and partially purified by (NH4)2SO4 fractionation. This preparation showed three main bands of enzyme activity after electrophoresis on polyacrylamide gel and incubation with either α-naphthyl acetate or acetylthiocholine as enzyme substrate. Two of the multiple forms were completely inhibited by 10μm-eserine and one only partially. Treatment with neuraminidase had no effect on the electrophoretic pattern; therefore sialic acid does not appear to determine or affect the ratios of the acetylcholinesterase multiple forms, unlike those of the serum cholinesterase. 2. Chromatography of the preparation on Sephadex G-200 revealed one major peak of enzyme activity and a suggestion of two minor zones of mol.wt. 546000, 184000 and 93000 (i.e. in the proportion 6:2:1). The main peak was almost completely separated from the Triton X-100 and the overall purification was about 600-fold. Further attempts to purify the enzyme by absorption on calcium phosphate gels were unsuccessful. 3. Electrophoresis of the enzyme preparation on a polyacrylamide gradient for 24h revealed three main bands that corresponded to the three values for molecular weights obtained by column chromatography. After 70h of electrophoresis a further three zones of activity developed making six molecular entities, the molecular weights of which were simple multiples of a monomer, thus resembling the cholinesterase found in serum.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLEN J. M., GOCKERMAN J. ELECTROPHORETIC SEPARATION OF MULTIPLE FORMS OF PARTICLE ASSOCIATED ACID PHOSPHATASE. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:616–633. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14230.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. The gel-filtration behaviour of proteins related to their molecular weights over a wide range. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):595–606. doi: 10.1042/bj0960595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERNSOHN J., BARRON K. D., HESS A. R. Multiple nature of acetylcholinesterase in nerve tissue. Nature. 1962 Jul 21;195:285–286. doi: 10.1038/195285a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellhorn M. B., Blumenfeld O. O., Gallop P. M. Acetylcholinesterase of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Apr 24;39(2):267–273. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90788-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froede H. C., Wilson I. B. On the subunit structure of acetylcholinesterase. Isr J Med Sci. 1970 Mar-Apr;6(2):179–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaffney P. J., Jr Human serum cholinesterase. I. Partial purification andnature of the heterogeneity of this system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jun 23;207(3):465–476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOBSEN C. F., LEONIS J., LINDERSTROM-LANG K., OTTESEN M. The pH-stat and its use in biochemistry. Methods Biochem Anal. 1957;4:171–210. doi: 10.1002/9780470110201.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juul P. Human plasma cholinesterase isoenzymes. Clin Chim Acta. 1968 Feb;19(2):205–213. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(68)90327-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaMotta R. V., Woronick C. L. Molecular heterogeneity of human serum cholinesterase. Clin Chem. 1971 Mar;17(3):135–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamotta R. V., McComb R. B., Noll C. R., Jr, Wetstone H. J., Reinfrank R. F. Multiple forms of serum cholinesterase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Mar 20;124(1):299–305. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90331-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leuzinger W., Goldberg M., Cauvin E. Molecular properties of acetylcholinesterase. J Mol Biol. 1969 Mar 14;40(2):217–225. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90470-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis P. R., Shute C. C. The distribution of cholinesterase in cholinergic neurons demonstrated with the electron microscope. J Cell Sci. 1966 Sep;1(3):381–390. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1.3.381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis J., Kenrick K. G. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in a continuous molecular sieve gradient. Anal Biochem. 1968 Oct 24;25(1):347–362. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90109-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maynard E. A. Electrophoretic studies of cholinesterases in brain and muscle of the developing chicken. J Exp Zool. 1966 Apr;161(3):319–335. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401610303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar David B., Grafius Melba A. The subunit molecular weight of acetylcholinesterase. FEBS Lett. 1970 Dec 23;12(1):61–64. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80596-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAUL J., FOTTRELL P. Tissue-specific and species-specific esterases. Biochem J. 1961 Feb;78:418–424. doi: 10.1042/bj0780418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright D. L., Plummer D. T. Solubilization of acetylcholinesterase from human erythrocytes by Triton X-100 in potassium chloride solution. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Feb 28;261(2):398–401. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(72)90064-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


