Abstract
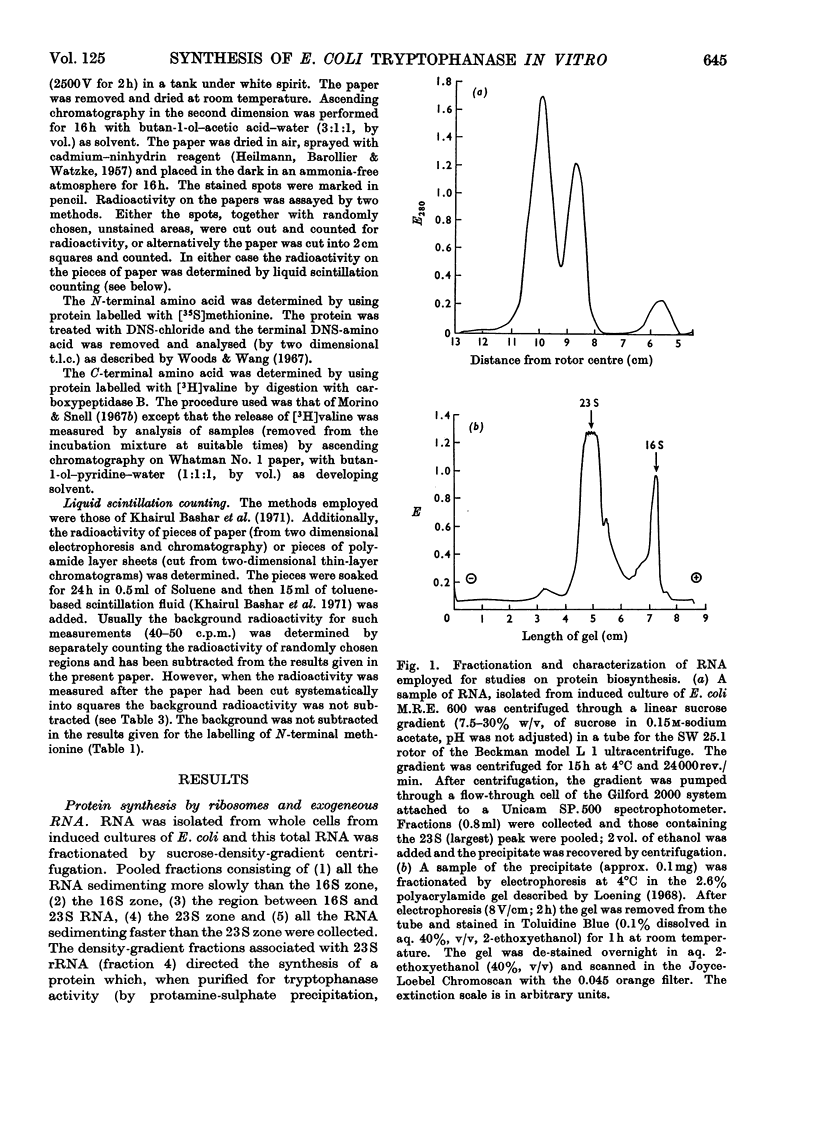
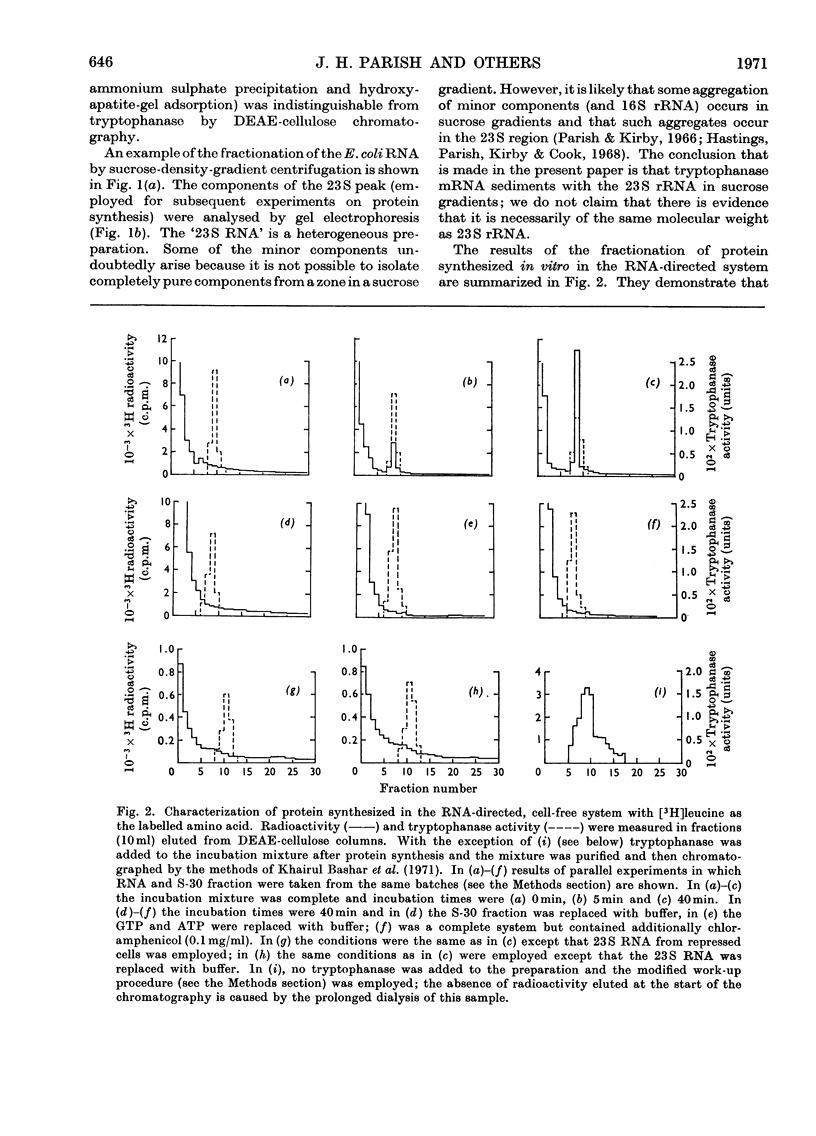
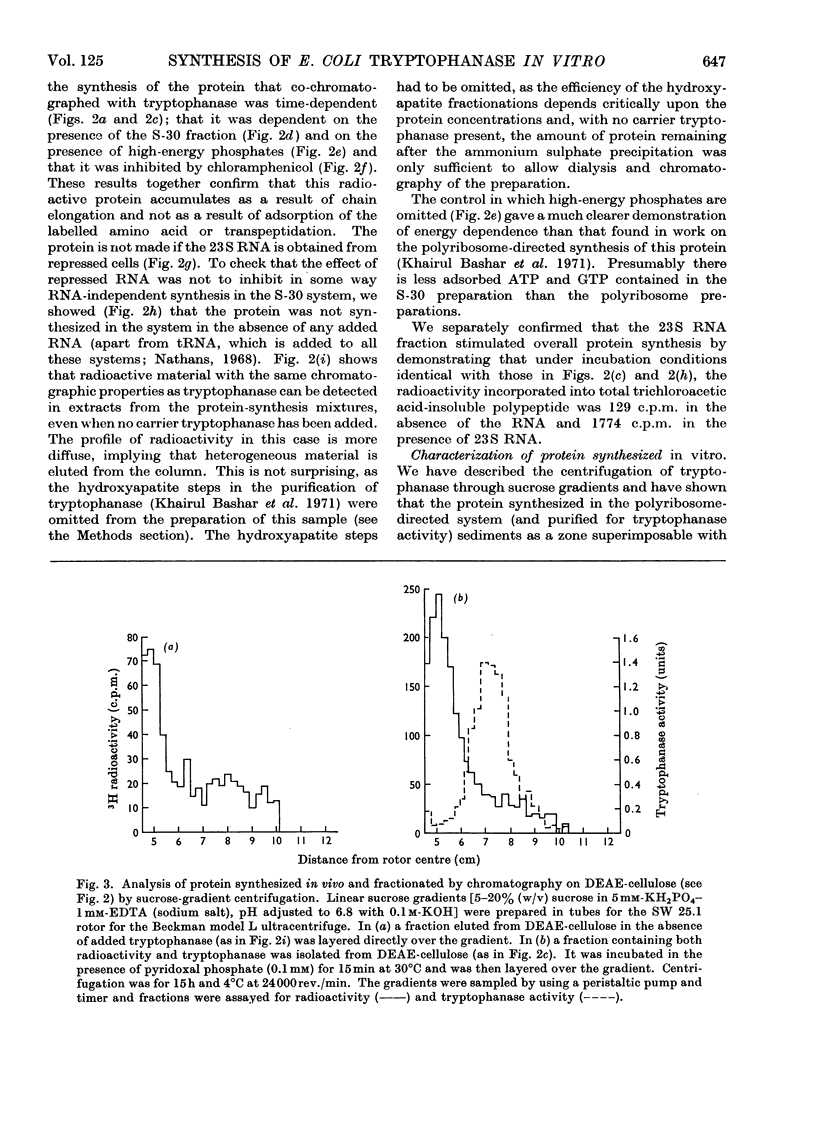
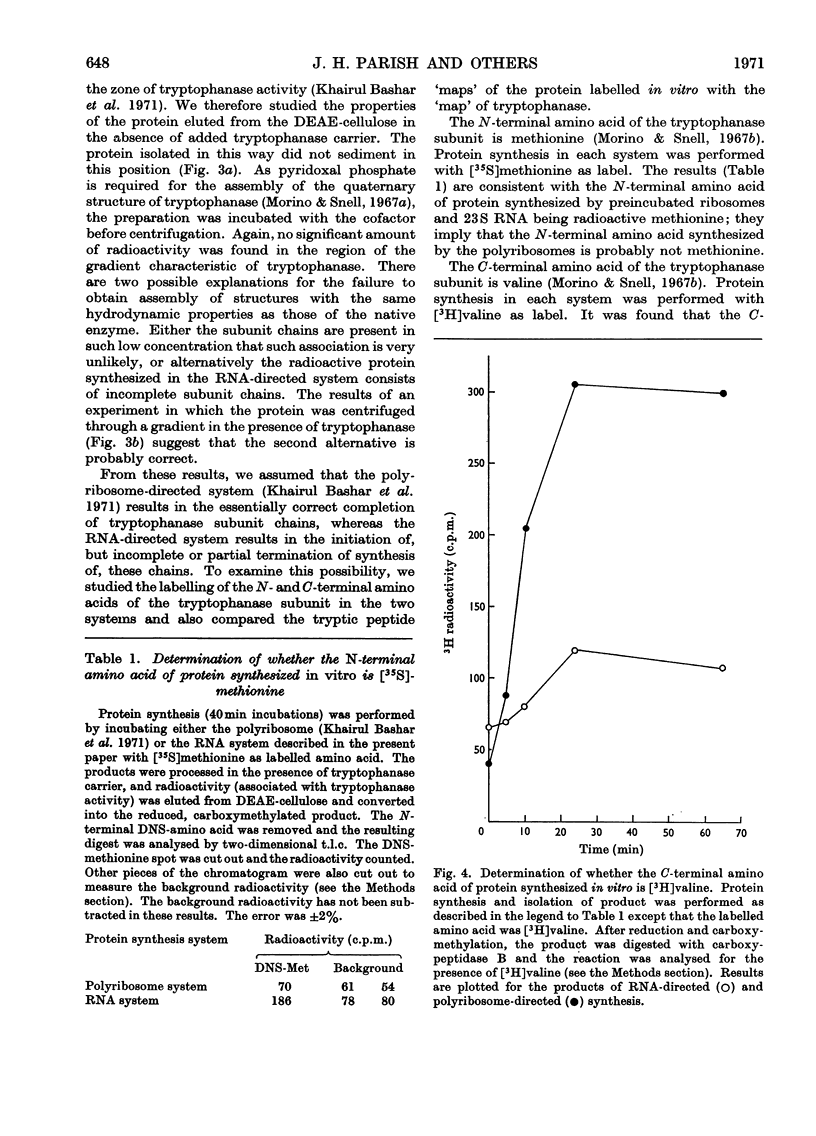
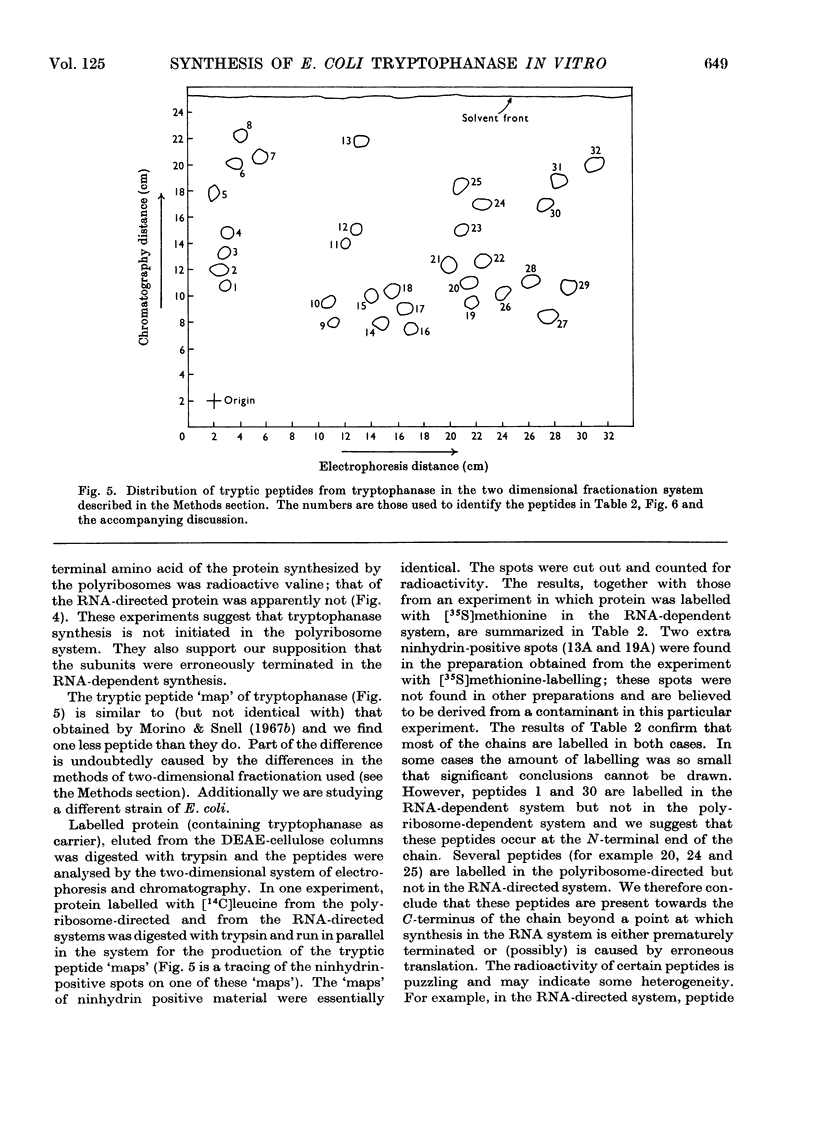
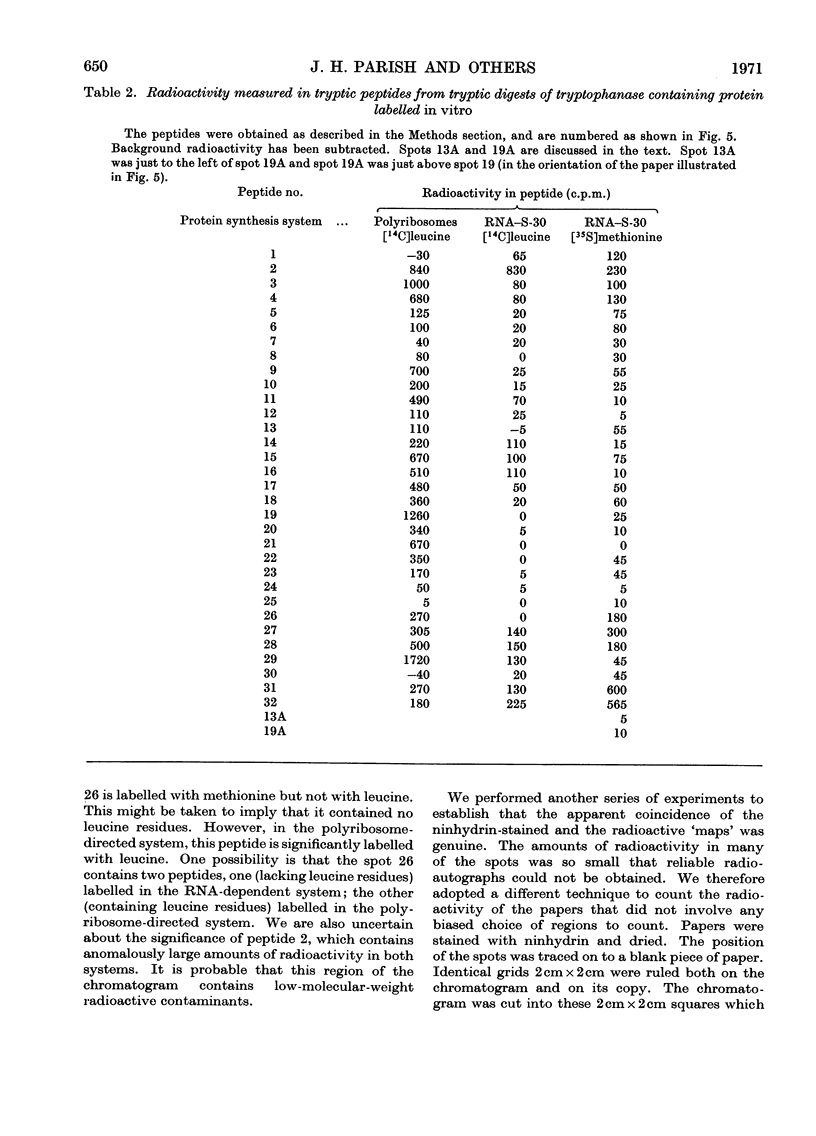
1. Polyribosomes and RNA were isolated from cultures in which tryptophanase (EC 4.2.1.–) was induced. The polyribosomes were incubated under conditions of protein synthesis, in the presence of a radioactive amino acid and a post-ribosomal supernatant fraction obtained from repressed cells. The RNA preparations were incubated under conditions of protein synthesis in the presence of a radioactive amino acid and a supernatant fraction containing ribosomes from repressed cells. 2. The system was characterized and the synthesis of a radioactive protein with the same chromatographic properties as tryptophanase was demonstrated. This synthesis was shown to be time-dependent and required the presence of RNA from induced cultures, ribosomes and an energy supply; it was inhibited by chloramphenicol. 3. The maximum activity for the synthesis of this protein was found to be associated with 23S rRNA isolated from sucrose gradients. 4. The N-terminal amino acid of tryptophanase was labelled in the protein synthesized in this system but not in the protein synthesized by polyribosomes (without added RNA). Conversely, the C-terminal amino acid of tryptophanase was labelled in the polyribosome system but not in the RNA-containing system. 5. Tryptic digests of protein labelled in vitro were compared with those of tryptophanase. No labelled tryptic peptides were identified other than tryptophanase tryptic peptides. An analysis of the results implied that in the polyribosome system almost the complete tryptophanase subunit chain was labelled but that in the RNA-containing system these chains were incompletely synthesized. 6. Sucrose-gradient analysis of protein synthesized in the RNA-containing system suggested that it cannot be converted into structures with the same sedimentation properties as native tryptophanase. 7. The significance of these results for the assay of tryptophanase mRNA and for an understanding of the control of the translation of this mRNA in vivo is discussed.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bashar S. A., Parish J. H., Brown M. Biosynthesis in vitro of tryptophanase by polyribosomes from induced cultures of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1971 Jul;123(3):355–365. doi: 10.1042/bj1230355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEILMANN J., BARROLLIER J., WATZKE E. Beitrag zur Aminosäurebestimmung auf Papierchromatogrammen. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1957;309(4-6):219–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastings J. R., Parish J. H., Kirby K. S., Cook E. A. Sedimentation of rapidly labelled RNA from rat liver in different gradients. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Feb 26;155(2):603–605. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90203-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morino Y., Snell E. E. The subunit structure of tryptophanase. I. The effect of pyridoxal phosphate on the subunit structure and physical properties of tryptophanase. J Biol Chem. 1967 Dec 10;242(23):5591–5601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morino Y., Snell E. E. The subunit structure of tryptophanase. II. A correlation of ultracentrifugal and chemical studies. J Biol Chem. 1967 Dec 10;242(23):5602–5610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse D. E., Mosteller R. D., Yanofsky C. Dynamics of synthesis, translation, and degradation of trp operon messenger RNA in E. coli. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:725–740. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newbold P. C., Harding N. G. Affinity chromatography of dihydrofolate reductase. Biochem J. 1971 Aug;124(1):1–12. doi: 10.1042/bj1240001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parish J. H., Kirby K. S. Reagents which reduce interactions between ribosomal RNA and rapidly labelled RNA from rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Dec 21;129(3):554–562. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90070-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I., Perlman R. L. Stimulation of tryptophanase synthesis in Escherichia coli by cyclic 3',5'-adenosine monophosphate. J Biol Chem. 1969 Apr 25;244(8):2226–2232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl J., Lawford G. R., Williams B., Campbell P. N. A requirement for the presence of cell sap in the reversible dissociation of rat liver polysomes to ribosomal sub-units. Biochem J. 1968 Aug;109(1):155–157. doi: 10.1042/bj1090155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods K. R., Wang K. T. Separation of dansyl-amino acids by polyamide layer chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Feb 21;133(2):369–370. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(67)90078-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


