Abstract
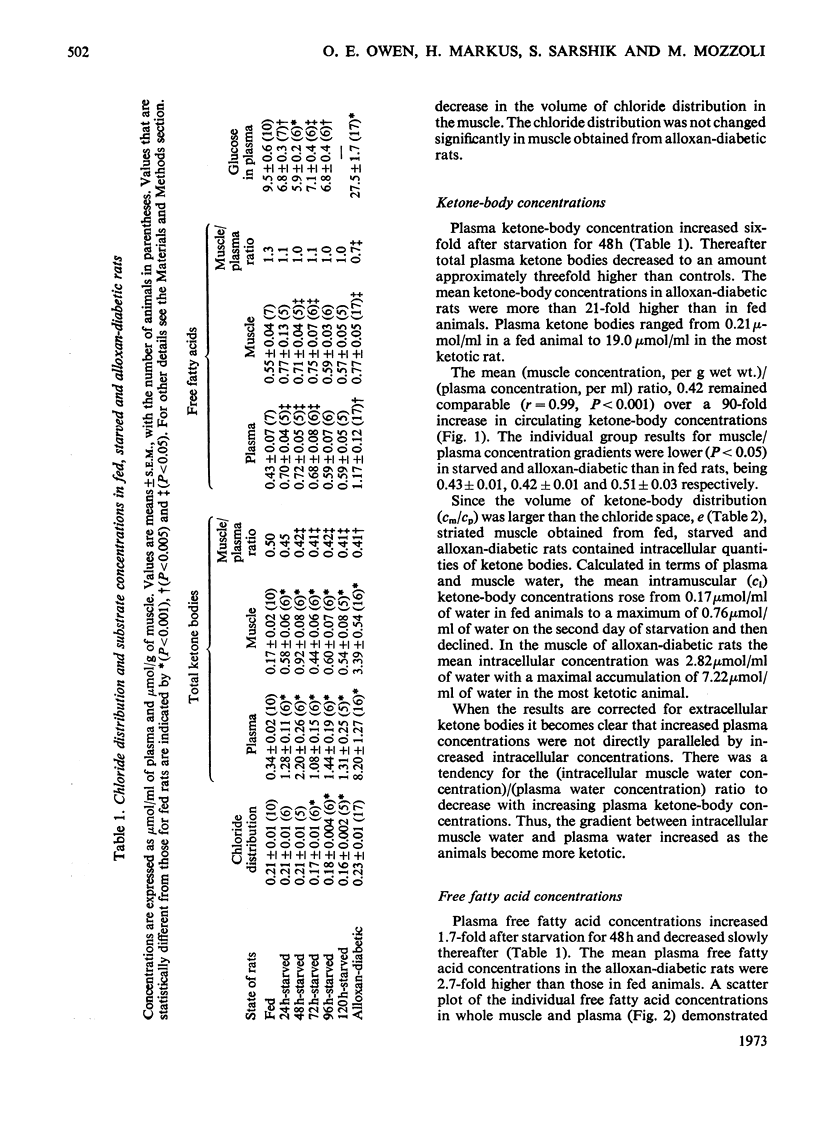
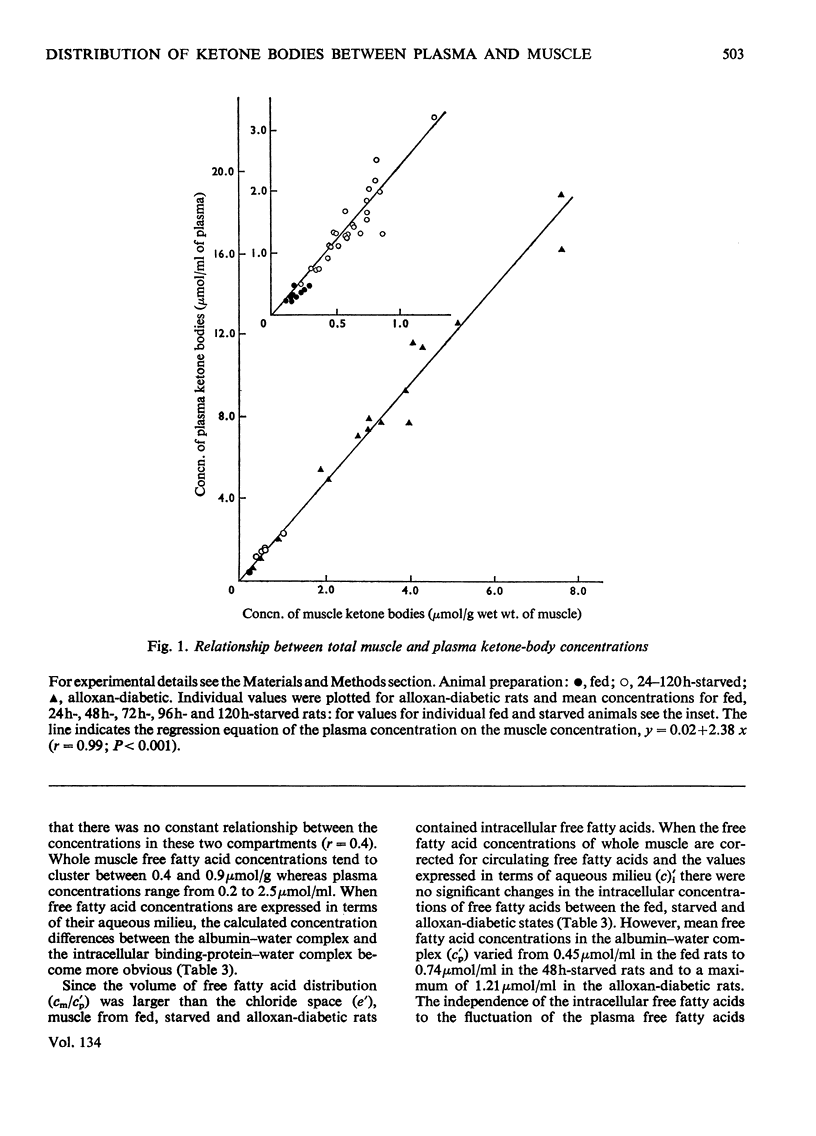
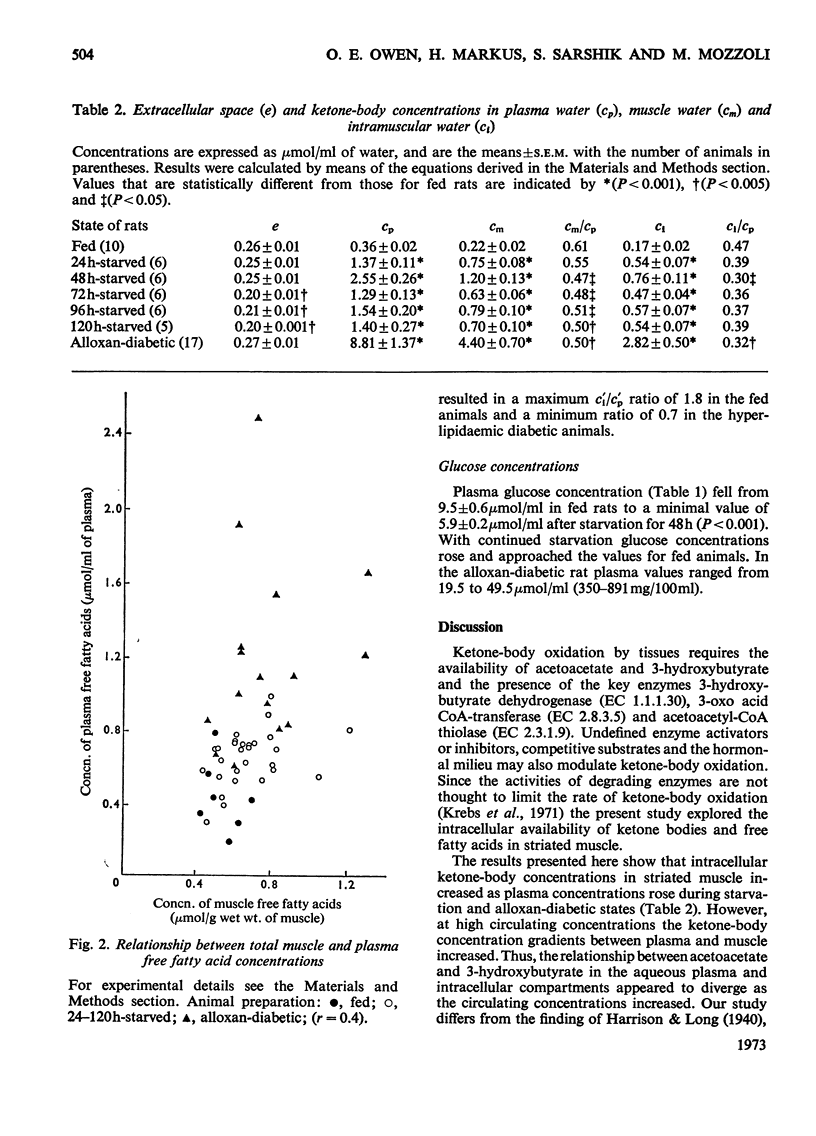
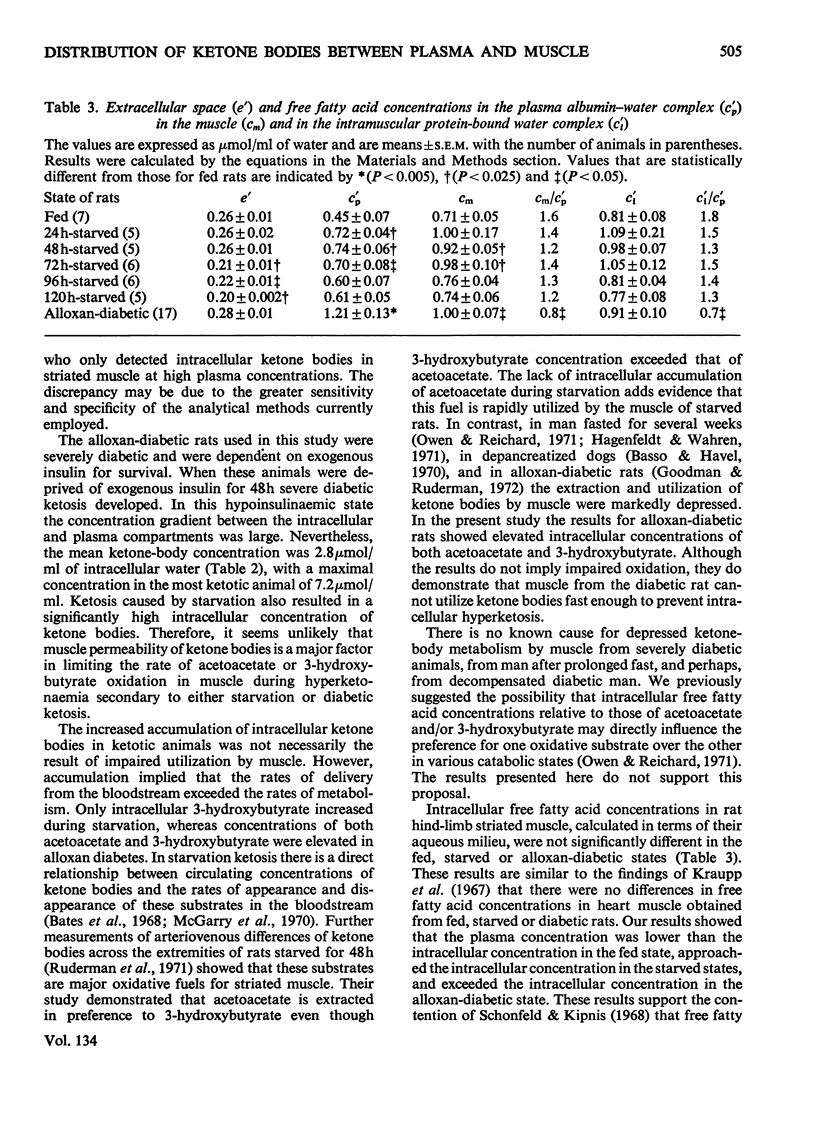
1. Concentrations of ketone bodies, free fatty acids and chloride in fed, 24–120h-starved and alloxan-diabetic rats were determined in plasma and striated muscle. Plasma glucose concentrations were also measured in these groups of animals. 2. Intracellular metabolite concentrations were calculated by using chloride as an endogenous marker of extracellular space. 3. The mean intracellular ketone-body concentrations (±s.e.m.) were 0.17±0.02, 0.76±0.11 and 2.82±0.50μmol/ml of water in fed, 48h-starved and alloxan-diabetic rats, respectively. Mean (intracellular water concentration)/(plasma water concentration) ratios were 0.47, 0.30 and 0.32 in fed, 48h-starved and alloxan-diabetic rats respectively. The relationship between ketone-body concentrations in the plasma and intracellular compartments appeared to follow an asymptotic pattern. 4. Only intracellular 3-hydroxybutyrate concentrations rose during starvation whereas concentrations of both 3-hydroxybutyrate and acetoacetate were elevated in the alloxan-diabetic state. 5. During starvation plasma glucose concentrations were lowest at 48h, and increased with further starvation. 6. There was no significant difference in the muscle intracellular free fatty acid concentrations of fed, starved and alloxan-diabetic rats. Mean free fatty acid intramuscular concentrations (±s.e.m.) were 0.81±0.08, 0.98±0.21 and 0.91±0.10μmol/ml in fed, 48h-starved and alloxan-diabetic states. 7. The intracellular ketosis of starvation and the stability of free fatty acid intracellular concentrations suggests that neither muscle membrane permeability nor concentrations of free fatty acids per se are major factors in limiting ketone-body oxidation in these states.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARTETA J. L., KONIG C., CARBALLIDO A. The effects of glucose and insulin on the diabetogenic action of alloxan. J Endocrinol. 1954 Jun;10(4):342–346. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0100342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEATTY C. H., PETERSON R. D., BOCEK R. M., WEST E. S. Acetoacetate and glucose uptake by diaphragm and skeletal muscle from from control and diabetic rats. J Biol Chem. 1959 Jan;234(1):11–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balasse E. O., Havel R. J. Evidence for an effect of inulin on the peripheral utilization of ketone bodies in dogs. J Clin Invest. 1971 Apr;50(4):801–813. doi: 10.1172/JCI106551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basso L. V., Havel R. J. Hepatic metabolism of free fatty acids in normal and diabetic dogs. J Clin Invest. 1970 Mar;49(3):537–547. doi: 10.1172/JCI106264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates M. W., Krebs H. A., Williamson D. H. Turnover rates of ketone bodies in normal, starved and alloxan-diabetic rats. Biochem J. 1968 Dec;110(4):655–661. doi: 10.1042/bj1100655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill G. F., Jr, Herrera M. G., Morgan A. P., Soeldner J. S., Steinke J., Levy P. L., Reichard G. A., Jr, Kipnis D. M. Hormone-fuel interrelationships during fasting. J Clin Invest. 1966 Nov;45(11):1751–1769. doi: 10.1172/JCI105481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLE V. P. A relation between non-esterified fatty acids in plasma and the metabolism of glucose. J Clin Invest. 1956 Feb;35(2):150–154. doi: 10.1172/JCI103259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncombe W. G. The colorimetric micro-determination of long-chain fatty acids. Biochem J. 1963 Jul;88(1):7–10. doi: 10.1042/bj0880007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischner G., Robbins J., Arias I. M. Immunological studies of Y protein. A major cytoplasmic organic anion-binding protein in rat liver. J Clin Invest. 1972 Mar;51(3):677–684. doi: 10.1172/JCI106856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILL J. B., KESSLER G. An automated determination of glucose utilizing a glucose oxidase-peroxidase system. J Lab Clin Med. 1961 Jun;57:970–980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenfeldt L., Wahren J. Human forearm muscle metabolism during exercise. VI. Substrate utilization in prolonged fasting. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1971 Jun;27(4):299–306. doi: 10.3109/00365517109080222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins R. A., Alberti K. G., Houghton C. R., Williamson D. H., Krebs H. A. The effect of acetoacetate on plasma insulin concentration. Biochem J. 1971 Nov;125(2):541–544. doi: 10.1042/bj1250541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIPNIS D. M., HELMREICH E., CORI C. F. Studies of tissue permeability. IV. The distribution of glucose between plasma and muscle. J Biol Chem. 1959 Jan;234(1):165–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEBANOFF S. J., GREENBAUM A. L. The effect of pH on the diabetogenic action of alloxan. J Endocrinol. 1954 Nov;11(4):314–322. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0110314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi N., Yonemura K. The extracellular space in red and white muscles of the rat. Jpn J Physiol. 1967 Dec 15;17(6):698–707. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.17.698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraupp O., Adler-Kastner L., Niessner H., Plank B. The effects of starvation and of acute and chronic alloxan diabetes on myocardial substrate levels and on liver glycogen in the rat in vivo. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Sep;2(2):197–214. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1967.tb00126.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahadevan S., Dillard C. J., Tappel A. L. A modified colorimetric micro method for long-chain fatty acids and its application for assay of lipolytic enzymes. Anal Biochem. 1969 Mar;27(3):387–396. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90052-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGarry J. D., Guest M. J., Foster D. W. Ketone body metabolism in the ketosis of starvation and alloxan diabetes. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 10;245(17):4382–4390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ockner R. K., Manning J. A., Poppenhausen R. B., Ho W. K. A binding protein for fatty acids in cytosol of intestinal mucosa, liver, myocardium, and other tissues. Science. 1972 Jul 7;177(4043):56–58. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4043.56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen O. E., Felig P., Morgan A. P., Wahren J., Cahill G. F., Jr Liver and kidney metabolism during prolonged starvation. J Clin Invest. 1969 Mar;48(3):574–583. doi: 10.1172/JCI106016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen O. E., Reichard G. A., Jr Human forearm metabolism during progressive starvation. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jul;50(7):1536–1545. doi: 10.1172/JCI106639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRAHL J. W., STEENROD W. J., Jr PRODUCTION OF ALLOXAN DIABETES AND KETOACIDOSIS IN THE LABORATORY RAT. Diabetes. 1965 May;14:289–294. doi: 10.2337/diab.14.5.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruderman N. B., Houghton C. R., Hems R. Evaluation of the isolated perfused rat hindquarter for the study of muscle metabolism. Biochem J. 1971 Sep;124(3):639–651. doi: 10.1042/bj1240639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schonfeld G., Kipnis D. M. Glucose-fatty acid interactions in the rat diaphragm in vivo. Diabetes. 1968 Jul;17(7):422–426. doi: 10.2337/diab.17.7.422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens J. M., Sulway M. J., Watkins P. J. Relationship of blood acetoacetate and 3-hydroxybutyrate in diabetes. Diabetes. 1971 Jul;20(7):485–489. doi: 10.2337/diab.20.7.485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLLENBERGER A., RISTAU O., SCHOFFA G. [A simple technic for extremely rapid freezing of large pieces of tissue]. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1960;270:399–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidemann M. J., Krebs H. A. The fuel of respiration of rat kidney cortex. Biochem J. 1969 Apr;112(2):149–166. doi: 10.1042/bj1120149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson D. H., Bates M. W., Page M. A., Krebs H. A. Activities of enzymes involved in acetoacetate utilization in adult mammalian tissues. Biochem J. 1971 Jan;121(1):41–47. doi: 10.1042/bj1210041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


