Abstract
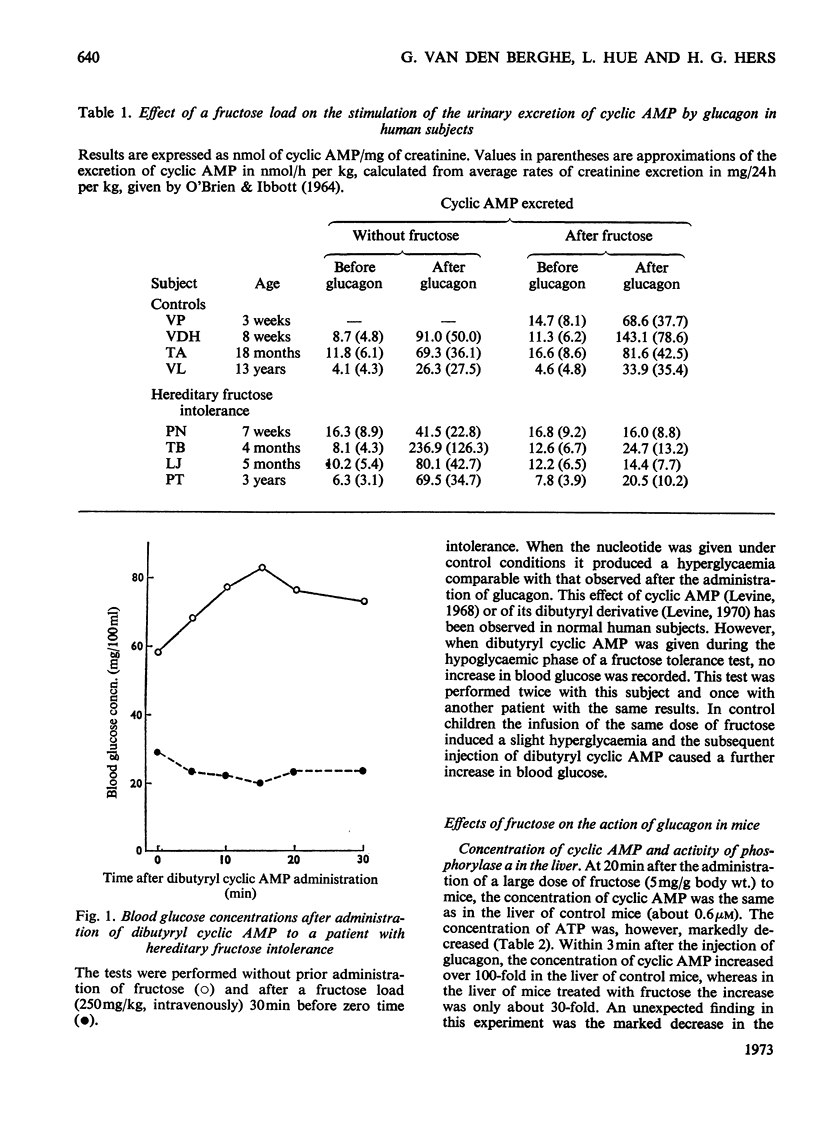
1. The mechanism by which the administration of fructose to patients with hereditary fructose intolerance makes them unresponsive to the hyperglycaemic action of glucagon was studied. In four patients, a 10-fold increase in the urinary excretion of cyclic AMP was induced by glucagon, but this effect was drastically decreased by the previous administration of fructose (250mg/kg). Further, the intravenous injection of 6-N,2′-O-dibutyryl cyclic AMP did not cause an increase in the blood glucose during fructose-induced hypoglycaemia. 2. The administration of a large dose of fructose (5g/kg) to mice decreased markedly both the concentration of ATP and the increase in the concentration of cyclic AMP caused by glucagon in the liver. Other ATP-depleting agents had a similar effect and a linear correlation could be drawn between the concentration of ATP and the change in cyclic AMP concentration; a half-maximal effect was obtained for a concentration of ATP close to the Km value of adenylate cyclase. 3. The administration of fructose to mice caused the inactivation of phosphorylase in the liver, but this effect was easily reversed by glucagon. 4. At a concentration of 10mm-fructose 1-phosphate and 1.5mm-Pi, purified liver phosphorylase a was inhibited by 70%. This inhibition appears to be a likely explanation for the unresponsiveness to glucagon of patients with hereditary fructose intolerance.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appleman M. M., Krebs E. G., Fischer E. H. Purification and properties of inactive liver phosphorylase. Biochemistry. 1966 Jun;5(6):2101–2107. doi: 10.1021/bi00870a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRECKENRIDGE B. M. THE MEASUREMENT OF CYCLIC ADENYLATE IN TISSUES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Dec;52:1580–1586. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.6.1580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUEDING E., HAWKINS J. T. ENZYMIC DEGRADATION AND MICRODETERMINATION OF GLYCOGEN. Anal Biochem. 1964 Jan;7:26–36. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(64)90116-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUTCHER R. W., SUTHERLAND E. W. Adenosine 3',5'-phosphate in biological materials. I. Purification and properties of cyclic 3',5'-nucleotide phosphodiesterase and use of this enzyme to characterize adenosine 3',5'-phosphate in human urine. J Biol Chem. 1962 Apr;237:1244–1250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baerlocher K., Gitzelmann R., Nüssli R., Dumermuth G. Infantile lactic acidosis due to hereditary fructose 1,6-diphosphatase deficiency. Helv Paediatr Acta. 1971 Dec;26(5):489–506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker L., Winegrad A. I. Fasting hypoglycaemia and metabolic acidosis associated with deficiency of hepatic fructose-1,6-diphosphatase activity. Lancet. 1970 Jul 4;2(7662):13–16. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)92474-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode C., Schumacher H., Goebell H., Zelder O., Pelzel H. Fructose induced depletion of liver adenine nucleotides in man. Horm Metab Res. 1971 Jul;3(4):289–290. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1096782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broadus A. E., Kaminsky N. I., Northcutt R. C., Hardman J. G., Sutherland E. W., Liddle G. W. Effects of glucagon on adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate and guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate in human plasma and urine. J Clin Invest. 1970 Dec;49(12):2237–2245. doi: 10.1172/JCI106442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch H. B., Lowry O. H., Meinhardt L., Max P., Jr, Chyu K. Effect of fructose, dihydroxyacetone, glycerol, and glucose on metabolites and related compounds in liver and kidney. J Biol Chem. 1970 Apr 25;245(8):2092–2102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch H. B., Max P., Jr, Ghyu K., Lowry O. H. Metabolic intermediates in liver of rats given large amounts of fructose or dihydroxyacetone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Mar 10;34(5):619–626. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90783-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAMBERS R. A., PRATT R. T. Idiosyncrasy to fructose. Lancet. 1956 Aug 18;271(6938):340–340. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(56)92196-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CORNBLATH M., ROSENTHAL I. M., REISNER S. H., WYBREGT S. H., CRANE R. K. HEREDITARY FRUCTOSE INTOLERANCE. N Engl J Med. 1963 Dec 12;269:1271–1278. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196312122692401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase L. R., Melson G. L., Aurbach G. D. Pseudohypoparathyroidism: defective excretion of 3',5'-AMP in response to parathyroid hormone. J Clin Invest. 1969 Oct;48(10):1832–1844. doi: 10.1172/JCI106149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARBER E., SHULL K. H., VILLA-TREVINO S., LOMBARDI B., THOMAS M. BIOCHEMICAL PATHOLOGY OF ACUTE HEPATIC ADENOSINETRIPHOSPHATE DEFICIENCY. Nature. 1964 Jul 4;203:34–40. doi: 10.1038/203034a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FROESCH E. R., PRADER A., LABHART A., STUBER H. W., WOLF H. P. Die hereditäre Fructoseintoleranz, eine bisher nicht bekannte kongenitale Stoffwechselstörung. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1957 Sep 14;87(37):1168–1171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FROESCH E. R., PRADER A., WOLF H. P., LABHART A. Die hereditäre Fructoseintoleranz. Helv Paediatr Acta. 1959 Jun;14(2):99–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FROESCH E. R., WOLF H. P., BAITSCH H., PRADER A., LABHART A. Hereditary fructose intolerance. An inborn defect of hepatic fructose-1-phosphate splitting aldolase. Am J Med. 1963 Feb;34:151–167. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(63)90050-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Günther M. A., Sillero A., Sols A. Fructokinase assay with a specific spectrophotometric method using 1-phosphofructokinase. Enzymol Biol Clin (Basel) 1967;8(5):341–352. doi: 10.1159/000458221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERS H. G. GLYCOGEN STORAGE DISEASE. Adv Metab Disord. 1964;13:1–44. doi: 10.1016/b978-1-4831-6748-0.50006-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERS H. G., JOASSIN G. [Anomaly of hepatic aldolase in intolerance to fructose]. Enzymol Biol Clin (Basel) 1961;1:4–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinz F., Junghänel J. Metabolitmuster in Rattenleber nach Fructoseapplikation. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1969 Jul;350(7):859–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hers H. G. Misuses for fructose. Nature. 1970 Jul 25;227(5256):421–421. doi: 10.1038/227421d0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson L. S., Exton J. H., Butcher R. W., Sutherland E. W., Park C. R. Role of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in the effects of insulin and anti-insulin serum on liver metabolism. J Biol Chem. 1968 Mar 10;243(5):1031–1038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KREBS E. G., LOVE D. S., BRATVOLD G. E., TRAYSER K. A., MEYER W. L., FISCHER E. H. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF RABBIT SKELETAL MUSCLE PHOSPHORYLASE B KINASE. Biochemistry. 1964 Aug;3:1022–1033. doi: 10.1021/bi00896a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs E. G. Protein kinases. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1972;5:99–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine R. A. Effects of exogenous adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in man. 3. Increased response and tolerance to the dibutyryl derivative. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1970 Mar-Apr;11(2):238–243. doi: 10.1002/cpt1970112238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine R. A. Effects of exogenous adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in man. II. Glucose, nonesterified fatty acid and cortisol responses. Metabolism. 1968 Jan;17(1):34–45. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(68)80005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUDD S. H., CANTONI G. L. Activation of methionine for transmethylation. III. The methionine-activating enzyme of Bakers' yeast. J Biol Chem. 1958 Mar;231(1):481–492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddaiah V. T., Madsen N. B. Kinetics of purified liver phosphorylase. J Biol Chem. 1966 Sep 10;241(17):3873–3881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäenpä P. H., Raivio K. O., Kekomäki M. P. Liver adenine nucleotides: fructose-induced depletion and its effect on protein synthesis. Science. 1968 Sep 20;161(3847):1253–1254. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3847.1253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERHEENTUPA J., PITKANEN E., NIKKILA E. A., SOMERSALO O., HAKOSALO J. Hereditary fructose intolerance. A clinical study of four cases. Ann Paediatr Fenn. 1962;8:221–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perheentupa J., Raivio K. O., Nikkilä E. A. Hereditary fructose intolerance. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1972;542:65–75. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1972.tb05320.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohl S. L., Birnbaumer L., Rodbell M. The glucagon-sensitive adenyl cyclase system in plasma membranes of rat liver. I. Properties. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1849–1856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raivio K. O., Kekomäki M. P., Mäenpä P. H. Depletion of liver adenine nucleotides induced by D-fructose. Dose-dependence and specificity of the fructose effect. Biochem Pharmacol. 1969 Oct;18(10):2615–2624. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(69)90192-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimann E. M., Walsh D. A., Krebs E. G. Purification and properties of rabbit skeletal muscle adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 10;246(7):1986–1995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STREHLER B. L., TOTTER J. R. Firefly luminescence in the study of energy transfer mechanisms. I. Substrate and enzyme determination. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1952 Sep;40(1):28–41. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(52)90070-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUTHERLAND E. W., CORI C. F. Effect of hyperglycemic-glycogenolytic factor and epinephrine on liver phosphorylase. J Biol Chem. 1951 Feb;188(2):531–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez J. J., González N. S., Pontis H. G. Fructokinase from rat liver. I. Purification and properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jan 13;227(1):67–78. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90168-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Berghe G., De Wulf H., Hers H. G. Concentration of cyclic 3':5'-adenosine monophosphate and glycogen metabolism in the liver. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Oct;16(2):358–362. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01089.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLF H., ZSCHOCKE D., WEDEMEYER F. W., HUBNER W. Angeborene hereditäre Fructose-Intoleranz. Klin Wochenschr. 1959 Jul 1;37(13):693–696. doi: 10.1007/BF01478217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLLENBERGER A., RISTAU O., SCHOFFA G. [A simple technic for extremely rapid freezing of large pieces of tissue]. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1960;270:399–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub B., Sarcione E. J., Sokal J. E. Effect of glucagon on phosphorylase activity of the isolated perfused liver. Am J Physiol. 1969 Mar;216(3):521–526. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.3.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods H. F., Alberti K. G. Dangers of intravenous fructose. Lancet. 1972 Dec 23;2(7791):1354–1357. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92791-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


