Abstract
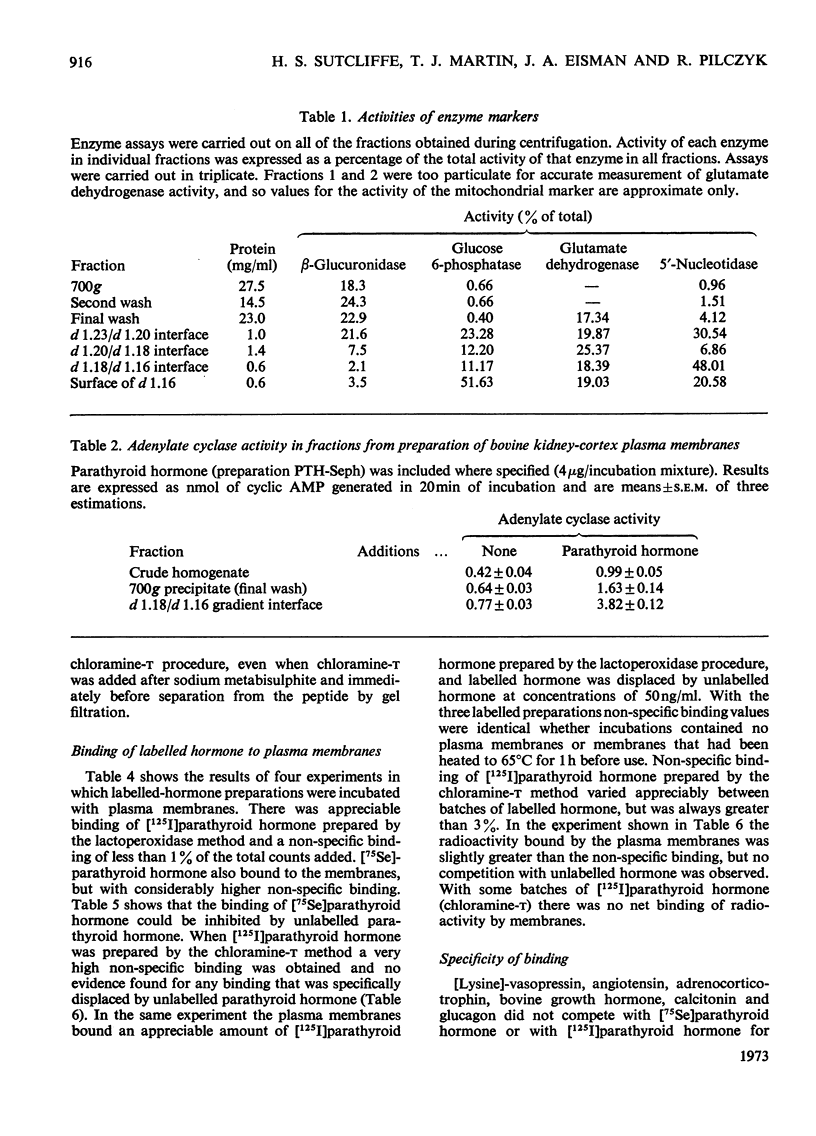
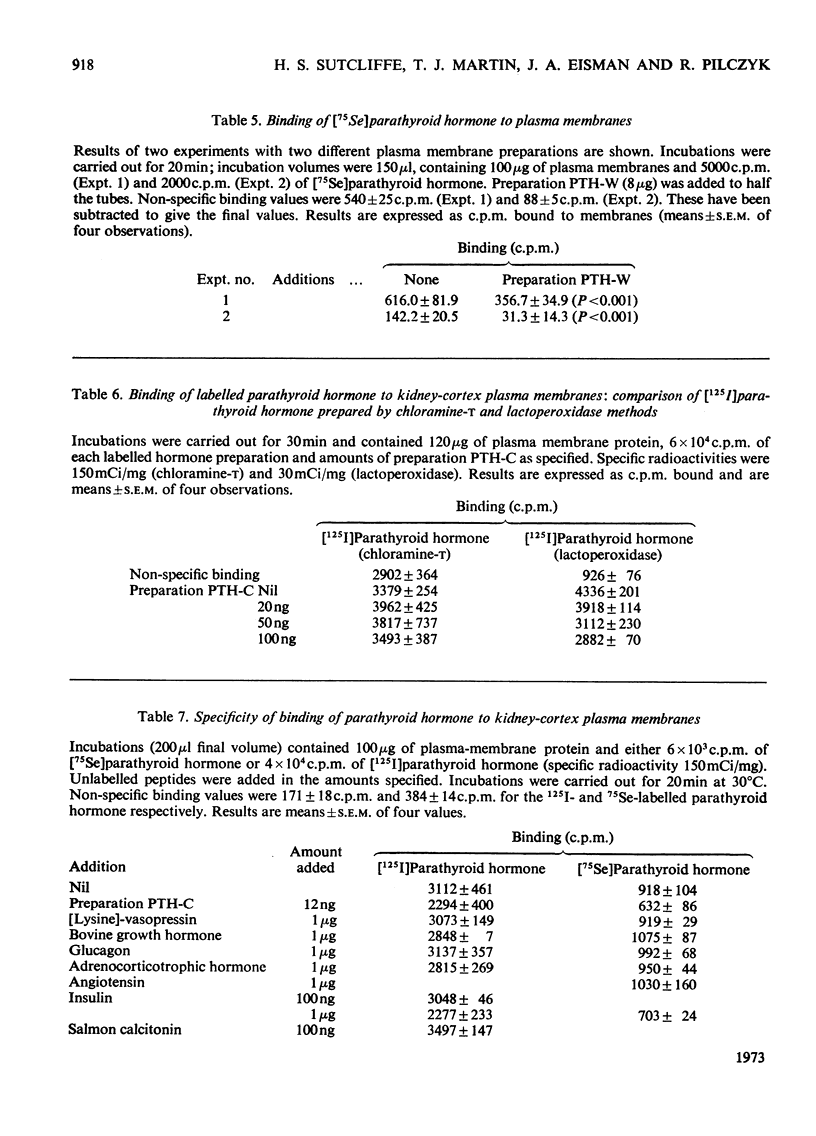
1. Plasma membranes were purified from bovine kidney cortex, with a fourfold increase in specific activity of parathyroid hormone-sensitive adenylate cyclase over that in the crude homogenate. The membranes were characterized by enzyme studies. 2. Parathyroid hormone was labelled with 125I by an enzymic method and the labelled hormone shown to bind to the plasma membranes and to be specifically displaced by unlabelled hormone. Parathyroid hormone labelled by the chloramine-t procedure showed no specific binding. 75Se-labelled human parathyroid hormone, prepared in cell culture, also bound to the membranes. 3. Parathyroid hormone was shown to retain biological activity after iodination by the enzymic method, but no detectable activity remained after chloramine-t treatment. 4. High concentration of pig insulin inhibited binding of labelled parathyroid hormone to plasma membranes and partially inhibited the hormone-sensitive adenylate cyclase activity in a crude kidney-cortex preparation. 5. EDTA enhanced and Ca2+ inhibited binding of labelled parathyroid hormone to plasma membranes. 6. Whereas rat kidney homogenates were capable of degrading labelled parathyroid hormone to trichloroacetic acid-soluble fragments, neither crude homogenates nor purified membranes from bovine kidney showed this property. 7. Binding of parathyroid hormone is discussed in relation to metabolism and initial events in hormone action.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AURBACH G. D. Isolation of parathyroid hormone after extraction with phenol. J Biol Chem. 1959 Dec;234:3179–3181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase L. R., Aurbach G. D. Parathyroid function and the renal excretion of 3'5'-adenylic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Aug;58(2):518–525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.2.518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase L. R., Aurbach G. D. Renal adenyl cyclase: anatomically separate sites for parathyroid hormone and vasopressin. Science. 1968 Feb 2;159(3814):545–547. doi: 10.1126/science.159.3814.545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Insulin--receptor interactions in adipose tissue cells: direct measurement and properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1264–1268. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Kretser D. M., Martin T. J., Melick R. A. The radioautographic localization of 125-I-labelled bovine parathyroid hormone. J Endocrinol. 1970 Apr;46(4):507–510. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0460507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang V. S., Tashjian A. H., Jr Studies on the role of the liver in the metabolism of parathyroid hormone. I. Effects of partial hepatectomy and incubation of the hormone with tissue homogenates. Endocrinology. 1972 May;90(5):1177–1184. doi: 10.1210/endo-90-5-1177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Kahn R., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Insulin interactions with liver plasma membranes. Independence of binding of the hormone and its degradation. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3953–3961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Monoiodoinsulin: demonstration of its biological activity and binding to fat cells and liver membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Apr 16;43(2):400–408. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90767-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg D. M., Jago G. R. The antibacterial action of lactoperoxidase. The nature of the bacterial inhibitor. Biochem J. 1970 May;117(4):779–790. doi: 10.1042/bj1170779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illiano G., Cuatrecasas P. Modulation of adenylate cyclase activity in liver and fat cell membranes by insulin. Science. 1972 Feb 25;175(4024):906–908. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4024.906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefkowitz R. J., Roth J., Pricer W., Pastan I. ACTH receptors in the adrenal: specific binding of ACTH-125I and its relation to adenyl cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Mar;65(3):745–752. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.3.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchalonis J. J. An enzymic method for the trace iodination of immunoglobulins and other proteins. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(2):299–305. doi: 10.1042/bj1130299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus R., Aurbach G. D. Adenyl cyclase from renal cortex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Aug 20;242(2):410–421. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90232-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus R., Aurbach G. D. Bioassay of parathyroid hormone in vitro with a stable preparation of adenyl cyclase from rat kidney. Endocrinology. 1969 Nov;85(5):801–810. doi: 10.1210/endo-85-5-801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. J., Greenberg P. B., Michelangeli V. Synthesis of human parathyroid hormone by cultured cells: evidence for release of prohormone by some adenomata. Clin Sci. 1973 Jan;44(1):1–8. doi: 10.1042/cs0440001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. J., Melick R. A., de Luise M. Metabolism of parathyroid hormone. Degradation of 125I-labelled hormone by a kidney enzyme. Biochem J. 1969 Feb;111(4):509–514. doi: 10.1042/bj1110509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H., Hawthorne J. N. The site of diphosphoinositide synthesis in rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Nov 22;21(4):333–338. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90198-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEVILLE D. M., Jr The isolation of a cell membrane fraction from rat liver. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1960 Oct;8:413–422. doi: 10.1083/jcb.8.2.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orimo H., Fujita T. Parathyroid hormone-like calcium mobilizing activity in dog kidney. Endocrinology. 1966 Apr;78(4):884–886. doi: 10.1210/endo-78-4-884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parvin R., Smith R. A. Determination of inorganic phosphate in the presence of labile organic phosphates. Anal Biochem. 1969 Jan;27(1):65–72. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90219-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohl S. L., Birnbaumer L., Rodbell M. The glucagon-sensitive adenyl cyclase system in plasma membranes of rat liver. I. Properties. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1849–1856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potts J. T., Jr, Aurbach G. D., Sherwood L. M., Sandoval A. Structural basis of biological and immunological activity of parathyroid hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Dec;54(6):1743–1751. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.6.1743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramachandran J. A new simple method for separation of adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate from other nucleotides and its use in the assay of adenyl cyclase. Anal Biochem. 1971 Sep;43(1):227–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90128-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M., Krans H. M., Pohl S. L., Birnbaumer L. The glucagon-sensitive adenyl cyclase system in plasma membranes of rat liver. 3. Binding of glucagon: method of assay and specificity. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1861–1871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streeto J. M. Renal cortical adenyl cyclase: effect of parathyroid hormone and calcium. Metabolism. 1969 Nov;18(11):968–973. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(69)90037-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White A. A., Zenser T. V. Separation of cyclic 3',5'-nucleoside monophosphates from other nucleotides on aluminum oxide columns. Application to the assay of adenyl cyclase and guanyl cyclase. Anal Biochem. 1971 Jun;41(2):372–396. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90156-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yalow R. S., Berson S. A. Purification of 131-I parathyroid hormone with microfine granules of precipitated silica. Nature. 1966 Oct 22;212(5060):357–358. doi: 10.1038/212357a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zull J. E., Repke D. W. Studies with tritiated polypeptide hormones. I. The preparation and properties of an active, highly tritiated derivative of parathyroid hormone: acetamidino-parathyroid hormone. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 10;247(7):2183–2188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zull J. E., Repke D. W. The tissue localization of tritiated parathyroid hormone in thyroparathyroidectomized rats. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 10;247(7):2195–2199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Luise M., Martin T. J., Greenberg P. B., Michelangeli V. Metabolism of porcine, human and salmon calcitonin in the rat. J Endocrinol. 1972 Jun;53(3):475–482. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0530475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Luise M., Martin T. J., Melick R. A. Tissue distribution of calcitonin in the rat: comparison with parathyroid hormone. J Endocrinol. 1970 Oct;48(2):173–179. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0480173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


