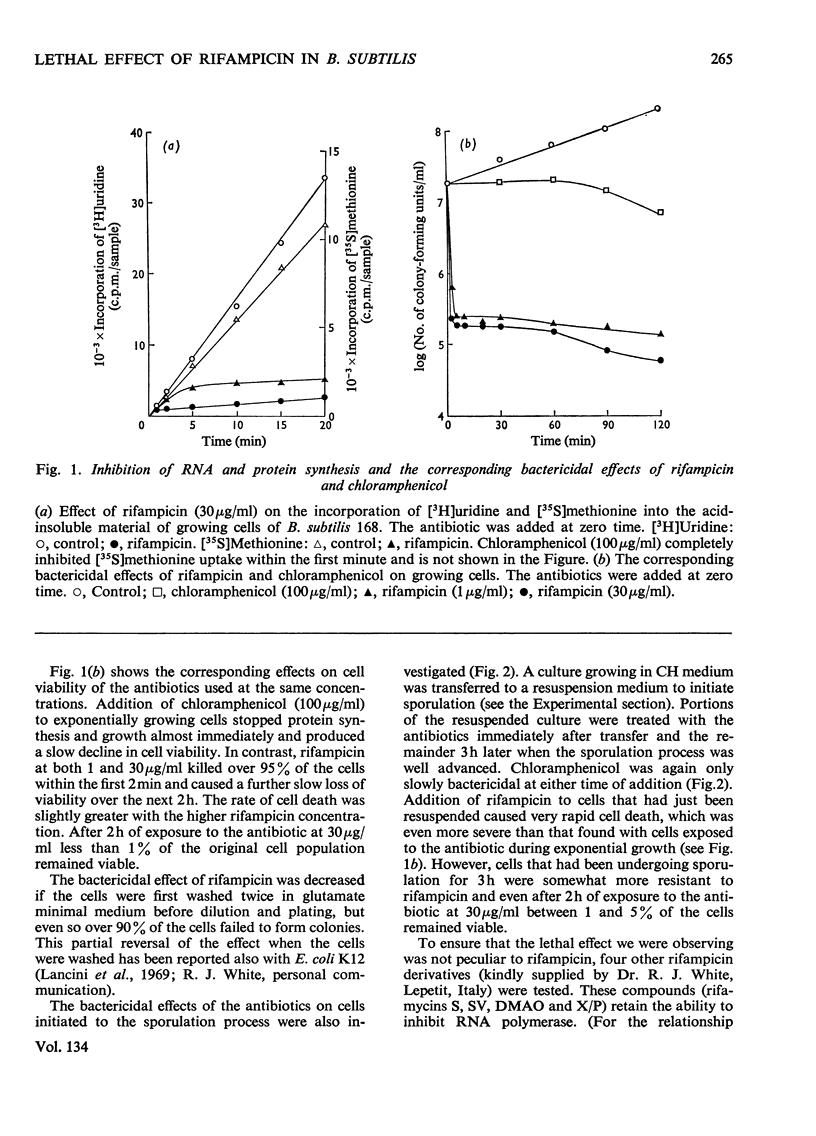
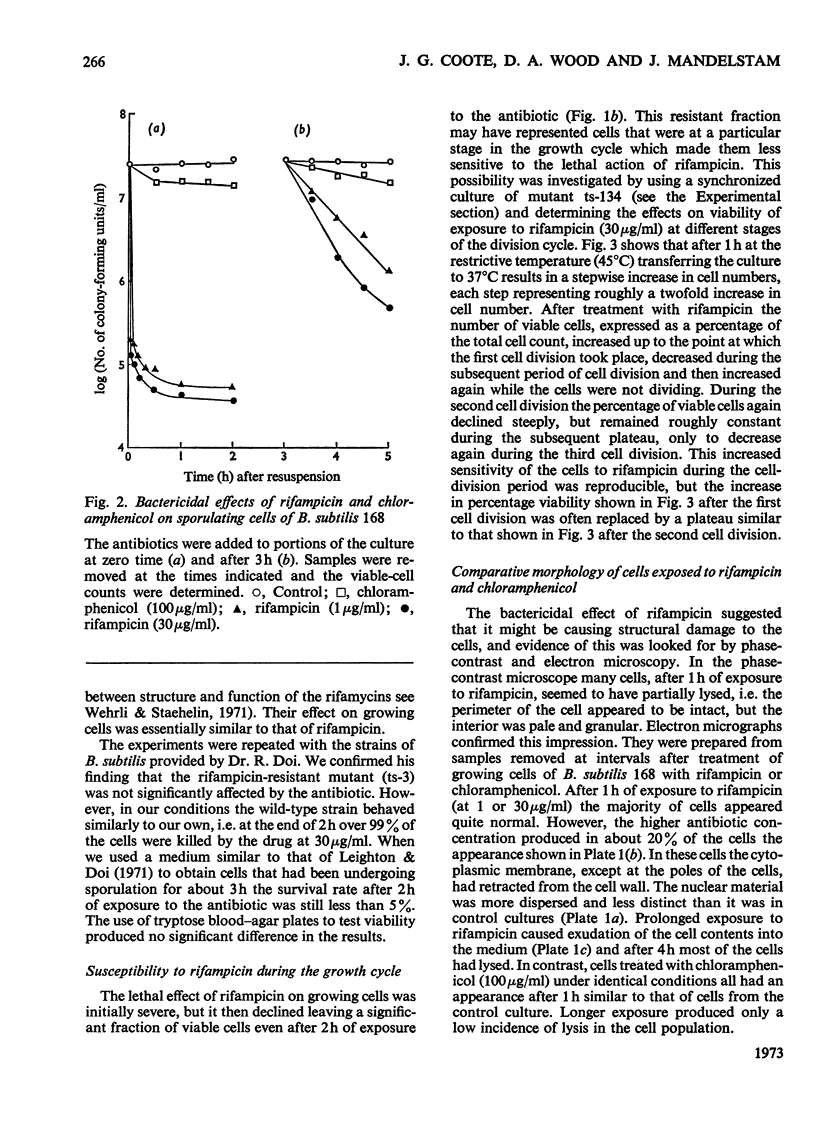
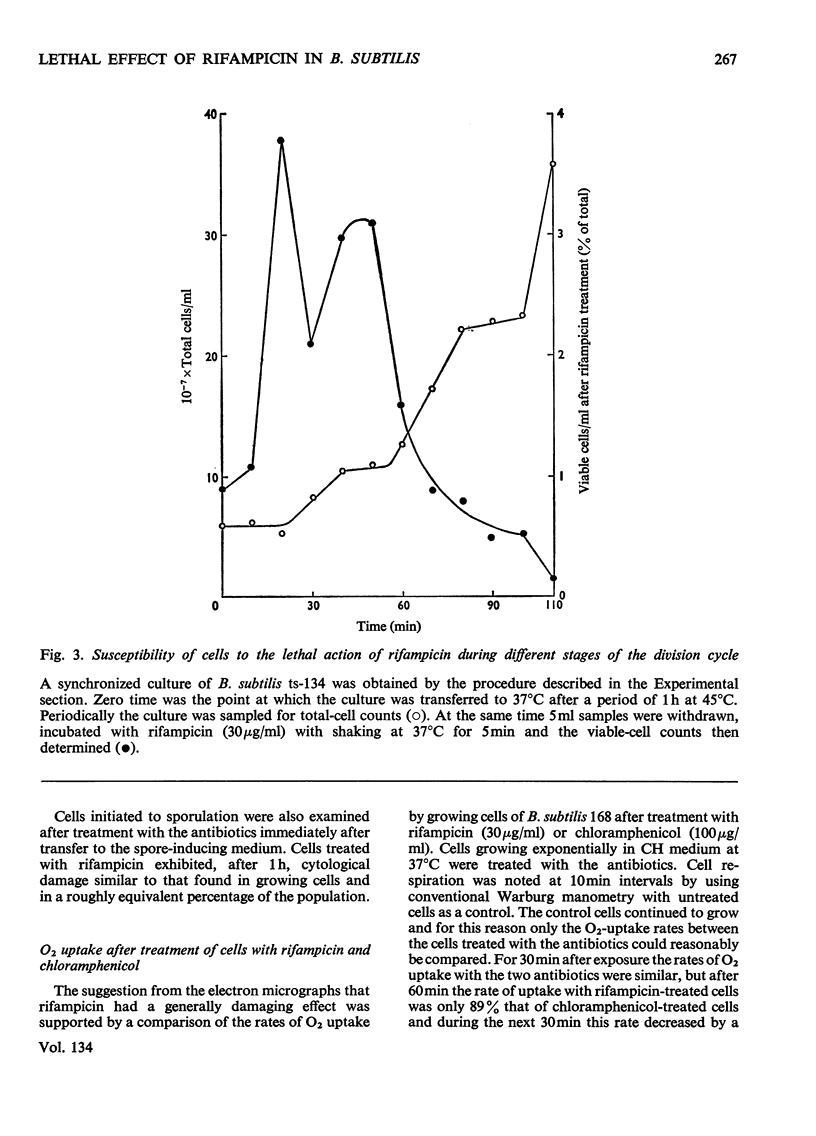
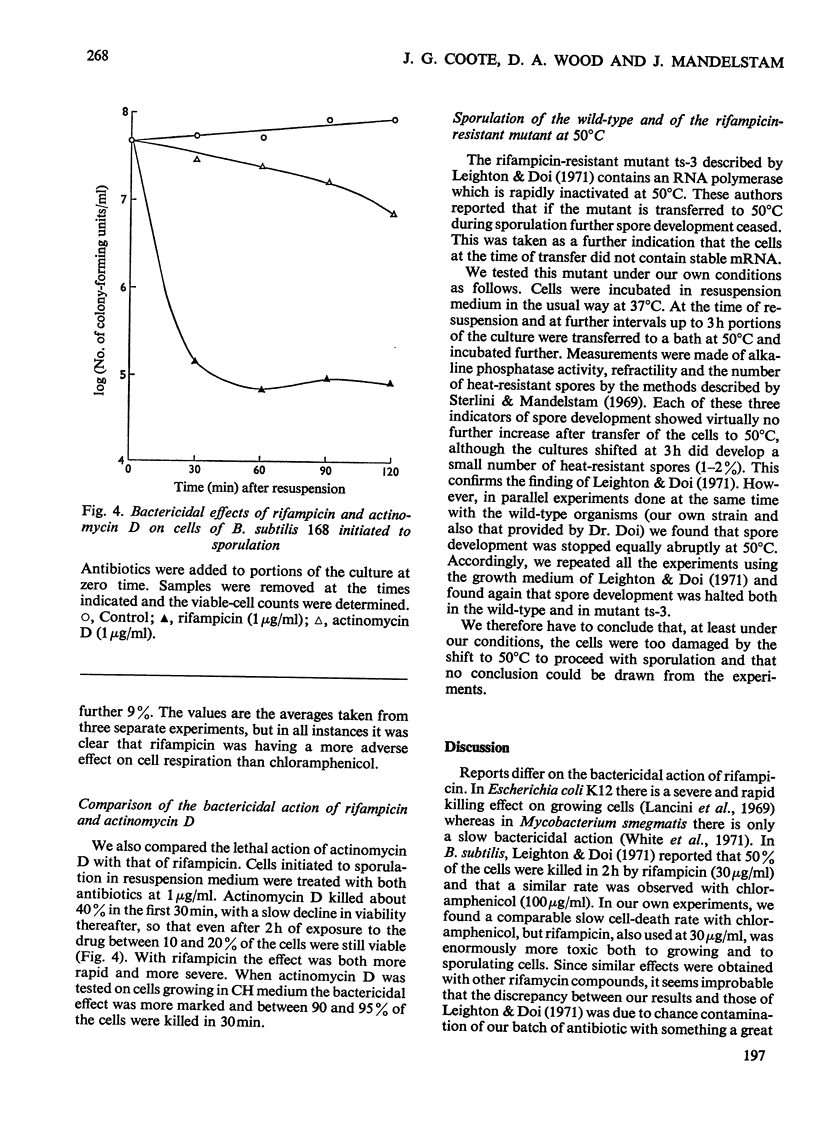
Abstract
The bactericidal action of rifampicin was compared with that of chloramphenicol in growing and in sporulating cultures of Bacillus subtilis 168. Chloramphenicol kills cells only very slowly, but exposure to rifampicin kills over 95% of cells in a few minutes, causing gross physical damage, which is visible in both phase-contrast and electron microscopy. This is accompanied by a fall in O2 consumption and by lysis. Experiments with synchronized cultures showed that susceptibility to the lethal effect of rifampicin is greater when the cells are dividing. The results suggest that the synthesis of some species of RNA other than mRNA may be necessary for the maintenance of cell integrity, although experiments with actinomycin D do not altogether fit this interpretation. However, we conclude that rifampicin is too toxic to use as an antibiotic for assessing the lifetime of mRNA.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ACS G., REICH E., VALANJU S. RNA METABOLISM OF B. SUBTILIS. EFFECTS OF ACTINOMYCIN. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Sep 17;76:68–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARONSON A. I., ROSASDELVALLE M. RNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS REQUIRED FOR BACTERIAL SPORE FORMATION. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jun 22;87:267–276. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(64)90222-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALASSA G. RENOUVELLEMENT DE L'ACIDE RIBONUCL'EIQUE AU COURS DE LA SPORULATION DE BACILLUS SUBTILIS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Nov 22;76:410–416. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90060-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiduschek E. P., Sklar J. Continual requirement for a host RNA polymerase component in a bacteriophage development. Nature. 1969 Mar 1;221(5183):833–836. doi: 10.1038/221833a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann G., Honikel K. O., Knüsel F., Nüesch J. The specific inhibition of the DNA-directed RNA synthesis by rifamycin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967;145(3):843–844. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90147-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heil A., Zillig W. Reconstitution of bacterial DNA-dependent RNA-polymerase from isolated subunits as a tool for the elucidation of the role of the subunits in transcription. FEBS Lett. 1970 Dec;11(3):165–168. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80519-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORN D., PROTASS J. J., LEIVE L. A NOVEL EFFECT OF ACTINOMYCIN D IN PREVENTING BACTERIOPHAGE T4 MATURATION IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 May 3;19:473–481. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90149-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
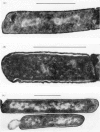
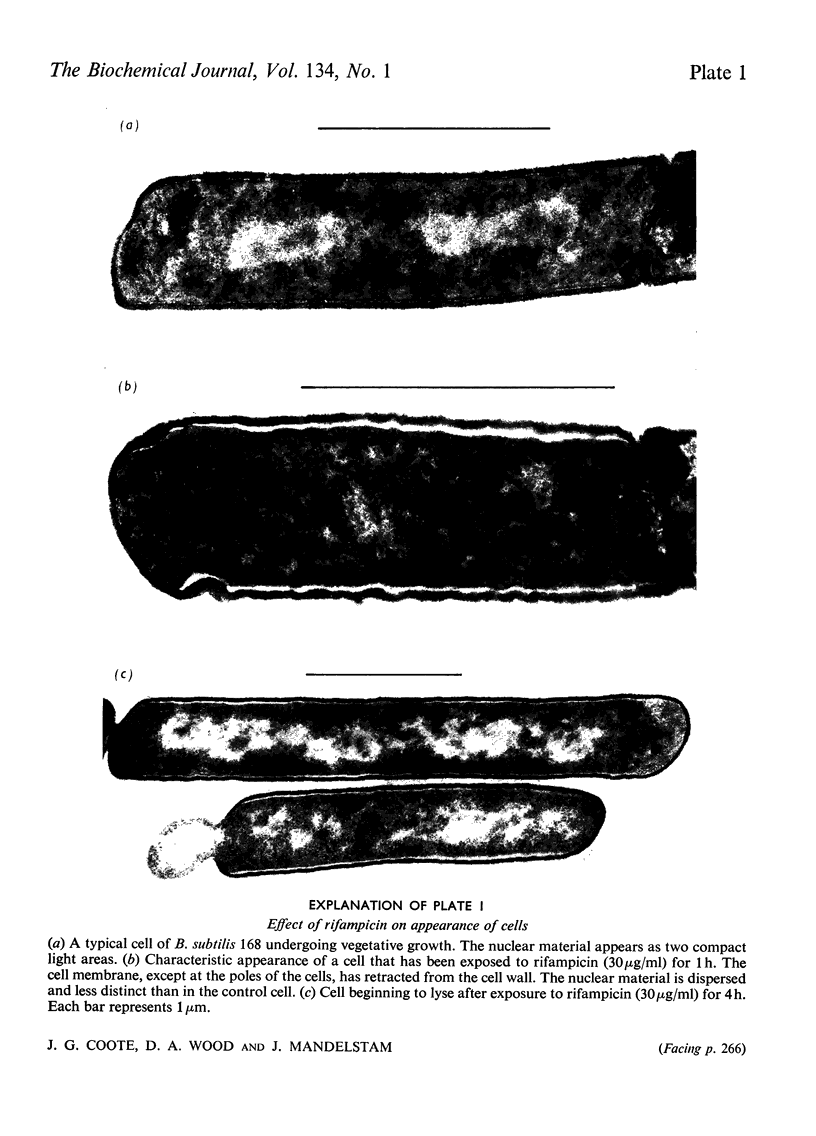
- Kay D., Warren S. C. Sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Morphological changes. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(5):819–824. doi: 10.1042/bj1090819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancini G., Pallanza R., Silvestri L. G. Relationships between bactericidal effect and inhibition of ribonucleic acid nucleotidyltransferase by rifampicin in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):761–768. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.761-768.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laszlo J., Miller D. S., McCarty K. S., Hochstein P. Actinomycin D: inhibition of respiration and glycolysis. Science. 1966 Feb 25;151(3713):1007–1010. doi: 10.1126/science.151.3713.1007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leighton T. J., Doi R. H. The stability of messenger ribonucleic acid during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 25;246(10):3189–3195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelson N. H., Gross J. D. Characterization of a temperature-sensitive mutant of Bacillus subtilis defective in deoxyribonucleic acid replication. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1603–1608. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1603-1608.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SZULMAJSTER J., CANFIELD R. E., BLICHARSKA J. [Action of actinomycin D on the sporulation of Bacillus subtilis]. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1963 Feb 25;256:2057–2060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenshein A. L., Losick R. RNA polymerase mutants blocked in sporulation. Nature. 1970 Aug 29;227(5261):906–909. doi: 10.1038/227906a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterlini J. M., Mandelstam J. Commitment to sporulation in Bacillus subtilis and its relationship to development of actinomycin resistance. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(1):29–37. doi: 10.1042/bj1130029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wehrli W., Staehelin M. Actions of the rifamycins. Bacteriol Rev. 1971 Sep;35(3):290–309. doi: 10.1128/br.35.3.290-309.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. J., Lancini G. C., Silvestri L. G. Mechanism of action of rifampin on Mycobacterium smegmatis. J Bacteriol. 1971 Nov;108(2):737–741. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.2.737-741.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]